| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture IV
18 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture IV
18 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In our previous meetings I have tried to direct you into what we understand as knowledge of the human being. Some of what is still missing will surely find its way into our further considerations during this conference. I have also told you that this knowledge of the human being is not the kind that will lead to theories, but one that can become human instinct, ensouled and spiritual instinct that, when translated into actions, can lead to living educational principles and practice. Of course, you must realize that in giving lectures of this kind, it is only possible to point the way, in the form of indications, to what such knowledge of the human being can do for the furtherance of practical teaching. But just because our primary goal is toward practical application, I can give only broad outlines, something that is very unpopular these days. Few people are sufficiently aware that anything expressed in words can, at best, be only a hint, a mere indication of what is far more complex and multifarious in actual life. If we remember that young children are essentially ensouled sense organs, entirely given over in a bodily-religious way to what comes toward them from the surrounding world, we shall see to it that, until the change of teeth, everything within their vicinity is suitable to be received through their senses, thereafter to be worked on inwardly. Most of all, we have to be aware that whenever the child perceives with the senses, at the same time the child also absorbs the inherent moral element of what is perceived through the soul and spirit. This means that at the approach of the change of teeth, we have already set the scene for the most important impulses of later life, and that when the child enters school, we are no longer faced with a blank page but with one already full of content. And now that we are moving more toward the practical aspects of education, we have to consider that between the change of teeth and puberty nothing entirely original can be initiated in the child. Instead, it is the teacher's task to recognize the impulses already implanted during the first seven years. They have to direct these impulses toward what is likely to be demanded of the pupils in their later lives. This is why it is of such importance for teachers to be able to perceive what is stirring within their pupils; for there is more here than meets the eye in these life-stirrings when children enter school. Teachers must not simply decide what they are going to do, or which method is right or wrong. It is far more important for them to recognize what is inwardly stirring and moving in these children—in order to guide and develop them further. Naturally, this is bound to raise a question, which we have thus far been unable to answer in the Waldorf school since it has not yet become practical to open a kindergarten. The work entailed in bringing up and educating children from birth until the change of teeth is certainly most important. But since in the Waldorf school we are already facing great difficulties in coping with the demands involved in teaching children of official school age, we cannot possibly think of opening a kindergarten, because every year we also have to open a new class for our oldest pupils.1 So far we have started with an eight-year course in the Waldorf school. At present we could not possibly entertain the idea of also opening a kindergarten, or something similar, as a preparatory step for our first grade. People who take a somewhat lighthearted view of these things may be of the opinion that the only thing needed is to begin with a nursery or kindergarten, and the rest will surely follow. But things are not that simple. A fully comprehensive, yet detailed program is needed that covers both the pedagogical and practical aspects of teaching in a nursery class. To devote oneself to such a task is impossible as long as a new class has to be added every year. The seriousness and responsibility involved in the so-called movements for school reform is recognized by far too few people. To unprofessional, although well-meaning persons, it seems enough to voice demands, which are easy enough to make. In our day, when everybody is so clever—I am not being sarcastic, I am quite serious—nothing is easier than to formulate demands. All that is needed in our society, which is simply bursting with cleverness, is for eleven or twelve people—even three or four would be brainy enough—to come together to work out a perfect program for school reform, listing their requirements in order of priority. I have no doubt that such theoretical demands would be highly impressive. These programs, compiled in the abstract today in many places, are very cleverly conceived. Because people have become so intellectual, they excel in achievements of an external and abstract kind. But if one judges these matters out of real life experience and not intellectually, the situation is not unlike one where a number of people have come together to discuss and decide what the performance of an efficient stove should be. Obviously they would come up with a whole list of “categorical imperatives,” such as that the stove must be capable of heating the room adequately, it must not emit smoke, and so on. But, though the various points made may be convincing enough, knowledge of them alone would hardly result in the necessary know-how to light it, keep it going, and control its heat. To be able to do this one has to learn other things as well. In any case, depending on the location of the room, the condition of the chimney and possibly on other factors as well, it may not even be possible to fulfill the conditions so competently set forth. But this is how most of the programs for school reform are arrived at today—more or less in an equally abstract manner as the requirements for the hypothetical stove. This is the reason why one cannot contravene them, for they no doubt contain much that is correct. But to cope with the practical needs of an existing school is something very different from making demands that, ideally speaking, are justified. Here one does not have to deal with how things ought to be, but with a number of actual pupils. Here one has to deal—allow me to mention it, for it is all part of school life—with a definite number of teachers of varying gifts and abilities. All this has to be reckoned with. There is no problem in planning a program for school reform in the abstract. But the concrete reality is that only a certain number of gifted teachers are available and it may not even be possible for them to fulfill the demands agreed upon in theory. This fundamental difference between life as it is and an intellectual approach to it is something our present society is no longer able to appreciate. Because it has become so accustomed to an intellectual interpretation of life, it can no longer perceive this quality, least of all where it is most patently present. Anyone who is aware of the great difference between theory and practice will detect the worst excesses of impractical theories in our present business life. In reality the structure of today's business life has become as theoretical as can be. Those in control grasp power with robust hands. They use their elbows and often brutally push through their theoretical policies. This goes on until the business is ruined. In the economic sphere it is possible to proceed intellectually. But in a situation where one meets life in the raw, such as in a school (where it is not simply a case of helping oneself, but where existing impulses have to be worked on) even the most beautiful theories are of little use unless they offer the possibility of working pragmatically and out of a truly individual knowledge of what the human being is. This is the reason why teachers whose heads are full of pedagogical theories are usually least fit for practical classroom situations. More capable by far are those who still teach out of a certain instinct, teachers who, out of their natural love for children, are able to recognize and to meet them. But today it is no longer possible to rely on instinct, unless it is backed by spiritual knowledge. Modern life has become too complex for such a way of life, which would be possible only under more primitive conditions, under conditions almost bordering on the level of animal life. All this has to be considered if one wishes to see what is being presented here in the right light, as a really practical form of pedagogy. Generally speaking, education has followed in the footsteps of our modern civilization, which has gradually become more and more materialistic. A symptom of this is the frequent use of mechanical methods in preference to organic methods, and this just during the early years of childhood up to the change of teeth, which is the most impressionable and important time of life. We must not lose sight of the fact that up to the second dentition the child lives by imitation. The serious side of life, with all its demands in daily work, is re-enacted in deep earnestness by the child in its play, as I mentioned yesterday. The difference between a child's play and an adult's work is that an adult's contribution to society is governed by a sense of purpose and has to fit into outer demands, whereas the child wants to be active simply out of an inborn and natural impulse. Play activity streams outward from within. Adult work takes the opposite direction, namely inwards from the periphery. The significant and most important task for grade school consists in just this gradual progression from play to work. And if one is able to answer in practical terms the great question of how a child's play can gradually be transformed into work, one has solved the fundamental problem during those middle years from seven to fourteen. In their play, children mirror what happens around them; they want to imitate. But because the key to childhood has been lost through inadequate knowledge of the human being, all kinds of artificial play activities for children of kindergarten age have been intellectually contrived by adults. Since children want to imitate the work of the adults, special games have been invented for their benefit, such as “Lay the Little Sticks,” or whatever else these things are called. These artificial activities actually deflect the child's inner forces from flowing out of the organism as a living stream that finds a natural outlet in the child's desire to imitate those who are older. Through all kinds of mechanical manipulations children are encouraged to do things not at all suitable to their age. Particularly during the nineteenth century, programs for preschool education were determined that entailed activities a child should not really do; for the entire life of a preschool class revolves around the children adapting to the few people in charge, who should behave naturally so that the children feel stimulated to imitate whatever their teachers do. It is unnecessary for preschool staff to go from one child to another and show each one what to do. Children do not yet want to follow given instructions. All they want is to copy what the adult does, so the task of a kindergarten teacher is to adjust the work taken from daily life so that it becomes suitable for the children's play activities. There is no need to devise occupations like those adults meet in life—except under special circumstances—such as work that requires specialized skills. For example, children of preschool age are told to make parallel cuts in strips of paper and then to push multi-colored paper strips through the slits so that a woven colored pattern finally emerges. This kind of mechanical process in a kindergarten actually prevents children from engaging in normal or congenial activities. It would be better to give them some very simple sewing or embroidery to do. Whatever a young child is told to do should not be artificially contrived by adults who are comfortable in our intellectual culture, but should arise from the tasks of ordinary life. The whole point of a preschool is to give young children the opportunity to imitate life in a simple and wholesome way. This adjustment to adult life is an immensely important pedagogical task until kindergarten age, with all its purposefulness, so that what is done there will satisfy the child's natural and inborn need for activity. To contrive little stick games or design paper weaving cards is simple enough. It is a tremendously important and necessary task to whittle down our complicated forms of life, such as a child does when, for example, a little boy plays with a spade or some other tool, or when a girl plays with a doll; in this way children transform adult occupations into child's play, including the more complicated activities of the adult world. It is time-consuming work for which hardly any previous “spade-work” has thus far been done. One needs to recognize that in children's imitation, in all their sense-directed activities, moral and spiritual forces are working—artistic impulses that allow the child to respond in an entirely individual way. Give a child a handkerchief or a piece of cloth, knot it so that a head appears above and two legs below, and you have made a doll or a kind of clown. With a few ink stains you can give it eyes, nose, and mouth, or even better, allow the child to do it, and with such a doll, you will see a healthy child have great joy. Now the child can add many other features belonging to a doll, through imagination and imitation within the soul. It is far better if you make a doll out of a linen rag than if you give the child one of those perfect dolls, possibly with highly colored cheeks and smartly dressed, a doll that even closes its eyes when put down horizontally, and so on. What are you doing if you give the child such a doll? You are preventing the unfolding of the child's own soul activity. Every time a completely finished object catches its eye, the child has to suppress an innate desire for soul activity, the unfolding of a wonderfully delicate, awakening fantasy. You thus separate children from life, because you hold them back from their own inner activity. So much for the child until the change of teeth. When children enter school, we are very likely to meet a certain inner opposition, mainly toward reading and writing, as mentioned yesterday. Try to see the situation through a child's eyes. There stands a man. He has black or blond hair. He has a forehead, nose, eyes. He has legs. He walks, and he holds something in his hands. He says something. He has his own thought-life. This is father. And now the child is supposed to accept that this sign, FATHER represents an actual father. There is not the slightest reason why a child should do so. Children bring formative forces with them, forces eager to flow out of the organism. Previously, these forces were instrumental in effecting the wonderful formation of the brain with its attendant nervous system. They accomplished the wonderful formation of the second teeth. One should become modest and ask how one could possibly create, out of one's own resources, these second teeth on the basis of the first baby teeth; what sublime powers of wisdom, of which we are totally unaware, work in all these forces! The child was entirely surrendered to this unconscious wisdom weaving through the formative forces. Children live in space and time, and now, suddenly, they are supposed to make sense of everything that is imposed on them by learning to read and write. It is not proper to lead children directly into the final stages of our advanced culture. We must lead them in harmony with what wants to flow from their own being. The right way of introducing the child to reading and writing is to allow the formative forces—which up to its seventh year have been working upon the physical organization and which now are being released for outer soul activities—to become actively engaged. For example, instead of presenting the child directly with letters or even complete words, you draw something looking like this:  In this way, by appealing to the formative forces in its soul, you will find that now the child can remember something that has actual meaning, something already grasped by the child's formative forces. Such a child will tell you, “That is a mouth.” And now you can ask it to say, “Mmmouth.” Then you ask it to leave out the end part of the word, gradually getting the child to pronounce “Mmm.” Next you can say, “Let us paint what you have just said.” We have left something out, therefore this is what we paint:  And now let us make it even simpler:  It has become the letter M. Or we might draw something looking like this.  The child will say, “Fish.” The teacher responds, “Let's make this fish simpler.” Again one will ask the child to sound only the first letter, in this way obtaining the letter F. And so, from these pictures, we lead to abstract letter forms. There is no need to go back into history to show how contemporary writing evolved from ancient pictography. For our pedagogical purposes it is really unnecessary to delve into the history of civilization. All we have to do is find our way—helped along by wings of fantasy—into this method, and then, no matter what language we speak, choose some characteristic words that we then transform into pictures and finally derive the actual letters from them. In this way we work together with what the child wants inwardly during and immediately after the change of teeth. From this you will understand that, after having introduced writing by drawing a painting and by painting a drawing (it is good for children to use color immediately because they live in color, as everyone who deals with them knows), one can then progress to reading. This is because the entire human being is active in writing. The hand is needed, and the whole body has to adapt itself—even if only to a slight degree; the entire person is involved. Writing, when evolved through painting-drawing, is still more concrete than reading. When reading—well, one just sits, one has already become like a timid mouse, because only the head has to work. Reading has already become abstract. It should be evolved by degrees as part of the whole process. But if one adopts this method in order to work harmoniously with human nature, it can become extraordinarily difficult to withstand modern prejudices. Naturally, pupils will learn to read a little later than expected today, and if they have to change schools they appear less capable than the other students in their new class. Yet, is it really justified that we cater to the views of a materialistic culture with its demands concerning what an eight-year-old child should know? The real point is that it may not be beneficial at all for such a child to learn to read too early. By doing so, something is being blocked for life. If children learn to read too early, they are led prematurely into abstractions. If reading were taught a little later, countless potential sclerotics could lead happier lives. Such hardening of the entire human organism—to give it a simpler name—manifests in the most diverse forms of sclerosis later in life, and can be traced back to a faulty method of introducing reading to a child. Of course, such symptoms can result from many other causes as well, but the point is that the effects of soul and spirit on a person's physical constitution are enhanced hygienically if the teaching at school is attuned to human nature. If you know how to form your lessons properly, you will be able to give your students the best foundation for health. And you can be sure that, if the methods of modern educational systems were healthier, far fewer men would be walking around with bald heads! People with a materialistic outlook give too little attention to the mutual interaction between the soul-spiritual nature and the physical body. Again and again I want to point out that the tragedy of the current materialistic attitude is that it no longer understands the material processes—which it observes only externally—and that it no longer recognizes how a moral element enters the physical. Already the way the human being is treated—one could almost say mistreated—by our natural science is likely to lead to misconceptions about what a human being is. You need only think of the usual kinds of illustrations found in contemporary textbooks on physiology or anatomy, where you see pictures of the skeleton, the nervous system, and the blood circulation. The way these are drawn is very suggestive, implying that they are a true representation of reality. And yet, they do not convey the actual facts at all—or at best, only ten percent of them, because ninety percent of the human body consists of liquid substances that constantly flow and, consequently, cannot be drawn in fixed outlines. Now you may say, “Physiologists know that!” True, but this knowledge remains within the circle of physiologists. It does not enter society as a whole, particularly because of the strongly suggestive influence of these illustrations. People are even less aware of something else. Not only does solid matter make up the smallest portion of our physical body, while the largest part by far is liquid, but we are also creatures of air every moment of our lives. One moment the air around us is inside us, and in the next, the air within our body is outside again. We are part of the surrounding air that is constantly fluctuating within us. And what about the conditions of warmth? In reality we have to discriminate between our solid, liquid, gaseous, and warmth organizations. These distinctions could be extended further, but for now we will stop here. It will become evident that meaningless and erroneous ideas are maintained about these matters when we consider the following: If these illustrations of the skeleton, the nervous system, and so on, really represented the true situation—always implying that the human being is a solid organism—if this were really the whole truth, then it would be little wonder if the moral element, the life of the soul, could not penetrate this solid bone matter or this apparently rigid blood circulation. The physical and moral life would require separate existences. But if you include the liquid, gaseous, and warmth organizations in your picture of the individual, then you have a fine agent, a refined entity—for example, in the varying states of warmth—that allows the existing moral constitution to extend also into the physical processes of warmth. If your picture is based on reality, you will come to find this unity between what has physical nature and what has moral nature. This is what you have to remember when working with the growing human being. It is essential to have this awareness. And so it is very important for us to look at the totality of the human being and find our way, unimpeded by generally accepted physiological-psychological attitudes. It will enable us to know how to treat the child who will otherwise develop inner opposition toward what must be learned. It should be our aim to allow our young students to grow gradually and naturally into their subjects, because then they will also love what they have to learn. But this will happen only if their inner forces become involved fully in these new activities. The most damaging effects, just during the age of seven to nine, are caused by one-sided illusions, by fixed ideas about how certain things should be taught. For example, the nineteenth century—but this was already prepared for in the eighteenth century—was tremendously proud of the new phonetic method of teaching reading that superseded the old method of making words by adding single letters—a method that was again replaced by the whole-word method. And because today people are too embarrassed to openly respect old ways, one will hardly find anyone prepared to defend the old spelling method. According to present opinion, such a person would be considered an old crank, because enthusiasm about an old-fashioned spelling method is simply not appropriate. The phonetic and the whole-word method carry the day. One feels very proud of the phonetic method, teaching the child to develop a feeling for the quality of sounds. No longer do young pupils learn to identify separate letters, such as P, N, or R; they are taught to pronounce the letters as they sound in a word. There is nothing wrong with that. The whole-word