| 283. Speech and Song
02 Dec 1922, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 283. Speech and Song
02 Dec 1922, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
I have already pointed out in recent lectures how certain functions or activities of the human being, which emerge in early childhood, are in reality a metamorphosis of activities which belong to man between death and a new birth, i.e. in his pre-earthly life. At birth the child is not yet fully adapted to the earthly gravitation, the earthly conditions of equilibrium. We see the child slowly and gradually adapt himself to these earthly conditions as he learns to stand and walk. Thus the adaptation of the body to the position of equilibrium for earthly life is a faculty which man does not bring with him. He must acquire it during his earthly life. Now we know that the physical body of man in all its form is the result of a mighty spiritual activity—an activity which man performs in unison with Beings of the Higher Worlds between death and a new birth. Yet that which man forms and creates in this activity—we may call it in a sense the spiritual germ of his future physical earthly body—is not so formed as already to contain the faculty of upright gait and posture. This faculty is only incorporated in man's nature when, after his birth, he gradually finds his way into the conditions of equilibrium, into the forces of earthly existence. For in the pre-earthly life, balance or equilibrium is not the same as it is on earth, where it signifies the power to walk and stand. In the pre-earthly life, balance and equilibrium signify the relation man has to the Angeloi, Archangeloi and so forth—to the Beings of the Hierarchies—a relation manifold and differentiated according as one feels oneself drawn more towards one Being or more towards another. This constitutes the state of equilibrium in the spiritual worlds. And this, man loses in a certain sense when he descends on to the earth. In the mother's womb he is neither in the conditions of equilibrium of his spiritual existence, nor is he yet in the conditions of equilibrium of his earthly life. He has left the former and has not yet entered into the latter. It is similar in the case of speech. The language which we speak here on earth is, of course, essentially adapted to earthly conditions. In the first place it is an expression of our earthly thoughts. These earthly thoughts contain earthly information and earthly knowledge; and to all this our speech or language is adapted during our life on earth. But in the pre-earthly life as I have already explained, man has a very different language—one which does not go from within outwards, which does not mainly follow the out-breathing process, but the spiritual in-breathing or inspiration (which we observe to correspond to breathing in the pre-earthly life). Thus in pre-earthly existence, man's language is a living with the cosmic Logos; it is a living within the cosmic Word—the cosmic language from out of which all things of the world are made. This too we lose when we descend on to the earth. We lose the life within the cosmic language, and acquire here on earth the language which serves us in the first place to express our thoughts—our earthly thoughts. This earthly language serves our mutual understanding—understanding as between human beings, all of whom are living on the earth. And so it is with our thoughts themselves—our earthly thinking. Here on earth, our thinking is gradually adapted to the earthly conditions. In pre-earthly existence on the other hand, our thought is a living within the creative thoughts of the Cosmos. Walking, Speaking and Thinking:—let us now consider, of these three, the middle member—human speech. We may indeed say that in speech there lies a most essential element of all earthly culture and civilisation. By speech, human beings come together here on earth, and one man finds the way to another. Bridging the gulf that lies between, soul meets with soul through speech. We feel that we have in speech something essential to our nature here on earth. And indeed our speech is the earthly reflection of our life in the Logos, in the cosmic Word. Thus it is particularly interesting to understand the connection of what man attains by great efforts here on earth, as speech and language, with the metamorphosis of speech and language yonder in the pre-earthly life. Indeed, when we study this relationship, we are led to perceive how the human being is inwardly constructed and organised out of the very element of spoken sound and music. And it is a happy coincidence at the present moment that in the cosmological studies we have pursued for some weeks, I can to-day insert the chapter on the expression of the human being through the words of speech and the sounds of song. It is our great pleasure in these days to be having so excellent a performance of song, here in our Goetheanum building.1 Allow me therefore to-day, if I may say so, to express my personal gratitude for this happy artistic event in our midst, by telling you a little of the connection between the speech and song of man here on earth, and his life in that element which corresponds to the Sound in speech and song, in the spiritual world. If we study the human organism as it stands before us here on earth, we know that it is through and through an image of the spiritual. Everything here—not only what man bears in himself, but also what surrounds him in external nature—is an image of the spiritual. Now when man expresses himself in speech or in song, he is really manifesting his whole nature—body, soul and spirit—not only outwardly but inwardly. In all that he brings forth by way of sound—whether the articulate sounds of speech or the musical notes of song—the full human being is in fact contained. How deeply and fully he is contained, we only begin to see when we understand more in detail what the human being is in that he speaks or sings. Let us take our start from speech. In the historic evolution of mankind, speech, as we know, proceeded from something which originally was song. The farther we go back into pre-historic ages, the more does speech become recitative and eventually song. In distant ages of human evolution upon earth, the expression of the human being through sound was not really differentiated into song and speech, but these two were one. What is so often referred to as the primeval language of man was such that we might as well speak of it as a primeval song. But we will now study speech in its present condition, where it has become very far removed from the pure element of song, and is steeped in the prosaic and intellectual quality. If we take speech as we have it to-day, we find in it two essential elements—consonant and vowel, All that we bring forth in speech is composed of a consonantal and of a vowel element. Now, the consonantal element is in reality entirely based upon the finer plastic structure of our body. Whether we pronounce a B or a P, an L or an M, in each case it rests upon the fact that something or other in our body has a certain plastic form. Nor is this confined by any means to the organs of speech and song alone. These organs only represent the highest culmination of what is here meant. For when the human being brings forth a musical note in song or an articulate sound in speech, his whole body really takes part in the process. The process that goes on in the organ of speech or song is but the final culmination of something that is taking place through the whole human being. Our human body therefore, as to its plastic form and structure, may really be conceived as follows. We take all the consonants there are in any language. They are always variations of twelve primary consonants, and indeed in the Finnish language you still find these twelve preserved very nearly in their pure, original nature; eleven are quite distinct, only the twelfth has grown a little indistinct, but it, too, is still present. Now, these twelve original consonants when rightly understood (and each of them can at the same time be conceived as a form), these twelve consonants taken together really represent the entire plastic structure of the human body. We may say therefore, without speaking figuratively in the least:—the human being is plastically expressed by the twelve primeval consonants. What then is this human body? From the point of view—the musical point of view—we are now taking, the human body is nothing else than a great musical instrument. Even the external musical instruments—the violin or any other instrument of music—even these you can best understand by somehow perceiving in their form and shape a consonant or consonants. You must see them, as it were, built up out of the consonants. When we refer to the consonant element in speech, there must always be something in our feeling reminiscent of musical instruments; and the totality, the harmony of all consonants, represents the plastic sculpture of the human body. And the vowel element—in this we have the soul which plays upon the instrument. The soul provides the vowel nature. Thus when you embody in speech the consonant and vowel elements, you have in every manifestation of speech or of song a self-expression of the human being. The soul of the human being plays in vowels upon the consonants of the musical instrument—the human body. Now if, as I said, we are considering the speech that forms a part of present-day civilisation, we find that our soul, whenever it brings forth vowel sounds, makes use to a very great extent of the brain, the system of head and nerves. In earlier ages of human evolution, this was not the case to the same degree. Let us consider for a minute the system of head and nerves. The whole structure of the head is permeated by forces which run along the nerve-strands. Now the activity which the nerve-strands here develop is entered and permeated by another activity, namely that which comes about through our breathing-in the air. The air which we breathe in passes through the spinal canal right up into the head, and the impact of the breathing beats in unison with the movements that are executed along the nerve-strands. Pressing upward to the head through the spinal canal, the current of the breath is perpetually meeting with the activity of the nerves in the head. We have not a separate nervous activity, and a separate breathing activity; we have in the head a harmony and mutual resonance of breathing activity and nervous activity. Now the man of to-day, having grown prosaic in his ordinary life, sets more store by the nerve forces than by the breathing impulses. He makes more use of his nervous system when he speaks; he permeates with nerve, if we might put it so, the instrument which through its consonantal nature shapes and forms the vowel currents. In earlier ages of human evolution, this was not the case. Man lived not so much in his nervous system; he lived in the breathing system. Hence the primeval language was more like song. Now when the man of to-day sings, he takes what he does in speech—where he permeates it with the nervous activity of the nervous system—and restores it to the current of the breath. He consciously calls into activity this second stream—the breathing. It is the continuation of the breathing into the head which is directly called into activity when, as in song, the uttering of the vowel is added to the bringing forth of the note. But here in song man does not leave the element of breath; he takes back his now prosaic language into the poetic and artistic nature of the rhythmic breathing process. The poet of to-day still strives to maintain the rhythm of the breath itself in the way he shapes and moulds the language of his poems. And he who writes for song takes it all back again into the breathing process (including the breathing process of the head). Thus we may say, the very process which man must undergo here on earth, in that he adapts his language to earthly conditions, is reversed in a certain sense when we pass from speech to song. Song is indeed a. real recollection—though by earthly means—of that which we experienced in the pre-earthly life. For in our rhythmic system we are far nearer to the spiritual world than in our thinking system. And it is of course the thinking system which takes hold of speech when speech becomes prosaic. When we utter the vowel sounds, we press what is living in our soul down into the body; and the body, by adding the consonantal element, does but provide the musical instrument for our soul to use. You will certainly have the feeling that in every vowel there is something of the soul, immediate and living. The vowel can be taken by itself. The consonant on the other hand is perpetually longing for the vowel, tending towards it. The plastic instrument of the body is in fact a dead thing until the vowel nature—the soul—strikes its chords. You can see this in detailed examples. Take for instance, in certain dialects of Middle Europe, the word mir as in the phrase Es geht mir gut. When I was a little boy, I simply could not conceive that the word should be written as it is. I always wrote it mia; for in the r the longing towards the a is quite inherent. Thus when we perceive the human organism as the harmony of all consonants, we find in it everywhere the longing for the vowel nature, that is to say for the soul. Now we are driven to ask, what is the origin of all these things? This human body, in the whole arrangement of its plastic structure here on earth, has to adapt itself to the earthly conditions. It is shaped as it is, because the earthly position of equilibrium and the whole system of the earthly forces would not allow it to be otherwise. And yet all the time it is shaped out of the spiritual world. This matter can be understood only by deeper spiritual-scientific research. The soul-nature, manifesting itself through the vowels, strikes upon the consonantal nature, which is plastically shaped and formed in accordance with earthly conditions. If we lift ourselves into the spiritual world, in the way I have described in my book Knowledge of the Higher Worlds and its Attainment, we first attain Imagination or Imaginative Cognition, as I have often told you. Now when we reach this point, we find that we have lost the consonants. We still possess the vowels, but the consonants—to begin with at any rate—are lost. In the Imaginative condition, we have in effect lost our physical body—i.e. we have lost the consonants. In the Imaginative world, the consonants no longer appeal to us. To describe what we have in that world adequately in spoken words, our words would have to consist, to begin with, of vowels only. We have lost the instrument, and we enter a pure world of sound, where the vowels are indeed coloured and shaded in manifold variety, but all the consonants of earth are in effect dissolved away in the vowels. You will therefore find that in those languages which were not yet so far removed from the primeval, the things of the super-sensible world were named in words consisting of vowels only. The word Jahve for example did not contain our present form of J or V. It consisted only of vowels, and was half-scanned, half-sung. We enter here into a vowel-language which it is only natural to sing. And when we reach from Imaginative to Inspired Cognition—when therefore we receive the direct manifestations of the spiritual world—then all the consonants we have on earth are changed into something quite different. The consonants, as such, we lose. But in place of it, a new thing comes forth in the spiritual perception which comes to us in Inspiration. And this new thing we find to be none other than the spiritual counterparts of the consonants. But the spiritual counterparts of the consonants are not there between the vowels; they live in them. In your speech here on earth you have the consonants and vowels side by side. You lose the consonants as you ascend into the spiritual world. You live your way into a vowel world of song. To put it truly one must say, “It sings,” for you yourself no longer sing. The World itself becomes cosmic song. But all this vowel world is variedly coloured or shaded in a spiritual sense. In effect, there is something living in the vowels—namely the spiritual counterparts of the consonants. Here on earth we have the vowel sound A for example, and—if you will the note C sharp in a certain octave. But when we reach the spiritual world, we do not have one A, or one C sharp in a given octave, but countless ones differing in inner quality. For it is another thing, whether a Being from the Hierarchy of the Angeloi speaks A to one, or a Being of the Hierarchy of the Archangeloi, or some other Being. Outwardly the manifestation is the same, but it is filled in each case with a different inner soul. We may say therefore:—Here on earth we have our body. The vowel sound strikes into it. Yonder in the spiritual world we have the vowel sound; and the soul strikes into it, and lives in it, so that the sound becomes the body for the soul. You are immersed in cosmic music, cosmic song; you are within the creative sound—within the creative Word. Let us now consider sound as it is on earth, including spoken sound. Sound has its earthly life in the element of air. It is, however, but a childish conception of Physics to believe that the peculiar forms in the air are the reality of sound. It is really childish. Imagine, for a moment, you have a piece of ground, and on it stands a man. The ground is most certainly not the man, yet the ground must be there for the man to stand on. Without it, the man himself could not be there. It will not therefore occur to you to seek to understand the man by examining the soil beneath his feet. In the same way the air must be there for the sound to have a basis of support. Just as man stands on the soil—only in a rather more complicated way the sound has its “soil,” its necessary basis or resistance in the air. For the sound itself, the air signifies no more than does the soil for the man who stands on it. The sound presses forward to the air, and the air gives it the possibility to stand. But the sound itself is spiritual. Just as the man is different from the earthly soil on which he stands, so, is the sound different from the air upon which it stands—in which it finds its support though of course in a more complicated way, in a manifold and varied way. Through the fact that we on earth can only speak and sing by means of the air, we have in the airy forming of the sound the earthly image of a thing of soul and spirit. The soul-and-spirit of sound belongs to the super-sensible world, and that which dwells here in the air is fundamentally the body of the sound. We need not therefore be surprised if we find the sound again in the spiritual world, though shorn of that which comes from the earthly—the earthly consonant-articulation. The vowel only is carried over there. The sound as such in its spiritual content goes with us when we rise into the spiritual world, only there it becomes filled with soul. Instead of being shaped and moulded outwardly by the nature of the consonants, the sound is inwardly ensouled. Now all this runs parallel with man's entry into the spiritual world in the widest sense. Think for a moment, my dear friends, man passes through the gate of death. The consonants he soon leaves behind, but the vowels—and especially the manifold intonations of the vowels—these he experiences all the more strongly, only with this difference. He no longer feels the sound proceeding from his own larynx, but he feels that there is singing all around him, and that in every sound of the song, he himself is living. It is so in the very first days after man passes through the gate of death. He is dwelling in a musical element, which is at the same time an element of speech; and this musical element reveals ever more and more as it becomes filled with living soul from the spiritual world. Now, as I have told you, man's going forth into the Universe after he has passed through the gate of death is at the same time a passing from the earthly world into the world of the stars. When we describe such a thing as this, we seem to be speaking in images, but our images none the less are reality. Imagine here the Earth. Around it are the planets, then the heavens of the fixed stars, conceived from time immemorial—and rightly so—as the Animal Circle or Zodiac. Man standing on the Earth sees the planets and the fixed stars in their shadowed radiance. He sees them from the Earth—or, shall we say, with due respect to earthly man, he sees them “from in front?” (The Old Testament, as you know, expressed it differently.) After death, when man goes farther and farther from the earth, he gradually comes to see the planets as well as the fixed stars “from behind.” But there he does not see these points of light or surfaces of light which are seen from the earth. Rather does he see the spiritual—the corresponding spiritual Beings. On all sides it is a world of spiritual Beings. Wherever he looks back, whether it be towards Saturn, Sun or Moon, or towards Aries, Taurus and the other constellations, he sees from yonder side the spiritual Beings. But this seeing is at the same time a hearing; and when he says:—Man sees from the other side—or from behind—Moon, Venus, Aries, Taurus and so forth, we might equally well express it thus:—Man hears the Beings, who have their dwelling in these heavenly bodies, resounding forth into the cosmic spaces. Try to imagine it in its totality. (It really looks as though we were speaking figuratively, but we are not, it is absolutely real.) Imagine yourself out there in the Cosmos—the planetary world farther from you now, the Zodiac with its twelve constellations nearer. From all the heavenly bodies it is singing, speaking as it sings to you, singing as it speaks; and all your perception is a listening to the speaking song, the singing speech of the World. You look out in the direction of Aries, and as you do so, receive the impression of a consonant soul-nature. Behind Aries maybe, is Saturn, a vowel element of soul. And in this vowel element as it radiates out into the cosmic space from Saturn—in it there dwells the soul-and-spirit Consonant:—Aries, or in another instance, Taurus. Thus you have the planetary sphere singing to you in vowels—singing forth into the cosmic spaces; and the fixed stars permeate the song of the planetary sphere with soul from the consonants. Picture it to yourselves as vividly as you can:—the sphere of the fixed stars at rest, and behind it the wandering planets. Whenever a planet in its course passes a constellation of the fixed stars, there bursts forth not a single note, but a whole world of sound. Then as the planet passes on from Aries to Taurus, a different world of sound rings forth. But behind it there follows, let us say, another planet:—Mars. Mars passing through the constellation of Taurus, causes a different world of sounds to ring forth once more. Thus you have in the heavens of the fixed stars, or the Zodiac, a wondrous cosmic instrument of music, while from behind it our planetary Gods are playing upon this instrument. We may truly say, my dear friends, when man down here on earth takes back his speech (which is now formed for his earthly needs, just as his walking is transformed, for earthly needs, from his spiritual power of orientation in the Cosmos)—when therefore man takes speech back again into the element of song, he really inclines himself to that cosmic pre-earthly existence from out of which he is born for earthly life. And indeed, all Art comes before man in this sense. It is as though, whenever he expresses himself in Art, he were to say, “’Tis human destiny—and rightly so that man as he begins his earthly course of life is placed into the midst of earthly conditions and must adapt himself to these. But in Art he goes back again a little step, leaves the earthly life to take its course around him, and retreating for a moment approaches once more the world of Soul and Spirit—the pre-earthly life from which he has come forth.” We do not understand Art, my dear friends, unless we feel in it the longing to experience the Spiritual—though it be but manifested, to begin with, in a world of beautiful semblance. Our creative fancy, whereby we develop all artistic things, is at bottom nothing else than the power of clairvoyance in an earthly form. We are tempted to say:—As sound dwells on earth in the element of air, so it is with the nature of the soul itself. That which is truly spiritual in the pre-earthly life has its earthly dwelling in the image of the spiritual. For when man speaks, he makes use of his whole body. The consonant nature becomes in him the plastic sculpture of the human frame, and the Soul makes use of the current of the breath which does not enter into solid form, to play upon this plastic instrument of music and now, in a twofold way we can turn once more to the Divine, what we thus are as human beings speaking upon earth. Take the consonantal human frame. Suppose we loosen it as it were from the solid form wherein the earthly forces—gravity and the like—or the chemical forces in the foodstuffs have enchained it. Suppose we liberate the consonant nature that permeates the human being for so we may now describe it. When we place a lung on the dissection table we find chemical substances in it, which we can investigate by chemical methods. But this is not the lung. What is the lung? It is a consonant, spoken forth out of the Cosmos, which has taken plastic form. The heart, if we lay it on the dissection table, consists of cells which we can investigate chemically and find the substances composing it. But this is not the heart. The heart again is a consonant—another consonant, spoken forth out of the Cosmos. And if we conceive the whole twelve consonants, cosmically spoken and resounding forth, we have in all essentials the human bodily frame. Thus as we look to the consonants, if we have the necessary clairvoyant power of imagination to see them in their real connection, there arises before us the human body in its plastic shape. If then we take the consonants out of the human being, we have the Art of Sculpture. If on the other hand we take the breath, which the soul uses to play upon the bodily instrument in song—if we take the vowel nature out of the human being, there arises the musical art, the Art of Song. Once more:—Take the Consonant-nature out of the human being, and there arises Form, which you must mould in plastic art. Take the Vowel-nature out of the human being, and there arises Song—Music, which you must sing. Man as he stands before us here on earth proceeds out of the two Cosmic Arts—a Cosmic Art of Sculpture from the one side, and a cosmic Art of Song or Music from the other. Two kinds of spiritual Beings join their activity together. The one provides the instrument, the other plays upon it; the one forms and moulds the instrument, the other plays upon it. Can we wonder that in olden time, when things like these were felt, it was said of the greatest of all artists, Orpheus, that his command over the soul was such that he was able, not only to use the ready-moulded human body as an instrument, but to cast even amorphous matter into plastic forms—forms which correspond to the notes of his music. My dear friends! You will understand that when we describe such things as these we must depart a little in our use of words from what is usual in this prosaic age. Nevertheless what I have said is not intended in a figurative or symbolic but in a most real sense. These things are indeed such as I have described them, albeit to describe them we must sometimes bring our language into greater flow and movement than is customary in its use to-day.
|
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The Acanthus Leaf
07 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The Acanthus Leaf
07 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
A thought that may often arise in connection with this building is that of our responsibility to the sacrifices which friends have made for its sake. Those who know how great these sacrifices have been, will realise that the only fit response is a strong sense of responsibility, for the goal at which we must aim is the actual fulfilment of the hopes resting in this building. Anyone who has seen even a single detail—not to speak of the whole structure, for no conception of that is possible yet—will realise that this building represents many deviations from other architectural styles that have hitherto arisen in the evolution of humanity and have been justified in the jugdment of man. An undertaking like this can of course only be justified if the goal is in some measure attained. In comparison to what might be, we shall only be able to achieve a small, perhaps insignificant beginning. Yet, may be, this small beginning will reveal the lines along which a spiritual transformation of artistic style must come about in the wider future of humanity. We must realise that when the building is once there, all kind of objections will be made, especially by so-called ‘experts,’ that it is not convincing, perhaps even dilettante. This will not disconcert us, for it lies in the nature of things that ‘expert’ opinion is least of all right when anything claiming to be new is placed before the world. We shall not, however, be depressed by derogatory criticism that may be levelled at our idea of artistic creation, if we realise, as a compensation for our sense of responsibility, that in our age, the origin of the Arts and of their particular forms and motifs is greatly misunderstood by technical experts. And then, gradually, we shall understand that all we are striving to attain in this building stands much closer to primordial forces of artistic endeavour which are revealed when the eye of the Spirit is directed to the origin of the Arts, than do the conceptions of art claiming to be authoritative at the present time. There is now little understanding of what was once implied by the phrase “true artistic conception.” It need not therefore astonish us if a building like ours, which strives to be in harmony with primordial Will and in accordance with the origin of the arts, is not well or kindly received by those who adhere to the direction and tendency of the present age. In order to bring home these thoughts to you, I should like to start to-day by considering a well-known motif in art—that of the so-called acanthus leaf—showing the sense in which our aims are in harmony with the artistic endeavours of humanity as expressed in the origin of this acanthus leaf as a decorative motif. Now because our endeavours are separated by many hundreds, nay even thousands of years, from the first appearance of this acanthus motif, they must naturally take a very different form from anything that existed in the days when, for instance, the acanthus leaf was introduced into the Corinthian capital. If I may be permitted a brief personal reference here, let me say that my own student days in Vienna were passed during the time when the buildings which have given that city its present stamp, were completed—the Parliament Buildings, the Town Hall, the Votivkirche and the Burgtheatre. The famous architects of these buildings were still living: Hanson who revived Greek architecture, Schmidt who elaborated Gothic styles with great originality, Ferstel who built the Votivkirche. It is perhaps not known to you that the Burgtheatre in Vienna was built according to the designs of an artist who in the seventies and eighties of the last century was the leading influence in artistic appreciation and development of form in architecture and sculpture. The Burgtheatre was built according to the designs of the great Architect, Gottfried Semper. At the Grammar School I myself had as a teacher a gifted admirer and disciple of Gottfried Semper, in the person of Josef Baier, so that I was able to live, as it were, in the whole conception of the world of architectural, sculptural and decorative form as inaugurated by the great Semper. Now, in spite of all the genius that was at work, here was something that well-nigh drove one to despair in the whole atmosphere of the current conceptions of the historical development of art, on the one side, and of the way to artistic creation on the other. Gottfried Semper was undoubtedly a highly gifted being, but in those days the usual conception of man and the universe was an outcome of the materialistic interpretation of Darwin, and the doctrine of evolution was also apparent in the current ideas of art. Again and again this materialistic element crept into the conceptions of art. It was, above all, considered necessary to possess a knowledge of the technique of weaving and interlacing. Architectural forms were derived in the first place from the way in which substances were woven together, or fences constructed so that the single canes might interpenetrate and hold together. In short, people were saturated with the principle that decoration and ornamentation were forms of external technique. This subject of course might be further elaborated, but I only want to indicate the general tendency which was asserting itself at that time—namely, the tendency to lead everything artistic back to external technique. The standpoint had really become one of ultilitarianism and the artistic element was considered to be an outcome of the use to which things were put. All treatises on the subject of art, and especially on decoration, invariably made mention of the special idiosyncrasies of the different technical experts. This of course was a stream running parallel to the great flood of materialistic conceptions that swept over the 19th century, chief among them being the materialistic conception of art. The extent to which materialism asserted itself in all spheres of life during the second half of the 19th century was enough to drive one to despair. Indeed I still remember how many sleepless nights I had at that time over the Corinthian capital. Now the main feature, the principal decoration of the Corinthian capital—although in the days of which I am speaking it was almost forbidden to speak of such a thing as ‘decoration’—is the acanthus leaf. What could be more obvious than to infer that the acanthus leaf, on the Corinthian capital was simply the result of a naturalistic imitation of the leaf of the common acanthus plant? Now anyone with true artistic feelings finds it very difficult to conceive that a beginning was somewhere made by man taking a leaf of a weed, an acanthus leaf, working it out plastically and adding it to the Corinthian column. Let us think for a moment of the form of the acanthus leaf. The basis of all artistic creation is a consciousness that comes to a standstill before the portals of the historical evolution of humanity as depicted by external documents. A certain consciousness that was once active in man, a remnant of the old clairvoyance, belonged to the fourth Post-Atlantean period, the Graeco-Roman. Although Egyptian culture belongs to the third Post-Atlantean epoch, all that was expressed in Egyptian art belongs to the fourth epoch. In the fourth epoch this consciousness gave rise to such intense inner feeling in men that they perceived how the movement, bearing and gestures of the human being, nay even the human form itself, develop outwards into the physical and etheric. You will understand me if you realise that in those times, when there was a true conception of artistic aim, the mere sight of a flower or a tendril was of much less importance than the feeling: ‘I have to carry something heavy; I bend my back and generate with my own form the forces which make me, as a human being, able to bear the weight.’ Men felt within themselves what they must bring to expression in their own postures. This was the sense in which they made movements when it was a question of taking hold of something or of carrying something in the hand. They were conscious of a sense of carrying, of weight, where it was necessary to spread the hands and finger outwards. Then there arose the lines and forms which passed over into artistic creation. It is as though one felt in humanity itself how man can indeed go beyond what he sees with his eyes and perceives with his other senses:—he can go beyond it when he enters into and adapts himself to a larger whole. Even in this case of a larger whole, when a man no longer merely lets himself go as he walks along, but is obliged to adapt himself to the carrying of a load—already here he enters into the organism of the whole universe.
I have drawn it diagrammatically, from the side view: a number of men are walking one behind the other. They form the procession which then passes round inside the circle; others are sitting in the circle looking on.
If you think of these two figures in alternation, you have the earth-motif and the sun-motif that were always carried by the people who formed the procession. This was one thing that in olden times was presented in circling procession. The people sat around in a circle and the actors passed around in a procession. Some of them carried emblems representing man's connection with the sun; and they alternated: earth-sun, sun-earth and so on:
Man sensed this cosmic power: earth-sun, and then he began to think how he could portray it. The best medium for purposes of art proved to be a plant or tree whose forms runs upwards to a point from a wider base. This was alternated with palms. Plants having a form like a wide bud were alternated with palms. Palms represented' the sun forces; bud-forms running upwards to a point, the earth forces. Feeling his place in the cosmos, man created certain forms, merely using the plants as a means of expression. He used plants instead of having to invent some other device. Artistic creation was the result of a living experience of cosmic connections; this is in accordance with the evolution of the creative urge in man and the process is no mere imitation of outer phenomena of nature. The artistic representation of the elements of outer nature only entered into art later on. When men no longer realised that palms were used to express the sun forces, they began to think that the ancients simply imitated the palm in their designs. This was never the case; the ancients used the leaves of palms because they were typifying the sun forces. Thus has all true artistic creation arisen, from a ‘superabundance’ of forces in the being of man—forces which cannot find expression in external life, which strive to do so through man's consciousness of his connection with the universe as a whole. Now all contemplation and thought both in the spheres of natural science and art, have been misled and confused by a certain idea which it will be very difficult to displace. It is the idea that complexity has arisen from simplicity. Now this is not the case. The construction of the human eye, for instance, is much more simple than that of many of the lower animals. The course of evolution is often from the complex to the simple; it often happens that the most intricate interlacing finally resolves itself into the straight line. In many instances, simplification is the later stage, and man will not acquire the true conception of evolution unless he realises this. Now all that was presented to the spectators in those ancient times, when it was always a question of portraying living cosmic forces, was later on simplified into the decoration, the lines of which expressed man's living experience when he presented these things. This alternation of Sun-motif, Earth-motif, presented itself to the artistic feeling of mankind as a decorative motif in the truest sense. Later on man no longer realised that he must see in this decorative motif a reproduction that had passed into the subconscious realm, of a very ancient dance motif, a ceremonial dance. This was preserved in the palmette motif. Now it is interesting to consider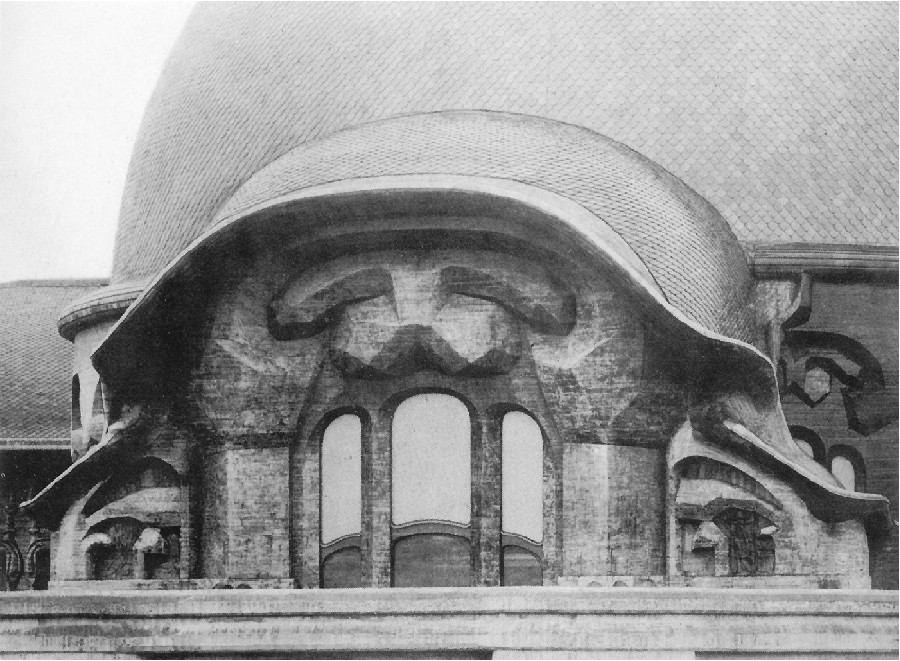  the following:—On the decorations of certain Doric columns one often finds a very interesting motif which I will sketch thus. In Greece, that wonderful land where the fourth Post-Atlantean period was expressed in all its fulness, there was a union of what came over from Asia with all that I have now described and which, as an after-image is there, on Doric columns together with the truly dynamic-architectonic principle of weight-bearing. This union came about because it was in Greece that the Ego was fully realised within the human body, and therefore this motif could find expression in Greek culture. Now you need only imagine what is merely indicated in the Ionic pillars, the middle portion, developing downwards to the perfect volute and you have the Corinthian column. The essential forms of art can no more arise from an imitation of nature than music can be created by an imitation of nature. Even in the so-called imitative arts, the thing that is imitated is fundamentally secondary, an accessory as it were. Naturalism is absolutely contrary to true artistic feeling. If we find that people think our forms here are grotesque we shall be able to comfort ourselves with the knowledge that this kind of artistic conception sees in the acanthus motive nothing but a naturalistic imitation. The acanthus motif, as we have seen, was created purely from the spirit and only in its late development came to bear a remote resemblance to the acanthus leaf. Artistic understanding in future ages will simply be unable to understand this attitude of mind which in our time influences not only the art experts who are supposed to understand their subject, but all artistic creation as well. The materialistic attitude of mind in Darwinism also confronts us in artistic creation, in that there is a greater and greater tendency to make art into a mere imitation of nature. My discovery of these connections in regard to the acanthus leaf has really been a source of joy to me, for it proves circumstantially that the primordial forms of art have also sprung from the human soul and not from imitation of external phenomena. I was only able really to penetrate to the essence of art after I had myself moulded the forms of our building here. When one moulds forms from out of the very well-springs of human evolution, one feels how artistic creation has arisen in mankind. It was a strange piece of karma that during the time when I was deeply occupied with following up a certain artistic intuition (this was after the forms for the buildings had already been made)—an intuition that had arisen during the General Congress in Berlin—it happened that I began to investigate what I had created in these forms, in order to get a deeper understanding. One can only think afterwards about artistic forms; if one “understands” them first and then carries them out, they will have no value. If one creates from concepts and ideas nothing of value will ensue, and the very thing that I perceived so clearly in connection with the acanthus leaf, and have shown to be erroneous, is an indication of the inner connections of the art in our building. I came upon a remarkable example which is purely the result of clairvoyant investigation. At one point I discovered a curious point of contact with Rigl, a fellow-countryman of mine. It is a curious name, not very aristocratic, but typically Austrian. This man Rigl did not achieve anything of great importance but while he was Curator of an Architectural Museum in Vienna he had an intuitive perception of the fact that these architectural decorations had not arisen in the way described by “Semperism” at the end of the 19th century. Rigl hit upon certain thoughts which are really in line with the metamorphosis of the palmette motif into that of the acanthus leaf. Quite recently, therefore, I have discovered a perfect connection between the results of occult investigation, and external research which has also hit upon this development of the so-called acanthus motif from the palmette. ‘Palmette’ is of course merely a name; what is really there in the palmette is the Sun-motif. In the first place, of course, one feels in despair about an idea like that of Rigl. He simply could not realise whence the palmette motif had originated and that it was connected with forces working and moving in man. Rigl remonstrates with the learned art critics who have brought Semper's ideas into everything and are for the most part mere naturalists, but in spite of this he did not get very far. He says that in regard to the acanthus leaf the learned art critics are still feeding upon the old anecdote quoted by Vitruvius. (It cannot be said that they are all feeding upon it, but it is true that they constantly quote it.) Rigl, however, only mentions this anecdote briefly; he does not think it worth while to go into all the details because it is too well known. What he leaves out is very characteristic. He says that Callimachos had seen a basket surrounded by acanthus leaves and that then the idea of the Corinthian column came to him. Rigl, too, leaves something out and this very thing shows that the typical conceptions of our age must despair of ever having real knowledge in this sphere. He leaves out the most important factor in the whole anecdote, which is that what Callimachos saw was over the grave of a Corinthian girl. That is the important thing, for it implies no less than that Vitruvius, although he wisely holds his tongue about it, intends to indicate that Callimachos was clairvoyant and saw, over a girl's grave, the Sun-motif struggling with the Earth-motif, and above this the girl herself, hovering in her etheric body. Here indeed is a significant indication of how the motifs of Sun and Earth came to be used on the capitals of columns. If we are able to see clairvoyantly what is actually present in the etheric world above the grave of a girl who had died, we realise that the palmette motif has arisen out of this, growing, as it were, around the etheric body that is rising like the sun. It seems as though men have never really understood the later Roman statues of Pytri-Clitia for they are nothing else than a clairvoyant impression that can be received over the graves of certain people; in these statues, the head of an extraordinarily spiritual, though not virginal Roman woman, seems to grow upwards as if from a flower chalice. Some time, my dear friends, we shall understand what really underlies the anecdote quoted by Vitruvius, but not until we grow out of the unfortunate habit which makes us perpetually ask, ‘What is the meaning of this or that?’ and is always looking for symbolic interpretations such as, ‘this signifies the physical body, that the etheric body, this or that the astral body.’ When this habit is eliminated from our Movement we shall really come to understand what underlies artistic form—that is to say, we shall either have direct perception of true spiritual movement, or of the corresponding etheric phenomenon. It is actually the case that in clairvoyant vision the acanthus leaf can be seen, in its true form, above a grave. If you will consider all these things; my dear friends, you will realise how important it is to understand the forms in the interior of our building, the forms that should adorn it, and to know the artistic principle from which they have arisen. On previous occasions I used a somewhat trivial comparison, but it is only a question of understanding the analogy. Although it is trivial, it does, nevertheless, convey what it is intended to convey. When we are trying to understand what will be placed in the interior of the building in these two different sized spaces, we may with advantage think of the principle of the mould in which German cakes are baked. It would have been my wish—only it was not to be—that we should have had no such surfaces as these (pointing to an architrave). They will only be right—when something is taken away from them. This roundness here must be eliminated. It would have been better if from the very beginning we had worked with the graver's chisel for then there would have been no protuberance but only a surface. What we must do is to feel from the models how the interior decoration is the plastic vesture for the Spiritual Science that is given its in the building. Just as the interior decoration has the quality of being ‘in-carved,’ so the outer decoration will seem as though it is ‘laid on.’ The interior decoration must always have the character of being in-carved. One can feel this in the model, for the essential thing is a true inner feeling for form in space. It is this that leaves one unsatisfied even in such writings as those of a man like Hildebrandt. He has a certain idea of the workings of form but what he lacks is the inner feeling of form—the inner feeling that makes one live wholly within the form. He simply says that the eye should feel at home when it looks at form. In our building we must learn to experience the forms inwardly, so that, holding the chisel in a particular way, we learn to love the surface we are creating—the surface that is coming into being under the mallet. I, for my part, must admit that I always feel as if I could in some way caress such a surface. We must grow to love it, so that we live in it with inner feeling and not think of it as something that is merely there for the eye to look at. Just recently someone told me after a lecture that a certain very clever man had accused us of straining after ‘externalities,’ as instanced by the fact that different kinds of wood have been used for the columns in the interior. This shows how little our work has been understood. Such a thing is considered to be a dreadful externality. This very intelligent man, you see, simply cannot realise that the columns must be of different woods. The real reason why he cannot understand, is that he has not paused to consider what answer he would have to make if he were asked: ‘Why must there be different strings on a violin? Would it not be possible simply to stretch four A strings instead?’ The use of different woods is a reality in just the same sense. We could no more use only one kind of wood than we could have only A strings on a violin. Real inner necessities are bound up with this. One can never do more than mention a few details in these matters. The whole conception of our building and what must be expressed in it, is based upon deep wisdom, but a wisdom that is at the same time very intimate. Of course there will be forms which are nowhere to be found in the outer physical world. If anything bears an apparent resemblance to a form in the animal or human body, this is simply due to the fact that higher Spirits who work in nature, create according to these forces; nature is expressing the same things as we are expressing in our building. It is not a question of an imitation of nature, but of the expression of what is there as pure etheric form. It is as though a man were to ask himself: ‘What idea must I have of my own being when I look away from the outer sense-world, and try to find an environment that will express my inner being in forms?’ I am sure that everyone will be struck by the plastic forms on the capitals and in the rest of the interior. Not a single one of these forms is without its own raison d'étre. Suppose anyone is carving the column just here (pointing to an architrave motif). At another place he will carve more lightly or deeper down into the wood. It would be nonsense to demand symmetry. There must be living progression, not symmetry. The columns and architraves in the interior are a necessary consequence of the two circular buildings with the two incomplete domes. And I cannot express this any more precisely than by saying that if the radius of the small dome were at all larger or smaller in proportion to the large dome, each of these forms would have to be quite different, just as the little finger of a dwarf is different from that of a giant. It was not only the differences in dimension, but the differences in the forms that called forth the overwhelming feeling of responsibility while we were erecting the building; down to the smallest detail it could not be other than it is. Each single part of a living organism has to exist within and in accordance with the whole living organism. It would be nonsense to say: I want to change the nose and put a different organ in the place where the nose now is.' It is a matter of actual fact that the big toe, and the small toe as well, would have to be different if the nose were different. Just as nobody in his senses would wish to re-model the nose, so it is impossible that the form here should be other than it is. If this form were different, the whole building would have to be different, for the whole is conceived in living, organic form. The advance we must make is this: all that was, in the early days of art, a kind of instinctive perception of a human posture transformed into artistic form must now enter with consciousness into the feeling life of man. In this way we shall have, in our interior decorations, etheric forms that are true and living, and we shall feel them to be the true expression of all that is to live in our building. It simply cannot be otherwise. Now the other day I received two letters from a man who, ten years ago, it is true, did belong to the Anthroposophical Movement, but who since then has left it. He asked me if he could be allowed to make the windows, for he was so well qualified for the work. He was really very insistent. But when you see the windows you will understand that they could only be made by somebody who has followed our work right up to the present. Suppose I were to press my hand into a soft substance: the impress could only be that of my hand, it could not be the head of an ox for instance! It is Spiritual Science that must be impressed into the interior decoration; and Spiritual Science must let in the sunlight through the windows in a way that harmonises with its own nature. The whole building is really constructed—forgive this analogy—according to the principle of the cake mould, only of course instead of a rising cake, it is filled with Spiritual Science and all the sacred things that inspire us. This was always the case in art, and above all it was so in the days when men perceived in their dim, mystical life of feeling the alternation of the principles of earth and sun in the living dance and then portrayed the dance in the palmette motif. So it must be when it is a question of penetrating the outer sense- veil of natural and human existence and expressing in forms things that lie behind the realm of sense perception—if, that is to say, we are fortunate enough to be able to carry this building through. How inner progress is related to the symptoms of onward-flowing evolution—this is what will be expressed in the building, in the dimensional proportions, forms, designs and paintings. I wanted to place these thoughts before you in order that you may not allow yourselves to be misled by modern conceptions of art, which have put all true understanding on one side. A good example of this is the belief that the Corinthian capital arose primarily from the sight of a little basket with acanthus leaves around it. The truth is that something springing from the very depths of human evolution has been expressed in the Corinthian capital. So also we shall feel that what surrounds us in our building is the expression of something living in the depths of human nature behind the experiences and events of the physical plane. To-day I only wanted to speak of this particular detail in connection with our building and with a certain chapter in the history of art. There may be opportunities during the coming weeks to speak to you of other things in connection with some of the motifs in the building. I shall seize every available opportunity to bring you nearer to what is indeed full of complexity, but yet absolutely natural and necessary, in a spiritual sense, for our building. In our days it is not at all easy to speak about problems of art, for naturalism, the principle of imitation, really dominates the whole realm of art. So far as the artist himself is concerned, naturalism has arisen out of a very simple principle; so far as other people are concerned it seems to have arisen from something less simple. The artist, when he is learning must, of course, copy the productions of his master; he must imitate in order to learn. Man now imitates nature out of instinct—for he has made the principle of pupil into that of master and has then put the master on one side because he will brook no authority. This principle is very convenient for artists, for they do not want to get beyond an artistic reproduction of the models before them. The layman to-day understands the principle of naturalism as a matter of course. Where can he find anything to take hold of when he sees forms like those in our building? How are these forms to stimulate any thought at all? He will tear his hair and ask, with a shrug of his shoulders: ‘Whatever is this?’ And he will be lucky if he finds anything at all to take hold of, for instance, if he discovers that some detail has a slight resemblance, maybe to a nose! Although this may be negative, he is delighted that he has discovered anything at all. To-day the layman is pleased if when he finds in the different arts something that transcends the purely naturalistic element, he can say: ‘This has a resemblance to something or other.’ Art will most certainly be misunderstood if people continue to think that it is only legitimate to express things that resemble something or other in the external world. Real art does not ‘resemble’ anything at all; it is something in itself, sufficient unto itself. And again from this point of view it was despairing to find that as a result of the materialism of the second half of last century, painters (not to speak of sculptors) were asking themselves for instance: ‘How am I to get the effect of that mist in the distance?’ And then all kinds of attempts were made to reproduce nature by pure imitation. It really was enough to drive one to despair! Ingenious things were produced, it is true, but what is the value of them? It is all far better in nature herself. The artists were wasting their time in their efforts to imitate, for nature has it all in a much higher form. The answer to this problem is to be found in the Prologue to “The Portal of Initiation.” [The first of Dr. Steiner's Mystery Plays.] Not long ago we happened to be going through the Luxemburg Gallery in Paris, and we saw a statue there. At first sight it was exceedingly difficult to make out what it was supposed to be, but by degrees it dawned on one that perhaps it was meant to represent a human figure. It was so distorted .... I will not imitate the posture, for it would be too much of a strain on the shoulders and knees! It is an absolutely hideous production, but I assure you that if it were to meet one in nature it would be much easier to understand than this “work of art.” People to-day do not realise the absurdity of giving plastic form to a motif that has been thought out, for there is, as a matter of fact, no real necessity to give it plastic form. That which is to be given plastic form must from the very beginning be there in itself and only conceived of plastically. No true sculptor will say that Rodin's productions are an expression of true plastic art. Rodin models non-plastic motifs very well, in an external sense, but true artistic feeling will always be prompted to ask if it amounts to anything, for true plastic conception is entirely lacking. All these things are connected, my dear friends. I have told you what happened in my young days, when I was about 24 or 25 years old, when I absorbed the doctrines of Semper. Already then they were enough to drive one to despair and their influence has not been got rid of yet. Therefore I ask you—and more particularly those who are working so devotedly and unselfishly at our building with all the sacrifices that their work entails—always to try to proceed from inner feeling for what this building ought to contain and to feel in life itself the forms which must arise, in order that we may free ourselves from the trammels of much so-called modern “art.” We must realise, in a new sense, that art is born from the depths of man's being. So greatly is this prone to be misunderstood in our age that people have taken the metamorphosis of of the Earth and Sun motifs to be an imitation of the acanthus leaf. If people will stop believing the anecdote quoted by Vitruvius, that Callimachos saw a basket strewn around with acanthus leaves and then used it as a motif on columns, and will listen to what he says about Callimachos having had a vision over the grave of a Corinthian girl, they will also realise that he had clairvoyant sight and they will have a better understanding of the evolution of art. They will realise that development of clairvoyance leads man to the realm lying behind the world of sense. Art is the divine child of clairvoyant vision—although it only lives as unconscious feeling in the soul. The forms that are seen by the clairvoyant eye in the higher worlds cast their shadow pictures, as it were, down to the physical plane. When people understand all that lives in the Spirit—the Spirit which has the power to impress itself into what surrounds us here in our building, finding its expression in the outer framework around us—they will also understand the goal we have set ourselves, and see in the forms of art the impress of what has to be accomplished and proclaimed in living words in our building. It is a living word this building of ours! Now that I have tried, scantily, it is true, to indicate something in regard to the interior we shall, before very long, be able to speak of the painting and also of the outside of the building.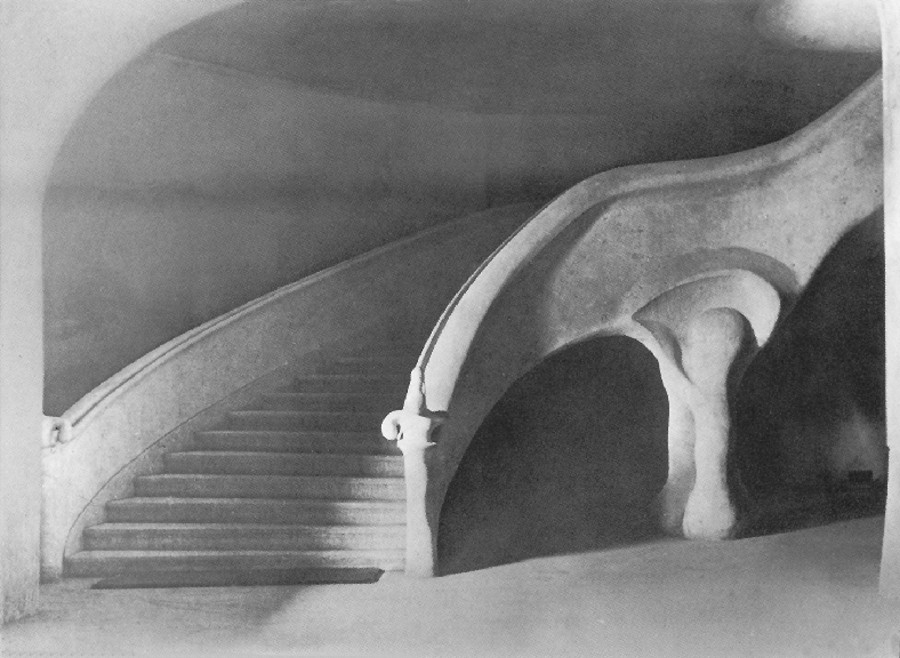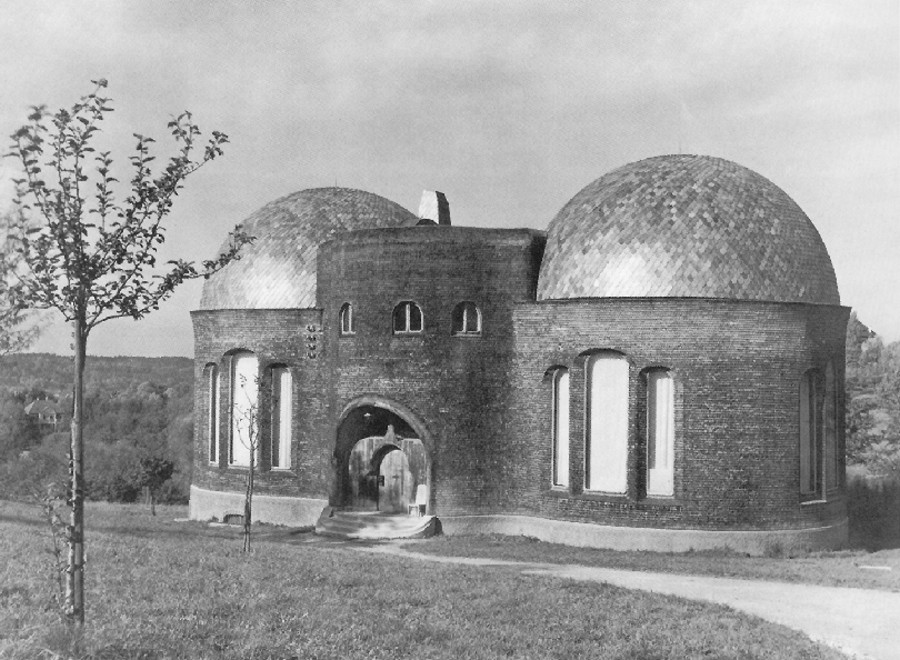   |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The House of Speech
17 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The House of Speech
17 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Even more than on the last occasion when I spoke to you about our building am I reminded to-day of the attitude we must have to this edifice, dedicated as it is to the cause of Spiritual Science. The sacrifices of those who have befriended the cause of Anthroposophy call for a sense of great responsibility. To-day is a splendid occasion for reminding ourselves of this responsibility, for the first of our auxiliary buildings is to be given over to its own tasks. We can be reminded of this responsibility by studies that arise naturally out of the tasks before us and the goal we are striving to attain. The immediate use to which these rooms will be put is the production of the glass windows for our building, and we cannot help being moved by the thought that our human faculties are not really mature enough as yet to accomplish the full task before us. I think it is healthy and good that all our work should be permeated by the feeling that we have not as yet grown equal to our task, for only this can enable us to accomplish the highest that lies within our power. We shall be able to create the first beginnings of an artistic vesture for Spiritual Science—to the extent to which our epoch and our means allow—if we are always pervaded by the feeling that we are, in truth, little qualified for the full task. The site on which our building stands is pervaded by an atmosphere which seems to say: “Do the very utmost of which your powers and faculties are capable, for you cannot do nearly enough in comparison with what ought to be achieved; and even when you have done your very utmost, it will not by any means suffice.” When we look at the site of our building we should be pervaded by an indefinable feeling—a presentiment that a mighty task is hovering before us. And more particularly should this be the case to-day when we are handing over this auxiliary building to our friend Rychter and his workers, in order that they may create something that in the fairest sense may be a living member in the whole organism of our building. Entering the room through this door, our feeling will be that we are indeed blessed, as individuals, in having the opportunity to co-operate in work like this. And when we think of the functions of the windows in the building, an atmosphere of the soul and spirit will hover around us, whispering of the deep spirituality which we pray may flow like purifying waves of healing through this room. When the building is once ready we shall again and again be conscious of a feeling which I may perhaps express as follows: ‘How infinitely necessary it is to grow beyond everything personal, if the forms of this framework for our Spiritual Science are to have real meaning for us.’ This again is, in a certain sense, the satisfying element in our building. Our architects, engineers, and all the other workers may well derive strength from the comforting feeling that apart from all the cares and troubles which the building involves, it can itself be for us a wonderful education—an education leading us above everything personal. The building demands a great deal more than the expression of any personal element. As we set about our work, and permeate the single forms with thought and feeling, we become conscious of new tasks of which we previously had no inkling. We feel that a mystery is there around us, calling out to the highest forces of soul, heart and mind to create something that transcends personality. This building can teach us how to fulfil the tasks which arise every day. It brings home to us a feeling that can ring in such sacred tones in the soul: How infinitely greater are the potentialities of the Universe than insignificant human beings! The highest we can create must be infinitely greater if it is to prove equal to the tasks before us in the objective world.' All that can ever be enclosed within the limits of the personal self must be transcended. The building itself, and the auxiliary house we have been able to open to-day can be a means of education for us. Indeed, the more they become a means of education, the greater understanding we shall have. Already now, as we look at the incomplete building and at this house, we cannot help thinking of what our feeling should be as we enter. How often we shall feel, ‘Ah, if only all human beings could be led here!’ Do we really deserve so sacred a framework—a framework we ourselves have helped to create—if we have any desire to exclude other human beings? Shall it not rather be our dearest wish to bring all men into the building? This will certainly be our desire if we realise the mission that such buildings will have to humanity, if they find imitators and followers? Think for a moment of many buildings erected in our times by clever architects. Some of them, although they show no signs of a new style and are not permeated with any new spirituality, are really creations of architectural genius. Yet they all have one thing in common. We may admire them from outside and think them beautiful inside, but they do not make us feel, as our building will do, that we are enclosed as if by organs of sense. The reason for this is that these other buildings are dumb—they do not speak. This is the thought that I would like to press home to you this evening. Let us think of buildings which express all the characteristics of our times. People pass in and out without in any way growing into their architecture, forms or art. Everywhere we feel that what ought to be expressed through the forms of art has to-day to be communicated to humanity by other means. In the present age man is more and more compelled to bring about order, stability, peace and harmony by means of external laws, decrees or institutions, definitions in words. This implies no syllable or thought of criticism, for it must be so in our age. But something must be added to this—something that signifies the onward evolution of humanity in a different sense. It is probable that our building will not be able fully to attain its goal—indeed we are only aiming at a primitive beginning. Yet if human culture is able to take what is expressed in our building (in so far as we fulfil the tasks set us by the higher Spirits) and develop it; if the ideas underlying such works of art find followers—then people who allow themselves to be impressed by these works of art and who have learnt to understand their language, will never do wrong to their fellow men either in heart or intellect, because the forms of art will teach them how to love; they will learn to live in harmony and peace with their fellow beings. Peace and harmony will pour into all hearts through these forms; such buildings will be ‘Lawgivers’ and their forms will be able to achieve what external institutions can never achieve. However much study may be given to the elimination of crime and wrong-doing from the world, true redemption, the turning of evil into good, will in future depend upon whether true art is able to pour a spiritual fluid into the hearts and souls of men. When men's hearts and souls are surrounded by the achievements of true architecture, sculpture and the like, they will cease to lie if it happens they are untruthfully inclined; they will cease to disturb the peace of their fellow men if this is their tendency. Edifices and buildings will begin to speak, and in a language of which people to-day have no sort of inkling. Human beings are wont to gather together in Congresses to-day for the purpose of putting their affairs in order, for they imagine that what passes from mouth to ear can create peace and harmony. But peace and harmony, and man's rightful position can only be established when the Gods speak to us. When will the Gods speak to us? Now when does a human being speak to us?—When he possesses a larynx. He would never be able to speak to us if he had no larynx. The spirits of nature have given us the larynx and we make this gift an organic part of the whole cosmos when we find the true forms of art, for they become instruments through which the Gods speak to us. We must, however, first learn how to make ourselves part of the great cosmos, and then our desire to lead all mankind through these doors will be the stronger. Out of this desire—for its fulfilment is not yet—the longing will develop to work so intensely for our spiritual movement that this aim may gradually be attained. Art is the creation of an organ through which the Gods are able to speak to mankind .... I have already spoken of many things in this connection. I have spoken of the Greek Temple and have shown how all its forms express the fact it is a dwelling place of the God. To-day I want to add something to this. If we try to understand the basic nature of the Greek art of building we shall realise that the very being and essence of the fourth Post-Atlantean epoch flowed into the Greeks' mode of perception and thence into their art of building. What is the basis of Greek perception and feeling? It is, of course, a wide subject, but I will only speak of one aspect. Here (see diagram) we have the wall surrounding the Greek Temple, with the horizontal structure resting upon it. When anything rises above the horizontal it is so constructed that it is upheld by its own forces which balance each other; just as when, in building, we place two beams together.
The presupposition here is that the earth with its gravity lies beneath. And translating this feeling into words, we may say: ‘In the fourth Post-Atlantean epoch man felt that the site of the earth was a gift of the God; it was as though Divine power overflowed into the creations of art.’ Therefore, by means of the forces in the earth given to man by the Gods, it was felt that gravity could be overcome. In the Greek Temple man controls the force of gravity and thereby creates a dwelling place for the God who has given him the earth. Neither this “dwelling-place of the God” nor the later Roman Temples can be thought of apart from the surrounding land. The land is part of the Temple itself. A Greek Temple is complete in itself even if nobody is within it, for its whole conception is that of the dwelling-place of the God; it is the sanctuary of the God. Human beings may live for miles around in the district; if nobody enters the Temple, it stands there, none the less, complete in itself—a dwelling-place of the God. In every detail we see how man expresses in the decorative forms of these dwelling- places of the Gods all that his feeling of veneration makes him feel he ought to do for the Gods. In the last lecture I tried to show you that the motif on the capitals has its origin in a dance motif—a dance that was performed as homage to the Gods of nature. And now let us pass on to the forms of the earliest Christian architecture. One thought in particular arises within us when we pass from the Greek Temple to the Church of Christendom. The Greek Temple stands within its surrounding territory, belongs to the territory. Human beings are not necessarily within the Temple; they live around it, outside it. The Temple belongs to the surrounding territory, is thought of as the altar of the land around it. The Temple hallows everything, even the trivial daily occupations of the human beings who live on the land. Service rendered to the earth becomes a divine office because the God stands or is enthroned as Lord and participates in the work on the land and in the pursuits of human beings living around the Temple. Man feels himself united with the God as he works on the land. Worship of the God is not yet separated from service to the earth. The Temple grows out of the human element, sometimes indeed out of the ‘all-too-human,’ and hallows everything around it. ‘Earth, be thou strong!’—This is the prevailing mood of the fourth Post-Atlatean epoch, when human beings are still at one with the earth which the Gods have given into their charge, when the Ego is still slumbering in a kind of dream consciousness, when man still feels himself connected with the Group-Soul of the whole of humanity. Then man grows out of this Group-Soul, becomes more and more individual, and he separates from the land, from daily life and activity, the worship he performs in his spiritual life. In the early days of Christianity the feelings of men were no longer the same as in the Greek age. Looking into the soul of the Greek, we see him sowing his fields and working at his industrial pursuits, pervaded by this unshakable feeling: There stands the Temple with the in-dwelling God and I am near. I may be carrying out my pursuits and working on the land but all the while the God is dwelling there within the Temple. Then man grows more individual, a strong sense of Ego, of “I” arises within him, and Christendom represents the emergence of something that had been prepared through the course of long ages by the ancient Hebrew civilisation. Out of the human soul arises the need to separate off from the affairs of everyday life the worship that is offered to the God. The building is separated from the land and the Church of Christendom comes into being. The land becomes independent; the building becomes an entity independent of the territory; it is an ‘individuality’ complete in itself. The Greek Temple was still a kind of altar for the whole territory, whereas the walls of the Christian Church now form a space set apart for those who are to worship. The forms of the Churches of Christendom and also of Roman architecture gradually come to express this individual, spiritual need of man, and they can only be understood in this sense. The place of the Greek within earthly existence was such that he said to himself: ‘I can remain here with my flocks, carrying out my occupations, doing my work on the land, for the Temple stands there like an altar for the whole countryside: the God is dwelling within it.’ In Christendom, man says: ‘I must leave my work and repair to this building, for there I must seek for the Spirit.’ The service of earth and the service of heaven are separated and the Christian Church more and more assumes a form where Greek and Roman architecture would no longer be suitable. It is a form which reveals that the community belongs to the church; the church is intended to enclose the community. Then, once again set apart from the community, we find the house of the priests, of those who teach. An image of the universe comes into being; the Spirit speaks to those who seek for the spirit, in precincts where they are enclosed within walls. The whole world was felt by the Greeks and Romans in former times in the same way in which the Christians afterwards felt the precincts of the Church with its enclosing walls. And what the Greek Temple itself had been now became the chancel. Men sought now for a distinct image of the world whereas formerly they had taken the world itself and only placed within it, visible to outer senses, the Temple as the dwelling-place of God. Gothic architecture is really only a branch of what was already being prepared. The essential feature of Gothic architecture is that the weight is taken away from the walls and placed upon the pillars. What is the origin of this whole mode of construction, where the weight rests on pillars, which are so moulded that they are able to bear it? It is based on a quite different conception from that of the Greek Temple. When we pass to the pillars of Gothic architecture which take away the weight from the walls, we are no longer concerned with the pure force of gravity. Here, man himself is working. In the Greek Temple it is as though he frees himself from the earth's gravity and having gained knowledge of it within the earthly realm, now rises above it. In that man makes use of the force of gravity, he overcomes it. In the weight-bearing Gothic pillars we are no longer concerned with the pure working of the force of gravity; in the Gothic building the art of handicraft is necessary, of higher and lower handicraft. The need for the creation of precincts which enclose the community also gives rise, in Gothic architecture, to the need for something wherein the activity of the community plays a part. In the single forms we see a continuation, as it were, of what the people have learnt. The art of the hand-workers flows into the forms, and in studying these forms we see the art of human beings who have contributed their share, who have worked together. The old Roman Churches are still edifices which enclose the God. The Gothic Church is an edifice built by the community to enclose the God but one where the people have contributed their own handicraft. They do not only enter the Churches but they themselves work at the building as a community. In Gothic architecture this labour of human beings unites itself with the Divine. The souls of men no longer receive the Divine as a matter of course; they do not only come together and listen to the word of the Spirit proceeding from the chancel, but they gather around the God in their labours. Gothic Churches are really crystallised handicraft. We can quickly pass over what came next, for it really amounted to a revival of classic architecture. In this connection it is not necessary to speak of the Renaissance; we will speak of what the fifth Post-Atlantean epoch demands of us. Let us consider the element of weight and support, following it to the point where it becomes crystallised handicraft in Gothic architecture. If we penetrate this with artistic feeling we realise that here is something at rest within itself, at rest within the earthly forces. All the forces of these edifices rest within the earthly element. The Greek Temple everywhere indicates the force of gravity and its own union with the earth. In the Greek Temple we can everywhere observe some manifestation of the force of gravity. Its very forms reveal a union with the earth. And now let us compare the basic form in our building that will confront everyone even from the outside. I will make a rough diagram of it. What is the characteristic of this motif? I should have to speak for a long time if I wanted to show that this is how the art of relief first assumes its real meaning, but I will only give you an indication of what I really have in mind. A certain eminent artist of modern times has spoken a great deal about the art of relief and has said some clever things. He tells us to think of two panes of glass standing parallel to each other and between them an intersected figure. We should then be looking in the direction of the arrow through the panes of glass at the figure ... Now there is in the world a relief which is full of meaning, only we pay no proper attention to it. There is a certain relief that has been created in accordance with the true idea—it is the earth with her plant kingdom. We must, however, pass away from the surface of the earth into cosmic space before we can study this relief. The earth is the living surface which brings forth its creatures from its own being. Our own art of relief must be based upon the conception that the wall is a living thing even as the earth brings forth her plants. This is how a true art of relief is attained. To go beyond this principle is to sin against the essence of the art of relief. When we look down upon the great relief of the earth, we see human beings and animals moving upon it, but they do not belong to the relief. They can be introduced into the relief, of course, because the arts can be developed in all directions, but this is no longer the pure essence of the art of relief. Our building must speak through the forms in its interior, but the speech must be that of the Gods. Think for a moment of the life of human beings on the earth, that is to say, immediately on the surface of the earth. Here we need not draw directly on our teachings—we need only turn to the Paradise Legend. If man had remained in Paradise he would have looked upon the wonderful relief of the earth with her plant kingdom from outside. He himself, however, was transplanted, as it were, into this relief. He could not observe it from outside for he was taken out of Paradise. The speech of the Gods cannot ascend from the earth to men for the speech of the earth drowns the speech of the Gods. Nothing in this architecture is there for its own sake alone. The one form leads over into the other; or, if the forms have a threefold character, the central form is the bridge between the other two. Here we have a rough sketch of the forms of the doors and windows.