method is also good, and it sometimes even begins by analyzing a complete sentence, from which the teacher progresses to separate words and then to single sounds. It is bad, however, when these things become fads. The ideas that underlie all three methods are good—there is no denying that each has its merits. But what is it that makes this so? Imagine that you know a person only from a photograph showing a front view. The picture will have created a certain image within you of that person. Now imagine that another picture falls into your hands, and someone tells you that this is the same person. The second picture shows a side view and creates such a different impression that you may be convinced that it could not be the same person. Yet in reality both photographs show the same individual, but from different angles. And this is how it always is in life: everything has to be considered from different angles. It is easy to fall in love with one's own particular perspective because it appears to be so convincing. And so one might, with good reasons, defend the spelling method, the phonetic method, or the whole-word method to the extent that anyone else with an opposite opinion could not refute one's arguments. Yet even the best of reasons may prove to be only one-sided. In real life, everything has to be considered from the most varied angles. If the letter forms have been gained through painting drawings and drawing paintings, and if one has gone on to a kind of phonetic or whole-word method—which is now appropriate because it leads the child to an appreciation of a wholeness, and prevents it from becoming too fixed in details—if all this has been done, there is still something else that has been overlooked in our materialistic climate. It is this: the single sound, by itself, the separate M or P, this also represents a reality. And it is important to see that, when a sound is part of a word, it has already entered the external world, already passed into the material and physical world. What we have in our soul are the sounds as such, and these depend largely on our soul nature. When we pronounce letters, such as the letter M, for example, we actually say “em.” Ancient Greeks did not do this; they pronounced it “mu.” In other words, they pronounced the auxiliary vowel after the consonant, whereas we put it before the consonant. In Middle Europe today, we make the sound of a letter by proceeding from the vowel to the consonant, but in ancient Greece only the reverse path was taken.2 This indicates the underlying soul condition of the people concerned. Here we have a significant and important phenomenon. If you look at language, not just from an external or utilitarian perspective (since language today has become primarily a way of transmitting thoughts or messages, and words are hardly more than symbols of outer things), and if you return to the soul element living in the word—living in language as a whole—you will find the way back to the true nature of the so-called sound; every sound with a quality of the consonant has an entirely different character from a vowel sound. As you know, there are many different theories explaining the origin of language. (This is a situation similar to photographs taken from different angles.) Among others, there is the so-called bow-wow theory, which represents the view that words imitate sounds that come from different beings or objects. According to this theory, when people first began to speak, they imitated characteristic external sounds. For example, they heard a dog barking, “bow-wow.” If they wanted to express a similar soul mood they produced a similar sound. No one can refute such an idea. On the contrary, there are many valid reasons to support the bow-wow theory. As long as one argues only from this particular premise, it is indisputable. But life does not consist of proofs and refutations; life is full of living movement, transformation, living metamorphosis. What is correct in one particular situation can be wrong in another, and vice versa. Life has to be comprehended in all its mobility. As you may know, there is another theory, called the ding-dong theory, whose adherents strongly oppose the bow-wow theory. According to this second theory, the origin of language is explained in the following way: When a bell is struck, the ensuing sound is caused by the specific constitution of its metal. A similar mutual relationship between object and sound is also ascribed to human speech. The ding-dong theory represents more of a feeling into the materiality of things, rather than an imitation of external sounds. Again, this theory is really correct in certain respects. Much could be said for either of these theories. In reality, however, language did not arise exclusively according to the ding-dong theory nor the bow-wow theory, although both theories have elements of truth. Many other related factors would also have to be considered, but each theory, in isolation, gives only a one-sided perspective. There are many instances in our language that exemplify the ding-dong theory, and many others where sound represents an imitation, as in “bow-wow,” or in the “moo” of lowing cattle. The fact is, both theories are correct, and many others as well. What is important is to get hold of life as it actually is; and if one does this, one will find that the bow-wow theory is more related to vowels, and the ding-dong theory related more to consonants. Again, not entirely, however; such a statement would also be one-sided, because eventually one will see that the consonants are formed as a kind of reflection of events or shapes in our environment, as I have indicated already in the little book The Spiritual Guidance of the Individual and Humanity.3 Thus the letter F is formed as a likeness of the fish, M as a likeness of the mouth, or L like leaping, and so on. To a certain extent, the origin of the consonants could be explained by the ding-dong theory, except that it would have to be worked out in finer detail. The vowels, on the other hand, are a way of expressing and revealing a person's inner nature. The forms of the letters that express vowel sounds do not imitate external things at all, but express human feelings of sympathy and antipathy. Feelings of joy or curiosity are expressed, therefore, by the sound EE; amazement or wonder; “I am astonished!” is expressed by AH; A (as in path) expresses “I want to get rid of something that irritates me.” U (as in you) expresses “I am frightened.” I (as in kind) conveys “I like you.” Vowels reveal directly feelings of sympathy and antipathy. Far from being the result of imitation, they enable human beings to communicate likes and dislikes. When hearing a dog's threatening bark, human beings—if their feelings are like those of the dog—adapt their own experiences to the bow-wow sound of the dog, and so on. Vocalizing leads outward from within, whereas forming consonants represents a movement inward from outside. Consonants reproduce outer things. Simply by making these sounds, one is copying outer nature. You can confirm this for yourselves if you go into further detail. Since all of this applies only to sounds rather than words, however, you can appreciate that, when using the analytic method, one is actually going from the whole word to the original soul condition. In general, we must always try to recognize what the child at each stage is requesting inwardly; then we can proceed in freedom—just as a good photographer does when asking clients to look in many different directions in order to capture their personalities while taking their pictures (and thereby making these sessions so tedious!). Similarly, a complete view is essential if one wants to comprehend the human being in depth. With the whole-word method one gains only the physical aspect. With the phonetic method one approaches the soul realm. And—no matter how absurd this may sound—with the spelling method one actually enters the realm of the soul. Today this last method is, of course, seen as a form of idiocy; without a doubt, however, it is more closely related to the soul than the other methods. It must not be applied directly, but needs to be introduced with a certain pedagogical skill and artistry that avoids an overly one-sided exercise in conventional pronunciation of the letters. Instead, the child will gain some experience of how letters came about, and this is something that can live within the formative forces, something real for the child. This is the core of the matter. And if young pupils have been taught in this way they will be able to read in due time—perhaps a few months after the ninth year. It doesn't really matter if they cannot read earlier, because they have learned it naturally and in a wholesome way. Depending on the various children's responses, this stage may occur a little earlier or later. The ninth year marks the beginning of a smaller life cycle—the larger ones have already been spoken of several times. They are: from birth to the change of teeth; from the change of teeth to puberty; and from then into the twenties. These days, however, by the time young people have reached their twenties, one no longer dares speak to them of another developmental phase, which will peak after the age of twenty-one. This would be considered a pure insult! At that age they feel fully mature—they already publish their own articles in newspapers and magazines. And so one has to exercise great discretion in speaking about life's later stages of development. But it is important for the educator to know about the larger life periods and also about the smaller ones contained in them. Between the ninth and the tenth years, but closer to the ninth, one of the smaller periods begins, when a child gradually awakens to the difference between self and the surrounding world. Only then does a child become aware of being a separate I. All teaching before this stage should therefore make the child feel at one with the surroundings. The most peculiar ideas have been expressed to explain this phenomenon. For example, you may have heard people say, “When a young child gets hurt by running into a corner, the reaction is to hit the corner.” An intellectual interpretation of this phenomenon would be that one hits back only if one has consciously received a hurt or an injury consciously inflicted. And this is how the child's response in hitting a table or other object is explained. This kind of definition always tempts one to quote the Greek example of a definition of the human being—that is, a human being is a living creature who has two legs but no feathers. As far as definitions go, this is actually correct. It leads us back into the times of ancient Greece. I won't go into details to show that present definitions in physics are often not much better, because there children are also taught frequently that a human being is a creature that walks on two legs and has no feathers. A boy who was a bit brighter than the rest thought about this definition. He caught a cockerel, plucked its feathers, and took it to school. He presented the plucked bird, saying, “This is a human being! It is a creature that walks on two legs and has no feathers.” Well, definitions may have their uses, but they are almost always one-sided. The important thing is to find one's way into life as it really is—something I have to repeat time and again. The point is that before the ninth year a child does not yet distinguish between self and surroundings. Therefore one cannot say that a little child, when hitting the table that caused it pain, imagines the table to be a living thing. It would never occur to a child to think so. This so-called animism, the bestowal of a soul on an inanimate object—an idea that has already crept into our history of civilization—is something that simply does not exist. The fantastic theories of some of our erudite scholars, who believe they have discovered that human beings endow inanimate objects with a soul, are truly astonishing. Whole mythologies have been explained away in light of this theory. It strikes one that people who spread such ideas have never met a primitive person. For example, it would never occur to a simple peasant who has remained untouched by our sophisticated ways of life to endow natural phenomena with a soul quality. Concepts such as ensouling or animation of dead objects simply do not exist for the child. The child feels alive, and consequently everything around the child must also be alive. But even such a primitive idea does not enter children's dim and dreamy consciousness. This is why, when teaching pupils under nine, you must not let the children's environment and all that it contains appear as something separate from them. You must allow plants to come to life—indeed, everything must live and speak to children, because they do not yet distinguish between themselves and the world as a whole. It is obvious from this that, before the ninth year, you cannot reach children with any kind of intellectual descriptions. Everything has to be transformed into pictures, into fresh and living pictures. As soon as you go on to a more direct description, you will not achieve anything during the eighth to ninth year. This approach becomes possible only later. One has to find the way into each specific life period. Until the ninth year children only understand a pictorial presentation. Anything else bypasses them, just as sound bypasses the eye. But between the ninth and tenth years, as children gradually become more aware of their own identity, you can begin to present more factual descriptions of plants. However, it is not yet possible to describe anything that belongs to the mineral kingdom, because the children's newly evolving capacity to differentiate between self and world is not yet strong enough to allow them to comprehend the significant difference between what is inherently alive and what belongs to the dead mineral world. Children at this stage can only appreciate the difference between themselves and a plant. Thereafter you can gradually progress to a description of animals. But again this has to be done so that the introduction to the animal world remains real for the child. Today there is an established form of botany, and along with that a tendency to introduce this subject just as it is in the lower grades. This is done out of a kind of laziness, but it really is an appalling thing to present the botany of adults to younger classes. What is this botany of ours in actuality? It is made up of a systematic classification of plants, arranged according to certain accepted principles. First come the fungi, then algae, ranunculaceae, and so on—one family placed neatly next to another. But if such a branch of science (which itself may be quite acceptable) is taught to young children in schools, it is almost like arranging different kinds of hairs, plucked from a human body, and classifying them systematically according to where they grew—behind the ears, on the head, on the legs, and so on. Following this method, you might manage to build up a very impressive system, but it would not help you understand the true nature of hair. And because it seems almost too obvious, one might easily neglect to relate the various types of hair to the human being as an entity. The plant world does not have its own separate existence either, because it is part of Earth. You may think that you know the laburnum from what you find about it in a botany book. I have no objections to its botanical classification. But to understand why its blossoms are yellow, you have to see it on a sunny slope, and you have to include in your observation the various layers of soil from which it grows. Only then can you realize that its yellow color is connected with the colors of the soil from which it grows! But in this situation you look at this plant as you would look at hair growing out of a human body. Earth and plants—as far as the child knows them already—remain one. You must not teach adult botany in the lower grades, and this means you cannot describe a plant without, at the same time, also talking about the Sun shining on it, about climatic conditions and the configuration of the soil—in a manner appropriate to the age of the child, of course. To teach botany as this is done in demonstrations—taking isolated plants, one next to another, violates the child's nature. Even in demonstrations everything depends on the choice of object to be studied. The child has an instinctive feeling for what is living and for what is truly real. If you bring something dead, you wound what is alive in the child, you attack a child's sense of truth and reality. But these days there is little awareness of the subtle differences in these qualities. Imagine contemporary philosophers pondering the concept of being, of existence. It would make very little difference to them whether they chose a crystal or a blossom as an object of contemplation, because both of them are. One can place them both on a table, and both things exist. But this is not the truth at all! In regard to their being, they are not homogeneous. You can pick up the rock crystal again after three years; it is by the power of its own existence. But the blossom is not as it appears at all. A blossom, taken by itself, is a falsehood in nature. In order to assign existence or being to the blossom, one has to describe the entire plant. By itself, the blossom is an abstraction in the world of matter. This is not true of the rock crystal. But people today have lost the sense for such differentiations within the reality of things. Children, however, still have this feeling by instinct. If you bring something to children that is not a whole, they experience a strange feeling, which can follow them into later life. Otherwise Tagore would not have described the sinister impression that the amputated leg had on him in his childhood. A human leg in itself does not represent reality, it has nothing to do with reality. For a leg is only a leg as long as it is part of a whole organism. If cut off, it ceases to be a leg. Such things have to become flesh and blood again so that, by progressing from the whole to the parts, we comprehend reality. It can happen all too easily that we treat a separate part in a completely wrong way if we isolate it. In the case of botany in the lower grades, therefore, we must start with the Earth as a whole and look at the plants as if they were the hair growing out of it. With regard to the animal world, children cannot relate properly to the animal at all if you follow the common method of classification. Since animal study is introduced only in the tenth or eleventh year, you can then expect a little more from the children. But to teach the study of animals according to the usual classification has little real meaning for students of that age, even if this method is scientifically justified. The reality is that the entire animal kingdom represents a human being that is spread out. Take a lion, for example; there you see a onesided development of the chest organization. Take the elephant; here the entire organization is oriented toward a lengthening of the upper lip. In the case of the giraffe, the entire organization strives toward a longer neck. If you can thus see a one-sided development of a human organic system in each animal, and survey the entire animal kingdom all the way down to the insect (one could go even further, down to the “geological” animals, though Terebratulida are not really geological animals any more) then you will realize that the entire animal kingdom is a “human being,” spread out like an opened fan, and the human physical organization makes up the entire animal kingdom, folded together like a closed fan. This is how one can bring the mutual relationship between the human being and the animal into proper perspective. Putting all this into such few words is making it into an abstraction, of course. You will have to transform it into living substance until you can describe each animal-form in terms of a one-sided development of a specific human organic system. If you can find the necessary strength to give your pupils a lively description of animals in this sense, you will soon see how they respond. For this is what they want to hear. And so the plants are linked to the Earth as if they were the hair of the Earth. The animal is linked to the human being and seen as a one-sided development of various human organic systems. It is as if human arms or legs—and in other instances, the human nose or trunk, and so on—had grown into separate existences in order to live as animals on Earth. This is how pupils can understand the animal-forms. It will enable the teacher to form lessons that are attuned to what lives in the growing human being, in the children themselves. A question is asked concerning religious instruction. RUDOLF STEINER: A misunderstanding has arisen from my preliminary remarks about child development and religious impulses. So far nothing has been said in my lectures about religious instruction itself, because I began to talk only today about the practical application of the Waldorf way of teaching. I told you that there is a kind of physical-religious relationship (I called it bodily-religious) between children and their environment. Furthermore, I said that what young children exercised—simply because of their organism—entered the sphere of thinking only after puberty, after approximately the fourteenth or fifteenth year. What manifests at first in a physical-spiritual way, continues in a hidden existence, and re-emerges in the thinking realm in approximately the fifteenth year; I compared that with an underground stream surfacing again on lower ground. For an adult, religion is closely linked to the thinking sphere. If teaching, however, is to be in line with the child's natural development, what will emerge later must already be carefully prepared for during an earlier stage. And thus the question arises: Bearing these laws of human development in mind, how should the religion lessons be planned for the students between the ages of six and fourteen? This is one of the questions that will be addressed in coming lectures. In anticipation, however, I would like to say that we must be clear that the religious element is simply inborn in the child, that it is part of the child's being. This is revealed particularly clearly through the child's religious orientation until the change of teeth, as I have already described it. What has eventually become religion in our general civilization—taken in an adult sense—belongs naturally to the world of ideas, or at least depends on ideation for its substance, which, true enough, lives primarily in the adult's feeling realm. Only after the fourteenth year is the adolescent mature enough to appreciate the ideal quality and substance of religion. For the class teacher (grades one through eight) the important question thus arises: How should we arrange our religion lessons? Or, more precisely: What part of the child must we appeal to through religion lessons during the time between the seventh and fourteenth years? During the first life period, until the change of teeth, we directly affect the child's physical organization through an educational influence. After puberty, fundamentally speaking, we work on the powers of judgment and on the adolescent's mental imagery. During the intervening years we work upon the child's feeling life. This is why we should lead the child into this period with a pictorial approach, because pictures work directly in soul life (Gemüt).4 The powers of mental imagery mature only gradually, and they have to be prepared well before their proper time. What we now have to do in religion lessons is appeal, above all, to the children's soul life, as I will describe it in regard to other subjects tomorrow. The question is: How do we do it? We work on the children's soul life by allowing them to experience feelings of sympathy and antipathy. This means that we act properly by developing the kind of sympathies and antipathies between the seventh and fourteenth years that will lead finally to proper judgments in the religious sphere. And so we avoid Thou shalt or Thou shalt not attitudes in our religion lessons, because it has little value for teaching a child of this age. Instead we arrange lessons so that feelings of sympathy are induced for what the child is meant to do. We do not explain our real aims to children. Using the pictorial element as medium, we present children with what fills them with feelings of sympathy