Now all that lives in the sculptured forms is three dimensional; relief is a conquest of the second dimension, surface, which is then brought into the third dimension. This is not realised if we merely take the standpoint of an observer or spectator: for we need a living feeling of how the earth allows the plants to grow out of her being. When I come to speak of the real nature of painting we shall understand the significance of the connection between colour and the inner element of soul in the universe. There would be no sense in painting with colours if colour were not something quite different from what physics imagines it to be. The principles of colour as the speech of the soul of nature, of the soul of the universe, will be the subject of a later lecture. I will now indicate how our glass windows are to represent the union of the outer with the inner. They will each in themselves be of one single colour, but different colours will be used at the various positions in the building. This expresses the spiritual, musical harmony of the outer with the inner world. And the single coloured window will only express this harmony in the thicker and thinner strata of the glass. That is to say, we shall have surfaces where the glass is thicker, more solid, and surfaces where the glass is thinner. The light will shine more strongly through the thinner places in the windows; it will shine less strongly, and produce darker colours, through the places where the glass is thicker. The connection between spirit and matter will be expressed in the glass windows; but the whole interior will strive to be an organ for the speech of the Gods. The larynx makes it possible for man to speak, and in the same way the whole of our relief-moulding is an organ for the Gods who should speak to us from all sides of the universe. So that when we make an aperture for the windows in the walls which allow the Gods to speak to us, we are seeking the path to the Spirits of the cosmos. These windows are intended to signify in their coloured shadings: ‘Thus, O man, thou findest the path to the Spirit.’ We shall see how the soul is connected with the spiritual world when it sleeps during the night and is living outside the body. We shall see the way in which the soul is connected with the spiritual world between death and a new birth in the disembodied state. The windows will show us how, when man approaches the threshold, he becomes aware of the abyss; the stations on the path to the spiritual world will be revealed. They will arise as light formations from the West, revealing to us the mysteries of Initiation. We are trying to create walls, the forms of which make the wall themselves seem to pass away. The designs must express how we pierce the walls, showing us how we find the path to the spiritual worlds, or traverse these worlds unconsciously, showing us what our relation to the spiritual worlds must be. The Greek Temple, the dwelling place of the God, and the later edifice, which was built for the community desiring to be united with their God, were building-sheaths which enclosed and shut off. Our building must not shut off anything in the universe; its walls must live, but live in accordance with truth itself. Truth flows into the beauty of our relief-moulding. If we had not been driven out of Paradise we should be conscious of the ' speaking ' relief proceeding from the earth herself in the plant forms, which grow even above the geological formations of the mountains and only allow these strata to be bare in places where it is right that they should be bare. The moment however when we find in our perceptual life the transition from the 'repose' where the Gods speak to us, from that ‘repose’ to our own activity, to what we must do in order to find the way to the Gods—in that moment we must have movement, inner movement; we must pierce the wall. We must have these windows which call to our souls to tread the path to those regions whence the words expressed by the forms of the walls have proceeded. Then each one of us will sit within the building and we shall say to ourselves: “The organs of the great Spirits themselves are round about us; it is for us to understand the language spoken though these forms.” But we must understand it in the heart and not merely be able to grasp it intellectually. Those who begin to, explain' the meaning of these forms are on the wrong track. They stand on the same ground as those who interpret the old myths symbolically and allegorically, and imagine for instance, that they are advancing the cause of Theosophy. A man who tries to ‘interpret’ the myths and explain external forms may be clever and ingenious but he is like one who tries to look under his chin to explain the symbolism of his larynx. We understand the speech of the Gods by learning how to listen with our hearts, not by using intellectual agility and giving symbolic or allegorical meanings to myths and artistic forms. ‘Here you sit and the Spirits of the Universe are speaking to you’—this must become a living feeling within us. When this becomes a living perception of what the soul must do if it is to find the way to those regions whence the speech of the Spirits proceeds, we shall direct our gaze to where the walls are pierced by the windows; and at those places there will be revealed to us the mysteries enacted in man as he consciously or unconsciously treads the path from the physical to the spiritual. I have tried to express the feelings of our hearts and souls to-day when this house is being given over to the charge of our friend Rychter and his colleagues for their work. May they feel, as they receive it, the sacred nature of their task and something of the holiness of which I have spoken. Up on the hill itself we are still working at the building which will reveal, to those who seek, organs through which the Gods may speak to them. But there must arise in these seekers a holy longing to find the ways and paths to the realms of the Gods. The work of Rychter and his colleagues in the rooms of this house will be taken up the hill and placed in the positions where the walls are pierced. It will move the souls of those gathered together in the building at the top of the hill and show them the path to the Spirit. May this holy mood pervade this house; may each drilling in the glass be carried out with the feeling: ‘Here I have to mould something that will lead to the realms of the Spirits those who see it up there in the building. My creations must make the soul's perception so living that the shadings in the coloured glass will represent the channels by which the spiritual worlds are speaking through the forms in the interior.’ The difficulties may be very great, indeed there may be only partial success in many cases and in other cases total failure, but the attitude I have described will be an unfailing help. I did not intend to-night merely to speak of matters which may help to make art more intelligible. I have spoken as I have because I pray that something of what I feel may flow from my heart to yours. I want your hearts to be livingly permeated with a feeling inwardly vibrant with the sense of the holiness of this work. We dedicate this house of labour most fitly if as we leave the doors we concentrate with all the forces of our hearts on love for the world of man and of spirit, to the end that the way to the Spirit may be found through what is accomplished here—to the Spirit whence peace and harmony can flow among men on the earth. If all our labours are made living by the Spirit, if all the work on this hill is filled with the Spirit of Love—which is at the same time the Spirit of true art—then from our building there will flow out over the earth the spirit of Peace, of Harmony, of Love. The possibility will be created for the work on this hill to find successors; many such centres of earthly and spiritual peace, harmony and love may thus spring up in the world. Let us realise the living nature of our work in this mood of peace and loving harmony, knowing that our labours flow from the Spirit of Life itself. There have been dwelling-places of the Gods, sanctuaries of the community, and there yet will be an organ of speech for the Spirit, a building which points out the way to the Spirit. The God dwelt in the Greek Temple; the spirit of the community may dwell within the Roman or Gothic edifice; but the world of the Spirit itself must speak through the building of the future. We have seen the house of earthly forces and forms arise and pass away in the course of human evolution; we have seen the house of the union of human souls arise and pass away in the spiritual evolution of the earth. It is for us to build the house of speech out of our love for true art, which is at the same time love for true spirituality and for all mankind.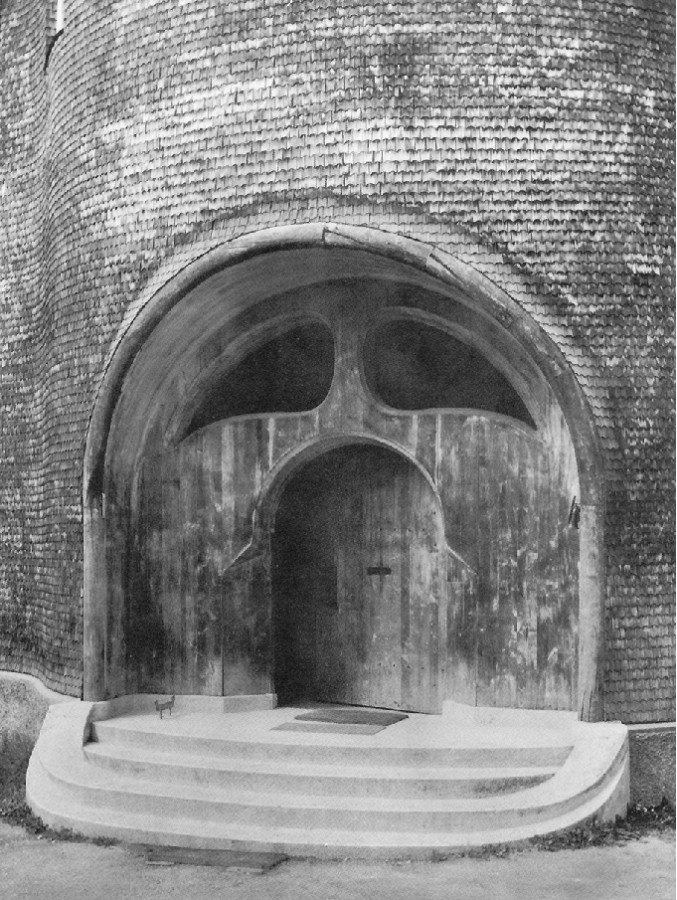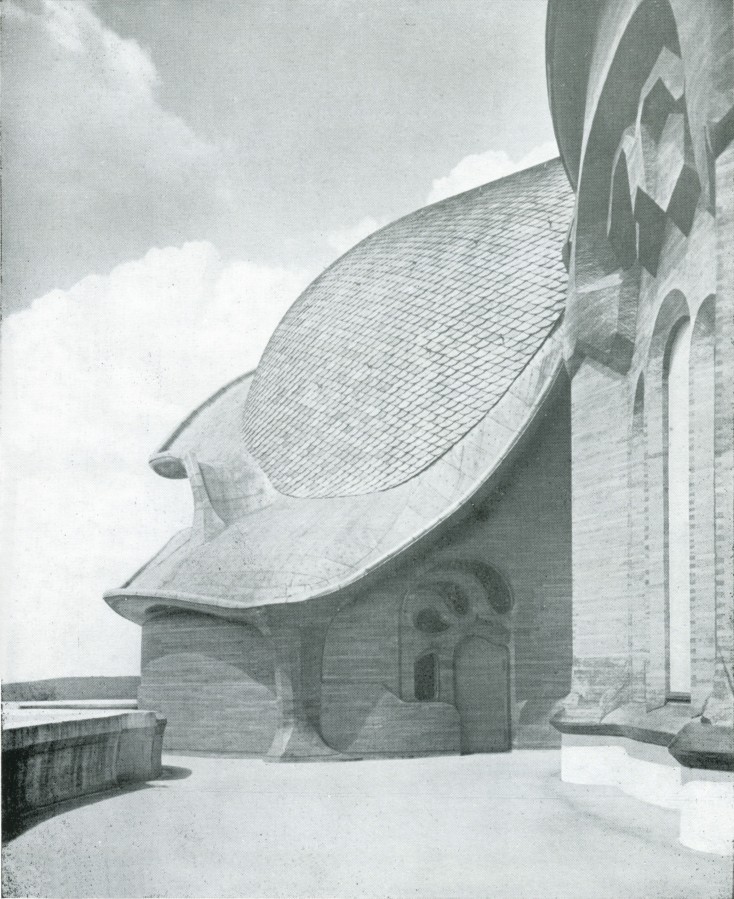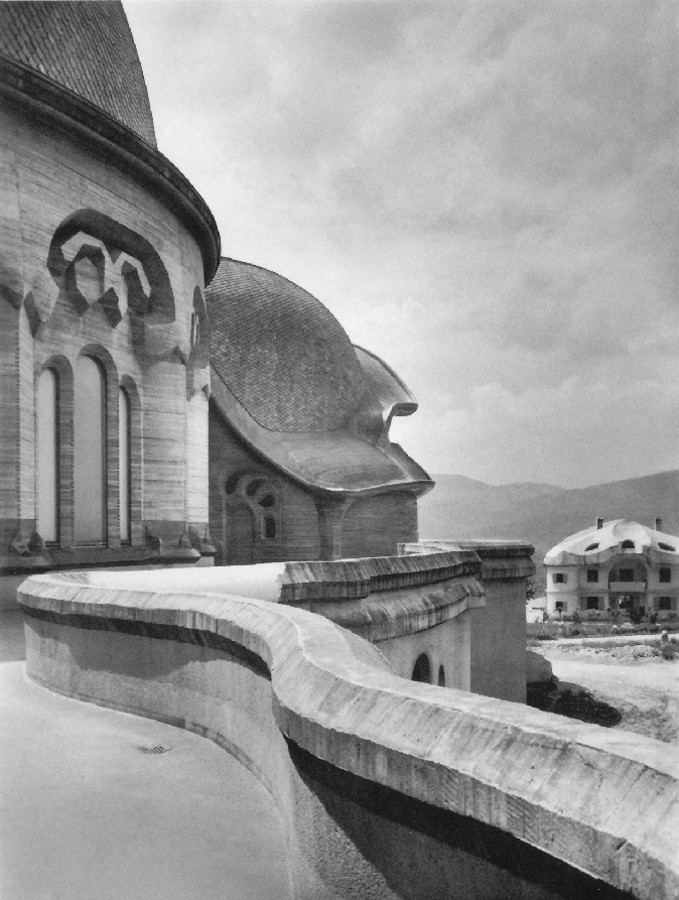    |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The New Conception of Architecture
28 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The New Conception of Architecture
28 Jun 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
During the time when the construction of our building is proceeding I think it is a very good thing for us to try to grow more and more into its meaning. We have already made a beginning with the two previous lectures and we will try as far as we can, by means of further study, really to become one with what is to be accomplished here. In the first place I should like to remind you of what I said when we opened the house dedicated to the work of constructing the glass windows. The lecture referred to the evolution of thought and conception underlying the art of building and I will just briefly recapitulate what I was then only able to indicate. In regard to the Greek Temple, I said that in a certain sense it formed a unity with the whole countryside—the whole countryside was one with it. The Temple stood there as the ‘dwelling place of the God.’ Nothing need be in the Greek Temple save the spiritual presence of the God and his physical image. The essence of the construction of the Temple was the fact that every man engaged in his daily pursuits on the land knew that within the region where he was carrying on his work he was not merely alone with the earth but united with the spiritual world. And the token for the fact that man, as he lived on the earth, was also united with the spiritual world, was the Temple standing there like an altar in the land. We then saw evidence of progress in architectural thought, in that the Christian art of building separated off the edifice from the land. Everyday life and the mood of exaltation by which man raised himself to the Spirit were separated from each other. The Church of Christendom is no longer actually one with the land; it serves the Spirit, apart from the countryside, and expresses the fact that when man is to rise to the Spirit he must leave the affairs of daily life, repair for a time to a place set apart and there be united with the spirit. The Church of Christendom, therefore, could no longer be what the buildings of Greece and also of Rome were in their real being. The Church of Christendom was in itself a duality, the house of the community and the house set apart for the altar and the priesthood. Man leaves the affairs of everyday life and enters into the precincts where he feels himself gazing upwards to the Spirit which comes to him from the chancel where the altar stands. This evolution in architectural thought naturally implies the transformation of the ancient Greek form of building (which was derived purely from static and dynamic factors, the factors of space and gravity) into the form corresponding to the conception of the community being set apart. Passing to the Gothic Cathedral we have a still later form of architectural conception. We have the striving of the community not only to bear their own personalities into the sanctuary but also their individual work, and this is expressed in the forms of Gothic architecture. We feel as if the work performed in the environment has passed into the architectural forms and rises to the Spirit like a prayer, a folding of the hands. I also said that a real advance in architectural conception must come to pass again in our times and that this is only possible if the nearness to the Spirit which was achieved to an ever-increasing extent from the period of the Greek conception of architecture onwards to that of Gothic building—if this nearness is gradually transformed into a complete union with the Spirit. This means that buildings which should now be dedicated to life in union with the Spirit must in their very form express inner correspondence with the Spiritual. We can indeed say—if we try not to explain the thing in abstractions but to grasp it with the whole of our feeling and soul—‘All that is embodied in our life of soul through Spiritual Science implies an actual penetration into the form that is created. The Spirit is revealed in freedom, having now descended to mankind.’ Whereas the Greek placed the Temple like an altar in the land, the future and, inasmuch as we are working from out of the future in our building, the present, are placing a true expression of the Spirit in the land as the result of what the Spirit expresses in its forms. A speech which has a message for man of the present day will arise. But all this requires that we endeavour to understand the Spirit in its forms of expression. In order to understand the Greek Temple, we tried, last time, to grasp the purely physical qualities of space and of gravity. But the Spirit does not only work according to the laws of mechanics and dynamics; it does not only reveal itself in conditions of space and energy. The Spirit is living, hence it must be expressed in our building in a living way, a truly living way. We shall not understand this any better by interpreting the Spirit symbolically, but by beginning to feel that the forms are living, that they are organs of speech flowing from the spiritual world. Is it possible for forms to speak from the spiritual world? It is indeed possible, in many ways. Let us take a thought that is specially near to us because on the one hand it is the expression of the highest, and on the other, in its Luciferic aspect it is submerged in the lowest—let us take the idea of the Ego, of Selfhood. The mere utterance of the word “I” or “Self” does not as yet evoke much thought in man. Many epochs will have to run their course in human history before a fully conscious idea can arise in the soul when the word “I” or “Self” is uttered. Nevertheless, Selfhood, Ego-hood, can be felt in form, and above all when we pass from a purely mathematical conception of form to a feeling in form we can acquire a perception of Ego-hood, Selfhood, in the perfect circle. If you realise this you will readily understand what follows from it. If the true, living, sentient human being, confronting a circle, senses the feeling of Ego-hood, Selfhood, arising in his soul, or if when he sees a fragment of a circle he feels that it typifies the independent Self, he is learning to live in forms. And the characteristic of really living feeling is the capacity for living in forms. If you keep this in mind you will easily be able to pass on to other things that follow from it. The first circle I have drawn here has an unbroken line (1).  This line however can be varied so that it shows these wavy projections (2).  Another characteristic variation is the third figure (3). Another characteristic variation is the third figure (3).  Both figures are only variations of the circle. What do these variations signify? The second (2) expresses the fact that the Self, the Ego has entered into relation with the outer world. The simple circle makes us feel that nothing of the rest of the world is there, only what is shut off within the circle. If we observe the circle in variation we can no longer feel that what is expressed by the circle is alone in the world. The variation in the line expresses a struggle, a kind of interplay with the outer world. If we really live into the form of the second variation (2) we shall feel: “The inner is stronger than the outer.” And in the case of the jagged circle (3): “The outer has bored its way in and is stronger than that which lies within the circle.” And now if we go into any building containing fragments of circles or rounded surfaces, and perceive variations of this kind, we shall feel in the case of the jagged lines, “here the outer has conquered,” and in the case of the wavy lines, “here the inner has conquered!” Our souls begin to live with the forms. We do not merely behold the forms but in our souls we have the living, pulsating feeling of “conquest and encroachment,” “victory and mastery.” The very soul lives with the form. And this union with form, this living in form is the very essence of true artistic feeling. Both figures are only variations of the circle. What do these variations signify? The second (2) expresses the fact that the Self, the Ego has entered into relation with the outer world. The simple circle makes us feel that nothing of the rest of the world is there, only what is shut off within the circle. If we observe the circle in variation we can no longer feel that what is expressed by the circle is alone in the world. The variation in the line expresses a struggle, a kind of interplay with the outer world. If we really live into the form of the second variation (2) we shall feel: “The inner is stronger than the outer.” And in the case of the jagged circle (3): “The outer has bored its way in and is stronger than that which lies within the circle.” And now if we go into any building containing fragments of circles or rounded surfaces, and perceive variations of this kind, we shall feel in the case of the jagged lines, “here the outer has conquered,” and in the case of the wavy lines, “here the inner has conquered!” Our souls begin to live with the forms. We do not merely behold the forms but in our souls we have the living, pulsating feeling of “conquest and encroachment,” “victory and mastery.” The very soul lives with the form. And this union with form, this living in form is the very essence of true artistic feeling.  But we can go further. Let us picture to ourselves a less simple variation (4). The form moves in one direction and becomes action. If we live in this form we have the feeling that it advances, that it moves. In the forms themselves we find the quality of movement. I have here made a simple sketch of something that will appear in a complicated form in the building, but you will find that there is an absolute correspondence. Passing from the entrance at the West and thence towards the smaller structure (at the East) you will find that all the forms in the interior will evoke the feeling that the whole structure is proceeding from the West onwards to the East. This is expressed in the forms. At the West you will feel in thought that you are within a vehicle that is bearing you to the East. The very essence and meaning of these relief variations is that they do not merely appear as dead, dynamic or mechanical forms; we seem to enter a vehicle that bears us onwards. In a spiritual sense we shall not “rest” in our building; we shall be led onwards. From this you will realise that the basic character of the forms here is quite different from the forms of the three stages of architectural thought which I have described. Up to our time architectural thought has been concerned with the qualities of lifeless, mechanical rest. Now, however architectural thought becomes the thought of speech, of inner movement, of that which draws us along with it. This is what is new in the whole conception, and the basic form must of course correspond to it. In what way does the basic form correspond to it? Now I have said that the most intimate of all impressions is that of the Self, the Ego, as expressed in the circle or sphere. Why is this? It is because the simple circle or sphere is of all forms the most easily perceptible. It is an absolutely simple matter to recognise a circle. All that is necessary is the most trivial thought that everything is equidistant from the central point. As soon as we picture to ourselves points standing at an equal distance from this centre, we have the sphere, or circle. It is the very easiest process that can be carried out in thought. As form, then, the circle is the simplest of all entities. This is also in accordance with external reality, for the Selfhood in every being, from the simplest cell to the complex human being, is the simplest of all impressions, just like the circle or sphere. Behind all this there is something much deeper and I want you now to follow me in a thought that will lead those who really understand it, to great profundities. Now the form of an ellipse is more complex than that of the circle. I will draw the form of an ordinary ellipse. It need not be exact but merely have the general character of an ellipse. The simplicity of the thought is no longer there when we pass to the ellipse. Although the ellipse is still spherical, we have no longer the nature of equality as in the case of the circle. Here I must ask those who have studied geometry—although for politeness sake we will assume that you all know a little of geometry though you may have forgotten some of it—to try to understand the following ideas. There is also order and regularity in the ellipse. Just as the circle is related to one point, the ellipse is related to two. In the case of the circle there is no such feeling of satisfaction, for the circle is so immediately obvious. The ellipse causes us greater joy because there we have to be inwardly active. The more one is inwardly active, the greater joy one has. What is often so difficult to realise is that man, in his inner being, craves for activity. If he wants to be lazy this is merely an affair of his conscious life. The astral body is not only wiser, but also more industrious and would like always to be active. Now there is another line consisting, of course, always of two portions. Those who have studied geometry will know that the hyperbola consists of two symmetrical curves. Man is thus a mathematician in the substrata of his consciousness and by means of subconscious calculation we create for ourselves regularity of form. We add and subtract, but we can also multiply. Here again we have two points. Multiplying the one by the other we again get a line that looks somewhat like the ellipse but is not the same. This line contains an inner process of multiplication.
This line has something mysterious about it. The circle is a simple entity, the ellipse already more complicated, the hyperbola still more so, for I do not think that the ordinary person sees only one single line in the two curves. The ordinary intellect believes there are two curves. The ordinary intellect believes there are two lines, but in reality this is not so. The other line is mysterious for another reason, for according to what is produced by multiplication the line is changed into this curious form. It is the curve of multiplication, the curve of Cassini, the lemniscate which plays so important a rôle in occult investigations. The line can develop in such a way that it assumes these forms. There are two lines, you see, but in the inner sense there is really one line, and when we feel it as one line in the astral world we know that this form (o-o) is only a specialisation of this form ( ∞ ). But now think—this form ( ∞ ) disappears into the fourth dimension—then appears again and enters the physical world. It is an unity because it ever and again disappears into the fourth dimension. This multiplication process has really three different forms. We have therefore a line of addition, a line of subtraction, a line of multiplication. Someone may say that there must then be a line of division, the fourth method of calculation.
Now we have something very remarkable indeed. When we really try to penetrate into the depths of nature they appear before the soul in all their wonder. The circle appears to be an utterly simple entity but it is, nevertheless, full of mystery. The circle can also be understood by taking two points and dividing, and inasmuch as the same result is arrived at, we get the circle. The circle is thus something very remarkable. It is the simplest of all entities and yet it is the product of an occult process of division that is brought into consciousness. It is just the same in the case of the self of man: the ordinary self is the simple entity and the higher self the mysterious entity resting in the depths of being—a self that can only be found when we transcend its limits and pay heed to the world with which it is connected. The circle is the same whether we say that it is the simplest of all forms or that the product of division from two points is always the same. Just as we have the same circle, so we have within ourselves a duality: something that belongs to everyday life and is readily perceptible, and something that we only grasp when we go out to the whole universe, conceiving of this entity as the most complicated product of the great cosmic struggle where Ahriman and Lucifer carry out the division and where our own higher self has to maintain itself as the quotient if it is ever to come to expression. Portions of the ellipse and of the hyperbola and also of the curves of Cassini will be found everywhere in our building, and your astral bodies will have plenty of opportunity to make these calculations! Here I will only mention one instance: when people go into our building and stand in the gallery where the organ and the singers will stand, their souls will be able to carry out this process of multiplication. The soul may not do so consciously but it will feel this process in the depths of its being, because this is the line of the structure around the organ. This line will be found in many places in the building. After what I have now told you about the twofold meaning of the circle you will be able to realise that when you enter the building from the West and feel yourselves surrounded by the circular structure, by the cupola above, that here is the image of the human self. But the other smaller space in the East is not at first sight so intelligible. The smaller structure will seem to be full of mystery because, although its form is also circular, it must be conceived of as the result of a process of division and it only outwardly resembles the larger space. There are two circles, but the one corresponds to the life of everyday and the other is connected with the whole cosmos. We bear within us a lower self and a higher self. Both again are one. Thus our building had to be a twofold structure. Its form expresses—not in any symbolical sense but in its very being—the dual nature of man. When the curtain in front of the stage is open we shall perceive an image of man not only as he is in everyday life, but as complete man. The forms themselves express a movement from West to East, the path of the lower to the higher Self. All that I have told you can actually be felt in the forms. The erection of a building of this kind reveals how the spiritual form of nature and the higher spiritual world can be expressed. Nobody who begins to think out all kinds of ingenious interpretations will Understand our building. It can only be understood by a living feeling of the development and being of the forms. For this reason I do not want to describe the building pictorially but to speak of the mode of its development, how spiritual being itself has become form and movement and has flowed into it. Suppose anyone were to look at the interior and begin to speculate thus: ‘Yes, two cupolas, two circular structures—lower Self, higher Self; a lower Self, a higher Self—a unity.’ This may be a neat interpretation but it would be of no more value than if it were said that Maria and Johannes Thomasius in the Mystery Plays are really one being. This is a mere speculation, for it results in an abstraction. The unity lies in the living ‘becoming.’ Naturally the living powers of becoming can bring forth both Maria and Thomasius but only as the result of a differentiation. Even in similarity the true occultist will always seek for diversity, for it would be false occultism to desire always to lead back diversity to unity. Hence the example of the circle. The circle is the simplest of all entities, where all points are equidistant from the centre—but it is also the result of division. In the circle we have something that is a unity in the outer world and complex in the spiritual world. These are some of the remarks I desired to make. On another occasion I shall speak further on these matters. I shall now speak briefly of other things. Man, as he enters the world, is really a highly complicated being. When he enters the world—as I have often said—he cannot at first stand upright; lie crawls, and at the very beginning of his existence he does not even crawl. Gradually he learns to control the forces which make him able to stand upright. The advance from Gothic architecture to that of Spiritual Science may be described as follows: Gothic architecture contains the prayer: ‘O Father of the Universe, may we be united with Thee, in Thy Spirit.’ Those who know what this prayer contains, who really understand the living development of Spiritual Science, will solve the riddle of the evolution of man. And then, when the forms of architectural thought strive to be united with the Spirit—expressing this striving in their very being—man will feel how he has been permeated with the hidden Spirit and can have around him a building which is a direct expression of the living, inner development of his being. ‘We dwell in the land, but the Spirit is among us.’ This is the Greek thought of architecture. ‘We dwell for a season in the sanctuary and the Spirit comes to us.’ This is the thought behind Christian architecture. ‘We dwell for a season in the sanctuary, but we uplift the soul by raising ourselves to the Spirit.’ This is the thought behind Gothic architecture. ‘We enter with reverence into the Spirit in order that we may become one with the Spirit poured out around us in the forms—the Spirit that moves and is active, because behind the Spirits of Form stand the Spirits of Movement.’ This is the thought behind the new architecture. Existence thus advances through earthly evolution and it is man's task to understand the inner meaning and purport of this existence. He only advances in the wake of true evolution when he endeavours, in every epoch, to experience what the spiritual world bestows in that epoch. Why do our souls pass through different, successive incarnations? Not in order that we may repeat the same experiences, nor that we may pass through re-birth, re-naissance, again and again, but in order that we may assimilate, ever and again, the new that pours into our souls from out the spiritual worlds. We are standing at a definite point in the evolution of humanity in the sphere of art and in many other spheres of spiritual life—at a point where the Spirit speaks clearly to us of new riddles. And just as in the time of the Renaissance man was destined primarily to orientate himself to the past in order to work his way through to the new, so it is with our own external knowledge and perception of the universe. All that has been produced by the modern age since the sixteenth century is only the preparation for a living experience of the universe in its forms and movements which now stand before us as riddles. This, then, is all for to-day. In another lecture I will try to approach questions of a still more intimate character—questions relating to the living soul of nature in connection with colour and the art of painting.  to the left the model made by him; in the middle, Christ, the Representative of humanity; above, Lucifer fallen; below, Ahriman imprisoned. From a drawing by W. S. Pyle.  Architraves and Capitals of Pillars during the Building Work.  Architraves and Capitals of Pillars during Building.  In the background the small Cupola with Stage (X) Here the great wooden sculptured group of the Representitive of Humanity was to have stood. |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: True Aesthetic Laws of Form
05 Jul 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: True Aesthetic Laws of Form
05 Jul 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In the last lecture we spoke of the Spirit which should pervade the forms in our building. From all that has been said you will have gathered that these forms are no more the result of imitation of the external physical world than of mere speculation. Your feeling will have been that the forms have been derived from the spiritual world of which man is an integral part and of which he may hope to become conscious in the development of his knowledge of Spiritual Science. I want to remind you once again of an important fact, of which mention has already been made, namely, that human life runs its course in periods of approximately seven years each, and—as I tried last time to explain to you from spiritual-scientific cosmology—when we observe the whole course of these periods of seven years, we may say that after each period a certain support is added to man's being. When he has passed through seven such periods, therefore, he has reached approximately his fiftieth year, he possesses seven pairs of these ‘life-supports.’ If we were now to imagine ourselves entering the building from the West, in the first two pillars we have the expression of the supports which man has raised in his own being after the first period of seven years has run its course; the second pair of pillars are an expression of the supports he has added after the second period of seven years; and so it goes on, only it must be remembered that in man these supports are intermingled, whereas in the building they have had to be placed one behind the other in space. We may then be permeated with the feeling that when we pass through the building from the West towards the East, all that works upon us from left and right is a revelation of processes in human life itself. This shows us that there are firmly established cosmic laws of which man is a part but which are infinitely deeper than the so-called ‘natural laws’ of the outer physical world, and furthermore that the forms in our building have been evolved from these deep cosmic laws. To study every detail from this point of view would lead us very far, although it could be done. In the present materialistic epoch, where there is no knowledge of Spiritual Science, there will be little understanding for these deeper laws of ‘being and becoming.’ We may therefore find ourselves faced with the question—and it is a wholly understandable one from the point of view of external knowledge—‘Why are the columns made of different kinds of wood?’ There is no allegorical or symbolical meaning in this, and anyone who raises such a question merely proves that life has afforded him no opportunity for the contemplation of deeper cosmic laws. The only rejoinder we can make is this: ‘Why, then, do you consider it necessary for a violin not to have only A strings?’ A man who wanted to use only A strings on a violin would be in exactly the same position as one who—perhaps quite unconsciously and naïvely—were to ask as the result of superficial knowledge, why our pillars are made of different woods. We can develop these matters slowly, for we shall often meet together here. We can allow subjects that may prove fruitful to enter gradually into our feelings. To-day, therefore, I only want to speak of one matter that will help to stimulate our perception of what underlies the laws of true aesthetic form, on the one hand in the cosmos, and on the other in the microcosm, in the constitution of man. Before very long, the so-called science of to-day will undergo an overwhelming expansion, and only then will there be understanding of the true and deeper laws of aesthetic form. In order to evoke a concrete perception of what I have here mentioned in mere abstract words, let us consider the following. I am going to place before you something that corresponds to a cosmological fact, a mighty cosmic fact. Now these three heavenly bodies (see diagram) stand in a certain mutual relationship to each other; they reveal their activities to each other and I want to speak of one particular aspect of these activities. To this end I will first divide the Sun diagrammatically as it actually appears to the occult seer when he directs his attention to these things. The Sun is seen divided into a kind of cross, into four chambers. The remarkable thing is that in the first moments of vision we see a kind of streaming current, but closer scrutiny reveals the fact that here we have to do with hosts of beings passing to and fro. We can see such a stream of spiritual beings passing from a certain “chamber” of the Sun to the Earth, penetrating the Earth and vitalising the Earth with solar essence, that is to say, with the spiritual force of the Sun, and thence streaming to their own chamber in the Sun. This is cosmic reality but one sees still more—one sees migrations of hosts of spiritual beings who are flowing around and through the Moon (see diagram). They proceed from another chamber of the Sun: but they also flow in the other direction and pour through the Moon. Up to this point we are perceiving the activities of the inhabitants of three chambers in the Sun. Another migration or stream arises from the fact that these beings always return to the Sun after having passed through the Moon; thus a double stream has arisen. On the one hand the beings return into the fourth chamber in the Sun after having poured through the Moon, but another stream is formed because certain beings do not take part in the migration to the Moon; before reaching the Moon they turn back again to the Sun. This configuration reveals to us a kind of mirror-image in the cosmos, but we will leave this image out of consideration for the moment. It would be formed by a symmetrical expansion of the figure that is engraved there in the cosmos. This means, in effect, that there is revealed to clairvoyant consciousness a marvellous combination of forms, a figure engraved in the cosmos representing the interplay between the forces of Sun, Moon and Earth. Now I will draw the diagram rather differently, with the Sun rather turned (Diagram II). The cross must also be turned. Now I will draw the diagram again differently (Diagram III). Here I have assumed hypothetically that Ahriman and Lucifer have entered, bringing disorder in their train. I will draw the Sun, Moon and Earth more irregularly and again trace the connections between them. What have I now drawn? Exactly the same thing as in the other diagrams, only somewhat distorted as a result of the intervention of Ahriman and Lucifer. I have now drawn a sketch of the blood circulation in man, a sketch of how the blood flows from the left ventricle of the heart through the body, on the one hand through the brain on the other through the rest of the body, returning as venous blood; you also see the course of the small circulatory stream through the right ventricle and lungs back again to the so-called left auricle. Thus we can read from the cosmos what man is as a microcosmos, only it must be remembered that Ahriman and Lucifer have approached him. If a figure were made of this diagram—that is to say, a figure copied from the cosmos and expressed in some motif—we should have before us a profound cosmic mystery merely in the combination of form. When a certain combination of lines underlies a figure of this kind—where perhaps only a few of these lines are expressed and the others drawn in quite another way—those who have real feeling and not merely intellectual understanding, will perceive a cosmic mystery in the very form itself. They will say to themselves: ‘What is it that this form expresses? I do not actually know, but I feel that it expresses a mystery.’ It is this that inspires our souls and makes our hearts glow when we look at certain forms. We cannot always be conscious of what lies behind them, but our astral body, our subconscious being, contains the mysteries of the cosmos and senses them in the depths just as it contains the secrets of mathematics, as I told you in the previous lecture. When a man says, ‘I feel beauty here, but I cannot explain to myself what it really is,’ something is taking place in his astral body. This he may express by saying that he senses the existence of deep and mysterious secrets of the cosmos which do not take the form of ideas and thoughts but are expressed in a feeling, ‘Ah, how beautiful this form is.’ The reason why he feels this as warmth pouring through his heart and soul is that if he were as conscious in his astral body as he is in his ego he would have a deep knowledge of the cosmos. These things must teach us to understand how art has gradually developed in human evolution and to realise that true works of art in the Goethean sense are ‘a manifestation of higher laws of nature than the ordinary intellect of man can divine.’ We find an inkling of the truth of these things more especially when we go back to what modern opinion holds to be the “primitive art” of earlier periods of human evolution. This is because in those olden times a certain primitive, atavistic clairvoyance was a common attribute of humanity and because man then created forms from out of this clairvoyance. Many of the forms to be found in primitive art can only be understood when we realise that they were the outcome of this primordial clairvoyant consciousness. Men experienced the content of their astral bodies as living movement, tried to express it in a kind of noble dance, and then converted it from the Dionysian dance into Apollonian design and painting. Such is the origin of certain forms of early art which often seem to us merely primitive, but which in truth have sprung from a deeper understanding of the spiritual world imparted by the clairvoyance of those times. This, I think, will show you that in the sense of true, genuine art, the easy phrase ‘there can be no disputing about taste’ is wholly incorrect in its ordinary sense. Fundamentally speaking, of course, one can dispute about everything, even about mathematical principles. When one man applies a mathematical principle and gets a different result from another who also applies it, disputes can naturally arise and even become acute, but one of the two has made an error. The error, of course, is not so easy to discover in the case of beauty or art. Nevertheless man can attain to a point of view which convinces him that the forms and laws of true art are firmly established and based upon the deeper laws of cosmic being. Perhaps it may be admitted that the principle ' there is no disputing about taste' only penetrates into life by dint of effort, that it is a conception only to be evolved very gradually. But in the course of his life a man can be convinced of the truth of it when he realises that art is a manifestation of higher laws of nature which without art would never be revealed. Here again I am using Goethe's words. Man can indeed be convinced that art is this manifestation of higher laws of nature about which there can fundamentally be no disputing. In the light of what now should be living within us, not so much as thought, but as feeling, we must gradually be able to work our way to another perception. What is really happening to us when we delight in forms that are truly artistic? We are passing out of ourselves, penetrating with the soul into something that is real, outside ourselves. Therefore it is not at all unnatural that in a building which belongs to the present and future we should set out in full consciousness to create forms which will help man to conquer the consciousness of merely physical and material actuality and feel himself expanded out into the cosmos through the architecture, sculpture and all that this work of art may contain. Much will have to be done, however, before this feeling will be able to penetrate into every sphere of art and be admitted by modern science. Darwinism, and all that it brought in its train in the nineteenth century, rendered great service to the progress of human knowledge and culture, but it gave rise to many one-sided conceptions, for instance, in the law of so-called “selection” which has been laid down as a universal law, although it only holds good in one connection. The knowledge of this law is very important, but to lay it down as a universal law is the result of distorted, one-sided conceptions. People have been led to think somewhat as follows. They ask, ‘Why is it that the structure of living beings is contrived in accordance with expediency? What is the origin of this?’ The monistic materialist of the present day answers: ‘We are no longer as stupid as our ancestors. We have great intelligence and do not therefore believe that some spiritual being or other has endowed living organisms with this “expedient” structure. It is part of nature that the expedient and the inexpedient (the fit and the unfit) should originally have arisen, concomitantly. These two elements then entered into the struggle for existence where the fit conquered and the unfit was exterminated. The fit passes down through heredity, so that after a certain time it alone remains.’ The ‘fitness’ of the organic structure was thus explained by the law of causality. This conception is then applied in a special instance. Some creature lives in a certain environment and has this remarkable characteristic, that its colouring is the same as that of its environment. Certain creatures live, let us say, in sand of a particular colour. In such cases observation shows that the creatures take on the colour of the sand. Those who adhere to the theory of selection and expediency say: ‘It is expedient for these creatures to have the colour of their environment, for their enemies do not see them and hence cannot pursue them. They are not destroyed. They have this advantage over other creatures whose colour differs from that of the sand. Once upon a time there were creatures who colours resembled the sand, while others were of every possible hue. But these latter were seen by their foes and destroyed; they were at a disadvantage in the struggle for existence.’ The others, however, who were, by chance of the same colour as the sand, remained, and this quality was transmitted to the following generations. The creatures who were differently coloured died out and those like the sand maintained themselves in the struggle for existence.' This is a highly plausible train of thought and it has dominated the minds of men for decades. In sandy places hosts of these tiny creatures of exactly the same colour as the sand are to be found. According to materialistic, monistic Darwinism they are supposed to have originated as I have described. But actual facts upset the conclusion, for, in spite of it all, as soon as these creatures show themselves they are destroyed by their foes. The whole conception is based upon a chain of argument that does not reckon with the actual facts. All these materialistic speculations and fantasies will one day be replaced by true insight which may indeed seem grotesque and paradoxical to many people but which will explain, for instance, why the polar bear is white and not black or brown. The insight will arise that there is an astral nature, that every animal has an astral body and that soul processes have their seat in this astral body. The greyish coloured creatures in the sand have of course no ego, but they have an astral body, primitive though it may be. An interplay arises between this astral body and the colour of the environment, and the effects produced by this interplay between the greyness, let us say, of the environment, and the astral body, pass into the dimmer consciousness of the astral body and permeate the whole being. It is just as if you were to look around here and say, ‘This is wood, I know that it is wood.’ The creature lives in the sand, its astral body is permeated with the colour of the sand and the consciousness of the colour of the sand' flows through its whole being. It takes on the colour, saturates itself with the colour of the environment which has been consciously absorbed. The colour is of course modified by every struggle arising between the immediate colour of the environment and the direct light of the sun. The influence of the direct light of the sun on the astral body, however, is such that, by way of the soul nature, something that in turn streams out and permeates the the whole being enters into the astral body. In the very colours of birds' feathers and skins of animals man will recognise the deeper effects of the consciousness, which is the result of the interplay between the astral body and the environment. The living being lives and moves in the flowing ocean of colour and identifies itself with this flowing colour essence. The human being also does this below the threshold of his ego, but in a higher sense. Our life, therefore, is bound up with the life of the flowing sea of colour. As human beings we have the advantage of the animals in one thing only. I can now do no more than hint at it. Think, by way of comparison, of certain animals which always swim under water and never come to the surface. They have water in their environment. They adapt themselves to what they take into themselves from the water. Others have to come to the surface and they too adapt themselves to what is above the surface of the water. Instead of the water, think now of a flowing sea of colour and light. All animals live, as it were, under the surface of the sea of colour and light, hence they adjust their outer covering primarily in accordance with this flowing colour and light. Man with his ego consciousness stretches out beyond the sea of colour and light and the very fact that he can do this gives him his ego consciousness. When man's colouring is influenced, as in the different races, the influence is not, in his case, the outcome of colour and light, but of the conditions of warmth and climate. The reason why humming birds in certain regions are decked with such a variety of colours is very different from the reason which causes human beings in the same region to be of a negroid black. The birds have been worked upon by colour conditions, and man by the warmth condition, because, in effect, the human being with his ego rises above the sea of colour and this only works in his astral body. Otherwise—to use a radical and therefore paradoxical expression—if the agricultural labourer who is perpetually surrounded by green had no ego whereby he reaches beyond the sea of colour, he would go about with a greenish skin; and the skin of the city man, living perpetually among grey houses and seldom leaving them, would have a horrible greyish tint—that is to say if primordial forces were at work., Our astral body none the less is immersed in the flowing sea of colour, but all that the astral body absorbs from this sea of colour has taken on a different activity. Our hair is not coloured, nor if we had feathers would they be coloured by what the astral body absorbs; instead of this, we have perceptions and feelings in connection with colour without diffusing the colours through our being. If we were simply to absorb the green or blue or red into our astral body and diffuse them through our being, thus giving ourselves the colouring of the outer world, we should have quite a different relationship to the world of colour than is actually the case. We do not, however, do this. We absorb the colours into our being in a spiritual sense, so that blue, for instance, becomes the expression of rest; red the expression of all that is passionate, fiery. Colour is changed into flowing perception or feeling in man, because he reaches out with his ego beyond the flowing sea of colour. Here is a proof that we float in the colour essence of the cosmos and that even when we are merely contemplating the colours of nature we must try to perceive in the aesthetic sense, to establish standards of beauty. This however implies that we must learn to grow into colours, to live in them as within our own element. One seldom finds this feeling for colour, even among people who think a great deal about art. Take, for instance, Hildebrand, who is an exceedingly good artist and who has written an ingenious book on the subject of artistic forms. We read there that colour alone cannot suffice for the real portrayal of things; there must first be the design, the drawing. This, however, is not correct. Hildebrand thinks that when he has a coloured wall in front of him, he is simply looking at colour, possibly blue or red, whereas if he draws contours or designs upon it he has an expression of something. If a surface is covered with blue or red it does not express anything definite—at least according to Hildebrand. Nor this is not the case. A surface covered with blue produces an impression which may be expressed in the following way. Instead of the area that appears blue, the feeling arises that blue takes one into greater and greater depths, to distances ever more remote, to the Infinite, as it were. The blue colour takes one along with it—on and on. Red seems to fight with one, to approach. This of course is somewhat radically expressed, but the whole colour scale thus reveals itself as living being. Just as forms with clear contours express something definite, so does colour place before us something quite definite, differentiated. To fathom these things, however, will be the task of future Art—and in what sense? To understand this we will consider the real nature of the spirit of human evolution. Human evolution proceeded from conditions of primitive, atavistic clairvoyant consciousness. Man gradually worked his way upwards through the different civilisations until, during the Graeco-Latin age, his ego came to birth in the intellectual or mind-soul. We are now living in an age when the ego rises into the consciousness soul (spiritual soul) and has then gradually to rise to Spirit-Self or Manas. In the ages preceding the birth of the ego, of the ego consciousness, art proceeded from direct inspiration which flowed into man from the spiritual world, and all the different forms in art were an expression of this. Suppose a man went out into the on-coming night and looked at the moon. The atavistic clairvoyant consciousness he still possessed gave him the knowledge that here was a revelation of the connection between his brain and the moon, that his lungs breathed in all that the earth's being was communicating to him. The sun had set, but he knew that in the pulsating beat of his heart he bore the sun workings within him. Then man felt—or rather he ‘saw’ it in the atavistic clairvoyance of those ancient times—he felt: ‘Yes indeed there is a connection between earth, sun and moon. Spiritual Beings are hovering up and down between the sun and moon!’
... Then came the age in human evolution when this old clairvoyance gradually passed away; man entered into a condition where he could only perceive the external world of sense. Nothing flowed into him from the spiritual world and it became necessary to resort to a different realm. Every artistic impulse lived originally in the moving being of man himself. He tried to imitate or copy what he perceived in the cosmos by expressing through his hands and with his hands the form that he felt to be living in his hands like a cosmic force. At that time he had to translate into form what he expressed in gestures. It did not occur to him to copy or imitate an object in the external sense. All that lived and pulsated within him, flowing and breathing into him from the cosmos, developed into art without any mere imitation, because the inner life surging within him used him as an instrument. He was the instrument guided by the cosmos itself. This was no longer the case after the old clairvoyant consciousness, which linked man to the cosmos, ceased. Imitative art came into being, for man no longer possessed within himself the power which guided the lines and other factors of art; he no longer felt, I will draw near to the Godhead. ‘There is the Godhead and I will approach.’ When a man felt himself rising to the Godhead he was conscious of the perception of blue, and if he wanted to give expression to this feeling he used the colour blue. But if he was conscious of the approach of an enemy, an alien being bearing down upon him, then he used red. He experienced the flowing sea of colour within himself and there was no need to imitate or copy. This was no longer the case when atavistic connection with the cosmos ceased. Imitative art came into being and attained its summit, so far as sculpture was concerned, in the Graeco-Latin epoch, and so far as painting was concerned, in the age which marked the transition to the fifth Post-Atlantean period. To those who have eyes to see, external history would also be able to prove the truth of these things. Try to think why it is that peoples from Northern and Central Europe who came into contact with Graeco-Latin culture remained so long in a state of barbarism and could not find their way to art. The reason is that these Celtic, Germanic, Slavonic peoples had remained at an earlier stage of evolution than the Graeco-Latin peoples. They had not reached the stage of the full birth of the ego and understood nothing of true imitative art. They came along afterwards with a reinforcing impulse. Hence when we study the art of the Middle Ages we find that the significant elements there are not those of imitative art. The characteristic qualities of mediaeval art are to be found in architecture where man does not imitate but creates out of his inner being. It is only gradually that the imitative element in art entered into the northern peoples. Nowadays, however, we are living in an epoch when man must again find his way into the spiritual world, when he must pass over from imitative art to a new form of artistic creation, when there must be a true renewal of art. The imitative arts reached their prime in the sculpture of antiquity, in Raphael, Michelangelo and others. Something different hovers before us now—a consciousness that penetrates into the spiritual world and at the same time brings down all that exists in forms and colours in the cosmic ocean flowing spiritually around us. A beginning must be made. Something that is not achieved by imitation and which is all around us must be brought down from the spiritual world. I have already spoken of the extent to which this conception has flowed into certain forms in our building and on another occasion we will speak of the new conception of the art of painting. To-day I only wanted to try to deepen the feelings and perceptions which must be ours if we are really to understand the transition which must come about before the old forms of art can pass over to the new. I hope that those friends whose unselfish and devoted labours are revealed each day that passes, will work in such a way towards a mastery of the forms which are necessary to our building, that although it be only a primitive beginning, there will none the less be a real beginning of a spiritualised art. I hope that they will find more and enthusiasm, greater and greater joy, in the consciousness that the World-Spirit demands us to help in the task of establishing in human evolution those things which must be established in our own fifth epoch and during the transition into the sixth. If we understand this, we link ourselves with the World-Spirit working in human evolution, of Whom we try to gain knowledge through true Spiritual Science. All the impulses of this Spiritual Science can pass over into artistic feeling, artistic activity and experience of the cosmos. True enthusiasm and devotion are necessary, but they will grow in us if we lovingly rise to the Spirit Who has guided mankind from the beginning of evolution. That Spirit will not forsake us if we dedicate ourselves to Him with upright hearts and in the real sense—if our labours are not a sentimental prayer, but a true one arising from the power flowing into our inner being from the World-Spirit Who is leading us, and if we are filled with the inspiration of the knowledge that we allow the work of our hands and souls to be guided by the power of the Spirit within us. In this sense, then, let us continue our work.   (Centaur and Slavonic Man) |
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The Creative World of Colour
26 Jul 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 286. Ways to a New Style in Architecture: The Creative World of Colour
26 Jul 1914, Dornach Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
To-day we will continue our study of subjects connected with art. The lectures are meant to help us in regard to the kind of thoughts which should permeate the work before us. If we would couple right thoughts with the task which we are here beginning in a primitive fashion, the necessity arises to bring before the soul many things that impress us when we study man's achievements in art and their connection with human civilisation. Herman Grimm, the very intuitive student of art in the nineteenth century, made a certain apparently radical statement about Goethe. He spoke of the date at which humanity would first have developed a real understanding of Goethe, placing it about the year 2000. According to Grimm's idea, therefore, a long time will have to elapse before mankind will have developed to the point of understanding the real significance of Goethe. And, indeed, when one observes the present age, one does not feel inclined to contradict such a statement. To Grimm, Goethe's greatest significance does not lie in the fact that he was a poet, that he had created this or that particular work of art, but that he always created from a full and complete manhood—the impulse of this full manhood lies behind every detail of his creative activity. Our age is very far from understanding this full manhood that lived, for instance, in Goethe. In saying this I have naturally no wish to speak derogatively of the specialisation that has entered into the study of science, which is indeed often deplored—for from one point of view this specialisation is a necessity. Much more significant than the specialisation in science is that which has crept into modern life itself, for, as a result of this, the individual soul, enclosed within some particular sphere of specialised conceptions or ideas, grows less and less capable of understanding other souls who specialise in a different sphere. In a certain sense all human beings are “specialists” to-day so far as their souls are concerned. More particularly are we struck with this specialised mode of perception when we study the development of art in humanity. And for this very reason it is necessary—although it can only be a primitive beginning—that there shall again come into existence a comprehensive understanding of spiritual life in its totality. True form in art will arise from this comprehensive understanding of spiritual life. We need not enter upon a very far-reaching study in order to prove the truth of this. We shall come to a better understanding if we start from something near at hand, and I will therefore speak of one small point in the numerous irrelevant and often ridiculous attacks made against our spiritual movement at the present time. It is so cheap for people to try, by means of pure fabrications, to slander us in the eyes of the world, saying, for instance, that we are on the wrong track because here or there we have given to our buildings a form that we consider suitable to our work. We are reproached for having coloured walls in certain of our meeting rooms and we are already tired of hearing about the ‘sensationalism’ in our building—which is said to be quite unnecessary for true ‘Theosophy’—that is how people express it. In certain circles ‘true Theosophy’ is thought to be a kind of psychic hotch-potch, teeming with obscure sensations, glorying to some extent in the fact that the soul can unfold a higher ego within. This, however, is really nothing but egotism. From the point of view of this obscure psychic hotch-potch people think it superfluous for a spiritual current to be expressed in any outer form, although this outer form, it is true, can only be a primitive beginning. Such people think themselves justified in chattering about these psychic matters no matter where they may be. Why, then—so they think—is it necessary to express anything in definite forms? We really cannot expect to find any capacity of real thought in people who hurl this kind of reproach at us—in fact we can expect it from very few people at the present time—but, nevertheless, we must be clear in our own minds on many points if we are to be able at least to give the right answers to questions that arise in our own souls. I want to draw your attention to Carstens, an artist who made his mark in the sphere of art at the end of the eighteenth century as a designer and painter of decided talent. I do not propose in any way to speak of the value of Carstens' art, nor to describe his work—neither am I going to give you a biographical sketch of his life. I only want to call your attention to the fact that he certainly possessed great talent for design, if not for painting. In the soul of Carstens we find a certain artistic longing, but we can also see what was lacking in him. He wanted to draw ideas, to embody them in painting, but he was not in the position of men like Raphael or Leonardo da Vinci—or to take an example from poetry—of Dante. Raphael, Leonardo and Dante lived within a culture that teemed with import—a culture that penetrated into and at the same time surrounded the soul of man. When Raphael painted his Madonnas they were living in men's hearts and souls and in the very highest sense something streamed from the soul of the public in response to the creations of this great artist. When Dante set out to transport the soul into spiritual realms he had only to draw his material, his substance, from something that was resounding, as it were, in every human soul. These artists possessed in their own souls the substance of the general culture of the age. In any work of the scientific culture of that time—however much it may have fallen into disuse—we shall find connecting links with an element that was living in all human souls, even down to the humblest circles. The learned men of the spheres of culture where Raphael created his Madonnas were fully cognisant of the idea at the back of the figures of the Madonna, nay more, the idea was a living thing within their souls. Thus artistic creations seem to be expressions of a general, uniform spiritual life. This quality came to light again in Goethe as a single individual, in the way that was possible at the turn of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. So little is this understood in our times, that, in Herman Grimm's opinion, as I have already said, it will be necessary to wait until the year 2000 before the world will again reveal such understanding. Let us turn again to Carstens. He takes the Iliad of Homer, and he impresses into his penciled forms the processes and events of which he reads. What a different relationship there is to the Homeric figures in the eighteenth and the beginning of the nineteenth century from the relationship that existed between the soul of Raphael and the figures of the Madonna and other motifs of that age! In the greatest epochs the content of art was immediately perceptible because it flowed from something that moved the innermost being of man. In the nineteenth century’ it began to be necessary for artists to seek for the content of their creations by dint of effort and we soon find that the artist becomes a kind of ‘cultural hermit,’ one who is only concerned with himself and of whom people ask, ‘What relationship is there between himself and his own particular world of form?’ A study of the history of art in the nineteenth century would reveal the true state of affairs in this connection. Thus there gradually arose, not only the indifferent attitude to art, but the cold one that exists nowadays. Think of someone in a modern city walking through a picture gallery or exhibition of pictures. The soul is not moved by what is seen, no inner confidence is felt in it. The person is faced by what really amounts to a multitude of riddles—to use a radical expression—riddles which can only be solved if to some extent penetration is made into the particular relationship of this or that artist to nature, or to other things. The soul is faced with purely individual problems or riddles, and the significant thing is, that although people believe they are solving the problems of art, they are, in the vast majority of cases, trying to solve problems not really connected with art itself—to wit, psychological problems. Such problems as: How does this or that artist look on nature—are problems of philosophy or the like and are of no importance when we really penetrate into the great epochs of art. On the contrary, when this penetration is undertaken, the problems that emerge not only for the artist but for the contemplator of the works of art, are truly artistic, truly aesthetic ones. For it is the manner that really concerns the creative artists, while the mere matter, the mere substance, is only the element that flows around him, in which he is immersed. We might even put it thus: our artists are no longer artists. They are contemplators of the world, each from a certain point of view and what they see, what strikes them in the world, this they contrive to shape. But these are theory, problems of history and so forth, while on the other hand our age has almost altogether lost the power—or indeed the heart—to perceive art in its essence, to perceive the manner, not the mere matter. Our conception of the world—theoretical from its very foundations—is a good deal to blame for this. Practical as men have become in technical, industrial and commercial affairs, they have become eminently theoretical so far as their thinking is concerned. The endeavour to build a bridge between modern science and the conception of the world held by the artist is not only fraught with difficulty, but with the fact that so few people feel there is any need to build it. Words like those of Goethe: “Art is the manifestation of secret laws of nature without which they could never find expression” are wholly unintelligible to our age, although here and there people think they understand them. Our age holds fast to the most external, the most abstract natural laws—laws which are themselves based on utterly abstract mathematical principles—and it will not admit the validity of any penetration into reality which transcends all abstract mathematics or systems of that kind. No wonder our age has lost the living element of soul which feels the working of the very substance of world connections—the substance that must indeed well up from these world connections before art can come into being. The thoughts and ideas evolved by the modern age in regard to the universe are inartistic in their very nature—nay more, they even strive to be so. Colours—what have they become according to modern scientific opinion? Vibrations of the most abstract substance in the ether, etheric vibrations of so many wave lengths. These waves of vibrating ether sought by modern science, how remote they are from the direct, living essence of colour! What else is possible than that man is led wholly to ignore the living essence of colour? I have already told you that this element of colour is, in its very being, fluidic and alive—an element moreover in which our soul lives. And a time will come—as I have also indicated—when man will again perceive the living connection of the flowing sea of colour with the colours of creatures and objects manifested in the external world. This is difficult for man because, since he has to develop his ego during earthly evolution, he has risen out of this flowing sea of colour to a mode of contemplation that proceeds purely from the ego. With his ego, man rises out of the sea of colour; the animal lives wholly within it and the fact that certain animals have feathers or skins of particular colours is connected with the whole relationship existing between the souls of these animals and the flowing sea of colour. The animal perceives objects with its astral body (as we perceive them with the ego) and into the astral body flow the forces living in the group-soul of the animal. It is nonsense to imagine that animals, even higher animals, behold the world as man beholds it. At the present time there is no understanding of these things. Man imagines that if he is standing near a horse, the horse sees him in exactly the same way as he sees the horse. What is more natural than to think that since the horse has eyes it sees him just as he sees it? This, however, is absolute nonsense. Without a certain clairvoyance a horse would no more see a human being than a human being, being without problems of psychological clairvoyance, would see an angel, for the man simply does not exist for the horse as a physical being, but only as a spiritual being. The horse is possessed of a certain order of clairvoyance and what the horse sees in man is quite different from what man sees in the horse: as we go about we are spectral beings to the horse. If animals could speak in their own language—not in the way they are sometimes made to ‘speak’ nowadays, but in their own language—man would realise that it never by any chance occurs to the animals to contemplate him as a being of similar order but as one who stands higher than themselves—a spectral, ghostlike being. Even if the animals assume their own body to consist of flesh and blood, they certainly have a different conception of the body of man. To the modern mind this of course sounds the purest nonsense—so far is the present age removed from truth! As a result of the relation between astral body and group-soul, a receptivity to the living, creative power of colour flows into the animal. Just as we may see an object that rouses desire in us and we stretch out towards it by movement of the hand, an impression is made in the whole animal organism by the direct creative power in the colour; this impression flows into the feathers or skin and gives the animal its colour. I have already said that our age cannot understand why it is that the polar bear is white; the white colour is the effect produced by the environment and when the polar bear ‘whitens’ itself, this, at a different level, is practically the same thing as when man stretches out with a movement of his hand to pick a rose in response to a desire. The living creative effects of the environment work upon the polar bear in such a way that an impulse is released within it and it ‘whitens’ itself. In man, this living weaving and moving in the element of colour has passed into the substrata of his being because he would never have been able to develop his ego if he had remained wholly immersed within the sea of colour and were, for instance, in response to an impression of a rosy hue of dawn to feel the impulse to impress these tints through creative imagination into certain parts of his skin. During the ancient moon period these conditions still obtained. The contemplation of scenes in nature like that of a rosy dawn worked upon man as he then was; this impression was reflected back, as it were, into his own colouring; it penetrated into the being of man in those times and was then outwardly expressed in certain areas of his body. During the earth period, this living bodily existence in the flowing sea of colour had to cease in order that man might be able to evolve his own conception of the world in his ego. So far as his form was concerned he had to become neutral to this sea of colour. The tint of the human skin as it appears in the temperate zones is essentially the expression of the ego, of absolute neutrality in face of the outer waves of colour; it denotes man's ascent above the flowing sea of colour. But even the most elementary facts of Spiritual Science remind us that it is man's task to find the path of return. Physical body, etheric body, astral body—these were developed during the periods of Saturn, Sun and Moon; the ego has to develop during the earth period. Man must find the ways and means to spiritualise his astral body once again, to permeate it with all that the ego has won for itself. And as he spiritualises his astral body and so discovers the path of return, he must again find the flowing, surging waves of colour out of which he arose in order that his ego might develop—just as a man who rises from the sea only sees what is over the sea. We are indeed already living in an age when this penetration into the spiritual flow of the powers of of nature—that is to say of the spiritual powers behind nature—must begin. It must again be possible for us not merely to look at colours, to reproduce them outwardly here or 'there, but to live with colour, to experience the inner life-force of colour. This cannot be done by merely studying in painting, for instance, the effects of the colours and their interplay as we look at them. It can only be done if once again we sink our soul in the flow of red or blue, for instance, if the flow of the colour really lives—if we are able to ensoul the essence of colour that instead of evolving any kind of colour symbolism (which would of course be the very opposite way of going to work) we really discover what is already living in colour just as the power of laughter exists in a man who laughs. Hence we must seek out the paths of return to the flowing world of colour, for as I have already said, man has risen above it with his ego. If he has no other perception save ‘here is red, here is blue’—which is often the case to-day—he can never press onwards to living experience of the real essence of colour. Still less is this possible when he gives an intellectualistic garb to this inner essence and perceives red as a symbol, blue as another, and so forth. This will never lead to real experience of colour. We must know how to surrender the whole soul to what speaks to us from out of colour. Then, when we are confronted with red we have a sense of attack, aggression—this comes to us from the red. If ladies were all to go about dressed in red, a man possessed of a delicate sense for colour would silently imagine, simply on account of their clothing, that they might at any moment set about him vigourously! In red, then, there is a quality of aggression, something that comes towards us. Blue has an element that seems to pass away from us, to leave us, something after which we gaze with a certain wistfulness, with yearning. How far the present age is removed from any such living understanding of colour may be realised from what I have already said about Hildebrand, an excellent artist, who expressly states that a colour on a surface is simply that and nothing more; the surface is there, overlaid with colour—that is all—though to be sure it is not quite the same in the case of form which expresses distance, for example. Colour expresses more than mere distance and we cannot help finding it deeply symptomatic of the whole nature of the present age that this is not perceived, even by an artist like Hildebrand. It is impossible to live into the essence of colour if one cannot immediately pass over from repose into movement, realising that a red disc approaches us, and that a blue disc, on the other hand, withdraws. These colours move in opposite directions. When we penetrate deeply into this living essence of colour we are led further and further. We begin to realise—if we really believe in colour—that we simply could not picture two coloured discs of this kind remaining there at rest. To picture such a thing would be to deaden all living feeling, for living feeling immediately changes into the realisation that the red and the blue discs are revolving round each other, the one towards the spectator, the other away from him. The relation between the red that is painted on a figure, in contrast to the blue, is such that the figure takes on life and movement through the very colour itself. The figure is caught up into the universe of life because this is shining in the colours. Form is of course the element that is at rest, stationary; but the moment the form has colour, the inner movement in the colour rises out of the form, and the whirl of the cosmos, the whirl of spirituality passes through the form. If you colour a form you endow it with the soul element of the universe, with cosmic soul, because colour is not only a part of form; the colour you give to a particular form places this form into the whole concatenation of its environment and indeed into the whole universe. In colouring a form we should feel: ‘Now we are endowing form with soul.’ We breathe soul into dead form when, through colour, we make it living. We need only draw a little nearer to this inner living weaving of colours and we shall feel as if we are not confronting them on a level but as if we were standing either above or below them—again it is as if the colour becomes inwardly alive. To a lover of abstractions, to one who merely gazes at the colours and does not livingly penetrate into them, a red sphere may indeed seem to move around a blue, but he does not feel the need to vary the movement in any sense. He may be a great mathematician, or a great metaphysician, but he does not know how to live with colour because it seems to pass like a dead thing from one place to another. This is not so in reality; colour radiates, changes within itself, and if red moves it will send on before it a kind of orange aura, a yellow aura, a green aura. If blue moves it will send something different on before it. We have, then, a play of colours as it were. Something actually happens when we experience in colour; thus red seems to attack, blue to pass away. We feel red as something which we want to ward off, blue as something we would pursue as if with longing. And if we could feel in colour in such a way that red and blue really live and move, we should indeed inwardly flow with the surging sea of colour, our souls would feel the eddying vortex of attacks and longings, the sense of flight and the prayer of surrender that intermingle with one another. And if we were to express this in some form, artistically of course, this form, which in itself is at rest, we should tear away from rest and repose. The moment we have a form which we paint, we have, instead of the form which is at rest, living movement that does not only belong to the form but to the forces and weaving being round about the form. Thus through a life of soul we wrest the material form away from its mere repose, from its mere quality of rigid form. Something like this must surely once be painted into this world by the creative elemental powers of the universe. [Note 1] For all that man is destined to receive by way of powers of longing—all this is something that could find expression in the blue. This on the one hand man must bear as a forming, shaping principle in his head, while all that finds expression in the red he must bear within him in a form that rushes upward from the rest of the body to the brain. Two such currents are indeed active in the structure of the human brain. Around man externally is the world—all that for which he longs—and this is perpetually being flooded over by that which surges upward from his own body. By day it happens that all which the blue half contains flows more intensely than the red and yellow: by night, so far as the physical human organism is concerned it is the opposite. And what we are wont to called the two-petalled lotus flower [Note 2] is indeed a true image of what I have here portrayed, for this two-petalled lotus flower does indeed reveal to the seer just such colours and movements. Nobody will really be able to fathom what lives in the world of form as the creative element, as the upper part of the human head, if he is not able to follow this flow of colour that in man is indeed a “hidden” flow of colour. It must be the endeavour of art again to dive down into the life of the elements. Art has observed and studied nature long enough, has tried long enough to solve all the riddles of nature and to express in another form all that can be observed by this penetration into nature. What lives in the elements is, however, dead so far as modern art is concerned. Air, water, light—all are dead as they are painted to-day; form is dead as is expressed in modern sculpture. A new art will arise when the human soul learns to penetrate to the depths of the elemental world, for this world is living. People may rail against this; they may think that it ought not to be, but such raillery is only the outcome of human inertia. Unless man enters with his whole being into the world of the elements, and absorbs into himself the spirit and soul of the external world art will more and more become a work of the human soul in isolation. This of course may bring many interesting things to light in regard to the psychology of certain souls, but it will never achieve that which art alone can achieve. These things belong to the far, far future but we must go forward to meet this future with eyes that have been opened by Spiritual Science—otherwise we can see in that future nothing but death and paralysis. This is why we must seek for inner connection between all our forms and colours here and the spiritual knowledge that moves innermost depths of the soul; we must seek that which lives in the Spirit in the same way as the Madonnas lived in Raphael, so lived in him that he was able to paint them as he did. The Madonnas were living in Raphael's very being, just as they were living in the learned men, the labourers in the fields and the craftsmen of his time. That is why he was the true artist of the Madonna. Only when we succeed in bringing into our forms in a purely artistic sense, without symbolism or allegory, all that lives in our idea of the world—not as abstract thought, dead knowledge or science, but as living substance of the soul—only then do we divine something of what the future holds in store. Thus there must be unity between what is created externally and all that permeates the soul in the innermost depths of her being—a unity that was present in Goethe as the result of a special karma. Bridges must be built between what is still to many people so much abstract conception in Spiritual Science and what arises from hand, chisel and paint brush. To-day the building of these bridges is hindered by a cultural life that is in many respects superficial and abstract, and will not allow life to flow into action. This explains the appearance of the wholly groundless idea that spiritual knowledge might cause the death of art. In many instances of course a paralysing effect has been evident, for instance in all the allegorising and symbolising that goes on, in the perpetual questioning, ‘what does this mean?’ ‘what does that mean?’ I have already said that we should not always be asking what things ‘mean.’ We should not think of asking about the ‘meaning’ of the larynx, for instance. The larynx does not ‘mean’ anything, for it is the living organ of human speech and this is the sense in which we must look at all that lives in forms and colours when they are living organs of the spiritual world. So long as we have not ceased asking about allegorical or symbolical meanings, so long as we interpret myths and sagas allegorically and symbolically instead of feeling the living breath of the Spirit pervading the cosmos, realising how the cosmos lives in the figures of the world of myths and fairy stories—so long have we not attained to real spiritual knowledge. A beginning, however, must be made, imperfect though it will be. No one should imagine that we take this beginning to be the perfect thing; but like many other objections to our spiritual movement made by the modern age, it is nonsense to say that our building is not an essential part of this spiritual movement. We ourselves are already aware of the facts which people may bring forward. We realise also that all the foolish chatter about the ‘higher self,’ all the rhapsodies in regard to the ‘divinity of the soul of man’ can also be expressed in outer forms of the present age; and of course we know that it is everywhere possible for man to promote Spiritual Science in its mental and intellectual aspects. But over and above this merely intellectual aspect we feel that if Spiritual Science is to pour life into the souls of men it demands a vesture of a different kind from any that may be a product of the dying culture of our day. It is not at all necessary for the outer world to remind us of the cheap truth that Spiritual Science can also be studied in its mental aspect in surroundings of a different kind from those which are made living by our forms. The ideal which Spiritual Science must pour into our souls must be earnest and grow ever more earnest. A great many things are still necessary before this earnestness, this inner driving force of the soul can become part of our very being. It is quite easy to speak of Spiritual Science and its expression in the outer world in such way that its core and nerve are wholly lacking. The form taken by the most vigorous attacks levelled against our spiritual movement creates a strange impression. Those who read some of these attacks will, if they are in their right minds, wonder what on earth they are driving at. They describe all manner of fantastic nonsense which has not the remotest connection with us, and then the opposition is levelled against these absurdities! The world is so little capable of absorbing new spiritual leaven that it invents a wholly grotesque caricature and then sets to work to fight against that. There are even people who think that the whole movement should be done away with. Attack of course is always possible but it is a reductio ab absurdum to do away with an invention that has no resemblance of any kind to what it sets out to depict. It behooves us, however, to realise what kind of sense for truth underlies these things, for this will make us strong to receive all that must flow to us from Spiritual Science, and, made living by this Spiritual Science, shine into material existence. That the world has not grown in tolerance or understanding is shown by the attitude adopted towards Spiritual Science. The world has not grown in either of these qualities. We can celebrate the inner confluence of the soul with Spiritual Science in no better way than by deepening ourselves in problems like that of the nature and being of colour, for in experience of the living flow of colour we transcend the measure of our own stature and live in cosmic life. Colour is the soul of nature and of the whole cosmos and we partake of this soul as we experience colour. This was what I wanted to indicate to-day, in order next time to penetrate still more deeply into the nature of the world of colour and the essence of painting. I could not help interspersing these remarks with references to the attacks that are being made upon us from all sides—attacks emanating from a world incapable of understanding the aims of our Anthroposophical Movement. One can only hope that those within our Movement will be able, by a deepening of their being, to understand something truly symptomatic of our times, the falsehood and untruth that is creeping into man's conception of what is striving to find its place within the spiritual world. We of course have no wish to seclude our spiritual stream, to shut it off from the world; as much as the world is willing to receive, that it can have. But one thing the world must accept if it is to understand us, and that is the unity of the whole nature of man—the unity which makes every human achievement the outcome of this full and complete ‘manhood.’ These words are not meant to be an attack on the present age. I speak them with a certain sense of pain, because the more our will and our efforts increase in this Movement of ours, the more malicious—perhaps not consciously, but more or less unconsciously malicious—do the opposing forces become. I have, moreover, spoken thus because the way in which these things must be looked at is not yet fully understood even among ourselves. The unshakable standpoint must be that something new, a new beginning, is at least intended in our Movement. What lies beyond this ‘intention’ has of course yet to come. We with our building can still do no more than ‘intend.’ Those who can do more than intend—they will come, even though it be not before the time Herman Grimm thinks must elapse before there will be a complete understanding of Goethe. A certain humility is bound up with the understanding of this and there is little humility in modern spiritual life. Spiritual Science is well suited to give this humility and at the same time to bring the soul to a realisation of the gravity of these things. A painful impression is caused by the opposition arising on all sides against our spiritual Movement, now that the world is now beginning to see real results. So long as the Movement was merely there in a spiritual sense the world could see nothing. Now that it does, and it cannot understand what it sees, dissonant voices are beginning to sound from every side. This opposition will grow stronger and stronger. When we realise its existence we shall naturally at first be filled with a certain sorrow, but an inner power will make us able to intercede on behalf of what is to us not merely conviction, but life itself. The soul will be pervaded by an ethereal, living activity, filled with something more than the theoretical convictions of which modern man is so proud. This earnest mood of soul will bring in its train the sure confidence that the foundations of our world and our existence as human beings are able to sustain us, if we seek for them in the spiritual world. Sometimes we need this confidence more, sometimes less. If we speak of sorrow caused by the echo which our spiritual Movement finds in the world—this mood of sorrow must give birth to the mood of power derived from the knowledge that the roots of man's life are in the Spirit and that the Spirit of man will lead him out beyond all the disharmony that can only cause him pain. Strength will flow into man from this mood of power. If in these very days one cannot help speaking of things spiritual with a sorrow even greater than that caused by the discrepancy between what we desire in our spiritual Movement and the echo it finds in the world—yet it must be said that the world's disharmonies will take a different course when men realise how human hearts can be kindled by the spiritual light for which we strive in anthroposophy. The sorrow connected with our Movement seems only slight when we look at all the sadness lying in the destiny of Europe. The words I have spoken to you are pervaded with sorrow, but they are spoken with the living conviction that whatever pain may await European humanity in a sear or distant future there may, none the less, live within us a confidence born from the knowledge that the Spirit will lead man victoriously through every wilderness. Even in these days of sorrow, in hours fraught with such gravity, we may in very truth, indeed we must, speak of the holy things of Spiritual Science, for we may believe that however dimly the sun of Spiritual Science is shining to-day, its radiance will ever increase until it is a sun of peace, of love and of harmony among men. Grave though these words may be, they justify us in thinking of the narrower affairs of Spiritual Science with all the powers of heart and soul, when hours of ordeal are being made manifest through the windows of the world.