in a heightened sense, as well as in a religious sense. Likewise, we try to induce feelings of antipathy toward what they are not meant to do. In this way, on the strength of feelings of right or wrong, and always through the pictorial element, we try to direct the young students gradually from the divine-spiritual in nature, through the divine-spiritual in the human being, toward having children make the divine-spiritual their own. This has to all reach the child through the life of soul, however, certainly until eighth grade. We must avoid a dogmatic approach and setting up moral commandments. We must do all we can to prepare the child's soul for what should develop later on as the adult faculty of forming sound judgments. In this way we will do far more for the child's future religious orientation than by presenting religious commandments or fixed articles of faith at an age when children are not yet ready for them. By clothing our subject in images, thus preparing the ground for what in later life will emerge as religious judgment, we prepare our students for the possibility of comprehending through their own spirituality what they are meant to grasp as their own innermost being—that is, their religious orientation. Through appealing to the children's soul-life in religion lessons—that is, by presenting our subject pictorially rather than through articles of faith or in the form of moral commandments—we grant them the freedom to find their own religious orientation later in life. It is extremely important for young people, from puberty right into their twenties, to have the opportunity to lift, by their own strength, what they first received through their soul life—given with a certain breadth from many perspectives—into conscious individual judgments. It will enable them to find their own way to the divine world. It makes all the difference whether children, during the age of authority, are brought up in a particular religious belief, or whether, by witnessing the teacher's underlying religious attitude, they are enabled “to pull themselves up like a plant on its tendrils,” and thus develop their own morality later in life. Having first found pleasure or displeasure in what was finally condensed into an attitude of Thou shalt or Thou shalt not, and having learned to recognize, through a pictorial contemplation of nature, how the human soul becomes free through an inner picture of a divine-spiritual weaving in nature and in history, a new stage is reached where young people's own images and ideas can be formed. In this way the possibility is given of receiving religious education out of the center of life itself. It is something that becomes possible only after puberty has been reached. The point is that future stages have to be prepared for properly—that is, based on the correct insight into human nature. In my lectures I have used the comparison of the river that disappears underground and resurfaces at a lower level. During the first seven years the children have an inborn religious attitude. This now enters the depths of their souls, becoming part of them, and does not resurface in the form of thinking until the arrival of puberty. During the second life period we must work into the depths of the students' souls through what is revealed to our individual insights. In this way we prepare them to grow into religious adults. We impede this process if we do not offer our students the possibility to find their own religious orientation later on. In every human being there is an individual orientation toward religion, which, after the fifteenth year, has to be gradually won. Our task is to prepare the ground so that this can happen properly. That is why, at this age, we have to treat the religion lessons just as we do the lessons in the other subjects. They must all work on the child's soul through the power of imagery; the child's soul life has to be stimulated. It is possible to introduce a religious element into every subject, even into math lessons. Anyone who has some knowledge of Waldorf teaching will know that this statement is true. A Christian element pervades every subject, even mathematics. This fundamental religious current flows through all of education. Because of prevailing circumstances, however, we have felt it necessary to come to the following arrangement regarding religious instruction. I would like to point out once more that Waldorf schools are not ideological but pedagogical schools, where the basic demand is that our teaching methods be in harmony with the child's nature. Thus we neither wish nor intend to teach our students to become anthroposophists. We have chosen anthroposophy to be the foundation simply because we believe that a true method of teaching can flow from it. Our Catholic students are taught by visiting Catholic priests, and our Protestant students by visiting Protestant ministers. Waldorf students, whose parents are free-thinkers, and who otherwise would not receive any religious instruction at all, are given religion lessons by our own teachers. The surprising fact has emerged, however, that nearly all of our Waldorf students now attend the religion lessons presented by Waldorf teachers. They have all flocked to the so-called “free” religion lessons, lessons that, in their own way, comprise what permeates all of our teaching.5 These free religion lessons have certainly caused us a great deal of concern. Our relationship to the school is very unusual regarding these lessons. We consider all the other subjects as necessary and intrinsic to our education from the point of view of the principles and methods resulting from anthroposophical research. But, regarding the free religion lessons, we feel that we are on the same footing as the visiting Catholic or Protestant teachers. In this sense, Waldorf teachers who give religion lessons are also “outsiders.” We do not want to have an ideological or confessional school, not even in an anthroposophical sense. Nevertheless, anthroposophical methods have proven to be very fertile ground for just these free religion lessons, in which we do not teach anthroposophy, but in which we build up and form according to the methods already characterized. Many objections have been raised against these free religion lessons, not least because so many children have changed over from the denominational to the free religion lessons. This has brought many other difficulties with it, for, despite our shortage of teachers, we had to find among our existing staff one new religion teacher after another. It is hardly our fault if pupils desert their denominational religion lessons because they wish to join the free religion lessons. The obvious reason is that the visiting religion teachers do not apply Waldorf methods, and the right methods are always the decisive factor, in religious instruction as well. A further question is asked about religious lessons. RUDOLF STEINER: The characteristic mark of Waldorf education should be that all educational questions and problems are considered only from the pedagogical angle, and religion lessons are no exception. The Reverend Mr. X would certainly acknowledge that the two directions mentioned, namely the possibility of replacing religion lessons by moral instruction on the one hand, and that of denominational schools on the other, have been raised from very different viewpoints. The suggestion of replacing religious instruction with lessons in moral conduct is usually presented by those who want to eliminate religion altogether, and who maintain the opinion that religion has become more or less superfluous. On the other hand, a tendency toward religious dogma can easily cause a longing for denominational schools. Neither of these are pedagogical points of view. In order to link them a little more precisely to the aspect of teaching method, I would like to ask: What constitutes the pedagogical point of view? Surely it is the assumption that a human being is not yet complete during the stage of childhood or youth—something very obvious. A child has to grow gradually into a full human individual, which will be achieved only during the course of life. This implies that all potential and dormant faculties in the child should be educated—and here we have the pedagogical point of view in its most abstract form. If someone who represents the purely pedagogical outlook that results from insight into human nature were to now declare that a child comes into the world with an inborn kinship to the religious element, and that during the first seven years the child's corporeality is steeped in religion, only to hear a call for replacing religion lessons by lessons in ethics, it must strike such a person as if those who hold such an idea would be unwilling to exercise a human limb, say a leg, because they had concluded that the human being needs to be trained in every respect except in the use of legs! To call for the exclusion of an essential part of the human being can only stem from a fanatical attitude, but never from a real pedagogy. Insofar as only pedagogical principles are being defended and pedagogical impulses scrutinized here, the necessity of religious teaching certainly follows from the pedagogical point of view. This is why we have established the free religion lessons for those children who, according to the regulations of the school authorities, would otherwise have been deprived of religious instruction, as already stated. Through this arrangement, and because all the children belonging to this category are attending the free religion lessons, there is no student in the Waldorf school who does not have religious instruction. This procedure has made it possible for us to bring back the religious life into the entire school. To speak of the proper cultivation of the religious life at school, and to counter the effects of the so-called “religion-free enlightenment,” by appealing to the inborn religious disposition in the young, may be the best way forward to a religious renewal. I consider it a certain success for the Waldorf school to have brought religion to the children of religious dissidents. The Catholic and Protestant children would have received religious instruction in any case, but it really was not at all easy to find the appropriate form that would enable us to open this subject to all our children. It was strived for only from the pedagogical point of view.
|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture V
19 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture V
19 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Between the ages of seven and approximately fourteen, the teacher's main concern must be directed toward the students' evolving life of feeling. It is really very important that educators acquire the ability to create the kind of mental imagery that can guide pupils through the tender transitional stages characteristic of this period. When children enter school, remnants of the previous “bodily-religious mood,” as I call it, still exist. There is still a longing in children to absorb through the senses everything happening in their surroundings; this perceiving, which is transformed into imitation, then connects with listening for what comes from the natural authority of the teacher. Truth, at this stage, is not based on the child's judgment, but comes in the guise of what the naturally revered authority of the teacher says. Similarly, what is considered false simply agrees with what this freely accepted authority considers false. This also applies to what is seen as beautiful or ugly, good or evil. Children can only develop the faculty of independent judgment in adulthood if they have gone through the experience of looking up to the voice of authority with uncritical veneration. Of course I am not referring to any kind of enforced authority here; the authority I am speaking of must never be imposed externally. And if, in some cases, an authoritarian approach is necessary for the sake of general society, the child should not be aware of it. The child must always feel secure in looking up with total confidence to the teacher's authority or that of another adult in charge. Everything has to be supported by this tender relationship to authority from the day the child enters the first grade until the ninth year, and especially during the seventh to ninth years. This relationship should be preserved even longer, but between the ninth and tenth years it will necessarily change somewhat. Within this same context we must now look at another point. During the initial period of life—that is, from birth until the change of teeth—the child lives like one great multifaceted sense organ, but as a sense organ where will forces were working in every moment of life. For me to use the expression “a sense organ where will forces are working,” may sound strange, but this is only because of the complete inadequacy of what we are told by contemporary physiology and the popular ideas derived from it. Today one does not associate will forces with the function of the human eye, for example. Nevertheless, even in the eye, the perceived image is due to will activity. The same is true of the functioning of every other sense organ: will-substance is instrumental in creating the inner sense impressions. The task of a sense organ, first of all, is to expose itself, or the human being, passively to the external world's influences. But within every sense organ an inner activity also occurs that has a will nature. This will element works very intensively throughout the child's whole body until the change of teeth. It also remains active after this event, with the result that, between entering school and the ninth year, this predominant will element in the child will tolerate only an approach to external nature and to the human being that is entirely human and pictorial. This is why we introduce not aesthetics but a thoroughly artistic element, especially in the younger classes. We do this by allowing children to use liquid colors from the very beginning, even if this practice is likely to cause rather uncomfortable consequences in the classroom. We let children handle colors because, by putting them on paper next to one another—not according to preconceived notions, but simply from an instinctive sense of color; and through the ensuing inner satisfaction, they work in harmony with their own formative forces. When given this opportunity, children reveal a wonderful instinct for painting artistic color combinations, and these soon show the teacher how to direct children's efforts toward drawing with colored pencils from which writing can eventually evolve. But one thing children at this age cannot do is follow explanations; they have no understanding for this at all. If a teacher tries to explain the subjects during the first school years, the children will react by becoming blunted and dull. This approach simply does not work. On the other hand, everything will go smoothly if, rather than explaining the subject matter, one forms the content into a story, if words are painted with mental images, and if rhythm is brought into one's whole way of teaching. If the teachers' relationship to music is not restricted to music in a narrow sense, but if they can introduce a musical element into their teaching—if their lessons are permeated by beat, rhythm, and other less obvious musical qualities—then children will respond spontaneously and with acute understanding. On the other hand, if the teachers who introduce the world by appealing to feeling in their students were to speak now of the human being as a separate entity, the children would feel inwardly resentful. They would reject it; indeed, they could simply not bear it. What children really want during this stage is for everything they learn about—even if it is part of inorganic nature—to be presented in living, human terms. The inner horror (I think one can put it that strongly) of facing a description of the human being remains with the child until about the twelfth year. From the ninth to the twelfth year we can use what I described yesterday as the content for the lessons. As long as we present it imaginatively we can speak about the plant world in terms of hair growing out of the Earth, and we can introduce animal study by showing how in every animal form we can see a part of the human organism, but specialized in a one-sided way. At this stage, however, we must not study the human being directly as an object, because children are not yet ready for this. Only toward the twelfth year do they experience a dim longing to gather together the entire animal kingdom in order to discover synthesis of the animal world in the human being. This can form the new content for the classes, then, following the eleventh and twelfth years. For you to be told that teachers should relate parts of the human organization to certain animal forms before their pupils have reached the necessary maturity to study the human being as a separate entity may sound contradictory, but life is full of such apparent contradictions. It is correct, nevertheless, to proceed in this way until the great moment comes when teachers can show their students how what is concentrated within one single human individual, is spread out over all of the animal kingdom. To allow children to experience very intensely such decisive moments in life is tremendously important in teaching; and one of these moments is the realization, passing through the child's soul, that the human being as seen physically is both the extract and the synthesis of the entire animal world, but on a higher level. The inner experience of such a climb over a childhood peak—if I may use this comparison—is more important than acquiring knowledge step by step. It will have a beneficial effect for the rest of the child's life. But because of the way our times have developed in an external scientific direction, there is little inclination to look so intimately at human nature. Otherwise things would not happen as they do in our civilization, especially in modern spiritual life. You only need to consider what I emphasized in our first meeting. Until the seventh year, soul forces are working in all of the child's physical processes, concluding to a certain extent during the change of teeth. I have compared this with a solution that forms a sediment at the bottom of a container. The precipitate represents the denser parts, while a more refined solution remains above it. The two substances have separated from each other. Similarly, until the change of teeth, we can look at the child's physical and etheric bodies as still forming a homogeneous solution until the physical is precipitated, leaving the etheric free to work independently. But now too much soul substance might be retained by the physical body. Part of the soul substance must always remain behind, because the human physical body must be permeated by soul and spirit throughout life. But too much soul and spiritual substance could be retained so that too little of it remains in the upper region. The result is a human being whose physical body is over-saturated with soul substance and whose soul and spiritual counterpart has become too insubstantial. This condition is met far too frequently, and with the necessary insight one can see it clearly in children between seven and fourteen. But in order to see this, one must be able to distinguish exactly between the coarser and the more refined components of our human organization. It is essential today that our society develops a physiology backed by a strong enough psychology and a psychology that is not abstract, but supported by the necessary background of physiology. In other words, one has to be able to recognize the interrelationship between body and soul; otherwise an amateurish physiology and an equally amateurish psychology will result. Because of this lack of ability to see clearly through the human being, contemporary scientific life has produced two such dilettante branches of science. The reciprocal effect between them has resulted in “dilettantism squared,” or as it is also called, psychoanalysis. Just as a number multiplied by itself is that same number squared, so also a dilettante physiology, when multiplied by dilettante psychology, equals psychoanalysis. This is the secret behind the origin of psychoanalysis. I am not saying this to cast aspersions on psychoanalysis. Things could hardly have been otherwise because, due to our present day scientific climate, society lives in a time when psychology has become too diluted and physiology too dense. Seen in this light, physiology, rather than becoming a genuine branch of science, assumes the role of the precipitate from what should have remained as a homogeneous solution. This is only a picture, but I hope that you understand it. We cannot avoid the need to be clear about how the growing human being develops, and about how we have to give appropriate attention to each particular stage in the life of children. Thus, we find that between the ninth and twelfth years children are receptive to whatever comes to them as pictures. Until about the ninth year they want to participate in the formation of the picture—they will not yet play the role of spectators. During this time teachers have to work with their students in such a living way that their joint efforts, in and of themselves, already have a pictorial quality. It doesn't matter whether actual picture-making is involved, such as painting, drawing, or similar activities; all of the work, the lessons themselves, must form a picture. And then, between the ninth and tenth years, the children develop a new sense for a more external presentation of the pictorial element, and this is when we may appropriately introduce botany and animal study. Those two subjects in particular must be presented pictorially and imaginatively; and the more one can do this, the better one is as a teacher for children between nine and twelve—in contrast to what one finds in the usual textbooks on botany, where a great lack of imagery is displayed. Portraying the plant world in its many forms with true imagination is very rewarding, because to achieve this requires that one be “co-creative.” This sharing in the world's creativity is just the thing our present culture awaits. People in the middle of life come to me, again and again, full of despair because they cannot comprehend anything pictorially. This shortcoming can be traced back to childhood when their needs were not adequately met. It is much too easy for the world to laugh when we say that the human being consists of a physical body, etheric body, astral body, and I-being. As long as one merely evaluates these matters with the yardstick of ordinary science, one cannot help but laugh. This is very understandable. But considering the serious tangle of our civilization, one would expect at least some willingness to look for what cannot be found elsewhere. There are many instances of apparent conundrums. Of course, it is easy enough to denigrate the following description of the human being: The physical body is born at birth. It develops through body-bound religiosity, by imitation, until the change of teeth. During these early years the etheric body and all the other forces are fully engaged in working on the child's physical body; they are soul and spiritual forces working in the child. The astral body is born only at puberty, and gains its independent existence from that time on. And as far as the human I is concerned—this is something that can be spoken of with certain reservations only—the I is fully born only after the twentieth year of life. Although it may be wisest to remain silent about this last point when talking to young people engaged in their first years of academic study, it is nevertheless an unalterable fact. If one does not know the characteristic differences between the four members of the human being, one is likely to look at these differentiations as being nonsense—or at least, something highly superfluous. This changes, however, as soon as one knows about the whole human being. You see, if we look at physical matter we find that its main characteristic is its exertion of a certain pressure. I could equally say that it occupies space. It presses on other matter, pushing it. It also presses on our body, and we experience this pressure through the sense of touch. Physical matter exerts pressure. The nature of the etheric has a quality all its own. During the last forty or fifty years natural science has seen the etheric as a rather peculiar phenomenon. If one were to speak about all the theories formulated concerning the essence of the etheric, one would be kept busy for a long time. This has already reached the degree that many people assert that the etheric is essentially the same as the principles of mathematics and mechanics that work in space, existing merely as some kind of linear force. To many investigating minds, the essence of the etheric is not much more than differential quotients flying around in space, or at least something that is mathematically calculable. As you can see, much hard thinking has delved into the question of what the etheric is, and this in itself is admirable enough. However, as long as one continues along these lines, nothing of real significance will be discovered about the etheric. One has to know that the etheric has the characteristic of being the polar opposite of pressure; it has the effect of suction. It always has the tendency to expedite physical matter out of space, to annihilate it. This is the characteristic feature of the etheric. Physical matter fills up space, and the etheric gets rid of space-occupying matter. It could be called negative matter, but in a qualitative sense and not from a quantitative perspective. This applies also to the human etheric body. Our relationship to the physical and etheric bodies consists of our constantly destroying and renewing ourselves. The etheric continually destroys material substance, and the physical body builds it up again. This statement contradicts the law of conservation of energy, which is generally accepted today. I am mentioning this only in passing, but it is a fact, nevertheless, that this law of conservation of energy is not compatible with the inner nature of the human being, and that it contradicts the truth. Strictly speaking, this law applies only to the inorganic realm. Within the organic world it is only true of the iron particles in the blood serum, but not concerning the whole human being, in whom a constant oscillation occurs between the suction process of the etheric, whose forces destroy matter, and the restoration affected by the physical body. The astral body not only draws in space but—strange as it sounds—it draws in time! It has the quality of leading backward in time. This will be clearer to us if we consider an older person's life. Imagine that you were, let's say, fifty years old. In your astral body, forces are always at work, leading you back to earlier times in your life, taking you back to times before puberty. Fifty-year-olds do not experience their present age in their astral body, but actually experience themselves as eleven, twelve, thirteen, or fourteen again. These past ages radiate back to them through the backward-leading activity of their astral bodies. This is the secret of life. In reality we grow older only with regard to the physical body, and with the etheric body and its oscillations. The astral body, however, leads us back again and again to previous stages of life. Regarding the astral body we are all still “adult children.” If we imagine the course of our lives expressed symbolically in the form of a tube, and if we have reached a certain point, say aged fifty, then our adult childhood shines right into our fifties, because the astral body always takes us back in time.  