|
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture I
18 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture I
18 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In the lectures which it has been my lot to deliver, I have often drawn attention to an observation which might be made in real life, and which shows the necessity of seeking everywhere below the surface of life's appearances, instead of stopping at first impressions. It runs somewhat as follows.—A man is walking along a river bank and, while still some way off, is seen to pitch headlong into the water. We approach and draw him out of the stream, only to find him dead; we notice a boulder at the point where he fell and conclude at first sight as a matter of course that he stumbled over the stone, fell into the river and was drowned. This conclusion might easily be accepted and handed down to posterity—but all the same it could be very wide of the mark. Closer inspection might reveal that the man had been struck by a heart-attack at the very moment of his coming up to the stone, and was already dead when he fell into the water. If the first conclusion had prevailed and no one had made it his business to find out what actually occurred, a false judgment would have found its way into history—the apparently logical conclusion that the man had met his death through falling into the water. Conclusions of this kind, implying to a greater or lesser degree a reversal of the truth, are quite customary in the world—customary even in scholarship and science, as I have often remarked. For those who dedicate themselves heart and soul to our spiritual-scientific movement, it is necessary not only to learn from life, but incessantly to make the effort to learn the truth from life, to find out how it is that not only men but also the world of facts may quite naturally transmit untruth and deception. To learn from life must become the motto of all our efforts; otherwise the goals we want to reach through our Building1 as well as in many other ways will be hard of attainment. Our aim is to play a vital part in the genesis of a world-era; a growth which may well be compared with the beginning of that era which sprang from a still more ancient existence of mankind—let us say the time to which Homer's epics refer. In fact, the entire configuration, artistic nature and spiritual essence of our Building attempts something similar to what was attempted during the happenings of that transitional period from a former age to a later one, as recounted by Homer. It is our wish to learn from life, and, what is more, to learn the truth from life. There are so very many opportunities to learn from life, if we wee willing. Have we not had such an opportunity even in the last day or two? Are we not justified in making a start with such symptoms, particularly with one that has so deeply moved us? Consider for a moment!2 On Wednesday evening last, many of our number either passed by the crossroads or were in the neighbourhood, saw the wagon overturned and lying there, came up to the lecture and were quite naturally, quite as a matter of course, aware of nothing more than that a cart had fallen over. For hours, that was the sole impression—but what was the truth of the matter? The truth was that an eloquent karma in the life of a human being was enacted; that this life so full of promise was in that moment karmically rounded off, having been required back in the worlds by the Spiritual Powers. For at certain times these Powers need uncompleted human lives, whose unexpended forces might have been applied to the physical plane, but have to be conserved for the spiritual worlds for the good of evolution. I would like to put it this way. For one who has saturated himself with spiritual science, it is a plainly evident fact that this particular human life may be regarded as one which the gods require for themselves; that the cart was guided to the spot in order that this karma might be worked out, and overturned in order to consummate the karma of this human life. The way in which this was brought home to us was heartrending, and rightly so. But we must also be capable of submerging ourselves in the ruling wisdom, even when it manifests, unnoticed at first, in something miraculous. From such an event we should learn to look more profoundly into the reality. And how indeed could we raise our thoughts more fittingly to that human life with which we are concerned, and how commemorate more solemnly its departure from earth, than by forthwith allowing ourselves to be instructed by the grave teaching of destiny which has come to us in these days. Yet it is a human trait to forget only too promptly the lessons which life insistently offers us! It is on this account that we have to call to our aid the practice of meditation, the exercise of concentrated thinking, in order to essay any comprehension of the world at all adequate to spiritual science; we must strive continually towards this. And I would like to interpose this matter now, among the other considerations relative to our Building, because it will serve as an illustration for what is to follow concerning art. For let us not hold the implications of our Building to be less than a demand of history itself—down to its very details. In order to recognise a fact of this kind in full earnest, it must be our concern to acquire the possibility, through spiritual science, of reforming our concepts and ideas, of winning through to better, loftier, more serious, more penetrating and profound concepts and ideas concerning life, than any we could acquire without spiritual science. From this standpoint let us ask the downright question What then is history, and what is it that men so often understand by history? Is not what is so often regarded as history nothing more at bottom than the tale of the man who is walking along a river's bank, died from a heart attack, falls into the water, and of whom it is told that he died through drowning? Is not history very often derived from reports of this kind? Certainly, many historical accounts have no firmer foundation. Suppose someone had passed by the cross-roads between 8 and 9 o'clock last Wednesday evening and had had no opportunity of hearing anything about the shattering event which had taken place there: he could have known nothing, only that a cart had been overturned, and that is how he would report it. Many historical accounts are of this kind. The most important things lying beneath the fragments of information remain entirely concealed; they withdraw completely from what is customarily termed history. Sometimes possibly one can go further and say that external reports and documents actually hinder our recognition of the true course of history. That is more particularly so if—as happens in nearly every epoch—the documents present the matter one-sidedly and if there are no documents giving the other side, or if these are lost. You may call this an hypothesis but it is no hypothesis, for what is taught as history at the present time rests for the most part upon such documents as conceal rather than reveal the truth. The question might occur at this point: How is any approach to the genesis of historical events to be won? In all sorts of ways spiritual science has shown us how, for it does not look to external documents but seeks to discern the impulses which play in from the spiritual worlds. Hence it naturally cannot describe the outward course of events as external history does, It recognises inward impulses everywhere. Moreover, the spiritual investigator must be bold enough, when tracing these impulses on the surface, to hold fast to them in the face of outer traditions. Courage with regard to the truth is essential, if we would take up our stand on the ground of spiritual science, The transition can be made by attempting to approach the secrets of historical “coming into being” otherwise than is usually done. Consider all the extant 13th and 14th century documents about Italy, from which history is so fondly composed. The tableau, the picture, obtained by thus assembling history out of such documents brings one far less close to the truth one can get by studying Dante and Giotto, and allowing what they created out of their souls to work upon one. Consider also what remains of Scholasticism, of its thoughts, and try to reflect upon, to reproduce in yourself, what Dante, Giotto and Scholasticism severally created—you will get a truer picture of that epoch than is to be had from a collection of external documents. Or someone may set himself the task of studying the rebellion of the Protestant spirit of the North or of Mid-Europe against the Catholicism of the South. What can you not find in documents! Yet it is not a question of isolated facts, but of uniting one's whole soul with the active, ruling, weaving impulses at work. You come to know this rising up of the Protestant spirit against the Catholic spirit through a study of Rembrandt and the peculiar nature of his painting. Much could be brought forward in this way. And so it comes about that historical documents are often more of a hindrance than a help. Perhaps the type of history bookworm who subsists upon documentary evidence would be elated by a pile of material on Homer's life, or Shakespeare's. From a certain point of view, however, one could say: Thank God there is no such evidence! We must only be wary not to exaggerate a truth of this kind, not to press it too far. We must indeed be grateful to history for leaving us no documents about Homer or Shakespeare. Yet something might here be maintained which is one-sidedly true—one sided, but true, for a one sided truth is nevertheless a truth. Someone might exclaim: How we must long for the time when no external documents about Goethe are available. Indeed, with Goethe it is often not merely disturbing, but an actual hindrance, to know what he did, not only from day to day but sometimes even from hour to hour. How wonderful it would be to picture for oneself the experience undergone by the soul of a man who at a particular time of life spoke the fateful words:
If one wished to find the answer oneself in the case of such men, one might well yearn for the time when all the Leweses, and so on, whatever their names may be, no longer tell us what Goethe did the livelong day in which this or that verse was set down. And what a hindrance in following the flight of Goethe's soul up to the time in which he inscribed these words:
What a hindrance it is that we are able to refer to the many volumes of his notebooks and correspondence, and to read how Goethe spent this period. This view is fully justified from one angle, but not from every angle; for although it is fully justified in the case of Homer, Shakespeare, and so on, it is one sided with regard to Goethe, since Goethe's own works include his “Truth and Poetry” (“Dichtung und Wahrheit”). An inherent trait of this personality is that something about it should be known, since Goethe felt constrained to make this personal confession in “Truth and Poetry”. Hence the time will never come when the poet of “Faust” will appear to humanity in the same light as the poet of the “Iliad” or the “Odyssey”. So we see that a truth brought home to us from one side only can never be given a general application; it bears solely on a particular, quite individual case. Yet the matter must he grasped still more profoundly. Spiritual science tries to do this. By pointing out certain symptoms, I have repeatedly endeavoured to show that modern culture aspires towards spiritual science. In my Rätsel der Philosophie3 I have tried to show how this is particularly true of philosophy. In the second volume you will notice that the development of philosophy presses on towards what I have sketched in the concluding chapter as “Prospect of an Anthroposophy”. That is the direction taken by the whole book. Of course this could not have been done without some support from our Anthroposophical Society, for the outer world will probably make little of the inner structure of the book as yet. I said that Goethe must be regarded differently from Homer. On the same grounds I would like to add: Do we then not come to know Homer? Could we get to know him by any better means than through his poems, although he lived not only hundreds but even thousands of years ago? Do we not get to know him far better in that way than we ever could from any documents? Yes, Homer's age was able to bring forth such works, through which the soul of Homer is laid bare. Countless examples could be given. I will mention one only one, however, which is connected with the deepest impulses of that turning-point during the Homeric age, much as we ourselves hope and long for in the change from the materialistic to the anthroposophical culture. We know that in the first book of the Iliad we are told of the contrast between Agamemnon and Achilles: the voices of these two in front of Troy are vividly portrayed. We know further that the second book begins by telling us that the Greeks feel they have stood before Troy quite long enough, and are yearning to return to their homeland. We know, too, that Homer describes the events as if the Gods were constantly intervening as guiding divine-spiritual powers. The intervention of Zeus is described at the beginning of this second book. The Gods, like the Greeks below, are sleeping peacefully; so peacefully, indeed, that Herman. Grimm, in his witty way, suggests that the very snoring of the heroes, of the Gods and of the Greeks below, is plainly audible. Then the story continues:
Zeus, then, sends the Dream down from Olympus to Agamemnon. He gives the Dream a commission, The Dream descends to Agamemnon, approaching him in the guise of Nestor, who we have just learned, is one of the heroes in the camp of the allies.
This, then, is what takes place. Zeus, the presiding genius in the events, sends a Dream to Agamemnon in order that he should bestir himself to fresh action. The Dream appears in the likeness of Nestor, a man who is one of the band of heroes among whom Agamemnon is numbered. The figure of Nestor, whose physical appearance is well-known to Agamemnon, confronts him and tells him in the Dream what he should do. We are further told that Agamemnon convenes the elders before he calls an assembly of the people. And to the elders he recounts the Dream just as it had appeared to him:
(Atreus' son then tells the elders what the Dream had said. None of the elders stands up excepting Nestor alone, the real Nestor, who utters the words:)
Do we not gaze unfathomably deep into Homer's soul, when we know—are able to know, to perceive, by means of spiritual science—that he can recount an episode of this kind? Have we not described how what we experience in the spiritual world clothes itself in pictures, and how we have first to interpret the pictures, how we should not permit ourselves to be misled by them? Homer spoke at a time when the present clairvoyance did not yet exist; at a time, rather, when the old form of clairvoyance had just been lost. And in Agamemnon he wanted to portray a man who is still able to experience the old atavistic clairvoyance in certain episodes of life. As a military commander he is still led to his decisions through the old clairvoyance, through dreams. We know what Homer knows and believes and how he regards the men he writes about; and suddenly, in pondering on what is described in this passage, we see that the human soul stands here at the turning-point of an era. Yet that is not all. We do not only behold in Agamemnon, through Homer, a human soul into which clairvoyance still plays atavistically, nor do we only recognise the pertinent description of this clairvoyance; but the whole situation lies before us in a wonderfully magical light. Homer is humorous enough to show us expressly that it is Nestor who appeared to Agamemnon; the same Nestor who is subsequently present and himself holds forth, Now Nestor has spoken in favour of carrying out the Dream's instructions. The people assemble; but Agamemnon addresses them quite differently from what is implied in the Dream, saying that it is a woeful business, this lingering before Troy: “Let us flee with our ships to our dear native land”, he exclaims. So that the people, seized by the utmost eagerness, hasten to the ships for the journey home. Thus it rests finally with the persuasive arts of Odysseus to effect their about-turn and the beginning of the siege of Troy in real earnest. Here, in fact, we gaze into Homer's soul and discern in Agamemnon a lifelike portrayal of the transition from a man who is still led by the ancient clairvoyance to a man who decides everything out of his own conclusions. And so with an overwhelming sense of humour he shows us how Agamemnon speaks to the elders while under the influence of the Dream, and later how he speaks to the crowd, having bade farewell to the spiritual world and being subject now, to external impressions alone. Homer's way of depicting how Agamemnon outgrows the bygone age and is placed on his own feet, on the spearhead of his own ego, is wonderful indeed. And he further implies that from henceforward everything must undergo a like transition, so that men will act in accordance with what the reason brings to pass, with what we term the Intellectual or Mind Soul, which must be ascribed pre-eminently to the ancient Greeks. Because Agamemnon is only just entering the new era and behaves in a quite erratic and contradictory way, first in accordance with his clairvoyant dream and then out of his own ego, Homer has to call in Odysseus, a man who reaches his decisions solely under the influence of the Intellectual Soul. Wonderful is the way in which two epochs come up against each Other here, and wonderfully apposite is Homers picture of it! Now I would ask you: Do we know Homer from a certain aspect when we know such a trait? Certainly we know him. And that is how we must come to know him if we want rightly to understand world-history—an impossible task if nothing but external documents were available. Many other traits could be brought forward, out of which the figure of Homer would emerge and stand truly before us. We can come close to him in this way, as we never could with a personality built up only from historical documents. Just think what is really known of ancient Greek history! Yet through traits of this kind we can approach Homer so closely that we get to know him to the very tip of his nose, one might say! At one time there were men who approached Homer in this way, until a crude type of philology came in and spoilt the picture. Thus does one know Socrates, as Plato and Xenophon depict him; so also Plato himself, Aristotle, Phidias. Their personalities can be rounded off in a spiritual sense. And if we thus hold these figures before our mind, a picture arises of Hellenism on the physical plane. To be sure, one must call in the aid of spiritual science. As the sun sheds its light over the landscape, so does spiritual science illumine for us the figure of Homer as he lived, and equally of Aeschylus, Socrates, Plato, Phidias. Try for a moment to visualise Lycurgus, Solon or Alcibiades as a part of Greek history. How do they present themselves? As nothing but spectres. Whoever has any understanding of an Individuality in the true sense must recognise that in the framework of history they are just like spectres, for the features that history sets itself to portray are so abstract as to have a wholly spectral quality. Nor are the figures of later ages which have been deduced from external documents any less spectral in character. I am saying all this in the hope that gradually—yes, even in things that people treat as so fixed and stable that the shocks of the present time are treated as mere foolishness—spiritual science in the hearts of our friends may acquire the strength and courage to bring home an understanding that a new impulse is trying to find its way into human evolution. But for this we shall need all our resources; one might say that we shall need the will to penetrate into the true connections that go to make up the world, and the power of judgment to perceive that the true connections do not lie merely on the surface. In this regard it is of surpassing importance that we should learn from life itself. For very often—to a far greater extent than one might at first suppose—error finds its way into the world through a superficial reliance on the external pattern of facts, which really can do nothing but conceal the truth, as we saw in the cases described. In the field of philosophy particularly, it is my hope that precisely through the mode of presentation in the second volume of the “Rätsel der Philosophie” many will find it possible to recognise the connection between the philosophic foundations of a world-conception, as presented in the “Philosophy of Spiritual Activity” and the “Outline of Occult Science”. If on the one hand we are looking for a presentation of the spiritual worlds as this offers itself to clairvoyant knowledge, then on the other hand there must be added to the reception of this knowledge a penetration of the soul with the impulses which arise from the conviction, that man does not confront the truth directly in the world, but must first wrest the truth from it. The truth is accessible only to the man who strives, works, penetrates into things with his own powers; not to the man who is ready to accept the first appearances of things, which are only half real. Such a fact is easily uttered in this abstract form, but the soul is inclined over and over again to back away from accepting the deeper implications of what is said. I believe many of those who have tried to enter into spiritual science with all the means now at their disposal will understand how in our Building, for example, the attempt has been made through the concord of the columns with their motifs and, with everything expressed in the forms, to enable the soul to grow beyond what is immediately before it. For a receptive person, beginning to experience what lies in the forms of the Building, the form itself would immediately disappear, and, through the language of the form, a way would open out into the spiritual, into the wide realms of space. Then the Building would have achieved its end. But in order to find this way, much has still to be learnt from life. Is it not a remarkable Karma for all of us, gathered here for the purpose of our Building, to experience through a shattering event the relationship between Karma and apparently external accident? If we call to our aid all the anthroposophical endeavours now at our disposal, we can readily understand that human lives which are prematurely torn away—which have not undergone the cares and manifold coarsenings of life and pass on still undisturbed—are forces within the spiritual world which have a relationship to the whole of human life; which are there in order to work upon human life. I have often said that the earth is not merely a vale of woe to which man is banished from the higher worlds by way of punishment. The earth is here as a training-ground for human souls. If, however, a life lasts but a short while, if it has but a short time of training, then forces are left over which would otherwise have been used up in flowing down from the spiritual world and maintaining the physical body. Through spiritual science we do not become convinced only of the eternality of the soul and of its journey through the spiritual world, but we learn also to recognise what is permanent in the effect of a spiritual force by means of which a man is torn from the physical body like the boy who was torn from our midst on the physical plane. And we honour, we celebrate, his physical departure in a worthy manner if, in the manner indicated and in many other ways, we really learn, learn very much, from our recent experience, Through Anthroposophy, one learns to feel and to perceive from life itself.
|
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture II
19 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture II
19 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Friends should feel the quality of universality in the style of the Dornach Building. This means that endeavours must be made to transform into feeling the results of spiritual-scientific investigations that have come before our souls in the course of the years. Out of inner feeling we. shall then be able to conceive of the forms in our Building as a universal script, full of meaning When I last spoke here I drew your attention to clues that help us to acquire a really comprehensive view of the evolution of humanity. I pointed out how in Homer's works we find a figure who represents the transition from ancient times—when everything in human evolution and culture was based upon a certain kind of clairvoyance—to the age in which we are living and into which the rays of the Mystery of Golgotha have radiated. I said that in Agamemnon and Achilles, Homer has created figures in which he has shown how the ancient cultural life of man, permeated as it was with clairvoyance, passes over to a different kind of feeling, thinking, perception, willing, a different way of acting. Fundamentally speaking, what has come about since the dawn of the Fourth Post-Atlantean epoch (the Greco-Latin age), and also what has developed among the different peoples as the goal of their strivings, can be understood only if it is conceived as resting on the foundation of ancient clairvoyance. Certainly, much that is new has been achieved in the Fourth Poet-Atlantean epoch of culture and in the part of the Fifth that has already elapsed. Yet in the root-impulses at work in these epochs—as can be clearly felt by one who is willing to feel it—there still live elements that have come over from ancient times. It is not so very easy to recognise on the surface of history this ancient heritage of human evolution. But if one is willing to penetrate into those forces which hold sway in human nature either more or less unconsciously, and reach into more recent phases of development, one perceives everywhere how the men of the Fourth and Fifth Post-Atlantean epochs bear, so to say, in their nerves and blood, elements that have come over from the First Post-Atlantean epoch (ancient Indian culture), from the Second (ancient Persian culture), from the Third (Egypto-Chaldean-Babylonian culture) and on into our own times from Greco-Latin culture. The achievements of humanity in these periods of culture are less easy to trace in outer history, but in the characters of men, how men inevitably—I say, inevitably—think and feel, it can be perceived and felt. The man of the Fifth epoch in which we are living is so constituted that his nerves, blood and astral body contain what he has received as a heritage from ancient times. It lives within him as feeling, as a fundamental impulse. He has received, in addition, impulses coming from higher worlds. As we live in the age when the Ego is developing, when culture based on external reason is the vogue and external philosophy is authoritative; what comes from above into the impulses of men in the physical world; from the guidance and leadership of the spiritual world; meets with little understanding. In order to kindle a feeling for the dynamic, let me indicate by a sketch how the men of the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch are placed in the whole evolutionary process of mankind. To indicate it in a few strokes, we can choose this motif (one of the carved forms in the Building), representing a force that works from below upwards, and illustrates as can be clearly felt—all those impulses which man bears in the blood; in the nerves, in the etheric body, in the astral body, and which originates in the preceding epochs, actually in the First Post-Atlantean epoch of culture. [ Figure 1 (a) ] As an impulse coming down from above we can indicate the force that works downwards from the spiritual world into the intuition of the individual but with less power than what man bears within him from ancient times.  Spiritual-scientific investigation helps us to understand the conditions in which we ourselves live. This investigation has shown how the different qualities of the soul are distributed among the cultures of the leading peoples of the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch. The peoples inhabiting the Italian and Spanish peninsulas—as peoples, not as individuals—have absorbed into their culture everything that is connected with the Sentient Soul. Consequently the characteristics of the Sentient Soul predominate in the culture of these two peoples. These peoples represent a particular continuation of the main process indicated in the diagram. In a more concrete, more definite way, they make manifest what lives in the impulses of the blood and the nerves, of the etheric and astral bodies, in the sense referred to everything that came over from ancient times takes exprestion in these peoples and their fundamental impulses in such a way that the forces striving upwards from below take on a more definite configuration. In these peoples there is something inorganic, purely mathematical in the other forces; there is no more than an indication of the impulses of the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch. If we are to understand the particular character of the peoples of the Italian and Spanish peninsulas, we must be clear that the impulses working in the blood, the nerves, the etheric and astral bodies, are developed consciously into greater concreteness of form, but with the force of the old. The impulse from below upwards in these peoples can be indicated by elaborating the lower part of the design [ Figure 2a ] and giving it a form that opens upwards like a flower, suggesting at the same time, in what comes down from above as spiritual guidance, the kind of capacity these particular peoples, have for understanding that guidance. All this is connected with the plastic forms on the columns of the Building.  These peoples still have little relation with what is expressed by this central part of the design [ Figure 2b ], but they take over all the qualities and characteristics which the Sentient Soul is able to take over from ancient times, all the secrets of the ancient forms, of the ancient artistic script, if I may put it so. A force that shapes itself into forms enters into the first design, like a renewed gift from above [ Figure 2c ] . The character of these peoplee is expressed by this second design. Everything we come to know from spiritual science must find verification in the realities of the outer world—when, as is essential, we really survey the outer world. If we are to absorb spiritual science in the right way, we must first take what it says into our hearts and souls and then put the question to the world whether what spiritual science says is actually realised there. This means that we must be able to find in the external culture of the peoples in question the living elements of the Sentient Soul. And we shall expect to find in the culture of the peoples of the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch a kind of resurrection of something that already existed in earlier times and to which the so-called Sentient Soul peoples gave expression. We shall expect to find a repetition of what lived in the Egypto-Chaldean age, but born anew, in a form corresponding to our age. What then, was characteristic of the souls of the Egyptian and Chaldean peoples? Abandonment to the outer world—in keeping with the character of the Sentient Soul—so that in the relation of the fixed stars to the planets men felt something that was connected with human destiny. Men looked out into the universe and found in what the stars expressed, the secret of happenings in the life of the human soul and spirit. The first stage of Fifth Post-Atlantean culture was to repeat what was contained in the former Sentient Soul culture, but now in the soul itself. If, therefore, spiritual science is a trigs guide, we shall expect to find in the peoples of the Italian peninsula something that on the one side expresses the character of the Sentient Soul in the Egypto-Chaldean epoch, but on the other side indicates the great inwardness brought about by the impulse of the Mystery of Golgotha. We shall expect to find something that is a re-creation of the ancient spiritual astrology, but is now applied to the inner world, to the human soul. (Second design.) We must feel everything that approaches from the stars as a blossom springing from the human soul, indicated here at [ Figure 3a ] in the second design the aspiring impulses in man are met by what comes into them from the stars, that is to say, from the spiritual world [ Figure 3b ]. There must be something within the culture of these Southern peoples which represents an astrology applied to the soul—Egypto-Chaidean astrology applied entirely to the soul.  You are naturally thinking of something that provides complete confirmation of what I have just said. It is what Dante has presented in the “Divine Comedy”. Dante is the spirit who has re-awakened the Egypto-Chaldean element in a new form—applied now to the life of soul. It will be easy for you to designate everything that relates to the basic impulses of ancient times as “Saturnian”. The fundamental impulse of all connection between the cultures of the Fifth Post-Atlantean period and the ancient cultures, bears the Saturnian character. The Saturnian element works its way upwards from the fundamental impulses of the human soul and receives from above the impulses that can spring from the culture arising from the Intellectual Soul and the Ego. It will also be easy for you to perceive the impulse that is Sun-like in character [ Figure 2 ]. I have indicated that this Sun-quality is present in Dante, who represents an important impulse of Latin-Italian culture. It need only be added that Italy is the motherland of all that is formative, of the Sun—qualities that come to man through the Sentient Soul. We might even expect a thinker of a distinct character to arise within this culture, one who out of unconscious impulses remembers this Sun-element. In the light of what we have learnt from spiritual sciences this would seem entirely natural. There might, for example, be a philosopher—perhaps not philsophieally clear about the impulse in his souls but feeling it and allowing it to dominate him—who maintains that the external life of the State must be planned in such a manner that it is irradiated by the Sun-element.—We have no reason to be surprised when we find such a case. Campanella wrote a philosophical treatise on the Sun-State, the solar State.1 You will become more and more convinced that everything, every details accords with what spiritual science brings down from the spiritual worlds, ad that life can be understood only when it is illuminated by the findings of spiritual science. We then come to the culture-epoch which, according to the findings of spiritual science, will be designated as that of the Intellectual Soul or Mind Soul. It is the culture that has developed particularly in the region of present-day France. To find a suitable design for this culture we must realise that it was destined—in a more concrete way than was the case at any point in Italian culture—to lead what comes from above to particular brilliance, to a higher stage of elaboration of the Intellectual Soul. What comes from above [ Figure 3b ] Intellectual Soul culture—brings the earlier culture [ Figure 3a ] to a state of greater concreteness. If you steep yourselves in the characteristics of this new culture, you will perceive that it is particularly adapted to absorb the culture of the Fourth Greco-Latin culture, permeated with what comes from above trickles into French culture as a liquid might trickle into a chalice [ Figure 3 ] . Spanish and Italian culture passes over into French culture but in such a way that in the latter, Greek culture undergoes a revival and renewal. I do not think that a better design than this could be found to express the gradual transition from Spanish into French culture. Even the outer quality of finish can be expressed by allowing the central part of the design to be enclosed to right and left by these lines [ Figure 3c ]. Anyone who asks whether the results of spiritual science are also demonstrated in external reality can easily find an answer if he will devote a little study to actual conditions. But it must be emphasised that these things must be judged on the foundation of facts as they are, not on that of pre-conceived ideas. This has constantly to be stressed at the present time, because everybody wants to pass judgment on everything ignoring, of course, facts which can be understood only by dint of effort. But I advise anyone who wants to gain insight into the very distinctive form in which the Greek element flows into French culture, to study how the Oedipus theme has found its way into French poetry; how Sophocles' Oedipus lives again in the Oedipus of Corneille and also in that of Voltaire. What I have just said can be confirmed down to the very details. It can be clearly discerned in these particular examples, although many could be quoted. It is, of course, a fact that most editions of Corneille's works no longer include the tragedy of Oedipus and that in those of Voltaire practically no value is attached to this work. But study will show that the new form into which the Oedipus theme has been cast by Corneille and Voltaire is a sign of the revival of the Greek age in French culture. It will be found that because Greco-Latin culture stands at the dividing line between the age of ancient clairvoyance and the modern age, the element that in Sophocles is received, as it were, out of the spiritual world in the age of ancient Greek heroic culture, has become in Corneille and Voltaire entirely an affair of the human soul itself. Whether Sophocles' Oedipus is more to one's liking than the form given to the story later on must be altogether disregarded; attention must be concentrated upon the trans formation that took place, bearing in mind that this transformation consists in the Oedipus story being reborn entirely out of the personal soul-nature of man. I said that all antipathy must be put aside. This done, it can be demonstrated quite objectively that what in Sophocles is linked with the figure of Oedipus: is woven into a human-universal destiny: such as can be indicated only by words as momentous me those with which Goethe describes such a destiny: that it exalts man in that it crushes him. The breath of magic emanating from Sophocles' Oedipus is due to the fact that in this drama the spiritual worlds which guide the destiny of peoples can be sensed: worlds which play into human destiny in a way that men are unable to fathom; therefore what the gods allow to befall may appear to be the most cruel injustice. One can conceive how every Greek was aware of the inscrutability of the fate in which the actual will of the gods was contained. The Greek felt: Yes: this is how the gods deal with man; their will remains inscrutable; fate can befall everyone as it befell Oedipus, but it remains inscrutable. The breath of magic emanating from Sophocles' tragedy of Oedipus has been drawn right into the sphere of the personal by Corneille and Voltaire: quite as a matter of course. The transition is made in Corneille; in Voltaire the situation has become quite distinct. In Voltaire's Oedipus there is a figure who would be quite unthinkable in ancient drama. This is Philoctetus, the family friend who makes the conjugal alliance into a triangle. Jocaste was already acquainted with Philoctetus before her first marriage; the situation continues until she is widowed and then she marries Oedipus, her own son. These are personal relationships of soul which would be unthinkable in an ancient drama. But we can go farther; we can try to understand what streamed through the souls of the great French poets, and then we shall find how the Greek element was absorbed. This is clearly expressed, not only in French poetry itself, but also in the theory of poetry. Do we not know how Lessing studied the way in which, as part of its theory, French poetry had taken over from Aristotle, the great Greek philosopher, the principle of the unity of Time, Place and Action, which is a feature in the works of Corneille, Racine and Voltaire? French classic poetry can be understood only by those who perceive how the spirit of ancient Greece shines into it. And if we want to find concrete evidence in French culture of the indications given by spiritual science, we can do so by asking: Where does the essence of this French culture appear in its most brilliant form? Where is it unparalleled? Where does it reach its highest peak? To answer this question rightly calls for great objectivity, and objectivity does not come easily to modern man, especially in our days. Nevertheless, for those who look at thinge objectively, the highest peak of French culture is to be found in the works of Molière. However strongly any culture may believe that what Molière achieved could be equalled among a people of a different character—leaving aside what has been achieved by Corneille and Racine, or also by more modern French culture—it would be foolish to assert that the particular perfection to be found in Molière has ever again been reached. In a different sphere there has been equal perfection, admittedly—perhaps even greater perfection—but not in this particular sphere. It would be a fallacy to maintain that Molière's essential quality.—born as it was from the Intellectual Soul or Mind Soul could be achieved again or even an echo of it. Molière represents the highest peak of the culture that is born out of the Intellectual Soul. Molière's comedy is comedy per se, comedy in its very essence. It cannot be understood inwardly, spiritually, unless one realises that the Intellectual Soul is dominant in it, in a way in which this uniqueness could never be repeated. For everything that arises in the evolution of humanity emerges at a characteristic point once and once only. Just as in one life the age of 18 or 25 is never reached twice, it is equally impossible for mankind to produce twice over that which reached the degree of finish it did in the personality of Molière. All this is indicated and can be felt in this design [ Figure 4 ].  If at this point we make a break and refer to what was said in my lecture-course on the Folk Souls about the European Folk Souls, of the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch, we can ask other questions of the same kind on the subject of Middle-European culture being the culture of the Ego. If this Middle-European culture is the Ego culture, its relation to the other cultures of which we have spoken will be similar to the relation of the Ego to the Sentient Soul, the Intellectual Soul and the Consciousness Soul (Spiritual Soul). Here, too, the outer reality must provide adequate confirmation of the indications given by spiritual science, If Italian culture represents what is received through the Sentient Soul, it must have a particular relationship to the Ego culture, to Middle-European culture: that is to say, Middle-European culture, which works essentially out of the Ego, would have to submerge itself in the Sentient Soul, to be fructified by it, in the way that happens with the Ego and the Sentient Soul in an individual man. Let us think of the relationship of the Ego to the Sentient Soul in man. The Ego, in which the impulses of its own inmost being are contained, must dive down into the Sentient Soul, otherwise it remains unfructified by what can work upon it from the outer world through the forms of that world. Man must ever and again dive down into his sentient experiences, his feeling. A relationship must be in operation between the impulses of the life of feeling and the Ego. Accordingly we may expect that those who belong to the Ego culture of Middle Europe will try to establish a living link with the Sentient Soul culture in the South; they will seek for a channel of expansion, not only in political but also in higher, spiritual connections. Look up the history of the Staufer dynasty, look up the events originating in the impulses of the Hohenstaufen and the Guelphs, or the accounts of the constant campaigns of the Saxon and Staufen rulers to Italy. Study all these relations of Middle Europe with Italy, and you have an exact picture of the life of the Sentient Soul in relation to the Ego. But it can be further ecpected that the Ego-nature will produce forms of art in keeping with the character of man; from the Ego-nature, gnarled, knotty forms must be expected, forms shaped by the characteristics of the Ego. Such forms are to be found in the creations of Holbein and Dürer. But they are found in Dürer only after he had gone to Italy and had been enriched by the culture born of the Sentient Soul. In more modern times we find the same phenomenon everywhere. From Goethe's journey to Italy, down to Cornelius and Overbeck, and on into our own time, we find evidence of the exchange between the Ego culture and the Sentient Soul culture. What goes on between Middle Europe and Italy is an image of the relation between the Ego and the Sentient Soul of man. In every detail the outer course of evolution provides confirmation when we study it in the light of the indications resulting from spiritual-scientific research. Now let us consider the relation between the Ego-nature in the soul and the Intellectual Soul. There too we must expect that what shows itself inwardly in human nature between the Ego and the Intellectual Soul will also make its appearance in external life. The nature of the relation between the Ego and the Sentient Soul is such that the Ego dives down uncritically, as it were into the Sentient Soul, lets itself be fructified by the Sentient Soul culture. Intellectual Soul culture quite naturally assumes a character that is more like an intellectual exchange, a “head” exchange, so to speak. The Intellectual Soul, or Mind Soul, is the middle member of the soul. It is at the same time that out of which the Ego arises and with which the Ego, for its own sake, must come to terms. (Try to form an idea of the nature of the Intellectual Soul from the book Theosophy.) We must expect an inner relationship to exist between Intellectual Soul culture and Ego culture. One can think of no more graphic illustration of this than the relation to French culture of the philosopher Leibnitz, who was through and through a Middle European in his way of thinking. Leibnitz transposes into the idiom of Middle Europe everything he absorbs from outside—for example, from Giordano Bruno in whom the Italian Sentient Soul is so alive—and also the Monad theory. Leibnitz wrote in French; he formulated a great deal in his philosophy in accordance with the demands of the French language. A process of exchange between the Ego culture and the Intellectual Soul culture is clearly to be seen when we follow the arguments in Lessing's Hamburgische Dramaturgie We see there the tension between what Lessing was striving for and the elements in French culture originating from Hellenism, from which he wants to free himself. Leseing engages in polemics, in intellectual controversy. This is an exact image of the exchange between the Ego and the Intellectual Soul. Lessing's “Hamburgische Dramaturgie” will be understood only when it is seen in this light. And there is something else that is apt to be overlooked today. The shape which external conditions have assumed in Middle Europe is in many respects connected with, the rise of the Prussian State, And who would not connect the emergence of the Prussian State with Frederick the Great? Of him it must be said, however, that he clung with every fibre of his being to French culture, and took over a great deal from it into his own. He said that he regarded Voltaire ae a far greater personality than Homer. He considered German culture to be still semi-barbarous He who laid the foundation of modern Prussia strove to promote culture by means of the French element. Frederick the Great must be understood in the light of his relation to the French element, for this still lives in modern Prussia today, just as everything originating from the Intellectual Soul lives in the Ego. All these things are important for an understanding of the Ego culture, just as an understanding of the Intellectual Soul is important for an understanding of the Ego—This is indicated in the book Theosophy. It would be extremely desirable if today, particularly, heed were paid to the real foundations of world-events before judgments are passed, so that the remarkable way of judging which has come to a head at the present time could be recognised at least by a few people as unreliable, hollow and superficial, and full of the shallow cynicism of the newspapers and the journalists. When we follow the course of evolution in the Fifth Post-Atlentean epoch we necessarily come to a further stage of elaboration in the forms of the columns. This advance can be expressed by indicating a powerful development of what comes from above as Intellectual Soul culture, accompanied by a certain shutting off from the Spiritual. This shutting off can be indicated by a dividing motif [ Figure 4c ]above the upper portions of the design. The element that comes from above flows in with greater definition and bears the stamp of the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch more distimetly; but it shuts itself off in a certain way. Here we come to the culture of the Consciousness Soul that is in preparation, and is to be especially characteristic of the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch, Whereas Italian culture has taken over qualities and traits of the Egypto-Chaldean age, and French culture those of the Greco-Latin age, we now come to what expresses the essential character of the Fifth epoch of Post-Atlantean nature which stands entirely and solely upon its own base. What must necessarily be the attitude of this culture to the outside world? The man who stands on his own base becomes a spectator, an onlooker, and as such he will be in a position to gaze deeply into the configuration of the beings of the world, into their organic structure and mechanism, in order to be able to re-create them from within outwards, so that they stand there as if created by Nature herself. We find there a culture of keen observation, penetration into the nature of beings and things which are then described from the standpoint of the spectator or onlooker. What does this culture produce when it is really great? One need mention one name only—that of Shakespeare. He is great and unsurpassable as a spectator, an observer of the world. Shakespeare's creations would be unthinkable in any earlier or subeequent culture. When I was describing the characteristic English philosophers in the first edition of my book Welt- und Lebensanschauungen fifteen years ago, I did not take into consideration the aspect we have in mind today But I tried to find an expressive word, which I used in the second volume of the book “Riddlee of Philosophy”. I tried to find a telling word to describe the fundamental character of John Stuart Mill's philosophy. I chose the word “spectator”, a “spectator” of the world. All the indications given by spiritual science are indeed confirmed in outer reality. The further questien regarding the exchange between the Ego and the Consciousness Soul discloses something very distinctive. We can expect that because the Consciousness Soul itself must tend and foster the Ego, what the Ego wishes to achieve comes to it in many ways from the Consciousness Soul. We can expect that much from the Consciousness Soul will flow into the Ego. But because the Ego wants to preserve and protect its independence, there is a great deal that it must ward off. It is a wonderful experience to watch the process of how modern physics receives its stamp from Newton, but how, in Goethe, the Ego culture of Europe rebels against the Consciousness Soul culture. Read Goethe's “Theory of Colour”—it is wonderful to see how he rises up in opposition against Newton. It is wonderful to see how two discoverers of the infinitesimal calculus appear contemporaneously in Leibnitz and Newton, entirely in conformity with the relation between the Ego and the Consciousness Soul. The conflict of the Ego with the Consciousness Soul is mirrored here. Much that is rooted in the nature of the Ego appears in a characteristic form in the spirituality of Jacob Boehme in the 16th century. A great deal is rooted in the Ego for which the Ego cannot immediately find the adequate words. The Consciousness Soul then finds the words, finds the elements that can be outwardly effective. Think of Goethe's efforts to understand the precess of natural development, in the sense of the Ego culture of Middle Europe. He discovers the principle of the natural development of living beings, from the simplest to the most complex. But the world does not understand the profound theory of this natural development because it is a product of the Ego culture. In Goethe's time the theory was not understood. Then a representative of the Consciousness Soul appears on the scene. Darwin produces, out of the Consciousness Soul, the same that Goethe had produced out of the Ego, and all the world understands it; even the Ego culture understands it! It is not possible to understand the drama of the evolution of mankind unless one is able to recognise the actual connections through the guiding lines given by spiritual science. The living forces in the evolution of humanity progrees from culture to culture as if they were based upon the eternal pillars of the primal laws of mankind. We can divine the progress when in these designs we feel the Saturnian quality in the fundamental character of the Fifth Post-Atlantean culture, the Sun quality in the character of Italian and Spanish cultures, the Moon quality in that of French culture, and then a Mars quality in the culture that develops in the British Isles. It is not possible to understand what really ought to be understood—the symphony of the Post-Atlantean cultures as if in chorus—unless one can feel the distinctive characteristic of those Post-Atlantean cultures. Those who live with lots of spiritual science should be able to feel the course of human evolution is one great whole. Consequently a dome is to arch overhead, rising over the forms which help us to feel how the evolution of mankind goes forward. The dome or cupola is to show how human beings, how peoples, work together; it is a picture, too, of the interworking of the soul-forces in man himself. It will work upon the soul when we go into our Building with inner, sensitive understanding. For in our Building the endeavor has been made to put aside everything of a personal nature, and in every line, in every form, to represent what is spiritual worlds reveal whether we try to express world-happenings in forms, in order that men may be able to feel the meaning and significance of these happenings. It must be admitted that the world today is nowhere near the stage of transforming into feeling those things that have now again been spoken of. This requires an ever-increasing spread of spiritual science, a greater and greater understanding of a new style of building that is connected with the secrets of the World-Order, as has been attempted in our Building. Naturally this Building can be a people beginning only—it cannot be more than that. But among individuals there does live, more or less unconsciously, something that can provide the basis for an understanding of the symphony created by the several cultures existing in the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch. And so even in our own grievous times certain things may be welcomed with a feeling of elation, because in what is now coming to light we must watch for signs that give some promise of a peaceful culture—culture that will not be inactive, but full of vigour, and can be understood only when efforts are made to promote mutual understanding of the essential qualities of the various peoples. Although any egoistic relationship to one culture or another falls far short of the ideal of spiritual science, it is nevertheless to be welcomed when some measure of insight is developed into the element that makes for a bond of union—for there lies the force that is truly creative. And so by the side of much that is so deeply grievous, we may be mindful of other voices which gladden us because they show that the principles of spiritual science can be appreciated also by one who stands outside our circle. Those who are willing to listen to spiritual science are still only few. But I have said that in Herman Grimm there was a longing for spiritual science, and I can also give another example from our own unhappy times. Among many voices I will quote only one—When some of the young men at a university in Middle Europe were to leave for the Front and some to remain at home, one of the tutors spoke words which cheer the heart and deserve to be known, because, although they were spoken without any knowledge of spiritual science, they reveal impulses of hope and longing for the mutual intercourse among the peoples that must one day result from spiritual science. This tutor said to his students: “You will come to know that nothing attunes the cultivated soul to Beauty more deeply than efforts to perform heroic deeds. You will come to know that nothing calls to the soul and steels it more effectively for renewed efforts, and that there is no purer bond from soul to soul, than that which resides in the hallowed realm of Beauty. Then, even if, as the most terrible consequence of this war there should remain a hatred among peoples such as was never known before, amid all the enmity you will not forget to love the higher soul of the enemy. You are fighting a good fight for the truth. There is no need for you to engage in the calumny and slander emanating from confused minds. You will receive Shakeapeare as a guest among the good spirits of German culture and know that, in the sense in which he is ours, just so much of English thought belongs your reputedly to our own spiritual life. you will remind yourselves of the noble struggles of the French mind for aesthetic culture in its great refinement. You remember how in Tolstoy and Dostoyevsky, Russia in our time had both her Homer and her Shakespeare. Certainly, the Russian State meted out to these two greatest of her sons nothing but sorrow and sometimes inhuman persecution. What would they think of present developments! Yet through them speaks, unforgettable in its inwardness and sincerity, the eternal evangel of the people of God, of the realm where love is a sustaining, helping power. The meaning of the war lies in the peace to which it leads. As warriors, bear the lofty meeting of the coming peace within you, in order that the hatred among the peoples may ultimately end in a new kingdom of love. The deepest German quality is to love everything that bears the countenance of man, to love every kind of people as a portion of humanity, as a revelation of God. Realm of human love, filled with understanding, is the realm of the German spirit.” These words were spoken by Eugen Kühnemann, any university tutor, on the 18 August 1914, to his students who were going to war. They are words to rejoice over in these momentous times when one experiences so much that is grievous. These words show great understanding of Shakespeare, who is ours to, in as much as through him English thought becomes part of our spiritual culture; they also show great understanding of French spiritual culture. They emphasize the significance of Tolstoy and Dostoyevsky for the new spiritual culture—and to emphasize that it is a great deal better than what is so often to be heard today from another side. May such an attitude of mind and heart not disappear in our days! Perhaps our friends may be able to do something to point to the fact that such an attitude does the deed exist and furthermore that it is by no means rare in Middle Europe. I will now close this lecture, and tomorrow at 7 o'clock I will speak about how the further stage of evolution—represented by Middle European culture and the Russian spirit—is indicated in the forms of the columns in our Building.
|
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture III
24 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture III
24 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Continuing our study of the evolution of European Cultures in the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch, we come to the culture for which I found the following design when I was working out the forms for the columns in our Building. It includes a drop-like motif above (a). The justification for this design can be felt when one studies the Middle-European culture of the Post-Atlantean epoch. I say Middle-European expressly. The reason for this will emerge from the subject-matter itself. In this Middle-European culture the most varied national elements have for centuries been gathered together, making it impossible to speak of a “national” culture in the same sense as in the case of the cultures of the Southern and Western peoples of Europe. In considering this Middle-European culture we must bear in mind at the outset that at the present time it is to all appearances composed of the people of two State-organisations. Remember, please, that in these lectures I am not speaking specifically of States but of cultures, and am saying here that the Middle-European culture is composed of two State-organisations—the German Empire and Austria. In the case of Austria we see immediately that it would be absurd to speak of a national State, for in Austria there is an agglomeration of national cultures of the most varied kinds. This has been brought about by history, and Austrian life really consists in the interplay of these national cultures. History is also responsible for the fact that the culture of the German Empire appears today in a certain unified form. Let us enquire, to begin with, only into the culture of the German population of Germany, and that of the German population of Austria, which has indeed many connections with that of Germany, geographically too, but on the other hand is geographically separated from it by great mountains. We will think first of the German element in a general sense. If we ask: What is German?—this question cannot be asked in the same sense as the question: What is French? What is English? What is Italian? This cannot be done, because a member of the German people—if this expression can be used at all—never knows in any particular period under what definition he stands. What he would necessarily express if he were to say: “I am a German”, would quickly change, and in a comparatively short space of time; from age to age he would nave continually to be moairying the concept of “German nationality” (Deutschtum). It is highly significant that when during Germany's period of distress Johann Gottlieb Fichte gave his famous “Addresses to the German Nation”, in two of these Addresses he struggled to find a concept to express “German-hood” (Deutschheit). It was a struggle to find a concept to express “German-hood”, just as one struggles to find concepts for something one confronts quite objectively—not subjectively, as a people usually confronts the concept of nationality. There lies in the striving of an inhabitant of Middle Europe a trait that must be described as an “aspiration to become something”, and not as an “aspiration to be something”. To “become” something, not to “be” something—so that in Middle Europe a an who understands his own nature would have to rebel against being classified under some particular concept. He wants to become what he is. What he is to become hovers before him as an ideal. Therefore Goethe's “Faust” characterises the innermost aspiration of Middle Europe in these words:
or again:
It is being in a state of becoming, being that is never stationary, perpetually aspirins towerds something, beholding in the far distance what it desires to become. And so it can be said that the work that is so essentially characteristic of the Middle-European nature was necessarily an outcome of human aspiration. This work is Goethe's “Faust”, which in spite of its many perfections has countless imperfections; it is not a work of art finished and complete in itself. “Faust” could be written again in a later epoch and written quite differently, but even so it would still be an expression of the nature of the man of Middle Europe. If we ponder deeply upon this we shall get the picture of the upward striving Ego in Middle-European humanity serpent-entwined. Serpent-entwined! This means, striving with the wisdom that is undetermined, the wisdom that is forming? in process of becoming never living in any certainty of complete fulfilment. Such is the situation of the man of Middle Europe. And then there is Faust's ascent into the spiritual world at the end of Part II. Through Goethe, Faust becomes a Messenger of the gods—if I may put it so. There can be no more graphic expression of this than the “caduceus”—the staff of Mercury. But in still another way this German element can best be described by saying that its members are “messengers”. The messenger of the Spirit was Mercury. It is only necessary to consider what has happened, and we shall find that to be a bearer of the message of culture lies in the deep foundations of the character of the German people. By way of illustration I will quote particular instances connected with Austrian culture. In examining the remarkable, very complicated structure of the Austrian State, we can recognise three filaments of the population. There were once—they have now for the moot part disappeared or are in process of disappearing—the inhabitants of northern Hungary in the Zipser district, certain inhabitants of Siebenbürgen and certain inhabitants of the lower Theiss district, the Banat. Who were these peoples? Thy were peoples who in earlier centuries: migrated from regions more to the West and had brought with them from there their German thinking and their German language. One of these filaments settled south of the Carpathians in northern Hungary. In my youth they were called the “Zipser Germans”. Today they are largely merged in the Magyars, They have entirely surrendered their folk-nature, but it has not entirely disappeared: it lives on in many impulses that are present among the Magyars, but also in the achievements of the industrious people of northern Hungary. They have not clamoured for any especial recognition from ths surrounding people, for they have made no real effort to avoid surrendering their German element to the general nature of their environment. The inhabitants of Siebenbürgen are Saxons; they are of Rhenish descent. I myself came across them in the year 1887 when I gave a lecture in Hermannstadt. Today they are on the point of being absorbed into the Magyars, like the Zipser Germans. The folk-substance lives on but no claim is made for stress to be laid upon their own national element. In the southern Theiss region (Banat) the people are pure Swabians who have migraterd. The inhabitants of Württemberg are called Swabians. The seine happened to them as to the people of the Zipser region; they were messengers, in the truest sense, of the element that is now dissipating under the influence of a quite different language. And if one is more closely acquainted with the situation, one knows how necessary it was that these people should be merged in a common Middle-European element, in order that this element might itself thrive. The same thing could be demonstrated in numbers of other cases. Anyone who wants really to understand and not merely to judge according to stereotyped concepts, will find that such things disclose an overcoming, a suppressing of the nationalistic principle. Everything in Middle Europe is adapted to lift man out of the nationalistic principle and to promote the expression of his own nature as man. Hence it would be ridiculous to call Faust a German figure, although he could have originated nowhere except in Middle Europe, and in the truest sense the play is to be numbered among the works most truly representative of Middle-European culture. If these matters are really to be understood, we must bear in mind the many intertwinings that take place in the evolutionary process and disclose themselves when we think, for example, of what was said yesterday: that in French culture there has been a revival of ancient Greek culture. In a certain respect, of course, ancient Greek culture also lives in German art, especially in German poetry and dramatic art. Does not the Greek Iphigenia live again in Goethe's Iphigenia? Did not Goethe write an “Achilleid”, or at any rate a part? One must always go to the very root of these matters. The Greek element does indeed live in Middle-European culture; but the essential point is how ancient Greek culture, born as it was out of the Intellectual Soul, lives again in the elements of the Intellectual South in French culture. The Greek element does not live in the thinking of the individual Frenchman, in his individuality, but in the way in which the folk-soul takes expression. In the individual Frenchman, indeed, it lives perhaps less consciously than, for example, in its reappearance in Goethe or in Schiller, but it is at work in French culture. The whole inner impulse of ancient Greek culture lights up in French culture. One can of course refer to some such thing as Voltaire wrote in a letter of the year 1768, where he says: “I have always believed, I still believe and shall continue to believe, that as far as tragedy and comedy are concerned, Athens is surpassed in every respect by Paris. I boldly declare that all Greek tragedies are like the works of tyros compared with the glorious scenes of Corneille and the consummate art of Racine's tragedies.” This sentiment can be compared with what Schiller once wrote to Goethe, saying, in effect: “As you were not born a Greek or an Italian, but in this northern clime, you have had to let an ideal Greece come to birth within you.”—But for all that, one must not suppose that Hellenism appeared in Middle Europe in a form as adequate as that in which it appeared in French culture. In Goethe's “Iphigenia” the yearning for Greek culture can be perceived. Goethe believed that he had acquired a new understanding for art after experiencing it in Italy, yet his “Iphigenia” has something about it that is quite different from anything in a Greek work of art. The essence of the matter is the artistic form in which things are presented. A very great deal could be said on this subject, but in these lectures I am trying merely to give indications. The revival of the Intellectual or Mind soul culture in the French people is shown in their way of living, their modus vivendi. When we study Voltaire's assessment of the evolutionary history of humanity, he seems to us entirely Greek. Here and there, of course, people have indulged in fantastic notions about ancient Greek culture. but if one known the kind of thing a Greek might have said and then reads a little poem by Voltaire, one can feel what is meant by speaking of the revival of Greek culture. The gist of this little poem is as follows: Full of beauties and of errors, the old Homer has my profoundest respect; he, like every one of his heroes, is garrulous, overdone—yet for all that, sublime. A Greek, of course, could never have expressed himself about Homer in this way, but about other things, certainly. It is quite typically Greek. Looking for an expression to use instead of the word “nationality” in the case of Middle-European culture, we find, even from geographical considerations, the words: “Striving after individuality”. And within this striving after individuality we include not the German only, for Middle Europe must be taken to embrace a number of other peoples as well, in all of whom this striving is present in a most marked degree. This striving after individuality is to be found in the Czechs, the Ruthenians, the Slovaks, the Magyars, in spite of all their external differences; and finally it is to be found at the other pole of German culture, in the Poles. In them, the element of individuality is developed to the extreme. Hence the intensely individualistic world-outlook of really great Poles: Tovianski, Slovacki, Mickiewitz. Hence, too, the very essence of Polish philosophy, which emanates entirely from the individual as such. (Whether this philosophy is attractive or the reverse, according to taste, is not the point at all; these things must be looked at objectively.) As for the Polish attitude to religion, the fact that in a given case the one concerned happens to be a Pole can always be ignored. And it is the same in this whole agglomeration of peoples which constitutes Middle European culture; one trait is common to them all a striving after individuality. Polish Meseianism is only the other pole of this striving; it takes the form more of a philosophical ideal, but it is the same in essence as what comes to expreesion in Goethe's “Faust” as the character of the striving personality, of the single individual. The following design expresses what is at work in Middle Europe. What comes from above is indicated in this upper, twofold motif; it must be two-fold, because on the one side there is the idealism that is present in Middle Europe and on the other, the sense for the practical. The important thing in the design is not the relative size of the forms but the fact that the one (a) is at the side of the motif and the other (b) arches above the motif. The latter (b) represents what expresses itself in the peculiar, not very strong, kind of tie which the population of Middle Europe has with the soil, in one case more, in another case less marked. The form at (a) indicates the trait that expresses itself in the thought element of Middle Europe, with its inclination towards philosophical speculation. There was a suggestion of these two motifs, although what they really indicate was but little understood, in a characterisation of the Germans once in in a foreign nation, to this effect: The Germans can till the soil and they can sail in the clouds—(this did not refer to ballooning, but to flights of mind)—but they will never be able to navigate the seas. This is a strange utterance when one thinks of the German Hanseatic League, but it was actually made. It does, after all, point to two capacities with which the spiritual worlds have endowed the Germans—and these are at the same time Middle-European capacities. The Ego is that principle in the human soul which has first and foremost to come to terms with itself; consequently there will be a seething and a swirling in this Ego-element. Whatever foreign wars the Germans have waged and will wage, the really characteristic wars are those which Germans have waged against Germans, in order to bring about inner clarification. If one follows the course of the wars fought out inside Germany, one has a faithful picture of what goes on within the enclosed Ego of man himself. I have pointed out—the thought is to be found in many of my lectures—that the Ego could never have become conscious of itself if it were not kindled anew every morning by the outer world. The Ego wakens into consciousness through being kindled by the outer world; if this did not happen the Ego would be there, certainly, but it would never become a centre of consciousness. Every guiding-line given by Spiritual Science concerning the being of man is confirmed by the external facts. The configuration assumed by the Middle-European States does not really originate from these States themselves but has been determined from outside. I will speak of Austria first. When I was young, numbers of people there were constantly saying that this agglomeration of peoples which constituted Austria must soon dissolve, that it was ready for dissolution. Those who understood something about world-evolution did not hold this view, because they knew that Austria was not held together from within but from outside. This can be demonstrated in all details by history. If one were to speak quite objectively of the latest configuration of Middle Europe, of the German Empire; one would have to say: The German has always talked of the ideal of the one united German Empire. But perhaps it would still not be there if the French had not declared war in 1870 and so forced on apace the founding of the German Reich. It was really consolidated frcm outside rather in the way the Ego is kindled each morning by the outside world. Otherwise it might still be a goal to be striven for, an ideal existing, perhaps, only in the minds of the people. All these things must be weighed quite objectively, particularly by those who adhere to the principles of Spiritual Science. Only so can one survey, calmly and dispassionately, what is taking place in the fifth Post-Atlantean epoch of culture. I can give guiding-lines only, for the subject could obviously not be exhausted in fifty lectures. And every lecture would present further proof of the truth of what can only very briefly be indicated here. So we may say that the spiritual scientist can acquire a picture of European culture in which he perceives the interworking of Sentient Soul, Intellectual Soul or Mind Soul, Consciousness Soul and Ego. And through this knowledge a lofty ideal can stand before us that of being able to play our part in bringing it about that in place of the present chaos, harmony shall arise in the individual human soul. This is possible, but only possible if every single individual presses on toward objectivity. The individual man stands at a higher level than the nation. in our time these things are obscured in many ways. It is necessary to say these things, once at any rate. It is my spiritual duty to say them, and only because it is my spiritual duty do I say them at the present time. We are living in an age when perception of what constitutes the harmony between the soul-members represented by the several peoples, and also of everything that is taking place around us, seems to be more clouded than ever before. In so saying I do not lay the main stress upon what is happening on the battlefields—for that must be judged in the light of other necessities—but upon the judgments now current among the peoples. They all seem to be at utter variance with what ought to be. I have already spoken here about a symptomatic experience I have had in connection with my last book (“Die Rätsel der Philosopnie”). I had written up to page 206, and then the war broke out. What follows after this point—the brief outline of Anthroposophy—was written actually during the war. I tried to give an objective picture of the philosophy of Boutroux and of Bergson. I do not believe that anyone could fail to realise the complete objectivity of what I said, even though only a brief space could ba allotted to the subject. It was necessary to call attention to the fact that Bergeon's philosophy is not original and in a certain way is lightly formulated. From pages 199-204, the views of Boutroux and Bergson were set forth without comment, and then on page 204, I said: “Out of easily formulated, easily attainable thoughts, Bergson presents an idea of evolution which, as the outcome of very profound thinking, W. H. Preuss had already presented in his book “Geist und Stoff” (“Spirit and Matter”) in 1882. Then, on pages 205-69 the philosophy of the lonely thinker Preuss is dealt with. It would naturally have been Bergeon's duty to make himself conversant with the ideas of Preuse. I say expressly, it would have been his duty to know something about the philosophy of Preues, for a philosopher ought to be aware of the ideas of his contemporaries if he proposes to write. Please bear in mind that I said, it would have been his duty to know this philosophy—for I may very possibly be accused of having said that Bergson intentionally kept silent about Preuss. I said no such thing and the passage quoted above stands there for all the world to see. Now suppose that everything the different peoples have said about each other during these last weeks had not been said—in that case the above reference to Bergson would have been considered an objective statement. But now it will in all probability not be so regarded. Naturally, I shall not at any other time be able to speak differently about this matter. Those who stand on the ground of Spiritual Seience must remain objective. At the present time, things that ought to be clearly perceived are clouded over; but when a sufficiently large number of people have taken Spiritual Science to their hearts and are really steeped in it there will emerge out of this obscurity the ideal arising from the truths of Spiritual Science. What we know of these truths—it is only a question of being steeped in them deeply enough—enables us to develop the right feeling for them. Let those who want to feel the true relationship between the different cultures, read what is contained in the forms of our columns and architraves, let them contemplate the curves and forme, and they will understand the spiritual relationships between the several nations. Not a single motif is accidental. When you look at a motif, when you see how it passes over from the third pillar to the fifth, you have there an expression of the relationship between the peoples corresponding to the two columns. From these architraves you can envisage the inner configuration of the soul-life of the peoples. You enter the Building by the West door, and as you move towards the East you can feel what makes man truly man, in that he gathers into his soul what is good and admirable in each of the particular cultures—and then, as we hope, it will all sound together in harmony in the second, smaller part of the Building under the small cupola. Those who open their hearts to the Building will find the way out of tie prevailing obscurity; those who do not, will be swept along in it. As we go towards the East, this next motif links on to the last (see pages 1 and 11). It is evident that this new form has arisen out of the foregoing Staff of Mercury! whereas in the latter the serpent-motif spreads horjzonally into the world, here the main motif points upwards and forks downwards, receiving what comes from above like a blossum opening downwards. In this, which is the Jupiter motif as the former was the Mercury motif, the East of Europe is expressed. With its tapering slenderness this motif suggests folded hands stretching upwards to what comes from above, and gliding by their side that with which earthly man has to connect himself as it comes down from above like a flower. It is not at all easy for the European to understand this motif and what lies behind it, because it is connected much more with the future than with the present. On account of the character of modern language it is extremely difficult to find words to characterise what lies behind this motif. For once spoken, the words would immediately have to signify something different, if they were to be really expressive. One cannot speak of the Russian element in the same way as one can speak of the English, French and Italian elements. We have already seen that we cannot speak of a “national” element in the case of Middle-European culture in the same sense as in the case of the cultures of Western Europe; still less can we speak of the Russian element in this sense. For does Russia present a picture similar to that presented by the English, French or Italian peoples? Most, certainly it does not! There is something in the Russian nature that is like a transformation of Western Europe, but a transformation into something totally different. In the West of Europe we see national cultures whose fundamental character can be discerned by deepening our knowledge of the culture actually existing there. In the German nature we find a state of incompleteness, a striving after something that is not present, but is there as an ideal only. But this striving after the ideal lives in the blood, in the astral body and the etheric body of the man of Middle Europe. Looking over to the East we see a magnificently finished philosophy of religion, a culture that is eminently a religious culture. But can it be called “Russian”? It would be absurd to call it Russian, even though the Russians themselves do so, for it is the culture that came over to them from ancient Byzantium; it is a continuation of what originated there. Naturally, what lives in the Sentient Soul comes from the Sentient Soul; what lives in the Intellectual Soul comes from the Intellectual Soul; what lives in the Consciousness Soul comes from the Consciousness Soul; and what lives in the Ego, even though it is in flow, in a perpetual state of becoming, proceeds from the Ego. But what comes from the Spirit Self is something that descends out of the Spirit into the Sentient Soul, the Intellectual Soul and the Consciousness Soul. The Spirit Self comes down from above towards Sentient Soul, Intellectual Soul, Consciousness Soul and Ego. This Spirit Self must announce itself through the fact that something foreign hovers down, as it were, upon the national culture. So we see that, fundamentally, everything it has hitherto experienced as its culture is foreign to tbe Russian soul, and has been foreign over since the time when the Greco-Byzantine culture was received, up to the external institutions that were imported from outside by Peter the Great. So we see bow through the Spirit Self there daecends the force which strives down to the soul-forces; but the Spirit Self will be able to give effect to its true force, its true character, only in the future. The Russian soul has, however, to make preparation for the reception of the Spirit Self. Quite obviously what has reached the Russian soul from foreign elements is not the Spirit Self that will come in the future. But just as the Byzantine influence, Eastern Christianity, Western culture, have descended upon Russian souls, so, one day, the Spirit Self will descend. At the present time there is nothing more than preparation for it, nothing more than an inclination towards receiving it. Examples can be given to illustrate everything for which Spiritual Science gives guiding-lines. Here is an example lying close at hand.—I have often spoken of the greatness of the philosopher Solovieff. His greatness was first revealed to me through spiritual observation, for I know that he is even greater, has effected even greater things, since his death in 1900 than he had effected before his death. But let us consider the facts; you can convince yourselves from Solovieff's own writings. Many of them have been translated. There are the translations by Nina Hoffmann, by Keuchel, and now the excellent translation by Frau von Vacano, “Die geistigen Grundlagen des Lebens”. If a man of Middle Europe steeps himself in the works of Solovieff, he can have a remarkable experience—especially since the latest translation has become available. It is extraordinarily interesting. One who is really conversant with Western and Middle-European philosophy will ask himself at first: Is there anything new in Solovieff? If we compare Solovieff with Western philosophy, we shall find not a single new thought as far as the actual text is concerned; there is nothing, absolutely nothing, not even in a turn of phrase, that could not equally well have been written in the West. And yet there is something altogether different. But if you search for this difference in the philosophy itself, in what has been written, reading it as you read an ordinary book, you will not discover what is different. For what is different is something that is not contained in the sentences themselves. It is not in them, and yet it is there. What is contained within and behind the sentences will eventually be found by the sensitive soul, despite the conviction, after reading the book, that it contains nothing that differs from West European philosophy. What is contained in Solovieff's works is a certain nuance of feeling which may seem to the man of Middle Europe like a sultry atmosphere. Sometimes one feels as though one were in an oven, particularly when great and far-reaching questions are involved. If you follow a sentence closely, you will discover that nothing of exactly the same kind emerges as it does in the case of a West European philosopher. There is a certain tone of feeling which resounds as if it were unending expectant; this tone of feeling has a mystical character; certainly, it is still a sultry mysticism which may even contain an element of danger for the man of Western Europe if he allows himself to be affected by it. But if one knows what lies in the substrata of the human soul—and it is necessary to know this—and really gets to the root of this element of sultriness, then it is certainly not dangerous. I believe that unless anyone has knowledge of the undertones of the life of soul, the essence of the difference in Solovieff's works will escape him and he will simply be convinced that he is reading a philosopher belonging to Western Europe. It is a very strange phenomenon, a phenomenon which clearly shows that what must come out of the East has not yet been uttered, above all has not yet been put into words. We can recognise the characteristic traits of the European cultures from another angle by considering, for example, the following.