In the astral body, one always lives backward, but this retrospective life naturally begins only with the advent of puberty. If one can earnestly accept this in all earnestness, then one will appreciate its implications for education, and will give students something that will serve their later lives. Whatever one decides to do with them would then be seen in the context of their entire lives, even if they live to the age of ninety! This awareness will endow teachers with an appropriate sense of responsibility. It is this feeling of responsibility, arising from the knowledge of what one is really doing, that truly matters. However, this awareness can be developed only if teachers learn to recognize the hidden interconnections that affect human life. And if this happens, teachers will not assert that children should be taught only what they can comprehend fully. Such an attitude is truly appalling if one considers the true nature of the human being; pedagogical textbooks and handbooks written from the perspective of concrete demonstrations can lead one to despair. There the aim is always to come down to the level of the children's present stage of development and to treat everything so that they will see through them in every detail. This method deprives children of immensely important values for life, as anyone can see who recognizes how childhood is related to human life as a whole. Let's take the example of a child who, at the age of eight, has accepted something that could not yet be comprehended, accepted something simply on the strength of a love and respect for the teacher, simply because whatever the teacher says must be right and good. Here, love for the teacher—or sympathy—was the vehicle for inner acceptance; the child may not understand the matter fully until sometime around the age of thirty-five. It is not easy to speak about such things to modern people, because they tend to disagree with the idea that sufficient maturity is gained only in the thirty-fifth year of life for understanding certain matters. It is nevertheless the truth, however, that only in the thirty-fifth year is one mature enough to understand certain things, things that one accepted as a child out of love for a teacher. Again, at this age one has experiences that result from the astral body's regressive forces. Something arises from within, a kind of a mirror reflection that, in reality, is a return to the days of childhood. It is like the arising of an inner vision. One is thirty-five years old, has become mature, and from the depths of one's soul there comes the realization: Only now do I understand what I accepted on trust when I was eight. This ability to understand something that, permeated with love, has thus lived in one's being for many years, has a tremendously revitalizing effect on one's life. We can give this potential force of rejuvenation to children by safeguarding their inborn feeling for authority—so that such feeling can become a vehicle for love and sympathy—and also by giving children what they cannot yet fully comprehend, but will gradually ripen during the coming years of life. Such interconnections are not recognized by teachers who bring to their classes only what lies within their pupils' present capacity to understand. On the other hand, the opposite view is equally wrong and out of place. A teacher who knows human nature would never tell a child, “You cannot yet understand this.” One must never resort to such a remark, because one can always clothe what one has to say in an appropriate garment if the necessary rapport has been established with the students. If the pedagogy we are speaking of here becomes instinctive, one will know just what to say at the right moment. Above all, one will avoid sharply defined or rigid concepts. It is really appalling when a teacher's ideas and concepts have been worked out to the degree that they are no longer adaptable or flexible. They would have an effect similar to the effect of iron gloves forced onto a child's little hands, preventing them from growing naturally. We must not chain children's minds to finished concepts, but give them concepts that can grow and expand further. We must give them living concepts that can be transformed. But this can be achieved only through an imaginative approach in every subject, certainly until the twelfth year; then the method of teaching I have thus far sketched for you will encourage you to use language creatively, to draw helpful drawings on the blackboard or to take up a paintbrush to make colorful illustrations of what you want to communicate. But there must always be an awareness that everything a teacher brings has to be inwardly mobile and capable of remaining so; for one must recognize that, with the approach of the twelfth year (actually very close to the twelfth year), something new begins to develop, and that is the sense for cause and effect. Before the approach of the twelfth year, the concept of causality does not exist in the minds of children. They have an eye for what is mobile. They can apprehend ideas that are flexible, and they can perceive what comes in the form of pictures or music; anything connected with causality, however, makes no sense to them until about the twelfth year. Consequently, this concept must be avoided at all costs until this time, and then we may consider a newly emerging understanding for the relationship between cause and effect. Only at that time do children begin to have their own thoughts about various things. Previously they saw the world in pictures; but now something begins to dawn that will light up only at puberty—that is, the life of thinking and the ability to form judgments, which is closely connected with thinking. Between the change of teeth and puberty, children live primarily in the realm of feeling; before the change of teeth, they live in the region of the will, which, while still far removed from the sphere of thinking, is intimately connected with the fact that children imitate their surroundings. But what enters the child's being physically at that time also contains moral and spiritual forces, which became firmly established in the child's organism. This is why, during the tenth and eleventh years (and in most cases until the beginning of the twelfth year) it is impossible to communicate knowledge that demands an understanding of causality. Consequently, one should not introduce students to the mineral kingdom until around the twelfth year. Also, concepts connected with physics should not be explored before that age, although these have to be prepared for earlier through imagery that bypasses causality. Anything relating to cause and effect in the inorganic world can be grasped by children only around the twelfth year. This is one side of the problem. We meet the other side when teaching history. Around the twelfth year it is impossible to awaken in students an understanding of the complex fabric of historical interconnections. Until that age it is wise for teachers to present graphic descriptions of historical personages whose actions, due to their goodness, truth, and other qualities of greatness, will stimulate sympathy or, in the case of negative qualities, antipathy in the souls of children. At this stage, historical content should appeal, above all, to the students' feelings. This can be accomplished by a wise selection of historical personalities and events; these should, in themselves, present a complete story, which should nevertheless remain flexible in the students' minds (in the sense mentioned). Causal links between earlier and later historical events can be taught meaningfully only at the dawn of the regressive forces of the astral body; these forces come increasingly into their own after the fourteenth year. At about the twelfth year, children enter this reverse stream, and this is the time when one can begin to appeal to a sense of causality in history as well. When this is done earlier (and closely connected with the concept of cause and effect is the formation of judgments) one puts something into motion that can become very damaging in later life. At first there is only the child's etheric body. Toward the twelfth year, the astral body slowly begins its process of birth, which is completed at puberty. But the etheric body was already fully developed before that. If you ask students to make judgments (which always have a yes or no quality), or if you have them remember prefabricated concepts, these will enter the etheric body instead of the still unborn astral body. But what else does the astral body carry? As you may conclude from the facts of sexual maturity, the astral body also carries human love. Love is, of course, already active in children before puberty, but it has not yet reached an independent existence, has not yet been born fully. Thus, critical judgments, with their attendant yes-or-no qualities, are instilled in the child's etheric body instead of in the astral body. On the other hand, when made at the right time, the astral body's power of love and benevolence becomes an integral part in forming judgments or criticisms. If you make the mistake of forcing children to form critical judgments—of making them decide between yes and no—too early, then you fill their etheric bodies with immature judgments. But the ether body is not benevolent. It draws in whatever is in its way. Indeed, in this context, it is even malicious; it has a destructive effect. And this is what you do to children when you ask them to decide yes-or-no judgments prematurely, because a yes-or-no judgment is always behind the concept of causality. On the other hand, a historical process that is complete in itself, or historical characters who are vividly described, can simply be looked at in the way one looks at pictures. As soon as one links later historical periods to earlier ones, however, one has to make judgments, one has to reject or accept, and this choice always contains an element of yes or no. The final outcome of such premature judgment in children under the age of fourteen is an inner resentment toward judgments that are generally accepted by society. If the power of judging is developed too early, the judgments of others are received with a latent destructive force rather than with benevolence. These things demonstrate the importance of doing the right thing at the right time. Keeping this in mind, let us again compare the animal with the human being. When looking at the animal's outer appearance, its form indicates everything it does. We can also observe the animal's behavior. But in the case of the human being, we have to look for inner causes. Since children are only mature enough to look for causes in the twelfth year, this is the proper time to present the animal world as a “spread-out human being,” or the human being as the synthesis of the entire animal kingdom. This is an instance where the teacher is asked to affect an experience in the child that satisfies an inner demand and readiness at this particular stage. But now you have to acknowledge that this marks a powerful reversal in the child's nature between the change of teeth and puberty. In a certain sense, the child's soul now proceeds entirely from within outward. Recall that, until the twelfth year, children could not stand listening to a description of the human being, and now they are beginning to look at themselves as mirrors of the world—and they do this conceptually, in the form of ideas. This new readiness for a portrayal of the human being—that is, a portrayal of themselves—really does represent a complete about-face of children's nature between the second dentition and puberty. During this same time—roughly between the ninth and tenth years—another very important transition occurs in the child's life. Individually, this change can vary; in some children it doesn't happen until after the tenth year. Each child, instinctively, unconsciously, faces a kind of riddle of life. This change of direction from within outward, this new awareness of being a self surrounded by an external world—whereas previously these two aspects were woven together—is something the child does not experience consciously, but through inner doubts and restlessness, which make themselves felt at that time. Physically, the breathing becomes properly integrated into the blood circulation, as the two processes begin to harmonize and balance each other. The relationship between the pulse and breathing is established. This is the physical aspect. The soul and spiritual counterpart is a new kind of dependence of the child on help from teachers or educators. This appeal for help is not necessarily expressed by direct questions, but in a characteristic form of behavior. And now the teacher is called on to develop the skill necessary to correctly weigh this great, but unspoken, life question that lives in every student, although differently in each individual. What is this great life question? Up to this point, the child's natural sense of authority resulted from the image of the teacher as representative and mediator for the whole world. For the child, the stars moved because the teacher knew the stars' movement. Things were good or evil, beautiful or ugly, and true or false because this was the teacher's assessment. Everything that came from the world had to find the child through the teacher, and this represented the only healthy relationship between teacher and child. Now however, between the ninth and the tenth years—sometimes a little later—a question arises within the child's soul, not as a concept or idea, but as a feeling. “From where does my teacher receive all this knowledge?” At this moment the teacher begins to become transparent to the student, if I may say it pictorially. The child wants to see the world as living behind the teacher, who must not fail now to confirm the student's heartfelt conviction that the teacher is properly attuned to the world, and embodies truth, beauty, and goodness. At this stage, the unconscious nature of children tests the teacher as never before. They want to discover whether the teacher is truly worthy of representing the entire world. Again, all this has to remain unspoken. If a teacher were ever to mention or allude to it, through explanations or in other ways, this would appear only as a sign of weakness to the child, whose present state of consciousness has not yet developed a sense of causality; anything that requires proof only shows weakness and inner uncertainty. It is unnecessary to prove what is experienced powerfully in the soul. This is also true concerning the history of our civilization. I do not want to go into details now, but merely give you a dynamic impression; until a particular time during the Middle Ages, people knew the meaning of the Last Supper. For them there was no need for proof. Then the situation suddenly changed. When seen in the proper light, this just shows that a real understanding of this event no longer existed. If someone is caught red-handed, no one would have to prove that such person is a thief. But if a thief escapes unseen, then proof must be found before that person can be properly called a thief. Proof is always demanded in cases of uncertainty, but not for what the facts of life tell us directly. This is why it is so ludicrous whenever people try to find the inner connection between formal logic and reality. This is somewhat like looking for the inner connection between a path leading to a mountain, and the mountain itself; the path is there to allow the wanderer to reach the mountain, and then the mountain itself begins. Logic is there only for the sake of reaching reality, and reality begins where logic ends. Awareness of these things is of fundamental importance. One must not make the mistake of wanting to prove to students, when they are going through this important stage in life, that the world is being truthfully interpreted for them. When adjusting to this new situation in the classroom, one has to bring about in the pupils an unreasoned conviction that the teacher knows even more than they had previously imagined. The proper relationship between teacher and students can be established once again, perhaps while surprising the children with an amiable off-hand remark about something new and unexpected, which will make them sit up and listen; this can now happen if students feel that, until now, their teacher has not yet shown his or her true courage at all, and can truly reach unexpected heights. One has to save some things for just such moments, so that the teacher's image will continue to command respect. The solution to an important question of life lies within the students' feeling that their teacher can grow beyond even the boundaries of the personality. Here also are the comfort and strength one must give to children at this stage, so that one does not disappoint the hopeful expectations with which they come. Inwardly, such children were longing for reassurance from the one person for whom they had already developed sympathy and love. If this critical moment goes unnoticed, teachers will have to go through the bitter experience of losing their authority and hold over students around the ages of nine to ten. They may well feel tempted, therefore, to prove everything they do, and this dreadful mistake will only make matters worse. When this view of education has become second nature, one will also find other helpful guidelines. But whatever is presented in class has to cohere; it has to fit together. I have already told you that we allow our young children paint quite freely and naturally, out of their own formative forces—at first not with colored pencils but with liquid colors. Through this, one soon realizes how much children live within the world of colors. After a while, the young student will come gradually to experience something distant—something that draws us away into far distances—as blue. It goes without saying that the teacher must have experienced this quality of blue as well. Yellow and red seem to move toward the beholder. Children can already experience this in a very concrete way during the seventh or eighth year, unless they have been plagued with fixed tasks in drawing or painting. Of course, if you force children to copy houses or trees representationally, this color experience will soon be lost. But if one guides children so they can feel: Wherever I move my hand, there the color follows—then the type of material used is of secondary importance. Or: The color really begins to live under my fingers—it wants to spread a little further. Whenever such feelings can be drawn out in children's souls, one enables them to discover something fundamental and significant—that is, color perspective. A child will feel that the reddening yellow comes towards us, and that mauve-blue takes us further away. This is how one can livingly prepare the ground for something that must be introduced at a later stage—linear perspective; it is very harmful to teach this subject before students have had an intensive experience of color perspective. To teach them quantitative perspective without their first having inwardly absorbed qualitative perspective—which is inherent in the experience of color—has the thoroughly harmful effect of making them superficial. But there are even further implications. If you prevent children from having an intensive experience of color perspective, they will not develop the necessary incentive while learning to read (always remembering the reservation expressed yesterday, that it is unnecessary to push a child into reading at the earliest possible time). These color experiences will stimulate mobility in the child's mental imagery, suppleness in feelings, and flexibility in the will activities. The child's entire soul life will become more sensitive and pliable. It may well be that, if you use the method of painting-drawing and drawing-painting, the child will not learn to read as quickly. But when the right time comes, reading will not be anchored too loosely, which can happen, nor too tightly, as if each letter were making a kind of a scratch upon the tender soul-substance of the child. The important thing is that whatever is comprehended through soul and spiritual faculties should find its proper realm within the human being. We should never ask: What is the point of teaching the child to paint, if it will never be used in later life? This represents an entirely superficial view of life because, in reality, a child has every need for just this activity; if one wants to understand the complexity of a child's needs, one just has to know something about the spiritual background of the human being. Just as the expression “You can't understand this” should never be used when talking to children, so also there should never be a skeptical attitude among adults concerning what a child needs or does not need. These needs should be recognized as flowing from the human constitution itself; and if they are, one will respond with the right instinct. One will not worry unduly, either, if a child forgets some of what has already been learned, because knowledge is transmuted into capacities, and these are truly important later in life. Such capacities will not develop if you overload a child with knowledge. It is