—Something of the very essence of French culture, the Intellectual Soul culture, is contained in a certain saying of Voltaire. It will certainly be discerned by anyone who is able to perceive realities from symptoms. The saying, “If God did not exist, he would have to be invented”, is rightly attributed to Voltaire. This presupposes—otherwise the utterance would have no sense that God would have to be believed in; for he would hardly be invented for amusement. Such a saying could be formulated only by a mind working entirely out of the Intellectual Soul, the Mind Soul, and having confidence in what arises from it—even in the matter of invention; for this belongs to the sphere of the Intellectual Soul. Now let us take a Russian: Bakunin. He formulated the saying differently—and that is very remarkable. He says, “If God existed, he would have to be abolished.” He discovers that he cannot tolerate the existence of God if he is to claim validity for his own soul.—And another saying of Bakunin is very characteristic: “God is—and man is a slave”—the one alternative. The other is: “Man is free—therefore there is no God.” He cannot conceive a way out of the circle and decides to choose between the two alternatives. He chooses the second: “Man is free—therefore there is no God.” This is a picture of the contrast between culture in Western and in Eastern Europe. West-European culture can still reconcile the idea of the free man with the idea of God. But in East-European culture there may be no God who coerces me, otherwise I am not free, I am a slave. One feels the whole cleft between Sentient Soul, Intellectual Soul, Consciousness Soul and Ego on the one side and the Spirit Self, which is present now, as it were, in counterpart, and is only preparing, its true being. We feel the whole cleft in what confronts us from the East, and we feel the lack of kinship of the East with the West when we perceive what effect representative personalities of the East make upon West-European culture. Who in the West, if he is not already a student of East-European culture, could understand what the Devil says to Ivan Karamazov? Who could reallyunderstand what Gorki calls “gruesome, yet veritable truth”?—“Yes, well, what is the truth? Man is the truth! What does it mean—Man? You are not it, nor am I it, and they are not it.—No! But you, I, they, old Luke, Napoleon, Mahomet all of us together are it! That is something quite tremendous! That is something wherein all beginnings are lodged, and all endings.—All in man, all for man. Man alone exists; all else is the work of his hands and of his brain. Man! Simply colossal! The very sound is exalted! MM—A—N! One should respect man! Not take pity on him—not degrade him by pitying him—but respect him!” And how does one who has been an actor speak about his relationship to the public? And how the convict?—“I have always despised those people who are too much concerned with satiety. Man himself is the main thing! Man stands at a higher level than the satisfied stomach!” It will be very difficult for the West to understand such things, for they give expression to the mystical suffering of the East; they let the cleft be felt between what is yet to come in the East and what lives in the West and in Middle Europe. This immense cleft indicates to us that what is there in the East today is not the real East at all. I should have a great deal to say on the subject but can only indicate these things. This East is something of which the East itself still knows little, something concerning which it only dimly senses what it will become in the future We understand well that it must be difficult for this East of the future to find, the bridge leading to its own true nature, to find itself, for we are confronted by no less a phenomenon than that the East still lives in feeling, still in something that is unutterable; it is seeking for a form of utterance. It seeks it in the East, seeks it in the West. The East was greatly enriched by what the Byzantine element brought to it but when the East gives expression to this, it no longer belongs to the East's own being; it is foreign to the East's own being. But one thing leads above all clefts, namely, what we know as the true Science of the Spirit. And if what is now going on in West and Middle Europe can show us that without Spiritual Science the further course of evolution must lead ad absurdum, the East shows us that progress is utterly impossible unless understanding is reached through Spiritual Science. Through Spiritual Science men will find and understand one another—in such a way that not only will their theoretical problems be answered, but the sufferings of culture will also be healed. Even more than elsewhere there will be opportunity for the East to feel the events of today as a hard testing. For what must needs be felt there in particular strength will be in complete opposition to every impulse, in the East that willed this war. And still more than in the West and still more than in Central Europe does it hold good for the East, that self-identification with the active motives of this war is a denial of its own true being. Everything in the East that has led to this war will have to disappear if the sun of salvation is to rise over the East. Our Building should become part of our very hearts, my dear friends, for it expresses everything that I try to say about it in sketchy words. More deeply than by any words you can understand what I have now said when you have a right feeling for the Building, when you feel that everything is contained there—in every curve, in every motif. Our Building should be something that can be called “A Dome of Mutual Understanding among European Humanity”, So it is perhaps in a particular sense—I must say this, for it is my duty to say it—also a contribution towards what is to be found in the preface to my book “Theosophy”, namely, that Spiritual Science is something that our age rejects in the intellect and on the other side longs for in the soul, and of which it is in dire need. When we contemplate the events of today we can say that Anthroposophy is something from which European humanity in the present epoch is as remote as it ought to be near, is something that it should long for with every fibre of its being. For if Spiritual Science penetrates our hearts in a way that could at the moment only be indicated in interpreting the forms of the columns and architraves, then the souls of European humanity will stand in the right relationship to each other. If Anthroposophy—and for our immediate present this is still more important—if Anthroposophy fulfils its task in the human soul in having a clarifying effect in the thoughts of men, bringing real clarity into them, permeating and rectifying them, then a very great deal will have been achieved for the immediate future. For as well as the fact that men's hearts are not rightly related to each other in our materialistic age, the karma of which we are experiencing, men's thought, too have gone astray. Men do not want to understand each other; but not only that; they have perhaps never lied about each other to such a colossal extent as they do in our time! That is still worse than what is happening out there on the battlefields, because its effect lasts longer and because it works up even into the spiritual worlds. But at bottom it is sheer slovenliness of thought that has brought us to the pass we have already reached. Therefore Anthroposophy is today the most urgent of all necessities in the evolution of humanity! Already one can ask the question: Are people today still capable of thinking? And further: Do not people feel that they must first have knowledge of the actual facts about which they want to think and speak? I raise these two questions today because, as I have said, it is my duty to do so. What is at work in Middle Europe was called “Bernhardism” by the American ex-President Roosevelt. I will not discuss what the ex-President has said but will point to something that is not usually noticed. Fundamentally, this book which I have in my hand and is the one alluded to by Roosevelt, is a very serious book: “Germany and the Next War”, by Friedrich Bernhardi, written in 1912. The author was one who knew a great deal about this impending war from an external, exoteric, point of view, and for this reason the book is extraordinarily instructive. But what kind of thinking do we find in a book that in its own way is honest and sincere? Here is a chapter entitled: “The Right to make War”. Naturally, if one talks of a right to make a war, one must take a standpoint determined by a community of people, not by individuals; in other words, one speaks out of the consciousness of the Luciferic and Ahrimanic spirits. Here is a passage which from the standpoint of the author is well meant, full of good intention. The attempt is made to explain that as long as there are separate nations, these nations have a right to make war on each other. The passage continues: “The individual can perform no nobler moral action than to sacrifice his own existence to the cause which he serves, or even to the conception of the value of ideals to personal morality... Similarly, nations and States can achieve no loftier consummation than to stake their whole power on upholding their independence, their honour, and their reputation.” The first part of the passage is correct, but the thought behind it as a whole is absurd; States cannot adopt a selfless standpoint, because with them totally different conditions prevail. We must be clear in our minds about this. Imagine yourselves in the shoes of an Austrian statesman after the events which culminated in the assassination of a Serb at Serajevo.—Can one speak there in the sense of the foregoing passage? Most certainly not! A statesman is obliged to act as the egoism of the State demands. And so quite correct utterances are made today while the thought behind them is utterly false. This is only one example. The spiritual-scientific attitude here will he illuminating in the truest sense of the word, if only there are a sufficient number of people to represent it. These are not trivial matters; they are matters of vast significance. For they have all combined into what has now led to this terrible outbreak of war. I say this, becausel I know it. I say it because at the same time I can truly say—so far as anything of this nature can be said in the sense in which an occultist means it—that I have suffered and am still suffering enough from the events of these last weeks. I have gone through enough shattering experiences beginning with the Serajevo assassination and including much else. Never before have I myself seen anything as astounding, nor have I heard from occultists of anything as astounding, as what followed upon the assassination at Serajevo. A soul was there lifted into the spiritual worlds who produced an effect entirely differerst from that produced by any other soul; this soul became, as it were, a cosmic soul, forming a cosmic centre of force around which all the prevailing elements of fear gathered, All the existing elements of fear gravitated towards this soul—and lo! in the spiritual world exactly the opposite effect was produced than had been produced in the physical world. In the physical world, fear held back the war; in the spiritual world it was an element that hastened on the war, hastened it rapidly. To have such experiences for the first time is one of the most shattering moments that can occur in occult observation. If at some time or other, what has happened in the last eight or ten weeks is objectively surveyed, it will be possible, even by following the outer events, to recognise something that is like a mirror-image of what was happening in the spiritual. It is the task of Anthroposophy, today more than ever, to learn objectivity from the evente of the time—true objectivity, which is so remote from the attitude prevailing today. I tried to bring out this point by asking two questions: “Are people today still capable of thinking?” and “Do people try, do they accustom themselves to look for the real facts when they want to think or speak?” Do they really do this? Wherever we look—when men and whole nations are lying about each other on such a colossal scale—everywhere it is evident that the feeling of duty to put facts to the test, to go into the real facts, is lacking, even in high places. This duty to test facts must be deeply engraved in the hearts of anthroposophists. We must learn to realise that among people who are to be taken. seriously, things must no longer happen as they are happening today, so universally. As anthroposophists we must realise that these things need to be kept firmly in minds for otherwise we shall not emerge from this chaos in cultural life. With strict earnestness we must adhere to our basic principle: “Wisdom is only in the Truth”. Our whole Building is an interpretation of this principle. We must learn to read our Building—that is the important thing. When it is rightly read, an attitude of earnestness, of conscientiousness, of longing for truth, will grow in our hearts in connection with cultural and spiritaal life. If our friends permeate themselves with the conviction that the truth rests upon the foundation of the facts of evolution, then their activities will bring blessing everywhere, no matter to which nation they belong. But if they themselves adopt a one-sidedly nationalistic standpoint, they will certainly not be able to do what is right in the anthroposophical sense. The reason why Blavatsky's Theosophy went astray was that from the outset the interests of one portion of humanity—not the English, but the Indian—were placed above the interests of mankind as a whole. And it is true in the deepest sense that only that leads to genuine occult truth which at all times places the interests of humanity as a whole above those of a portion of humanity—but does so earnestly, with the most earnest, deepest feelings. Occult truth is clouded over the very moment the interests of one part of humanity are made to override the interests of the whole. Difficult as this may be at a time like our own, nevertheless it must be striven for by those who in the true sense of the word call themselves anthroposophists. |
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture IV
25 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 287. The Building at Dornach: Lecture IV
25 Oct 1914, Dornach Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In the last two lectures an endeavour was made to interpret the sequence of columns in the Buildings to give one of the many possible interpretations to which the Building naturally lends itself. It is possible for one who enters the Building from the West to feel, as it were, in the very heart of humanity, because the forces working in the various cultural communities are given expression in the forms of the capitals, and the mutual relationships of the single European cultures in the architraves. It may have occurred to some of you that mention has not been made of all the European peoples. It is of course, impossible on every occasion to present a subject in all its aspects, for it is a matter of indicating the principles involved, not of making dogmatic statements. In the single motifs of the capitals, artistic expression has been given to the impulses at work in the souls belonging to European civilisations—in the inhabitants of the Italian peninsula, or rather the South-westerly peninsulas, of Western Europe, Middle Europe and Eastern Europe. The subject was presented as it was because the character of these civilisations enables them to be expressed by a single design, a single motif. The design and the cultural community concerned are therefore related. From West to East, the second pillar is an expression of the civilisation of the peninsulas in the South-West of Europe; the third pillar of that of France; the fourth of that of the British people, and so on. But there are also other European peoples. I cannot deal with all of them but will again speak of the underlying principles. It may be said that the cultures already referred to are the simpler cultures, however strange that may seem; they are simpler at any rate as far as the occultist is concerned. For the occultist, the Danish, Swedish and Norwegian cultures, for example, are much more complicated than those already mentioned, for many things which to the observer on the physical plane may seem the simpler, are for the occultist the more complicated. Thus if we are speaking of Danish culture, the queation may arise: How should we approach the designs in this case? In entering from the West we should have to look, first, at the capital of the third column, and then also at that of the fifth, seeing the third column, as it were, through the fifth. Obviously there is something more complicated here, for two capitals have to be taken into consideration. Now take Sweden. There we should have to view the capital of the second column from the West through the capital of the fifth column. And now, Norway. We should have to take the capital of the fourth column from the West and look at it through that of the fifth. It would be a matter of superimposing these capitals, and then we should have the same expression of feeling in connection with the cultures of Denmark, Sweden and Norway as we have for the Italian-Spanish, the French, the British and the Middle-European cultures when we look at the corresponding capitals. Really, everything is contained in these motifs of the capitals. Now that the principle has been explained, it might be very interesting to study for example, how it applies to the civilisations of Holland, Switzerland, and so forth. But I leave that to your own occult studies. So you see, when we speak of our Building we are truly not speaking of anything arbitrary, of anything whose forms and other artistic content have arisen in such a way that one can remain stationary at these forms and think of them as one is obliged to think of the forms of painting motifs produced at the present time. As I have already said, everything we have absorbed of Spiritual Science in the course of the years, and a great deal more besides, is expressed in this Building—but the appeal is to perceptive feeling, not to theoretical, intellectual cogitation. It would therefore be possible to speak about this Building without ever finishing. But again I leave it to your own hearts to elaborate the indications I have given you. For the aim of the Building is to bring hearts and souls into movement when, in contemplating the forms and their relationships, people do not interpret them intellectually or symbolically but allow the heart and mind and soul to speak when they are inside and outside the Building. What I now have to say can be explained by taking a particular motif of four columns embraced above by a cupola or dome. To regard any such motif as completely self-contained would be to take too constricted a view. Nothing in the world is completely self-contained—not a blossom, not an animal, not a human being. Neither, then, is a motif such as this, for part of its very essence is that forces are present entirely apart from the geometrical aspects. There are four columns embraced shows by a dome. But this geometrical aspect is only part of the whole. What belongs to the motif in addition is a set of forces which inhere in the whole structure of the universe and enable the columns to support the dome. The dome rests on the columns, the columns stand on the earth; the force of gravity comes into play.  If we really feel this motif, we do not feel the geometrical aspect only, but also the other, which I have often called the dynamic element, or element of force—the insertion into the configuration of forces of the whole universe, more particularly of the earth. This motif, then, has the peculiarity 0f being symmetrical at every point in its circumference. It is symmetrical in every direction of space, as far at least as the dome is concerned. So we can say: On the body of the earth there is a motif which stretches heavenwards and at its periphery is symmetrical. The important thing is to have an artistic feeling for such a motif. If we try to feel this motif in the right way—it is of course a matter of really sinking oneself in the character of the forms themselves—we shall come to realise: This motif, which rises upwards from the earth and in its upper part at least is symmetrical in every direction, seems to impel us to go down into ourselves, to experience our feeling inwardly. If you want to make progress in occultism it is essential to abandon the one-sidedness of an abstract, intellectual approach, and to adopt an approach which originates in actual experience. For this reason many things must be expressed, not in terms of the intellect, but in terms of experience. It is particularly difficult for the man of the present day to accept forms of experience in the same way that he accepts forms of the intellect. I will tell you what I mean by a form of experience. I can do no more than indicate, but everyone can understand it who makes the effort to go through it as an actual experience of his own. How can one develop a feeling for such a motif and what it expresses? This can be done in the following way.—In the morning, on getting out of bed to set about the day's work, you can say to yourself consciously: “I have now passed from the lying position into the position of standing or walking.” That is an actual experience—one of which few people make themselves conscious, but it is an experience to pass from the lying position into that of standing and walking. When one is lying down, the force of gravity works upon one as it does upon a sack, let us say a sack of flour. The force of gravity also works in a deeper sense, for when you are lying down you always lie on some area of the body and this area presses upon what is underneath. So pressure is always being exercised upon the area of the body on which you are lying. True, you are not aware of this pressure in the ordinary way, but for all that, it is there; it is connected with your sentient experience of the force of gravity and it works into your astral body. When a man begins to be conscious of this pressure-experience, he becomes aware at the same time of the elemental spirits of the earth. It is here that he is very well able to be aware of them, for when he is standing or walking the only area of pressure is that of the soles of the feet. When you stand up after having been lying down, you leave the sphere of the pressure; you assert yourself against the force of gravity; you insert the axis of your own body into the field of gravity, no longer resigning yourself to it like a sack of flour; you enter actively into the sphere of gravity. That is an actual experience different in character from some thought-experience of the brain which thinks in abstractions. In the lectures I gave on “Occult Reading and Hearing” I spoke of three brains. As soon as a man begins to experience things with his middle brain, he experiences them in a living way; feeling begins to be a middle brain experience. Very well, then, when we have made ourselves conscious of the experience of standing up, we have the experience of Feeling the World, and we know for the first time what feeling really is. This can be achieved in many other ways too, but we do really begin to realise what feeling is when we make the act of standing up a conscious experience. If it is brought to consciousness in the real sense this experience will lead us to understand the form here (see diagram). We say to ourselves: This form differs from what I myself am, in that it cannot stand up but must remain always in the lying position. To achieve my experience it would have to turn through 90° into the vertical plane. This dome stretches heavenwards. When man standing upright, has a feeling of the world, this upward stretching impulse works especially through his hands. And if he were to lie down and were able to feel what is above him, he would feel with his hands something of the nature of a cupola arching over him. What comes to expression in this architectural motif is contained in the sphere of feeling.  If man were able to lie bound to the earth, reaching out spiritually into the universe with his hands, he would feel the spiritual world above him as though he were inside a great dome, symmetrical in every direction. In a certain respect the Greeks had a similar experience. Greek culture, which sprang primarily from the Intellectual Soul, was, in one of it aspects, a, culture born from a peaceful union between man and the earth; while peacefully united with the earth, man felt the heavens above him.—There may appear to be a contradiction here, but when we are, finding our way into occultism such apparent contradictions must be faced and understood. We in our age have not the impulses that were at work in the inner life of the Greeks, nor have we within us what is now for the first time beginning in the evolution of humanity and is to come to expression in our Building.  A man who rises out of repose must not merely make the transition into the standing position, but he must also begin to move, to go forward. As well as the sphere of feeling he must come to know the sphere of will. This can be expressed in art only by transforming what was symmetrical on all sides (the dome) into something that is symmetrical about a single axis only. We can therefore say that when the dome-motif is transformed into a motif that has only one axis of symmetry, we have expressed in the Building not only what is experienced by the man who passes from repose into the sphere of feeling, but also by the man who pasees from feeling into willing, into progression, going forwards. The motif of will is a motif that leads onward. Hence the experience of one who is looking at the architraves and capitals must also lead him onwards; it must be an experience of progression. This was indicated in the two foregoing lectures.  Now the will is the sphere in man's being that is connected with subconscious experiences. It is that element which, in the case of man as he is at present, is for the most part directed by the gods. Naturally, then, by Lucifer and Ahriman as well. Hence there can also be evil will. Nevertheless, the will is borne onwards by the gods, and only in the rarest of cases is man able to know what goes on in his will. What a man expresses quite involuntarily when he is speaking belongs to what is conditioned in his will- nature and to which his will gives rise. One may even say that this is as it should be. It is not at all necessary, to begin with, for man to be fully conscious when he gives himself up to the primal, fundamental nature of his will, when he allows the impulses of the gods to be active in his will. The impulses of the will are the most fundamental of all. Hence the human being is able in his successive incarnations to progress from nation to nation. This is expressed in our Building through the progression in the series of columns. Man is able to progress from nation to nation, from people to people with every incarnation he is born into a different people. He experiences what proceeds from the sphere of his will as coming in a certain sense from the gods. Neither, to begin with, can he change very much that belongs to this sphere of the will. A man who is born in some particular place on the earth cannot alter the fact that he is born at some place represented in one or another of the forms of the columns. For he stands at this particular place in the evolutionary process through the subconscious foundations of his life of will. The way in which the members of the different nations think about each other, the way in which they mutually—let us say—esteem each other, is basically connected with what rises up like smoke out of the substrata of the sphere of will; it springs from nothing else than the impulses of the will. From what has been said we shall realise that it is possible for us to raise ourselves above these impulses of the will. But then we must naturally take a different direction. The direction of the will-impulses is it ˂—: it is the direction of progression. The direction of the impulses of feelings, however, is from below upwards. Man can raise himself out of what proceeds entirely from the impulses of will. He can do this through contemplating what is expressed in the motifs of the columns and architraves. Is not our whole mental horizon widened by these thoughts? And is not Spiritual Science a means of attaining this wider mental horizon? Only think of all that could be done to enable men of every cultural community to acquire mutual understanding of one another if what was presented in the two last lectures were to become living feeling, living knowledge. How could a member of one cultural community hate and abuse a member of another if he understood the things that were spoken of in those lectures? The limitations of what springs from the sphere of will in a single cultural community expand into the harmony formed by all such communities together when we know what mission each one has to fulfil. We begin to feel the single communities as we feel our own soul-members. This too had to be given artistic expression in the structure of our Building, in the direction from below upwards. And what is indicated as a theoretical, ethical principle in the first declared Object of our Movement (the universal brotherhood of peoples) has been given concrete expression in the forms of the Building, when these forms are contemplated in their flow from below upwards, inside and, as well, outside the Building. Now the whole is always contained in the part, so we have not only the direction of the will impulses ˂—, and the direction of the feeling-impulses (up), but something else as well. We have something else as well through the fact that there is a closure, an endings, overhead. In referring to this motif I have so far spoken of the supporting force, with its upward direction. But I can also speak of the closure above, the covering, the roofing in. The motifs may thus be described as motifs which progress, ascend, and enclose. You can also picture the Staff of Mercury. If you carry it, forward, it progresses; if you lift it up, it ascends; if you press the spirals together at the top, allow them to become rigid in themselves you have the closure above. This closure represents the thought-sphere, just as the progression represents the will sphere, and the ascent the feeling nature.  A true feeling of the whole evolution of humanity will develop in one who absorbs what is contained in the form-motifs of our columns and architraves in their flow from below upwards. They are motifs which express the principles of mutual understanding between the members of the different cultures and civilisations on the earth. To pass from the sphere of the will into the sphere of feeling one must rise above the state of isolation, of separateness; one must actually participate in what is expressed in this movement from below upwards. A certain element which will become more and more essential in the modern age will then be laid into the life of feeling, into the sympathies and antipathies of the members of the different spheres of culture. The Unconscious is an even stronger factor than what man has in his actual consciousness. The will impulses belong to the Unconscious; the feeling-impulses are more conscious, but still partly unconscious. The thought-impulses belong to the sphere of Consciousness, for a man is conscious of what he is thinking about. He is conscious of it, but only when he is really thinking, when he lives in the thoughts. But he does not always do this; when he is speaking he more often brings the impulses of the spheres of feeling and of will to expression. It is a peculiarity of man that he can speak but by no means always gives expression to thoughts; what seems to be thought in what he says is often maya—nothing more than an unburdening of the spheres of his will or feeling. To think in the real sense is something different, something more. Despite the fact that it is man's privilege to have thought-impulses, it is nevertheless one of the most difficult things to fill these impulses with real thoughts. Although it suffices for daily intercourse, if one desires to have adequate thoughts about the great impulses at work in the evolution of humanity, it will certainly not do to remain content with what originates from feeling, still less with what originates from the will. Thinking must be irradiated by something still higher; it is not enough merely to let the successive spheres of culture work upon the soul; there is something that works still more deeply in these spheres of culture. This can be brought to expression only in the effect made by the dome, the cupola. So one who passes through the Building from West to East will have in the progression of the columns the expression of will; and as he becomes aware of what flows from below upwards, he will feel the nature of the several European cultures, and a great deal else as well. What will come to him from the dome? The secrets of the evolution of all earthly humanity. Therefore, as he looks up into the dome or cupola he will see on the one side the portrayal of the primeval Indian inspiration: how through the Rishis there flowed into mankind what was to come from spiritual spheres into ancient Indian civilisation. What had to come to mankind in those days in conformity with the character of the ancient Indian epoch will be painted in one part of the dome. How Zarathustra gave the ancient Persian culture its stamp—the sunlight battling as it were with the darkness—this will be seen at a second place in the dome. Then how the Egypto-Chaldean culture gradually comes right out to the physical plane but is still permeated with astrological, spiritual realities—this will be found in a third area of the dome. At a fourth place will be portrayed the Greek, as if standing by an abyss. This is the culture born of the Intellectual Soul or Mind Soul. What man is, comes to the fore, how he is faced with the necessity of having to solve the riddle of the Sphinx, how, through solving it, he thrusts the Sphinx down into the abyss—that is to say, down into his own being—this will be portrayed in a fourth area of the dome. How the eternal, divine forces and powers work into this evolution of man will come to expression inasmuch as what lies still deeper in the evolution of humanity than the Post-Atlantean impulses, namely the impulses of the Atlantean and Lemurian epochs, will be portrayed at the points of the compass: Atlantean evolution in the South, Lemurian evolution in the North of the dome. And finally, the outcome of the Lemurian and Atlantean evolution will be portrayed: namely, our own era. Implicit within it is that impulse in world-evolution which expresses itself in the “J A O”. This will meet the gaze of one who looks from West to East towards the smaller cupola., Not that “J A O” is represented symbolically, but it is expressed in the motif. One who looks from East to West will see that which speaks out of the depths of the Cosmos into the development of culture, just as the “J A O” speaks from within into the development of the soul. But all that I have described is perceptible to a man only if he overcomes the dome which arches over his brain; if he frees the etheric body of his head and looks from within outwards, then what I have described comes to him as a mighty Imagination. These things are realities, are actually seen. when the etheric body is liberated from its physical foundation. Then one sees what presents itself inwardly to the etheric brain which has expanded to the Cosmos. The whole earthly evolution of man is represented here. (See sketches for paintings in the large cupola.) To have thoughts about the realities of the evolution of humanity is possible only when we penetrate the secrets that are to be portrayed in paintings in the interior of our dome. In the same way that we can reach the sphere of feeling—that is to say, unprejudiced feeling devoid of sympathies and antipathies—when we experience what comes to expression from below upwards in the motifs of the columns and architraves, so through these motifs (of the paintings) we can penetrate to what is living reality in human evolution at every hour, every moment. Only when we know what is actively at work in the human soul at every moment, can we know what has been evolved in the course of millions of years. For everything that was contained in the Atlantean and Lemurian cultures lives in every soul—otherwise no soul would be as it now is. A human soul in all its depths can be understood in thought only if it is understood as the product of the whole process of world-evolution. And so our Building expresses—if I may use the word “expresses”—Willing, Feeling, Thinking, but in their evolution, what they should become in the human being who is striving to achieve a measure of self-development. Thus neither the forms as they are, nor the things that are done here, are the result of arbitrariness, but everything comes out of the very core of what we also try to grasp in Spiritual Science. How often, when we are trying to describe the secrets of manes nature, do we not have to consider Willing, Feeling and Thinking? We have portrayed them in our Building and there, just as in man's own nature, willing, feeling and thinking are mysteriously linked with one another. If we go from West to East in this Building, we are moving as the Will-sphere of man moves; if we direct our gaze from below upwards in contemplating the forms of the columns and architraves, we sink down into the Feeling-sphere of human nature; if in what arches over the Building in the painting of the domes we study what we experience inside the Building, then we are studying the secrets of the sphere of human Thinking. In a production such as this Building, everything corresponds to a certain inner necessity, everything comes into being as it inevitably must. And that is part of the significance of a Building of this kind. What makes us realise that some Imagination, Inspiration or Intuition contains objective reality? We realise it through the fact that when we have the Imagination, the Inspiration or the Intuition, we have the actual experience that it is not something that has arisen out of ourselves but has its place within the harmony of the whole Cosmos. From now onwards into the future, humanity must have a concept of art which has as its essential characteristic what is felt to be inner necessity. We must feel that a truly artistic creation is not due to ourselves but that the gods create it through us, because it is their will that it shall be in the world. We may well be convinced that the real progress of 0f human nature will depend upon such feelings and ideas gaining wider and wider recognition and taking the place of those that are current today. What I mean by saying this, is that everyone who is working on this Building or is in any way connected with it, should feel above all that it is his business to compare what is aimed at here, what is expressed by and in this Building, with what is dominant in the world today. Such a comparison can give rise to the fervent question; What was it that enabled Christianity in its earliest form to come into being? I have often spoken of this, for all such impulses in cultural life have arisen in the same way: namely, through the fact that in the case of a genuine, initial impulse of culture, those who were the first to ally themselves with it, were sufficiently strong in their souls to let this impulse completely dominate them. What would have become of Christianity if in the souls of the first Christians the Christian impulses had not been all-powerful? In the Roman world above them, in the physical light of day, a different culture prevailed; we know that Christianity developed in the darkness, down below in the little cells in the catacombs, and then rose above the surface. Nothing of this Roman culture has remained—what developed down below in the catacombs rose up and conquered the world. This came to pass because Christianity became part of the hearts and souls of those down there in the catacombs. Today the position is not quite the same—if it were, we should have to hollow out this Dornach hill into catacombs so that nobody should see anything of what we are doing. We need not hollow out the hill, we need not keep anything in concealment, we need not prepare the new culture underneath the earth while what is now taking place on the surface runs its course. Spiritually, however, the situation is the same. How much of what we want to inscribe in our hearts and souls is to be found in the culture of the present day? As much as there was of early Christianity in Rome! Even though we do not worship physically in the catacombs, spiritually we are in the catacombs, and our feeling is true if we realise that this is indeed our situation. Our feeling for the Building is true only if we say to ourselves: There, in the sunshine, the dome of our Building with its glistening grey slate roof gleams. over the countryside. We are under this arching vault, above all, spiritually under it. By these words I wanted again to indicate what must be the attitude of those who understand the inmost impulse of Spiritual Science towards what is to be found in the outside world. Oh, those early Christians—they heard the Word that resounded through their souls, their hearts, the Word that came from the Mystery of Golgotha, and they did not succumb to the temptation of what was taking place above the catacombs! May it be the same today—spiritually—within our Movement! A certain difficulty lies in the word “spiritually”. The difficulty is expressed in the fact that if one considers the actual situation, one might sometimes be tempted—I say, might be, not is tempted—to wish that there were still present today the dire compulsion for inner deepening that would be there if we were forbidden by all the means of present-day culture to build on the Dornach hill, so that we should literally have to go into caves and there, in concealment, take up our abode. Confronted with such a prospect we should realise more strongly how our own impulses, which should be those of Spiritual Science, must differ from the blustering racket overhead. These are things which can be expressed only by analogies such as I have now put into words. You can feel something of what is meant—and more is meant than seems, to be contained, in these analogies—if you penetrate a little into the gist of these words. May you feel all that I have meant to convey in today's lecture and in these concluding words. |


 I will draw a rough sketch of the form of the Acanthus Spinoza. This was supposed to have been worked out plastically and then added to the Corinthian column. Now there is, of course, something behind this. Vitruvius, the learned compiler of the artistic traditions of antiquity, quotes a well-known anecdote, which led to the adoption of the “basket hypothesis” in connection with the Corinthian column. The expression is a good one, for what, according to the materialistic conception of art, was the origin of the decoration on the Corinthian capital? Little baskets of acanthus leaves that were carried about! When we enter more deeply into these things we realize that this is both symptomatic and significant. It becomes evident that their understanding of the finer spiritual connections of the evolutions of humanity has led investigators to a basket, to basket-work, and as a kind of token of it we have the “basket hypothesis” of the Corinthian column. Vitruvius says that Callimachos, the Corinthian Sculptor, once saw a little basket standing on the ground somewhere, with acanthus plants growing around it, and he said to himself: There is the Corinthian capital! This is the very subtlest materialism imaginable. Now let me show you the significance of this anecdote narrated by Vitruvius. The point is that in the course of the modern age the inner principle, the understanding of the inner principle of artistic creation has gradually been lost. And if this inner principal is not re-discovered, people simply will not understand what is meant and desired in the forms of our building, its columns and capitals. Those who hold fast to the basket hypothesis—in a symbolical sense of course—will never be able rightly to understand us.
I will draw a rough sketch of the form of the Acanthus Spinoza. This was supposed to have been worked out plastically and then added to the Corinthian column. Now there is, of course, something behind this. Vitruvius, the learned compiler of the artistic traditions of antiquity, quotes a well-known anecdote, which led to the adoption of the “basket hypothesis” in connection with the Corinthian column. The expression is a good one, for what, according to the materialistic conception of art, was the origin of the decoration on the Corinthian capital? Little baskets of acanthus leaves that were carried about! When we enter more deeply into these things we realize that this is both symptomatic and significant. It becomes evident that their understanding of the finer spiritual connections of the evolutions of humanity has led investigators to a basket, to basket-work, and as a kind of token of it we have the “basket hypothesis” of the Corinthian column. Vitruvius says that Callimachos, the Corinthian Sculptor, once saw a little basket standing on the ground somewhere, with acanthus plants growing around it, and he said to himself: There is the Corinthian capital! This is the very subtlest materialism imaginable. Now let me show you the significance of this anecdote narrated by Vitruvius. The point is that in the course of the modern age the inner principle, the understanding of the inner principle of artistic creation has gradually been lost. And if this inner principal is not re-discovered, people simply will not understand what is meant and desired in the forms of our building, its columns and capitals. Those who hold fast to the basket hypothesis—in a symbolical sense of course—will never be able rightly to understand us. And, from the feeling of the lines of force which man has to develop in himself, arose the lines that gave birth to artistic form. Such lines are nowhere to be found in external reality. Now spiritual research is often confronted by a certain wonderful akashic picture; it represents the joining together of a number of human beings into a whole, but a harmonious, ordered joining together. Imagine a kind of stage, and as an amphitheatre around it, seats with spectators; certain human beings are now to pass in a procession round and inside the circle. Something higher, super-sensible—not naturalistic—is to be presented to man.
And, from the feeling of the lines of force which man has to develop in himself, arose the lines that gave birth to artistic form. Such lines are nowhere to be found in external reality. Now spiritual research is often confronted by a certain wonderful akashic picture; it represents the joining together of a number of human beings into a whole, but a harmonious, ordered joining together. Imagine a kind of stage, and as an amphitheatre around it, seats with spectators; certain human beings are now to pass in a procession round and inside the circle. Something higher, super-sensible—not naturalistic—is to be presented to man.
 Now the persons (in the procession) are to portray something of great significance, something that does not exist on the Earth, of which there are only analogies on the Earth; they are to represent something that brings man into connection with the great sphere of the cosmos. In those times it was a question of representing the relationship between the earthly forces and the sun forces. How can man come to feel this relationship of the earthly forces to the sun forces? By feeling it in the same way as, for instance, the state of carrying a load. He can feel it in the following way: all that is earthly rests upon the surface of the earth and as it rises away from the earth (this is only to be thought of in the sense of force) it runs to a point. So that man felt the state of being bound to the earth expressed in a form with a wide base, running upwards to a point. It was this and nothing else, and when man sensed this working of forces, he said to himself: ‘I feel myself standing on the earth.’
Now the persons (in the procession) are to portray something of great significance, something that does not exist on the Earth, of which there are only analogies on the Earth; they are to represent something that brings man into connection with the great sphere of the cosmos. In those times it was a question of representing the relationship between the earthly forces and the sun forces. How can man come to feel this relationship of the earthly forces to the sun forces? By feeling it in the same way as, for instance, the state of carrying a load. He can feel it in the following way: all that is earthly rests upon the surface of the earth and as it rises away from the earth (this is only to be thought of in the sense of force) it runs to a point. So that man felt the state of being bound to the earth expressed in a form with a wide base, running upwards to a point. It was this and nothing else, and when man sensed this working of forces, he said to himself: ‘I feel myself standing on the earth.’ In the same way he also became aware of his connection with the sun. The sun works in upon the earth and man expressed this by portraying the lines of forces in this way. The sun, in its apparent journey round the earth, sends its rays thus, running downwards to a point.
In the same way he also became aware of his connection with the sun. The sun works in upon the earth and man expressed this by portraying the lines of forces in this way. The sun, in its apparent journey round the earth, sends its rays thus, running downwards to a point.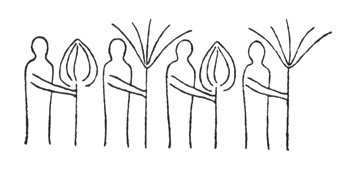
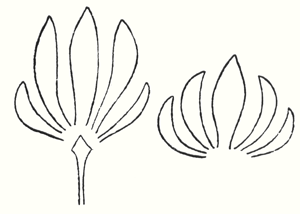 I might make the following design in order to express how man, from his conception of the course of evolution from the complex to the simple, developed the lines into a decoration. If you think of the lines in alternation you have a simplified reproduction of the circling procession of Sun-motif—Earth-motif, Sun-Motif—Earth-motif. That is what man experienced in the decorative motif. This decorative motif was already a feature of Mesopotamian art and it passed over into Greek art as the so-called Palmette, either in this or in a similar form, resembling the lotus petal.
I might make the following design in order to express how man, from his conception of the course of evolution from the complex to the simple, developed the lines into a decoration. If you think of the lines in alternation you have a simplified reproduction of the circling procession of Sun-motif—Earth-motif, Sun-Motif—Earth-motif. That is what man experienced in the decorative motif. This decorative motif was already a feature of Mesopotamian art and it passed over into Greek art as the so-called Palmette, either in this or in a similar form, resembling the lotus petal. Underneath what has to bear the capital we find the following. Here we have the torus of the Doric column, but underneath this we find, in certain Doric columns, introduced as a painting around the pillar, the Earth-motif somewhat modified, and the Sun-motif. Up above we have the Doric torus and the decorative motif below as an ornament. We actually find the palmette motif on certain Doric columns, carried out in such a way that it forms a procession: Sun-Earth, Sun-Earth and so on.
Underneath what has to bear the capital we find the following. Here we have the torus of the Doric column, but underneath this we find, in certain Doric columns, introduced as a painting around the pillar, the Earth-motif somewhat modified, and the Sun-motif. Up above we have the Doric torus and the decorative motif below as an ornament. We actually find the palmette motif on certain Doric columns, carried out in such a way that it forms a procession: Sun-Earth, Sun-Earth and so on. The Ego, when it is within the body, must grow strong if it has to bear a load. It is this strengthening process that is felt in the volute. We see the human being, as he strengthens his Ego in the fourth Post-Atlantean period, expressed in the volute. Thus we come to the basic form of the Ionic pillar; it is as if Atlas is bearing the world, but the form is still undeveloped in that the volute becomes the weight bearer.
The Ego, when it is within the body, must grow strong if it has to bear a load. It is this strengthening process that is felt in the volute. We see the human being, as he strengthens his Ego in the fourth Post-Atlantean period, expressed in the volute. Thus we come to the basic form of the Ionic pillar; it is as if Atlas is bearing the world, but the form is still undeveloped in that the volute becomes the weight bearer.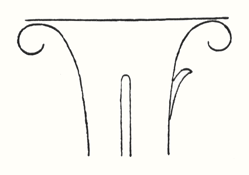 The middle portion is simply extended downward, as it were, so that the character of weight bearing becomes complete. And now think of this weight bearing in the form of a plastic figure and you have the human force bent into itself—the Ego bent round, in this case bearing a weight. An artistic principle is involved when we reproduce in miniature anything that is worked out on a large scale, and vice-versa. If you now think of an elaboration of the Corinthian column with the volute bearing the abacus here, and repeat this artistic motif lower down where it only serves as a decoration, you have plastically introduced in the decoration something that is really the whole column. Now imagine that the Doric painting which grew out of the decorative representation of a very ancient motif, is united with what is contained in the Corinthian column and the intuition will arise that the decoration around it is the same as an earlier painting. The painting on the Doric column was worked out plastically—I can illustrate this to you by the diagram of the motif containing the the palmette—and the urge arose to bring the palmette into the later decorative motif. Here it was not a motif representing the bearing of a load; what was mere painting in the Doric column (and therefore flat) was worked out plastically in the Corinthian column and the palm leaves are allowed to turn downwards. To the left I have drawn a palmette and on the right the beginning of it that arises when the palmette is worked out plastically.
The middle portion is simply extended downward, as it were, so that the character of weight bearing becomes complete. And now think of this weight bearing in the form of a plastic figure and you have the human force bent into itself—the Ego bent round, in this case bearing a weight. An artistic principle is involved when we reproduce in miniature anything that is worked out on a large scale, and vice-versa. If you now think of an elaboration of the Corinthian column with the volute bearing the abacus here, and repeat this artistic motif lower down where it only serves as a decoration, you have plastically introduced in the decoration something that is really the whole column. Now imagine that the Doric painting which grew out of the decorative representation of a very ancient motif, is united with what is contained in the Corinthian column and the intuition will arise that the decoration around it is the same as an earlier painting. The painting on the Doric column was worked out plastically—I can illustrate this to you by the diagram of the motif containing the the palmette—and the urge arose to bring the palmette into the later decorative motif. Here it was not a motif representing the bearing of a load; what was mere painting in the Doric column (and therefore flat) was worked out plastically in the Corinthian column and the palm leaves are allowed to turn downwards. To the left I have drawn a palmette and on the right the beginning of it that arises when the palmette is worked out plastically. 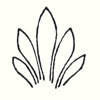 If I were now to continue, the painted Doric palmette would thus pass over into the Corinthian plastic palmette. If I did not paint the palmette we should in each case have the acanthus leaf. The acanthus leaf arises when the palmette is worked out plastically; it is the result of an urge not to paint the palmette but to work it out plastically. People then began to call this form the acanthus leaf; in early times, of course, it was not called by this name. The name has as little to do with the thing portrayed as the expression ‘wing’ has to do with the lungs and lobes or ‘wings’ of the lungs. The whole folly of naturalistic imitation in the case of the acanthus leaf is exposed, because, in effect, what is called the acanthus leaf decoration did not arise from any naturalistic imitation of the acanthus leaf, but from a metamorphosis of the old Sun motif in the palmette that was worked out plastically instead of being merely painted. So you see that these artistic forms have proceeded from an inner perception and understanding of the postures of the human etheric body (for the movement of a line is connected with this)—postures which man has to set up in his own being.
If I were now to continue, the painted Doric palmette would thus pass over into the Corinthian plastic palmette. If I did not paint the palmette we should in each case have the acanthus leaf. The acanthus leaf arises when the palmette is worked out plastically; it is the result of an urge not to paint the palmette but to work it out plastically. People then began to call this form the acanthus leaf; in early times, of course, it was not called by this name. The name has as little to do with the thing portrayed as the expression ‘wing’ has to do with the lungs and lobes or ‘wings’ of the lungs. The whole folly of naturalistic imitation in the case of the acanthus leaf is exposed, because, in effect, what is called the acanthus leaf decoration did not arise from any naturalistic imitation of the acanthus leaf, but from a metamorphosis of the old Sun motif in the palmette that was worked out plastically instead of being merely painted. So you see that these artistic forms have proceeded from an inner perception and understanding of the postures of the human etheric body (for the movement of a line is connected with this)—postures which man has to set up in his own being. The cake rises in the mould and when it is taken out its surface shows all the forms which appear on the sides of the mould in negative. The same principle may be applied in the case of the interior decoration of our building, only that of course there is no cake inside; what must live there is the speech of Spiritual Science, in its true form. All that is to be enclosed within the forms, all that is to be spoken and proclaimed, must be in correspondence, as the dough of the cake corresponds to the negative forms of the baking mould. We should feel the walls as the living negative of the words that are spoken and the deeds that are done in the building. That is the principle of the interior decoration. Think for a moment of a word, in all its primordial import, proceeding from our living Spiritual Science and beating against these walls. It seems to hollow out the form which really corresponds to it. Therefore I at least was satisfied from the very outset that we should work in the following way: with chisel and mallet we have a surface in mind from the beginning, for with the left hand we drive the driving chisel in the direction which will eventually be that of the surface. From the very outset we drive in this direction. On the other hand we hold the graver's chisel at right angles to the surface.
The cake rises in the mould and when it is taken out its surface shows all the forms which appear on the sides of the mould in negative. The same principle may be applied in the case of the interior decoration of our building, only that of course there is no cake inside; what must live there is the speech of Spiritual Science, in its true form. All that is to be enclosed within the forms, all that is to be spoken and proclaimed, must be in correspondence, as the dough of the cake corresponds to the negative forms of the baking mould. We should feel the walls as the living negative of the words that are spoken and the deeds that are done in the building. That is the principle of the interior decoration. Think for a moment of a word, in all its primordial import, proceeding from our living Spiritual Science and beating against these walls. It seems to hollow out the form which really corresponds to it. Therefore I at least was satisfied from the very outset that we should work in the following way: with chisel and mallet we have a surface in mind from the beginning, for with the left hand we drive the driving chisel in the direction which will eventually be that of the surface. From the very outset we drive in this direction. On the other hand we hold the graver's chisel at right angles to the surface.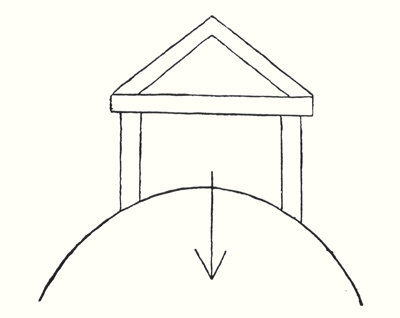
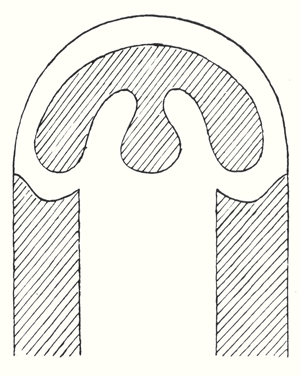 If you compare it with the Greek Temple you will discover the difference. The Greek motif is complete in itself. This other motif, when it is a wall—for instance the separate perpendicular wall—only has meaning when it is not merely wall, but when it grows out of the whole. The wall is not merely wall, it is living, just like a living organism that allows elevations and depressions to grow out of itself. The wall lives—that is the difference. Think of a Greek Temple. Although there are many columns, the whole is none the less governed by gravity. In our building, however, nothing is mere wall. The forms grow out of the wall. That is the essential thing. And when we pass around inside our building we shall find one plastic form, a continuous relief sculpture on the capitals, plinths, architraves. They grow out of the wall, and the wall is their basis, their soil, without which they could not exist. There will be a great deal of relief carving in wood in the interior of the building, and forms which, although they are not to be found elsewhere in the physical world, represent an onward flowing evolution. Beginning between the Saturn columns at the back, there will be a kind of symphonic progression to the culmination in the East. But the forms are no more present in the outer physical world than melodies are present there. These forms are walls that have become living. Physical walls do not live, but etheric walls, spiritual walls are indeed living.
If you compare it with the Greek Temple you will discover the difference. The Greek motif is complete in itself. This other motif, when it is a wall—for instance the separate perpendicular wall—only has meaning when it is not merely wall, but when it grows out of the whole. The wall is not merely wall, it is living, just like a living organism that allows elevations and depressions to grow out of itself. The wall lives—that is the difference. Think of a Greek Temple. Although there are many columns, the whole is none the less governed by gravity. In our building, however, nothing is mere wall. The forms grow out of the wall. That is the essential thing. And when we pass around inside our building we shall find one plastic form, a continuous relief sculpture on the capitals, plinths, architraves. They grow out of the wall, and the wall is their basis, their soil, without which they could not exist. There will be a great deal of relief carving in wood in the interior of the building, and forms which, although they are not to be found elsewhere in the physical world, represent an onward flowing evolution. Beginning between the Saturn columns at the back, there will be a kind of symphonic progression to the culmination in the East. But the forms are no more present in the outer physical world than melodies are present there. These forms are walls that have become living. Physical walls do not live, but etheric walls, spiritual walls are indeed living. (Dr. Steiner here read a passage from a book) ... The author is trying to form a conception of what relief really is. But the conception is built up simply from what the eye perceives, as he plainly shows when he says that the relief is produced when one thinks of the background as a pane of glass and that which lies in front of the pane as shut off by another pane of glass. He therefore bases his conception of relief on the eye and in order to make it clear he uses the two panes of glass on which the whole figure is projected. As against this conception we have our own which passes over from what is made visible by glass and projection to that which lives. We want to make relief a living thing. Relief has no meaning when one simply designs figures on a wall. It only has meaning when it calls forth the intuition that the wall itself is living and can bring forth the figures.
(Dr. Steiner here read a passage from a book) ... The author is trying to form a conception of what relief really is. But the conception is built up simply from what the eye perceives, as he plainly shows when he says that the relief is produced when one thinks of the background as a pane of glass and that which lies in front of the pane as shut off by another pane of glass. He therefore bases his conception of relief on the eye and in order to make it clear he uses the two panes of glass on which the whole figure is projected. As against this conception we have our own which passes over from what is made visible by glass and projection to that which lives. We want to make relief a living thing. Relief has no meaning when one simply designs figures on a wall. It only has meaning when it calls forth the intuition that the wall itself is living and can bring forth the figures. If we pay heed to the organs of the Gods which they themselves created when, as the Elohim, they gave the earth to man, if we pay heed to the etheric forms of the plants and mould in accordance with them, we are creating in the same way as nature created the larynx in man in order that he might speak—we are indeed creating a larynx through which the Gods may speak to us. If we hearken to the music of the forms on our walls which are the larynx for the speech of the Gods, we are seeking the way back to Paradise. I will speak of painting in another lecture. To-day I want to speak of the relief work and sculpture which will be produced in this house we have opened to-day. I have tried to explain how relief may become an organ for the speech of the Gods and on some future occasion we will speak of how colours become soul-organs for the speech of the Gods. Our age has little understanding for the kind of conceptions that must inspire us if we are really to fulfil our task. The Greek Temple was the dwelling place of the God, the Church of Christendom the framework around the community who would fain be united with the Spirit. What is our building to be? This is already revealed in its ground-plan and rounded form. The building is bipartite but the architectural forms of the two sections have equal importance. There is no difference as in the case of the chancel and the space for the congregation in a Christian Church.
If we pay heed to the organs of the Gods which they themselves created when, as the Elohim, they gave the earth to man, if we pay heed to the etheric forms of the plants and mould in accordance with them, we are creating in the same way as nature created the larynx in man in order that he might speak—we are indeed creating a larynx through which the Gods may speak to us. If we hearken to the music of the forms on our walls which are the larynx for the speech of the Gods, we are seeking the way back to Paradise. I will speak of painting in another lecture. To-day I want to speak of the relief work and sculpture which will be produced in this house we have opened to-day. I have tried to explain how relief may become an organ for the speech of the Gods and on some future occasion we will speak of how colours become soul-organs for the speech of the Gods. Our age has little understanding for the kind of conceptions that must inspire us if we are really to fulfil our task. The Greek Temple was the dwelling place of the God, the Church of Christendom the framework around the community who would fain be united with the Spirit. What is our building to be? This is already revealed in its ground-plan and rounded form. The building is bipartite but the architectural forms of the two sections have equal importance. There is no difference as in the case of the chancel and the space for the congregation in a Christian Church.  The difference in the dimensions of the two sections of our building merely signifies that in the large cupola the physical preponderates and that in the small cupola we have tried to make the spiritual predominate. This very form expresses aspiration to the Spirit. Every single detail must express this aspiration to the Spirit, inasmuch as we are striving to create an organ for the speech of the Gods. I have said that those who really understand our building fully will put away lying and unrighteousness; the building may indeed become a ‘Lawgiver,’ and the truth of this can be studied in the different forms and in the architraves. Everything in the building will have an inner value. Every part of the larynx has inner value; no words could be uttered if the larynx did not contain a a particular form at the right place. If, for instance, we were to make an indention here (see diagram) and think of a kind of roofing over it, the whole form expresses the fact that this building must be filled with the feeling of hearts striving together in love.
The difference in the dimensions of the two sections of our building merely signifies that in the large cupola the physical preponderates and that in the small cupola we have tried to make the spiritual predominate. This very form expresses aspiration to the Spirit. Every single detail must express this aspiration to the Spirit, inasmuch as we are striving to create an organ for the speech of the Gods. I have said that those who really understand our building fully will put away lying and unrighteousness; the building may indeed become a ‘Lawgiver,’ and the truth of this can be studied in the different forms and in the architraves. Everything in the building will have an inner value. Every part of the larynx has inner value; no words could be uttered if the larynx did not contain a a particular form at the right place. If, for instance, we were to make an indention here (see diagram) and think of a kind of roofing over it, the whole form expresses the fact that this building must be filled with the feeling of hearts striving together in love.
 The lines between any point of the ellipse and the two foci will naturally differ, but the two lines together will come to the same length (a + b = c + d in diagram). You can add the distances of each point from these two foci and you will always get the same length. This is so simple in the case of the circle that there is no need for an mental process. In the case of the ellipse, however, we must make an addition. All lines to the centre of the circle are equal, but in the ellipse we have to make an addition. Now you will say: ‘Yes, but I do not add when I see an ellipse.’ You yourself do not, it is true, but your astral body does; what the geometrician does consciously the astral body does unconsciously. The astral body is a finished geometrician. You have no idea of all the knowledge that is contained in your astral bodies; in the astral body you are all the wisest of geometricians, only of course the geometry you know in the astral body can only be brought into consciousness by the ‘sweat of the brow.’ You must pardon this expression but it is permissible to-day (... it was very hot on the day this lecture was given.) Everything is there in the astral body and if those who teach geometry, instead of using their wonted methods, could apply a pump in order to extract what is in the astral body, they would no longer need to teach—the knowledge would well up of itself. We add, then, the two distances from the foci and always get the same result. When an ellipse form seems beautiful, what does this really imply? It implies that the astral body is adding and the sum total is always the same. And now picture to yourselves that you are adding without knowing it and every time getting the same result. You feel pleased. Now you go to another point and carry out the same process. ... The same total again—oh! what joy! This is the living experience of the ellipse.
The lines between any point of the ellipse and the two foci will naturally differ, but the two lines together will come to the same length (a + b = c + d in diagram). You can add the distances of each point from these two foci and you will always get the same length. This is so simple in the case of the circle that there is no need for an mental process. In the case of the ellipse, however, we must make an addition. All lines to the centre of the circle are equal, but in the ellipse we have to make an addition. Now you will say: ‘Yes, but I do not add when I see an ellipse.’ You yourself do not, it is true, but your astral body does; what the geometrician does consciously the astral body does unconsciously. The astral body is a finished geometrician. You have no idea of all the knowledge that is contained in your astral bodies; in the astral body you are all the wisest of geometricians, only of course the geometry you know in the astral body can only be brought into consciousness by the ‘sweat of the brow.’ You must pardon this expression but it is permissible to-day (... it was very hot on the day this lecture was given.) Everything is there in the astral body and if those who teach geometry, instead of using their wonted methods, could apply a pump in order to extract what is in the astral body, they would no longer need to teach—the knowledge would well up of itself. We add, then, the two distances from the foci and always get the same result. When an ellipse form seems beautiful, what does this really imply? It implies that the astral body is adding and the sum total is always the same. And now picture to yourselves that you are adding without knowing it and every time getting the same result. You feel pleased. Now you go to another point and carry out the same process. ... The same total again—oh! what joy! This is the living experience of the ellipse. The hyperbola also has two foci which lie approximately here. Again we can draw lines to these two points. The strange thing here is that we do not add but subtract. We always get the same result by subtracting the lesser from the greater. Our astral body subtracts and is glad that the difference is always the same. In this inner feeling of equality the astral body experiences the source of the hyperbola.
The hyperbola also has two foci which lie approximately here. Again we can draw lines to these two points. The strange thing here is that we do not add but subtract. We always get the same result by subtracting the lesser from the greater. Our astral body subtracts and is glad that the difference is always the same. In this inner feeling of equality the astral body experiences the source of the hyperbola.
 There we must divide two distances instead of adding, subtracting or multiplying. That is to say, it must be possible for our astral body to determine two points—and also other points if it takes the larger line—and to divide the greater distance by the smaller. The astral body, then, must be able to divide and when it does this it gets a line (see diagram). All the points are so that their distances from two points are the same in the division.
There we must divide two distances instead of adding, subtracting or multiplying. That is to say, it must be possible for our astral body to determine two points—and also other points if it takes the larger line—and to divide the greater distance by the smaller. The astral body, then, must be able to divide and when it does this it gets a line (see diagram). All the points are so that their distances from two points are the same in the division. Let me try to make a diagrammatic sketch of this process. Underneath we have the Earth. Man is at first a horizontal being; then he stands upright—in the vertical position. It is an achievement of man's nature itself to attain the vertical position but he has the help of all the hierarchies as he passes through the course of his life. What is it that comes to his aid when he stands upright and walks? The forces that work from the Earth out into the expanses of cosmic space. These are the earthly forces. To-day physicists only speak of purely physical forces of the Earth—forces of attraction, of gravity and the like. The Earth, however, is not merely physical body but a being of spirit and soul and when, as little children, we raise ourselves to the upright position and walk, we are uniting ourselves with the forces of Will rising out of the Earth. The Earth-Will permeates our being; we allow the Earth -Will to flow into us and place ourselves in the upright position—the direction of the Earth-Will. This process is a union with the Earth-Will. But in opposition to the Earth-Will there is a will that works in from all sides of the cosmos. We have no knowledge of it, but yet it is the case that as we raise ourselves to the upright position, forces (from the cosmos) are working in from all sides and we come up against these forces that are pouring in from outside. This has no particular significance to-day, on the Earth, but during the ancient Moon period it had a tremendous significance. On the ancient Moon, conditions were such that from his earliest childhood man had a different orientation, in that he had to place himself in line with the direction of the Moon-Will. As the result of this he acquired the first germs of the skull formation. To-day we have inherited them, but on the Moon it was a question of acquiring them. In those times man worked in himself against the outer will-forces somewhat in the way a locomotive works when it has to push away snow. He pressed back the will-forces of the cosmos and his soft skull formation compressed itself into the hard skull covering. To-day this process is no longer necessary. The skull formation is inherited. It is no longer necessary to build up the skull bones. In the etheric body, however, we still build them, for as we rise to the upright position there is a densification in the head, representing the result of the fight between the forces streaming in from all sides of the cosmos. Thus, when we observe the etheric body, we may say that in his two legs, man builds up two lines of force and works against the forces that proceed from without. The etheric body is densified and this form arises (see next diagram). We raise ourselves upright. The physical legs have their junction above, but the etheric legs rise still higher.
Let me try to make a diagrammatic sketch of this process. Underneath we have the Earth. Man is at first a horizontal being; then he stands upright—in the vertical position. It is an achievement of man's nature itself to attain the vertical position but he has the help of all the hierarchies as he passes through the course of his life. What is it that comes to his aid when he stands upright and walks? The forces that work from the Earth out into the expanses of cosmic space. These are the earthly forces. To-day physicists only speak of purely physical forces of the Earth—forces of attraction, of gravity and the like. The Earth, however, is not merely physical body but a being of spirit and soul and when, as little children, we raise ourselves to the upright position and walk, we are uniting ourselves with the forces of Will rising out of the Earth. The Earth-Will permeates our being; we allow the Earth -Will to flow into us and place ourselves in the upright position—the direction of the Earth-Will. This process is a union with the Earth-Will. But in opposition to the Earth-Will there is a will that works in from all sides of the cosmos. We have no knowledge of it, but yet it is the case that as we raise ourselves to the upright position, forces (from the cosmos) are working in from all sides and we come up against these forces that are pouring in from outside. This has no particular significance to-day, on the Earth, but during the ancient Moon period it had a tremendous significance. On the ancient Moon, conditions were such that from his earliest childhood man had a different orientation, in that he had to place himself in line with the direction of the Moon-Will. As the result of this he acquired the first germs of the skull formation. To-day we have inherited them, but on the Moon it was a question of acquiring them. In those times man worked in himself against the outer will-forces somewhat in the way a locomotive works when it has to push away snow. He pressed back the will-forces of the cosmos and his soft skull formation compressed itself into the hard skull covering. To-day this process is no longer necessary. The skull formation is inherited. It is no longer necessary to build up the skull bones. In the etheric body, however, we still build them, for as we rise to the upright position there is a densification in the head, representing the result of the fight between the forces streaming in from all sides of the cosmos. Thus, when we observe the etheric body, we may say that in his two legs, man builds up two lines of force and works against the forces that proceed from without. The etheric body is densified and this form arises (see next diagram). We raise ourselves upright. The physical legs have their junction above, but the etheric legs rise still higher.  As a result of this the etheric head is densified and as a result of the formation of the brain there arises in the etheric body, in our age as well, the densified etheric body. This does not only take place in childhood but as man passes through seven life periods (from the first to the seventh year, from the seventh to the fourteenth year and so on) new lines are formed, lines of different forces which pass upwards. So that when we have reached the age of full and complete manhood—when we have passed the fiftieth year of life—we have added new pairs of pillars to that first strong pair formed during the first seven years of life. They appear in the etheric body in different colours. We strengthen our etheric sheath every time we develop these ‘life pillars’—for so indeed they may be called. After the first period of seven years the first pair of life pillars is completed, at the fourteenth year the second pair, at the twenty-first year the third pair, and finally, with the forty-ninth year, the seventh pair. Each pair of life pillars makes our etheric skull-covering more secure. Man passes through his life and after every seven years raises within himself different pillar formations which bear his skull. When we have understood this we shall have a living conception of the inner form of the larger section of our building. We enter at the West and say to ourselves: ‘Up to the first pair of pillars we see how man develops in the first seven years of his life; the second pair of pillars denotes his development to his fourteenth year, then on to the twenty-first year and so on.’ And the etheric sheath of the head is always around us. Man, the living being, is poured out into the forms as an etheric being.
As a result of this the etheric head is densified and as a result of the formation of the brain there arises in the etheric body, in our age as well, the densified etheric body. This does not only take place in childhood but as man passes through seven life periods (from the first to the seventh year, from the seventh to the fourteenth year and so on) new lines are formed, lines of different forces which pass upwards. So that when we have reached the age of full and complete manhood—when we have passed the fiftieth year of life—we have added new pairs of pillars to that first strong pair formed during the first seven years of life. They appear in the etheric body in different colours. We strengthen our etheric sheath every time we develop these ‘life pillars’—for so indeed they may be called. After the first period of seven years the first pair of life pillars is completed, at the fourteenth year the second pair, at the twenty-first year the third pair, and finally, with the forty-ninth year, the seventh pair. Each pair of life pillars makes our etheric skull-covering more secure. Man passes through his life and after every seven years raises within himself different pillar formations which bear his skull. When we have understood this we shall have a living conception of the inner form of the larger section of our building. We enter at the West and say to ourselves: ‘Up to the first pair of pillars we see how man develops in the first seven years of his life; the second pair of pillars denotes his development to his fourteenth year, then on to the twenty-first year and so on.’ And the etheric sheath of the head is always around us. Man, the living being, is poured out into the forms as an etheric being. The drawing can of course only be diagrammatical. Let us suppose that this diagram represents, here the Sun, here the Earth and here the Moon. The sketch is only diagrammatical, for naturally I cannot express the dimensional proportions and distances of the heavenly bodies. That, however is not the point at issue. When the clairvoyant consciousness of the occult seer enters into a certain relationship with these three heavenly bodies, that is to say, with what they represent spiritually, the whole universe seems to be pervaded through and through with the interplay of the spiritual content of these various heavenly bodies. Beings have their home on all the heavenly bodies, as you have often heard; not only so, but they send forth their workings. Higher beings inhabit the heavenly bodies for long ages; subordinate beings are sent from one heavenly body to another and are the cause of currents being set in motion in the cosmos. These currents are often nothing less than the beings who are sent forth by certain elementary or higher beings from one cosmic body to the other. In the first place, therefore, clairvoyant consciousness perceives how magnetic or electric currents in the cosmos flow from one heavenly body to another; in more exact observation this resolves itself into a host, a stream, a swarm of spiritual beings passing from one heavenly body to another.
The drawing can of course only be diagrammatical. Let us suppose that this diagram represents, here the Sun, here the Earth and here the Moon. The sketch is only diagrammatical, for naturally I cannot express the dimensional proportions and distances of the heavenly bodies. That, however is not the point at issue. When the clairvoyant consciousness of the occult seer enters into a certain relationship with these three heavenly bodies, that is to say, with what they represent spiritually, the whole universe seems to be pervaded through and through with the interplay of the spiritual content of these various heavenly bodies. Beings have their home on all the heavenly bodies, as you have often heard; not only so, but they send forth their workings. Higher beings inhabit the heavenly bodies for long ages; subordinate beings are sent from one heavenly body to another and are the cause of currents being set in motion in the cosmos. These currents are often nothing less than the beings who are sent forth by certain elementary or higher beings from one cosmic body to the other. In the first place, therefore, clairvoyant consciousness perceives how magnetic or electric currents in the cosmos flow from one heavenly body to another; in more exact observation this resolves itself into a host, a stream, a swarm of spiritual beings passing from one heavenly body to another. The line connecting with the Moon Moon must now be drawn differently. I am representing the same streams as in the first diagram only the Sun is turned a little. The lines are somewhat different but they arise within and flow into the same heavenly bodies.
The line connecting with the Moon Moon must now be drawn differently. I am representing the same streams as in the first diagram only the Sun is turned a little. The lines are somewhat different but they arise within and flow into the same heavenly bodies. Man is bound up with the cosmos; he is an actual expression of all the great cosmic connections. Now you need only think of the heart in man as the microcosm of the Sun, the lungs as the microcosm of the Earth (of this particular hierarchy of forces) and the brain as the microcosm of the Moon, and you have something both highly suggestive and significant.
Man is bound up with the cosmos; he is an actual expression of all the great cosmic connections. Now you need only think of the heart in man as the microcosm of the Sun, the lungs as the microcosm of the Earth (of this particular hierarchy of forces) and the brain as the microcosm of the Moon, and you have something both highly suggestive and significant.