essential to realize—and actually practice—that one should impress in the student's memory only what is demanded by social life, that there is no purpose in overburdening the student's memory. This brings us to the question concerning the relationship between the individual and society, national or ethnic background, and humanity as a whole. When addressing this problem, we must try to avoid harming human nature when blending external demands with our educational practice. A question is asked regarding music lessons given to a seventeen-year-old girl. RUDOLF STEINER: The essential thing is what Mister Baumann has already presented to us.1 With the beginning of puberty and during the following years, a certain musical judgment takes the place of a previous feeling for music and of a general musical experience. The faculty of forming musical judgments emerges. This becomes very noticeable through the phenomenon characterized by Mister Baumann—that is, a certain self-observation begins to manifest, a self-observation of the student's own singing and, with it, the possibility of using the voice more consciously, and so on. This has to be cultivated methodically. At the same time, however, something else becomes noticeable—that is, from this stage on, natural musical memory begins to weaken a little, with the effect that students have to make more effort to remember music. This is something that has to be especially remembered during music lessons. Whereas, before puberty the children's relationship to music was spontaneous and natural, and because of this their musical memory was excellent, some of them now begin to encounter difficulties—not in taking in music, but in remembering it. This needs to be addressed. One must try to go over the same music several times, not by immediate repetition, but intermittently. Another characteristic sign at this particular stage is that, whereas previously the instrumental and vocal parts of a piece were experienced as a unity, after the sixteenth to seventeenth years they are listened to with clear discrimination. (From a psychological point of view there is a fine and intimate difference between these two ways of listening.) At this age, musical instruments are listened to far more consciously. There is also a greater understanding for the musical qualities of various instruments. Whereas earlier the instrument appeared to join in with the singing, it is now heard as a separate part. Listening and singing become two separate, though parallel, activities. This new relationship between singing and the appreciation of the part played by musical instruments is characteristic of this new stage, and the methods of teaching must be changed accordingly. What is important is not to introduce any music theory before this age. Music should be approached directly and any theoretical observations a teacher may wish to make should come from the students' practical experience of it. Gradually it should become possible for pupils of this age to make the transition toward forming musical judgments on a more rational basis. What Mister Baumann indicated at the end of his contribution is absolutely correct: one can make use of the ways pupils express themselves musically to increase certain aspects of their self-knowledge. For example, in the Waldorf school we let the older students do some modeling, and from the very beginning one can perceive individual characteristics in what they produce. (When you ask children to model something or other, their work will always display distinctly individual features.) But with regard to musical activities, the teacher cannot go into the pupils' more individual characteristics until the age of sixteen or seventeen. Then, to avoid one-sidedness, it is proper to address questions presented by too much attraction toward a particular musical direction. If pupils of that age develop a passion for certain types of music—for example, if they are strongly drawn to Wagner's music (and in our times many young people slide into becoming pure Wagnerians almost automatically)—then the teacher must try to counterbalance their tendency to be too emotionally swept away by music, rather than developing an appreciation of the inner configuration of the music itself. (This in no way implies any criticism of Wagner's music.) What happens in such a case is that the musical experience slips too easily into the emotional sphere and consequently needs to be lifted again into the realm of consciousness. A musician will notice this even in the quality of a pupil's singing voice. If music is experienced too much in the realm of feeling, the voice will sound differently from that of a young person who listens more to the formation of the tones, and who has a correct understanding of the more structural element in music. To work toward a balanced musical feeling and understanding is particularly important at this age. Of course, the teacher, who is still the authority, does not yet have an opportunity to work in this way before the student reaches puberty. After puberty, the teacher's authority no longer counts, but the weight of the teacher's musical judgments does. Until puberty, right or wrong is concurrent with what the teacher considers to be right or wrong. After puberty reasons have to be given—musical reasons also. Therefore it is very important to go deeply into the motivation of one's own musical judgments if there is an opportunity for continuing music lessons at this age. The whole night could be spent talking about this theme, if one wished to. Question: Is there not an element of dishonesty in asking a child a question if one knows the answer? RUDOLF STEINER: There is something very interesting at the bottom of this question. Usually, if I ask a question it is because I want to find an answer to something I don't know. If I now question a child—knowing the answer—I commit an untruth. However, in teaching there are always imponderables to be reckoned with, and sometimes it becomes necessary to become clear about this point. To do that, I often use the following example: If, as a teacher, one wants to speak about the question of immortality in a religious and imaginative way, one might choose the following procedure, and say to oneself: Since children cannot yet comprehend conceptual thoughts, I will use an image to convey the idea of the soul's immortality. As the teacher, I am the one who knows, and my students are uninformed. From my knowledge I will create a picture for them and say, “Look at a cocoon. When the time is right it opens, and a beautiful butterfly flies out. And just as the butterfly flies out of the cocoon, so the immortal soul flies out of the body when a human being dies.” This is one way to approach the subject. Fine; but if such is one's attitude, one may find that the chosen image does not make a deep impression in the children at all. This is because the teacher, with all ingenuity, does not believe the truth of this image, which is used only to illustrate the issue of immortality to “uninformed” children. But there is another possibility as well—that the teacher believes the truth of this picture. Then one's attitude could be: Despite my limited knowledge and wisdom, I am aware of what is real in the world, and I do believe the truth of this image. I know that I did not invent it, but that it was placed in the world through the powers that ordained the world. Through the butterfly creeping from the cocoon, what happens when the immortal human soul leaves the body is represented on a lower level, but in sense-perceptible form. And I can and do believe in this revelation. Notice the difference: If teachers believe in the truth of their images and the words used to describe them, their inner attitude will communicate itself to the students. Innumerable examples of this can be found. And so, similarly, imponderables play into the interesting question just raised. It's not important that, as the teacher, one has the opinion: I know my subject, the child does not know it; now I will ask my question, pretending that I want to hear the answer to something I do not know. It does make a great difference, after all, whether I ask the child a question, for example, about the Battle of Zabern, and I know the answer but the child does not, or whether I know the answer and the child also knows it. The untruth would be in asking something I already know. But I could also have a different attitude—that is, I am interested in how the child answers the question. I may phrase my question to find out what the child feels and thinks about a particular point. In this case I don't know in advance what the child will say. The child's answer could have many different shades or nuances. Let's assume that the teacher's ideal attitude—something I have often emphasized in my lectures—is that even the wisest is not beyond the capacity to learn, even from a tiny baby. For, no matter how far one may have advanced in scientific knowledge, a baby's cry can still teach one very much. If this is the ideal, the way a child answers each question will help teachers learn how to teach. If teachers ask questions, it does not imply that they want to hear something from their pupils that they already know, but that they themselves want to learn from the way a child answers. They will then also phrase their questions properly. For example, they may formulate a question like this: What does this mean to you? Even the tone of voice may indicate the teacher's interest in how the child will answer. It is a fact that much depends on the imponderables that affect what happens between teacher and child. If what is going on in the child's subconscious is known, one will also discover many other things. The whole question of untruth in the teacher is part of this theme also—that is, what we find when teachers stand before their classes teaching from books or written notes. It can certainly be very convenient for them, but such expediency has a very devastating effect on the actual teaching. This is because, in their subconscious, the children are continually forming the judgment: Why should we be made to learn what even teachers do not know? Why are we made to know what they are reading from their books? This is an even greater untruth that enters the classroom than if teachers ask questions. Even when dictating, teachers should avoid doing so from books. If one perceives what is happening in the child, and if the child can feel the teacher's genuine interest in the pupils, and thus not asking questions with false undertones, the whole situation is entirely different. Then teachers can safely ask their questions without fear of introducing an element of untruth into their lessons.
|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture VI
20 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture VI
20 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Questions of ethical and social education are raised when we consider the relationship between growing children and their surroundings. We will consider these two issues today—even though briefly and superficially, due to the shortness of time. Once again, the kernel of the matter is knowing how to adapt to the individuality of the growing child. At the same time, you must remember that, as a teacher and educator, you are part of the social setting, and that you personally bring the social environment and its ethical attitudes to the growing pupil. Again, pedagogical principles and methods must be formed so that they offer every opportunity of reaching the child's true nature—one must learn to know the child's true nature according to what has been shown here briefly during the last few days. As always, much depends on how one's material is brought to the students during their various ages and stages. Here we need to consider three human virtues—concerning, on the one hand, the child's own development, and on the other hand, what is seen in relation to society in general. They are three fundamental virtues. The first concerns everything that can live in will to gratitude; the second, everything that can live in the will to love; and third, everything that can live in the will to duty. Fundamentally, these are the three principal human virtues and, to a certain extent, encompass all other virtues. Generally speaking, people are far too unaware of what, in this context, I would like to term gratitude or thankfulness. And yet gratitude is a virtue that, in order to play a proper role in the human soul, must grow with the child. Gratitude is something that must already flow into the human being when the growth forces—working in the child in an inward direction—are liveliest, when they are at the peak of their shaping and molding activities. Gratitude is something that has to be developed out of the bodily-religious relationship I described as the dominant feature in the child from birth until the change of teeth. At the same time, however, gratitude will develop very spontaneously during this first period of life, as long as the child is treated properly. All that flows, with devotion and love, from a child's inner being toward whatever comes from the periphery through the parents or other educators—and everything expressed outwardly in the child's imitation—will be permeated with a natural mood of gratitude. We only have to act in ways that are worthy of the child's gratitude and it will flow toward us, especially during the first period of life. This gratitude then develops further by flowing into the forces of growth that make the limbs grow, and that alter even the chemical composition of the blood and other bodily fluids. This gratitude lives in the physical body and must dwell in it, since it would not otherwise be anchored deeply enough. It would be very incorrect to remind children constantly to be thankful for whatever comes from their surroundings. On the contrary, an atmosphere of gratitude should grow naturally in children through merely witnessing the gratitude that their elders feel as they receive what is freely given by their fellow human beings, and in how they express their gratitude. In this situation, one would also cultivate the habit of feeling grateful by allowing the child to imitate what is done in the surroundings. If a child says “thank you” very naturally—not in response to the urging of others, but simply by imitation—something has been done that will greatly benefit the child's whole life. Out of this an all-embracing gratitude will develop toward the whole world. The cultivation of this universal gratitude toward the world is of paramount importance. It does not always need to be in one's consciousness, but may simply live in the background of the feeling life, so that, at the end of a strenuous day, one can experience gratitude, for example, when entering a beautiful meadow full of flowers. Such a subconscious feeling of gratitude may arise in us whenever we look at nature. It may be felt every morning when the Sun rises, when beholding any of nature's phenomena. And if we only act properly in front of the children, a corresponding increase in gratitude will develop within them for all that comes to them from the people living around them, from the way they speak or smile, or the way such people treat them. This universal mood of gratitude is the basis for a truly religious attitude; for it is not always recognized that this universal sense of gratitude, provided it takes hold of the whole human being during the first period of life, will engender something even further. In human life, love flows into everything if only the proper conditions present themselves for development. The possibility of a more intense experience of love, reaching the physical level, is given only during the second period of life between the change of teeth and puberty. But that first tender love, so deeply embodied in the inner being of the child, without as yet working outward—this tender blossom will become firmly rooted through the development of gratitude. Love, born out of the experience of gratitude during the first period of the child's life, is the love of God. One should realize that, just as one has to dig the roots of a plant into the soil in order to receive its blossom later on, one also has to plant gratitude into the soul of the child, because it is the root of the love of God. The love of God will develop out of universal gratitude, as the blossom develops from the root. We should attend to these things, because in the abstract we usually know very well how they should be. In actual life situations, however, all too often these things turn out to be very different. It is easy enough, in theory, to say that people should carry the love of God within themselves—and this could not be more correct. But such demands, made abstractly, have a peculiar habit of never seeing the light of day in practice. I would like to return to what I said during one of the last few days. It is easy enough to think of the function of a stove in the following way: You are a stove and we have to put you here because we want to heat the room. Your categorical imperative—the true categorical “stove-imperative”—tells you that you are obliged to heat the room. We know only too well that this in itself will not make the slightest difference in the temperature of the room. But we can also save our sermonizing, and, instead, simply light the stove and heat it with suitable logs. Then it will radiate its warmth without being reminded of its categorical imperative. And this is how it is when, during various stages of childhood, we bring the right thing to children at the right time. If, during the first period of life, we create an atmosphere of gratitude around children, and if we do something else, of which I shall speak later, then, out of this gratitude toward the world, toward the entire universe, and also out of an inner thankfulness for being in this world at all (which is something that should ensoul all people), the most deep-seated and warmest piety will grow. Not the kind that lives on one's lips or in thought only, but piety that will pervade the entire human being, that will be upright, honest, and true. As for gratitude, it must grow; but this can happen with the intensity necessary for such a soul and spiritual quality only when it develops from the child's tender life-stirrings during the time from birth to its change of teeth. And then this gratitude will become the root of the love of God. It is the foundation for the love of God. Knowing all this will make us realize that, when we receive children into the first grade, we must also consider the kinds of lives they have led before reaching school age. There should really be direct contact with the parental home—that is, with what has happened before the child entered school. This contact should always be worked for, because teachers should have a fairly clear picture of how the present situation of children was influenced by their social conditions and the milieu in which they grew up. At school, teachers will then find plenty of opportunities to rectify any possible hindrances. For this to happen, however, knowledge of the child's home background, through contact with the parents, is of course absolutely essential. It is necessary that teachers can observe how certain characteristics have developed in a child by simply watching and imitating the mother at home. To be aware of this is very important when the child begins schooling. It is just as much part of teaching as what is done in the classroom. These matters must not be overlooked if one wants to build an effective and properly based education. We have already seen that, in the years between the child's change of teeth and the coming of puberty, the development of a sense for the authority of the teacher is both natural and essential. The second fundamental virtue, which is love, then grows from that when the child is in the process of also developing the physical basis of love. But one must see love in its true light, for, because of the prevailing materialistic attitudes of our time, the concept of love has become very one-sided and narrow; and because a materialistic outlook tends to see love only in terms of sexual love, it generally traces all manifestations of love back to a hidden sexuality. In an instance of what I called “amateurism squared” the day before yesterday, we find, if not in every case, that at least many psychologists trace human traits back to sexual origins, even if they have nothing whatsoever to do with sex. To balance such an attitude, the teacher must have acquired at least some degree of appreciation for the universal nature of love; for sexual love is not the only thing that begins to develop between the child's second dentition and puberty, but also love in its fullest sense, love for everything in the world. Sexual love is only one aspect of love that develops at this time of life. At that age one can see how love of nature and love for fellow human beings awaken in the child, and the teacher needs to have a strong view of how sexual love represents only one facet, one single chapter in life's book of love. If one realizes this, one will also know how to assign sexual love to its proper place in life. Today, for many people who look at life with theoretical eyes, sexual love has become a kind of Moloch who devours his own offspring, inasmuch as, if such views were true, sexual love would devour all other forms of love. The way love develops in the human soul is different from the way gratitude does. Gratitude has to grow with the growing human being, and this is why it has to be planted when the child's growing forces are at their strongest. Love, on the other hand, has to awaken. The development of love really does resemble the process of awakening, and, like awakening, it has to remain more in the region of the soul. The gradual emergence of love is a slow awakening, until the final stage of this process has been reached. Observe for a moment what happens when one awakes in the morning. At first there is a dim awareness of vague notions; perhaps first sensations begin to stir; slowly the eyelids struggle free of being closed; gradually the outer world aids one's awakening; and finally the moment arrives when that awakening passes into the physical body. This is also how it is with the awakening of love—except that, in the child, this process takes about seven years. At first love begins to stir when sympathy is aroused for whatever is taught during the early days at school. If we begin to approach the child with the kind of imagery I have described, we can see how love especially comes to meet this activity. Everything has to be saturated with this love. At that stage, love has a profoundly soul-like and tender quality. If one compares it with the daily process of waking up, one would still be deeply asleep, or at least in a state of sleeping-dreaming. (Here I am referring to the child's condition, of course—the teacher must not be in a dream, although this appears to happen all too often!) This condition then yields to a stronger jolt into wakefulness. And in what I described yesterday and the day before about the ninth and tenth years—and especially in the time leading up to the twelfth year—love of nature awakens in the child. Only then do we see it truly emerging. Before this stage, the child's relationship to nature is completely different. A child then has a great love for all that belongs to the fairyworld of nature, a love that has to be nourished by a creative and pictorial approach. Love for the realities in nature awakens only later. At this point we are faced with a particularly difficult task. Into everything connected with the curriculum at this time of life (causality, the study of lifeless matter, an understanding of historical interconnections, the beginnings of physics and chemistry) into all of this, the teacher must introduce—and here I am not joking, but speak very earnestly—the teacher must introduce an element of grace. In geometry or physics lessons, for example, there is every need for the teacher to allow real grace to enter into teaching. All lessons should be pervaded with an air of graciousness, and, above all, the subjects must never be allowed to become sour. So often, just during the ages from eleven and a half, or eleven and three-quarters, to fourteen or fifteen, work in these subjects suffers so much by becoming unpalatable and sour. What the pupils have to learn about the refraction and reflection of light or about the measurement of surface areas in a spherical calotte, is so often spoken of not with grace, but with an air of sourness. At just this time of life the teacher must remember the need for a certain “soul-breathing” in the lessons, which communicates itself to the pupils in a very strange way—soul-breathing must be allowed for. Ordinary breathing consists of inhaling and exhaling. In most cases, or at least on many occasions, teachers, in their physics and geometry lessons, only breathe out with their souls. They do not breathe in, and the outbreath is what produces this acidity. I am referring to the outbreathing of soul expressed in dull and monotonous descriptions, which infuses all content with the added seriousness of inflated proportion. Seriousness does have its place, but not through exaggeration. On the other hand, an in-breathing of soul brings an inherent sense of humor that is always prepared to sparkle, both within and outside the classroom, or whenever an opportunity arises for teachers and pupils to be together. The only possible hindrance to such radiating humor is the teachers themselves. The children certainly would not stand in its way, nor would the various subjects, provided they were handled with just the right touch during this particular age. If teachers could feel at home in their subjects to the degree that they were entirely free of having to chew over their content while presenting lessons, then they might find themselves in a position where even reflected light is likely to crack a joke, or where a spherical skullcap might calculate its surface area with a winning smile. Of course, jokes should not be planned ahead, nor should they be forced on the classroom situation. Everything should be tinted with spontaneous humor, which is inherent within the content, and not artificially grafted onto it. This is the core of the matter. Humor has to be found in things themselves and, above all, it should not even be necessary to search for it. At best, teachers who have prepared their lessons properly need to bring a certain order and discipline into the ideas that will come to them while teaching, for this is what happens if one is well prepared. The opposite is equally possible, however, if one has not prepared the lessons adequately; one will feel deprived of ideas because one still has to wrestle with the lesson content. This spoils a healthy out-breathing of soul and shuts out the humor-filled air it needs. These are the important points one has to remember at this particular age. If teaching follows its proper course in this way, the awakening of love will happen so that the student's soul and spirit are properly integrated into the human organization during the final stage of this awakening—that is, when the approach of puberty, begins. This is when what first developed so tenderly in the child's soul, and then in a more robust way, can finally take hold of the bodily nature in the right and proper way. Now you may wonder what teachers have to do to be capable of accomplishing their tasks as described. Here we have to consider something I would like to call the “social aspect” of the teaching profession, the importance of which is recognized far too little. Too often we encounter an image that a certain era (not ancient times, however) has associated with the teaching profession, whose members are not generally respected and honored as they should be. Only when society looks upon teachers with the respect their calling deserves, only when it recognizes that the teachers stand at the forefront of bringing new impulses into our civilization—not just in speeches from a political platform—only then will teachers receive the moral support they need to do their work. Such an attitude—or perhaps better still, such a sentiment—would pave the way toward acquiring a wider and more comprehensive view of life. This is what the teachers need; they also need to be fully integrated into life. They need more than just the proper qualifications in educational principles and methods, more than just special training for their various subjects; most of all teachers need something that will renew itself again and again: a view of life that pulsates in a living way through their souls. What they need is a deep understanding of life itself; they need far more than what can pass from their lips as they stand in front of their classes. All of this has to flow into the making of a teacher. Strictly speaking, the question of education should be part of the social question, and it must embrace not just the actual teaching schools, but also the inner development of the teaching faculty. It should be understood, at the same time, that the aims and aspirations for contemporary education, as presented here, are in no way rebellious or revolutionary. To believe that would be a great misunderstanding. What is advocated here can be introduced into the present situation without any need for radical changes. And yet, one feels tempted to add that it is just this social aspect of education that points to so many topical questions in life. And so, I would like to mention something, not because I want to agitate against present conditions, but only to illustrate, to put into words, what is bound to come one day. It will not happen in our current age, so please do not view what I am going to say as something radical or revolutionary. As you know, it is customary today to confer a doctorate on people who, fundamentally speaking, have not yet gained any practical experience in the subjects for which they are given their degree, whether chemistry, geography, or geology. And yet, the proof of their knowledge and capacity would surely have to include the ability to pass their expertise on to other candidates, of teaching them.1 And so a doctor's degree should not really be granted until a candidate has passed the practical test of teaching and training others who wish to take up the same vocation. You can see great wisdom, based on instinctive knowledge, in the popular expression; for, in the vernacular, only a person capable of healing, capable of giving tangible proof of healing abilities, is called a “doctor.” In this instance the word doctor refers to someone engaged as a practical healer, and not just to a person who has acquired specialized medical knowledge, however comprehensive this might be. Two concepts have arisen gradually from the original single concept—that of educating as well as that of healing. In more distant times, teaching or educating was also thought of as including healing. The process of educating was considered synonymous with that of healing. Because it was felt that the human being bore too many marks of physical heredity, education was viewed as a form of healing, as I have already mentioned during a previous meeting here. Using the terminology of past ages, one could even say teaching was considered a means of healing the effects of original sin.2 Seen in this light, the processes of healing, set in motion by the doctor, are fundamentally the same as those of teaching, though in a different realm of life. From a broader perspective, the teacher is as much of a healer as a doctor. And so the weight the title “doctor” usually carries in the eyes of the public could well become dependent on a general awareness that only those who have passed the test of practical experience should receive the honor of the degree. Otherwise, this title would remain only a label. However, as I have already said, this must not be misunderstood as the demand of an instigator for the immediate present. I would not even have mentioned it except in a pedagogical context. I am only too aware of the kind of claims that are likely to be listened to in our times, and the ones that inevitably give the impression one is trying to crash through closed doors. If one wants to accomplish something in life, one must be willing to forgo abstract aims or remote ideals, the attempted realization of which would either break one's neck or bruise one's forehead. One must always try to remain in touch with reality. Then one is also justified in using something to illustrate certain needs of our time, even if these may only be fulfilled in the future; for what I have spoken of cannot be demanded for a very long time to come. It may help us to appreciate, nevertheless, the dignity within the social sphere that should be due the teaching profession. I have mentioned all of this because it seemed important that we should see this question in the proper light. If teachers can feel moral support coming from society as a whole, then the gradual awakening of love in the young will become the close ally of their natural sense of authority, which must prevail in schools. Such things sometimes originate in very unexpected places. Just as the love of God is rooted in gratitude, so genuine moral impulses originate in love, as was described. For nothing else can be the basis for truly ethical virtue except a kind of love for humankind that does not allow us to pass our fellow human beings without bothering to know them, because we no longer have an eye for what lives in them—as happens so easily nowadays. The general love toward all people is the love that reaches out for human understanding everywhere. It is the love that awakens in the child in the time between the change of teeth and puberty, just as gratitude has grown between the child's birth and the loss of the first teeth. At school, we must do everything we can to awaken love. How are children affected by what happens in their immediate surroundings during the first period of life—that is, from birth to the change of teeth? They see that people engage in all kinds of activities. But what children take in are not the actual accomplishments in themselves, for they have not yet developed the faculty to perceive them consciously. What they do perceive are meaningful gestures. During this first period of life we are concerned with only a childlike understanding of the meaningful gestures they imitate. And from the perception of these meaningful gestures the feeling of gratitude develops, from which the gratitude-engendered will to act arises. Nor do children perceive the activities happening in their environment during the subsequent years, between the change of teeth and puberty—especially not during the early stages of this period. What they do perceive—even in the kinds of movements of the people around them—no longer represents the sum total of meaningful gestures. Instead, events begin to speak to the children, become a meaningful language. Not just what is spoken in actual words, but every physical movement and every activity speaks directly to the child during this particular time. It makes all the difference, therefore, whether a teacher writes on the blackboard:  Or writes the same word thus:  Whether the teacher writes the figure seven like this:  Or like this:  Whether it is written in an artistic, in a less-refined, or even in a slovenly way, makes a great difference. The way in which these things affect the child's life is what matters. Whether the word leaf is written in the first or second way (see above), is a meaningful language for the child. Whether the teacher enters the classroom in a dignified manner, or whether the teacher tries to cut a fine figure, speaks directly to the child. Likewise, whether the teacher is always fully awake to the classroom situation—this will show itself in the child's eye by the way the teacher handles various objects during the lessons—or, during wintertime, whether it could even happen that the teacher absent-mindedly walks off with the blackboard towel around his or her neck, mistaking it for a scarf—all of this speaks volumes to the child. It is not so much the outer actions that work on the child, but what lives behind them, whether unpleasant and ugly, or charming and pleasant. In this context, it is even possible that a certain personal habit of a teacher may generate a friendly atmosphere in the classroom, even if it might appear, in itself, very comic. For example, from my thirteenth to eighteenth year I had a teacher—and I always considered him to be my best teacher—who never began a lesson without gently blowing his nose first. Had he ever started his lesson without doing so, we would have sorely missed it. I am not saying that he was at all conscious of the effect this was having on his pupils, but one really begins to wonder whether in such a case it would even be right to expect such a person to overcome an ingrained habit. But this is an altogether different matter. I have mentioned this episode only as an illustration. The point is, everything teachers do in front of children at this stage of life constitutes meaningful language for them. The actual words that teachers speak are merely part of this language. There are many other unconscious factors lying in the depths of the feeling life that also play a part. For example, the child has an extraordinarily fine perception (which never reaches the sphere of consciousness) of whether a teacher makes up to one or another pupil during lessons or whether she or he behaves in a natural and dignified way. All this is of immense importance to the child. In addition, it makes a tremendous difference to the pupils whether teachers have prepared themselves well enough to present their lessons without having to use printed or written notes, as already mentioned during our discussion. Without being aware of it, children ask themselves: Why should I have to know what the teachers do not know? After all, I too am only human. Teachers are supposed to be fully grown up, and I am only a child. Why should I have to work so hard to learn what even they don't know? This is the sort of thing that deeply torments the child's unconscious, something that cannot be rectified once it has become fixed there. It confirms that the sensitive yet natural relationship between teachers and students of this age can come about only if the teachers—forgive this rather pedantic remark, but it cannot be avoided in this situation—have the subject completely at their fingertips. It must live “well-greased” in them—if I may use this expression—but not in the sense of bad and careless writing.3 I use it here in the sense of greasing wheels to make them run smoothly. Teachers will then feel in full command of the classroom situation, and they will act accordingly. This in itself will ensure an atmosphere where it would never occur to students to be impudent. For that to happen among children of ten, eleven, or twelve would really be one of the worst possible things. We must always be aware that whatever we say to our pupils, even if we are trying to be humorous, should never induce them to give a frivolous or insolent reply. An example of this is the following situation: A teacher might say to a student who suddenly got stuck because of a lack of effort and attention, “Here the ox stands held up by the mountain.” And the pupil retorts, “Sir, I am not a mountain.”4 This sort of thing must not be allowed to happen. If the teachers have prepared their lessons properly, a respectful attitude will emerge toward them as a matter of course. And if such an attitude is present, such an impertinent reply would be unthinkable. It may, of course, be of a milder and less undermining kind. I have mentioned it only to illustrate my point. Such impudent remarks would destroy not only the mood for work in the class, but they could easily infect other pupils and thus spoil a whole class. Only when the transition from the second life period to the third occurs, is the possibility given for (how shall I call them now in these modern times?) young men and young women to observe the activities occurring around them. Previously the meaningful gesture was perceived, and later the meaningful language of the events around the child. Only now does the possibility exist for the adolescent to observe the activities performed by other people in the environment. I have also said that, by perceiving meaningful gestures, and through experiencing gratitude, the love for God develops, and that, through the meaningful language that comes from the surroundings, love for everything human is developed as the foundation for an individual sense of morality. If now the adolescent is enabled to observe other people's activities properly, love of work will develop. While gratitude must be allowed to grow, and love must be awakened, what needs to evolve now must appear with the young person's full inner awareness. We must have enabled the young person to enter this new phase of development after puberty with full inner awareness, so that in a certain way the adolescent comes to find the self. Then love of work will develop. This love of work has to grow freely on the strength of what has already been attained. This is love of work in general and also love for what one does oneself. At the moment when an understanding for the activities of other people awakens as a complementary image, a conscious attitude toward love of work, a love of “doing” must arise. In this way, during the intervening stages, the child's early play has become transmuted into the proper view of work, and this is what we must aim for in our society today. What part do teachers and educators have to play in all of this? This is something that belongs to one of the most difficult things in their vocational lives. For the best thing teachers can do for the child during the first and second life period is to help what will awaken on its own with the beginning of puberty. When, to their everlasting surprise, teachers witness time and again how the child's individuality is gradually emerging, they have to realize that they themselves have been only a tool. Without this attitude, sparked by this realization, one can hardly be a proper teacher; for in classes one is faced with the most varied types of individuals, and it would never do to stand in the classroom with the feeling that all of one's students should become copies of oneself. Such a sentiment should never arise—and why not? Because it could very well happen that, if one is fortunate enough, among the pupils there might be three or four budding geniuses, very distinct from the dull ones, about whom we will have more to say later. Surely you will acknowledge that it is not possible to select only geniuses for the teaching profession, that it is certain that teachers are not endowed with the genius that some of their students will display in later life. Yet teachers must be able to educate not only pupils of their own capacity, but also those who, with their exceptional brightness, will far outshine them. However, teachers will be able to do this only if they get out of the habit of hoping to make their pupils into what they themselves are. If they can make a firm resolve to stand in the school as selflessly as possible, to obliterate not only their own sympathies and antipathies, but also their personal ambitions, in order to dedicate themselves to whatever comes from the students, then they will properly educate potential geniuses as well as the less-bright pupils. Only such an attitude will lead to the realization that all education is, fundamentally, a matter of self-education. Essentially, there is no education other than self-education, whatever the level may be. This is recognized in its full depth within anthroposophy, which has conscious knowledge through spiritual investigation of repeated Earth lives. Every education is self-education, and as teachers we can only provide the environment for children's self-education. We have to provide the most favorable conditions where, through our agency, children can educate themselves according to their own destinies. This is the attitude that teachers should have toward children, and such an attitude can be developed only through an ever-growing awareness of this fact. For people in general there may be many kinds of prayers. Over and above these there is this special prayer for the teacher: Dear God, cause that I—inasmuch as my personal ambitions are concerned—negate myself. And Christ make true in me the Pauline words, “Not I, but the Christ in me.” This prayer, addressed to God in general and to Christ in particular, continues: “... so that the Holy Spirit may hold sway in the teacher.” This is the true Trinity. If one can live in these thoughts while in close proximity to the students, then the hoped-for results of this education can also become a social act at the same time. But other matters also come into play, and I can only touch on them. Just consider what, in the opinion of many people, would have to be done to improve today's social order. People expect better conditions through the implementation of external measures. You need only look at the dreadful experiments being carried out in Soviet Russia. There the happiness of the whole world is sought through the inauguration of external programs. It is believed that improvements in the social sphere depend on the creation of institutions. And yet, these are the least significant factors within social development. You can set up any institutions you like, be they monarchist or republican, democratic or socialist; the decisive factor will always be the kind of people who live and work under any of these systems. For those who spread a socializing influence, the two things that matter are a loving devotion toward what they are doing, and an understanding interest in what others are doing. Think about what can flow from just these two attributes; at least people can work together again in the social sphere. But this will have to become a tradition over ages. As long as you merely work externally, you will produce no tangible results. You have to bring out these two qualities from the depths of human nature. If you want to introduce changes by external means, even when established with the best of intentions, you will find that people will not respond as expected. And, conversely, their actions may elude your understanding. Institutions are the outcome of individual endeavor. You can see this everywhere. They were created by the very two qualities that more or less lived in the initiators—that is, loving devotion toward what they were doing, and an understanding interest in what others were doing. When one looks at the social ferment in our times with open eyes, one finds that the strangest ideas have arisen, especially in the social sphere, simply because the current situation was not understood properly. Let me give you an example: Today, the message of so-called Marxism regarding human labor and its relationship to social classes is being drummed not just into thousands but into millions of heads.5 And if you investigate what its author alleges to have discovered—something with which millions of people are being indoctrinated so that they see it as their socialist gospel, to use as a means for political agitation—you will find it all based upon a fundamental error regarding the attitude toward social realities. Karl Marx wants to base the value of work on the human energy spent performing it.6 This leads to a complete absurdity, because, from the perspective of energy output, it makes no difference whether someone cuts a certain quantity of firewood within a given time, or whether—if one can afford to avoid such a menial task—one expends the same energy and time on treading the pedals of a wheel specially designed to combat incipient obesity. According to Karl Marx's reckoning, there is no difference between the human energy expended on those two physical activities. But cutting firewood has its proper place within the social order. Treading the pedals of a slimming cycle, on the other hand, is of no social use, because it only produces a hygienic effect for the person doing it. And yet, Karl Marx's yardstick for measuring the value of work consists of calculating the food consumption necessary for work to be done. This way of assessing the value of labor within the context of the national economy is simply absurd. Nevertheless, all kinds of calculations were made toward this end. The importance of one factor, however, was ignored—that is, loving devotion toward what one is doing and an understanding interest in what others are doing. What we must achieve when we are with young people is that, through our own conduct, a full consciousness of the social implications contained in those two things will enter the minds of adolescents. To do so we must realize what it means to stand by children so that we can aid in their own self-education.
|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture VII
21 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture VII
21 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
As you can probably imagine, it is not easy for one who is free from a fanatical or sectarian attitude to accomplish the kind of education, based on knowledge of the human being that we have spoken of in the past few days. Many of you will have noticed already that what is considered here to be both right and good in education differs in many ways from what is found in conventional forms of education, with their regulations, curricula, and other fundamental policies. In this respect, one finds oneself caught in a dilemma. On the one hand, we stand on the firm ground of a pedagogy that derives from objective knowledge, and that prescribes specific curricular and educational tasks for each year (as you will have discovered already from what you have heard so far). To ascertain what must be done in this education, we take our cue from the children themselves; and not only for each year, but also for each month, each week, and, in the end, each day. Here I feel justified in expressing appreciation for how much the teachers of the Waldorf schools have responded to the objective demands of a truly grounded pedagogy, and also for their insight into how this pedagogy is related to the needs of the growing child.1 They have come to realize that not a single detail of this pedagogy is arbitrary, that everything in it is a direct response to what can be read in the child's own nature. This represents one side of what has led to the dilemma. The other side consists of demands made by life itself. Those who are free of any fanaticism despite their own ideals (or whatever else you choose to call these things), and who feel the need for firm roots in life's realities, experience this other aspect with particular acuity. Sectarianism to any degree or fanatical zeal must never be allowed to creep into our educational endeavors, only to find at the end of the road that our students do not fit into life as it is; for life in the world does not notice one's educational ideals. Life is governed by what arises from the prevailing conditions themselves, which are expressed as regulations concerning education, as school curricula, and as other related matters, which correspond to current ways of thinking. And so there is always a danger that we will educate children in a way that, though correct in itself, could alienate them from life in the world—whether one considers this right or wrong. It must always be remembered that one must not steer fanatically toward one's chosen educational aims without considering whether or not one might be alienating one's students from surrounding life. Opponents of anthroposophy have often attributed fanaticism and sectarianism to this movement, but this is not the case, as you will see. On the contrary, it is precisely these two attributes that are alien to its nature. They may appear within some individual members, but anthroposophy itself always strives to enter fully into the realities of life. And just because of this, one is only too aware of the difficulties encountered in dealing with the practical sides of life. From the very beginning of the Waldorf school something had to be done. It is difficult to give it a proper name, but something bad or negative had to be agreed upon—that is, a kind of compromise—simply because this school is not grounded in fanaticism but in objective reality. At the very beginning, a memorandum addressed to the local school authorities had to be worked out. In it I made the following points: During the first three years the students in our school are to be educated, stage by stage and wherever possible, according to what is considered relevant to their inner needs. At the same time, the standards generally achieved in other schools are to be respected to the extent that, after completion of the first three years, the students of the Waldorf school should be able to fulfill the necessary requirements for entering corresponding classes in other schools, if desired. Such an offer, for our teachers, amounted to an “ingratiating compromise”—forgive this term, I cannot express it otherwise. A realistic mind has to take such a course, for discretion is essential in everything one does. A fanatic would have responded differently. Naturally, many difficulties have to be ironed out when such a policy is chosen, and many of our teachers would find it preferable to steer a straight course toward our aims and ideals. Lengthy and minutely detailed discussions occurred before a passage was found through these two conflicting approaches. Another point in my memorandum was that, after completion of their twelfth year—that is, when our pupils are in the sixth grade, counting upward from the first grade—they should again be able to fulfill the requirements for entry into the corresponding class in another school. My choice for this particular age is based on the fact that it marks the end of a period of development, as already described during a previous meeting. And finally, it was presented in the memorandum that, in their fourteenth year, our students should have reached again the necessary standards of learning that would enable them, if desired, to change schools. In retrospect, one could say that during the first three grades this plan has worked fairly well. At that level it has been tolerably successful. With a great deal of effort and trouble, it is still workable until the students' twelfth year. However, the real difficulties begin during the following years, for out of a dark subconsciousness, some knowledge of what is happening in a young child lingered from the distant past into our present time, however dim this insight may have become today. And because of this it is now customary to send children to school when they are losing their first teeth. Today people hardly realize that these two things are connected. Nevertheless, entering school at about six is still the result of ancient wisdom, passed on through the ages, which today has become only vague and instinctive. Since these things are no longer recognized, however, there is a tendency toward arbitrarily establishing the age for entering school at the completion of the sixth year, which is always a little premature, and therefore not in keeping with the child's nature. There is nothing one can do about it, because if parents do not send their children to school when they have completed their sixth year, the police or bailiff, or whatever else such people are called, will come and take the children to school. However, as previously mentioned, it is relatively easy to work with this compromise during the first three years. Admittedly, if one or another student has to leave the Waldorf school for another school during this time because of circumstance, one is usually told that such students are behind in reading and writing. They may be considered far ahead in artistic subjects, such as in drawing or eurythmy, but these, so we are told, are not generally considered to be very important. Such official judgments, however, can even be seen as an affirmation of Waldorf methods! They prompt me to tell you something interesting about the young Goethe.2 If you look at his spelling, even when he was much older than seven or eight, you will find it full of atrocious mistakes. It is easy to deduce from this that far more is expected of an eight-year-old child today (if “more” is the right word) than what Goethe managed to achieve at seventeen (only with regard to spelling, of course). This certainly demonstrates that there is also another way of judging the situation, for Goethe owed much to the fact that, even at the age of seventeen, he was still likely to make spelling errors because, not having been too fettered to rigid rules, his inner being could remain flexible with regard to the unfolding of certain soul forces. If one knows how these things interact with each other (and a more sensitive kind of psychology is needed for this than is frequently encountered today) one will be no more influenced by adverse criticism than by the superficial criteria of such a historical fact, which is interesting, at least. Another interesting example can be found in so-called Mendelisms, which emerged around the beginning of the twentieth century (perhaps even around the end of the nineteenth century), and which was considered by natural scientists to be the best theory for explaining the phenomena of heredity. It received its name from a certain Gregor Mendel,3 a botanist who lived during the middle of the nineteenth century and was also a teacher at a Realschule in Moravia.4 Gregor Mendel made careful experiments with plants in order to investigate their inherited properties. His writings remained obscure for a long time, only to surface again toward the turn of the century, to be hailed as the most convincing theory regarding heredity. Now it is interesting to consider the biography of Gregor Mendel. As our Austrian friends here know, monastic clerics had to pass an examination before they could become eligible for a teaching post at a high school. Mendel failed his exam brilliantly, which meant that he was considered incapable of becoming a high school teacher. But an Austrian regulation existed permitting failed candidates to retake their exams after a certain period of time. Gregor Mendel did so and again failed spectacularly. I believe that even today in Austria such a person could never find a high school teaching position. In those days, however, regulations were a little less stringent. Because of a shortage of teachers at the time, even failed candidates were sometimes hired as teachers, and so Gregor Mendel did finally become a high school teacher, even though he had twice failed his exam. Since this had been made possible only through the grace of the headmaster, however, he was considered to be a second-rate staff member by his colleagues and, according to the rules governing high school teachers, he was not entitled to add “Ph.D.” to his name. Successful exam candidates usually write these abbreviated degrees after their names, for example, “Joseph Miller, Ph.D.” In the case of Gregor Mendel these letters were missing, the omission of which indicated his inferior position. Well, several decades passed, but after his death this same individual was hailed as one of the greatest naturalists! Real life presents some strange examples. And, although it is impossible to plan the education of young people to suit the practical demands of later life (since, if this were the only aim, some very strange requests would certainly be made), even though one cannot adapt the curricula to what life itself will bring to maturity later on, one must nevertheless be ready to listen with inner clarity and a sense of psychology to what the many occurrences in life are trying to tell us, with regard to both primary and secondary education. So it could certainly be said that it is not really a tragedy when a Waldorf student has to leave during the third grade, a student who has not yet reached the same level of achievement in certain elementary skills as students in another school, who were drilled using bad methods, the harmful effects of which will surface only later in life. Many life stories could be told to substantiate this claim. Strange things sometimes show up when one looks at obituaries. R¶ntgen, for example, was also excluded from teaching at a high school, and only through the special kindness of an influential person was he allowed to gain a teaching post at all. [Wilhelm Konrad von Röntgen (1845–1923) German physicist, discoverer of the “Röntgen” rays or X-rays.] As already said, one cannot base one's educational ideas on such things, but they should be noticed, and one must try to comprehend their significance through a more discriminating psychology. Returning to our point, after the twelfth year it becomes increasingly difficult to find a workable compromise in our way of teaching. Until the twelfth year it is just possible to do so, as long as one really knows what is going on inside the students. But afterward, the situation begins to get more and more difficult, because from that time on, the curricula and the required standards for achievement no longer have any relationship to the nature of the growing human being; they are chosen entirely arbitrarily. The subject matter to be covered in any one year is chosen entirely autocratically, and one simply can no longer bridge the conflicting demands, on the one hand, from the powers that be, and, on the other hand, those that arise directly from the evolving human being. Remember what I said yesterday: by the time puberty is passed, the adolescent should have been helped toward developing sufficient maturity and inner strength to enter the realm of human freedom. I referred to the two fundamental virtues: gratitude, for which the ground has to be prepared before the change of teeth, and the ability to love, for which the ground needs to be prepared between the change of teeth and puberty; this was the theme developed yesterday. Furthermore, we have seen that, with regard to the ethical life, the soul life of the child must also experience feelings of sympathy and antipathy toward what is good and evil. If one approaches a student at this age with a “thou shalt” attitude, proper development will be hindered in the years to come. On the other hand, when one instead moves the pre-adolescent child, through natural authority, to love the good and hate the evil, then during the time of sexual maturity, from the inner being of the adolescent, the third fundamental virtue develops, which is the sense of duty. It is impossible to drill it into young people. It can only unfold as a part of natural development, based only on gratitude—in the sense described yesterday—and on the ability to love. If these two virtues have been developed properly, with sexual maturity the sense of duty will emerge, the experience of which is an essential part of life What belongs to the human soul and spirit realm has to develop according to its own laws and conditions, just as what belongs to the physical realm must obey physical laws. Just as an arm or a hand must be allowed to grow freely, according to the inner forces of growth, just as these must not be artificially controlled by, for example, being fixed into a rigid iron frame—although in certain places on Earth there is a custom of restricting the free growth of feet similar to the way we impede the free unfolding here of the child's soul life—so must adolescents feel this new sense of duty arising freely from within. The young person will then integrate properly into society, and Goethe's dictum will find its noblest fulfillment: “Duty is a love for what one demands of oneself.” Here again you see how love plays into everything, and how the sense of duty must be developed so that one eventually comes to love it. In this way one integrates properly as a human being into society. And then, from the previous experience of right authority, the ability to support oneself by one's own strength will evolve. What is finally revealed as genuine piety, when seen with spiritual eyes, is the transformed body-related, natural religiousness during the time before the change of teeth, which I described to you in fair detail. These are all things that must be rooted deeply in a true pedagogy, and applied practically. Soon enough, one will realize how necessary it is to allow the curriculum—from the twelfth year until puberty, and, most of all, after puberty—to be more and more inclined toward practical activities. In the Waldorf school, the ground for this task is prepared early. In our school, boys and girls sit side by side. Although interesting psychological facts have emerged from this practice alone—and each class has its own psychology, of which we will speak more tomorrow—one can definitely say: if one lets boys and girls practice their handcrafts side by side as a matter of course, it is an excellent preparation for their adult lives. Today there are only a few men who recognize how much the ability to knit can help toward healthy thinking and healthy logic. Only a few men can judge what it means for one's life to be able to knit. In our Waldorf school, boys do their knitting alongside the girls, and they also mend socks. Through this practice, the differentiation between the types of work performed by the two sexes will find its natural course later on, should this become necessary. At the same time, a form of education is being implemented that considers fully the practical aspects of the students' future lives. People are always extremely surprised when they hear me say (and the following assertion not only expresses my personal conviction, but is based on a psychological fact) that I cannot consider anyone to be a good professor in the full meaning of the word unless that person can also mend a shoe in an emergency; for how could it be possible for anyone to know something of real substance about being and becoming in the world, unless that person can also repair a shoe or a boot if the situation demands it? This is, of course, a rather sweeping statement, but there are men who cannot even sew on a button properly, and this is a lamentable failing. Knowledge of philosophy carries little weight, unless one can also lend a hand to whatever needs doing. This is simply part of life. In my opinion, one can only be a good philosopher if one could have just as well become a shoemaker, should this have been one's destiny. And, as the history of philosophy shows, it sometimes happens that cobblers become philosophers.5 Knowledge of the human being calls on us to make adequate provision in our curricula and schedules for preparing pupils for the practical side of life. Reading in the book of human nature, we are simply led to introduce the children—or rather, the young men and women, as we should call them now—to the art of setting up a loom and weaving. From there it follows quite naturally that they should also learn to spin, and that they gain a working idea of how paper is made, for example. They should be taught not only mechanics and chemistry, but also how to understand at least simple examples of mechanical and chemical processes used in technology. They should reproduce these on a small scale with their own hands so they will know how various articles are manufactured. This change of direction toward the more practical side of life must certainly be made possible. It has to be worked toward with honest and serious intent if one wants to build the proper curriculum, especially in the upper classes. But this can place one in terrible difficulties. It is just possible to equip children under nine with sufficient learning skills for a transfer into the fourth grade of another school, without neglecting what needs to be done with them for sound pedagogical reasons. This is also still possible in the case of twelveyear-olds who are to enter the seventh grade. It is already becoming very difficult indeed to bring pupils to the required standards of learning for their transfer to a high school. Tremendous difficulties have to be overcome if pupils from our higher grades have to change to a high school. In such cases one would do well to recall ancient Greece, where a wise Greek had to put up with being told by an Egyptian, “You Greeks are like children—you know nothing about all the changes the Earth has gone through.” A wise Greek had to listen to the judgment of a wise Egyptian. But nevertheless, the Greeks had not become so infantile as to demand of a growing youth, who was to be educated in one or another particular subject, that knowledge of the Egyptian language should first be acquired. They were very satisfied that the young person use the native Greek language. Unfortunately, we do not act today as the Greeks did, for we make our young people learn Greek. I do not want to speak against it; to learn Greek is something beautiful. But it is inconsistent with fulfilling the needs of a particular school age. It becomes a real problem when one is told to allocate so many lessons to this subject on the schedule at a time when such a claim clashes with the need for lessons in which weaving, spinning, and a rough knowledge of how paper is made should be practiced. Such is the situation when one is called on to finalize the schedule! And since we very well know that we shall never receive permission to build our own university anywhere, it is absolutely essential for us to enable those of our pupils who wish to continue their education at a university, technical college, or other similar institution, to pass the necessary graduation exam. All this places us in an almost impossible situation, with almost insurmountable difficulties. When one tries to cultivate the practical side in education, prompted by insight into the inner needs of adolescent pupils, one has to face the bitter complaints of a Greek teacher who declares that the exam syllabus could never be covered with the amount of time allocated to the subject, and that, consequently, the candidates are doomed to fail their exams. Such are the problems we have to tackle. They certainly show it is impossible for us to insist on pushing our ideals with any fanatical fervor. What will eventually have to happen no longer depends solely on the consensus of a circle of teachers about the rights and wrongs of education. Today it has become necessary for much wider circles within society to recognize the ideals of a truly human education, so that external conditions will render it possible for education to function without alienating pupils from life. This is obviously the case if, after having gone through a grammar school kind of education in one's own school, pupils were to fail their graduation exams, which they have to take somewhere else.6 Speaking of failing an exam—and here I am speaking to specialists in education—I believe that it would be possible to make even a professor of botany, however clever, fail in botany—if that were the only intention! I really believe such a thing is possible, because anyone can fail an exam. In this chapter of life also, some very strange facts have shown up. There was, for example, Robert Hamerling, an Austrian poet, whose use of the German language was later acclaimed as the highest level any Austrian writer could possibly attain.7 The results of his exam certificate, which qualified him for a teaching position at an Austrian Gymnasium, make interesting reading: Greek—excellent; Latin—excellent; German language and essay writing—hardly capable of teaching this subject in the lower classes of a middle school. You actually find this written in Hamerling's teaching certificate! So you see, this matter of failing or passing an exam is a very tricky business. The difficulties that beset us, therefore, make us realize that society at large must provide better conditions before more can be accomplished than what is possible by making the kind of compromise I have spoken of. If I were to be asked, abstractly, whether a Waldorf school could be opened anywhere in the world, I could only answer, again entirely in the abstract, “Yes, wherever one would be allowed to open.” On the other hand, even this would not be the determining factor because, as already said, in the eyes of many people these are only two aspects of one and the same thing. There are some who struggle through to become famous poets despite bad exam results in their main subject. But not everyone can do that. For many, a failed graduation exam means being cast out of the stream of life. And so it must be acknowledged that the higher the grade level in our school, the less one can work toward all of one's educational ideals. It is something not to be forgotten. It shows how one has to come to terms with actual life situations. The following question must always be present for an education based on an understanding of the human being: Will young people, as they enter life, find the proper human connection in society, which is a fundamental human need? After all, those responsible for the demands of graduation exams are also members of society, even if the style and content of their exams are based on error. Therefore, if one wants to integrate Waldorf pedagogy into present social conditions, one has to put up with having to do certain things that, in themselves, would not be considered right or beneficial. Anyone who inspects our top classes may well be under the impression that what is found there does not fully correspond to the avowed ideals of Waldorf pedagogy. But I can guarantee you that, if we were to carry out those ideals regardless of the general situation—and especially, if we attempted to make the transition to the practical side of life—all of our candidates for the graduation exam would fail! This is how diametrically opposed matters are today. But they have to be dealt with, and this can be done in great variety of ways. At the same time, awareness has to emerge regarding the degree of change necessary, not just in the field of education, but in all of life, before a truly human form of education can be established. Despite all obstacles, the practical activities are being accomplished in the Waldorf school, at least to a certain extent—even though it does happen, now and then, that they have to be curtailed in some cases because the Greek or Latin teacher claims some of these lessons. That is something that cannot be avoided. From what I've said, you can see that puberty is the proper time to make the transition, leading the adolescent into the realities of ordinary life. And the elements that will have to play more and more into school life, in a higher sense, are those that will make the human individual, as a being of body, soul, and spirit, a helpful and useful member of society. In this regard, our current time lacks the necessary psychological insight; for the finer interrelationships in the human spiritual, soul, and physical spheres are, in general, not even dreamed of. These things can be felt intuitively only by people who make it their particular task to come to understand the human psyche. From personal self-knowledge I can tell you in all modesty that I could not have accomplished in spiritual science certain things that proved possible, if I had not learned bookbinding at a particular time in my life—which may seem somewhat useless to many people. And this was not in any way connected with Waldorf pedagogy, but simply a part of my destiny. This particularly human activity has particular consequences to most intimate spiritual and soul matters, especially if it is practiced at the right time of life. The same holds true for other practical activities as well. I would consider it a sin against human nature if we did not include bookbinding and box-making in our Waldorf school craft lessons, if it were not introduced into the curriculum at a particular age determined by insight into the students' development. These things are all part of becoming a full human being. The important thing in this case is not that a pupil makes a particular cardboard box or binds a book, but that the students have gone through the necessary discipline to make such items, and that they have experienced the inherent feelings and thought processes that go with them. The natural differentiation between the boys and girls will become self-evident. Yet here one also needs to have an eye for what is happening, an eye of the soul. For example, the following situation has come up, the psychology of which has not yet been fully investigated, because I have not been able to spend enough time at the Waldorf school. We will investigate it thoroughly another time. But what happened was that, during lessons in spinning, the girls took to the actual spinning. The boys also wanted to be involved, and somehow they found their task in fetching and carrying for the girls. The boys wanted to be chivalrous. They brought the various materials that the girls then used for spinning. The boys seemed to prefer doing the preparatory work. This is what happened and we still need to digest it from the psychological perspective. But this possibility of “switching our craft lessons around”—if I may put it that way—allows us to change to bookbinding now, and then to box-making. All are part of the practical activities that play a dominant role in Waldorf pedagogy, and they show how an eye for the practical side of life is a natural byproduct for anyone who has made spiritual striving and spiritual research the main objective in life. There are educational methods in the world, the clever ideas of downright impractical theoreticians, who believe they have eaten practical life experience by the spoonful, methods that are nevertheless completely removed from reality. If one begins with theories of education, one will end up with the least practical results. Theories in themselves yield nothing useful, and too often breed only biases. A realistic pedagogy, on the other hand, is the offspring of true knowledge of the human being. And the part played by arts and crafts at a certain time of life is nothing but such knowledge applied to a particular situation. In itself this knowledge already presents a form of pedagogy that will turn into the right kind of practical teaching through the living way in which the actual lessons are given. It becomes transformed into the teacher's right attitude, and this is what really matters. The nature and character of the entire school has to be in tune with it. And so, in the educational system cultivated in the Waldorf school, the center of gravity iis within the staff of teachers and their regular meetings, because the whole school is intended as one living and spirit-permeated organism. The first grade teacher is therefore expected to follow with real interest not only what the physics teacher is teaching to the seventh grade, but also the physics teacher's experiences of the various students in that class. This all flows together in the staff meetings, where practical advice and counseling, based on actual teaching experience, are freely given and received. Through the teaching staff a real attempt is made to create a kind of soul for the entire school organism. And so the first grade teacher will know that the sixth grade teacher has a child who is retarded in one way or another, or another who may be especially gifted. Such common interest and shared knowledge have a fructifying influence. The entire teaching body, being thus united, will experience the whole school as a unity. Then a common enthusiasm will pervade the school, but also a willingness to share in all its sorrows and worries. Then the entire teaching staff will carry whatever has to be carried, especially with regard to moral and religious issues, but also in matters of a more cognitive nature. In this way, the different colleagues also learn how one particular subject, taught by one of the teachers, affects a completely different subject taught by another teacher. Just as, in the case of the human organism, it is not a matter of indifference whether the stomach is properly attuned to the head, so in a school it is not insignificant whether a lesson from nine to ten in the morning, given to the third grade, is properly related to the lesson from eleven to twelve in the eighth grade. This is in rather radical and extreme terms, of course. Things do not happen quite like that, but they are presented this way because they correspond essentially to reality. And if thinking is in touch with reality, judgments about matters pertaining to the sense-perceptible world will differ greatly from those based on abstract theories. To illustrate this point I would like to mention certain lay healers who give medical treatment in places where this is not illegal. They are people who have acquired a certain measure of lay knowledge in medicine. Now one of these healers may find, for example, that a patient's heart is not functioning normally. This may be a correct diagnosis, but in this case it does not imply that the cure would be to bring the heart back to normality. And according to such a lay healer, the patient may have adapted the entire organism to the slightly abnormal function of the heart. This means that if now one were to get the heart to work normally again, such a “cured” heart, just because of its return to normality, might upset the entire organism, thus causing a deterioration of the patient's general condition. Consequently the therapy could actually consist of leaving the heart as it is, with the recommendation that, should the symptoms of the slight heart defect return, a different course of treatment should be given from what would normally be done through the use of medications under similar circumstances. I said yesterday that educating and healing are related activities. And so something similar is also called for in the field of education. That is, a kind of conceptual and sensitive feeling approach, both comprehensive and in touch with reality, since it would have to apply to other realms of cognition directly related to practical life. If we look at what contemporary anatomy and physiology tell us about the human being—not to mention psychology, which is a hodgepodge of abstractions anyway—we find a certain type of knowledge from which a picture of the human being is manufactured. If this picture is used as a means of selfknowledge, it creates the impression that we are merely a skeleton. (Within certain limits, knowledge of the human being is also self-knowledge—not the introspective kind, but rather a recognition of essentially human qualities found in each individual.) If, when looking at ourselves, we had to disregard everything within and around our skeleton, we would naturally conclude that we were only skeletons. This is how the whole human being—body, soul, and spirit—would appear to us if we used only what contemporary anatomy and physiology offers as a picture of the human being. Psychology needs to truly permeate the human psyche with spirit. If this is done, we can follow the spiritual element right into the physical realities of the body, because spirit works in every part of the human body. I have already said that the tragedy of materialism is its inability to understand the true nature of matter. Knowledge of spirit leads to true understanding of matter. Materialism may speak of matter, but it does not penetrate to the inner structures of the forces that work through matter. Similarly, pedagogy that observes only external phenomena does not penetrate to the regions of the human being that reveal what should be done about practical life. This causes a situation that, to the spiritual investigator, is very natural, but would appear paradoxical for many people. They wonder why a pedagogy grown from anthroposophy always emphasizes the necessity of training children at specific ages in certain practical activities—that is, the necessity of training them in the correct handling of material processes. Far from leading students into a foggy mysticism, the principles and methods of the education based on anthroposophical research will not estrange them from life. On the contrary, it will induce spirit and soul substance to penetrate their physical bodies, thus making them useful for this earthly life, and at the same time, provide them with the proper conditions to develop inner certainty. This is why we feel it necessary to expand the practical type of work, and, of course, difficulties therefore increase with the beginning of every new school year when we have to add a new class to the existing ones (we began with eight grades, adding the ninth, tenth, and eleventh, and we are about to open our first twelfth grade). This has led to the situation where, while other problems facing the anthroposophical cause were being dealt with very recently, a memorandum was handed in by the pupils of the current highest grade level in the Waldorf school. Those among them who were expecting to have to take their graduation exam had worked out a remarkable document, the deeper aspects of which will be appreciated only when the whole matter is seen in the proper light. They had sent more or less the following memorandum to the Anthroposophical Society: Since we are being educated and taught in the sense of the true human being8 and, consequently, since we cannot enter existing types of colleges, we wish to make the following proposal to the Anthroposophical Society: That a new anthroposophical college is to be founded where we can continue our education. No negative judgment regarding colleges in general is implied in this wording, although such judgments are frequently encountered in contemporary society. All of this presents us with the greatest difficulties. But since you have made the effort to come here to find out what Waldorf pedagogy is all about—something we very well know how to appreciate—these problems should also be aired. Any sincere interest in what is willed in this education deserves a clear indication of all the difficulties involved. Thus far, Waldorf pedagogy is being practiced only by the teachers of the one existing Waldorf school, and there we find our difficulties increase the higher we go with the school. I can only assume that the problems would be even greater in a college operated anthroposophically. But since such a college is only a very abstract ideal, I can only speak about it hypothetically. It has always been my way to deal directly with the tasks set by life, and this is why I can talk about this education only up to the twelfth grade, which is opening soon. Things that belong to a misty future must not take up too much time for people standing amid life, since it would only detract from the actual tasks at hand. One can say only that problems would increase substantially, and that obviously there would be two kinds of difficulties. First, if we were to open a college, our exam results would not be recognized as proper qualifications, which means that successful candidates could not take up professional positions in life. They could not become medical doctors, lawyers, and so on; professions that in their present customary forms are still essential today. This presents one side of the problem. The other side would conjure up really frightening prospects, if certain hard facts did not offer relief from such anxieties; for, on the strength of the praiseworthy efforts made by our young friends, an association has actually been founded with the express aim of working toward the creation of such a college, based on the principles of Waldorf pedagogy. The only reason there is no need to feel thoroughly alarmed about the potential consequences of such an endeavor is that the funds needed by this association will certainly not reach such giddy heights that anyone would be tempted to seriously consider going ahead with the project. The underlying striving toward this aim is thoroughly laudable, but for the time being it remains beyond the realm of practicality. The real worry would come only if, for example, an American millionaire were to suddenly offer the many millions needed to build, equip, and staff such a college. The best one could do in such a situation would be to promote, en masse, the entire teaching staff of the Waldorf school to become the teachers of the new college. But then there would no longer be a Waldorf school! I am saying all this because I believe actual facts are far more important than any kind of abstract argument. While acknowledging that the idea of basing education, including college education, on true knowledge of the human being represents a far-reaching ideal, we must not overlook the fact that the circle of those who stand firmly behind our ideals is extremely small. This is the very reason one feels so happy about every move toward an expansion of this work, which may gain further momentum through your welcome visit to this course. At the same time, one must never lose sight of all that must happen so that the Waldorf ideal can rest upon truly firm and sound foundations. This needs to be mentioned within the context of this course, for it follows from the constitution of the Waldorf school. Tomorrow, in the concluding lecture, I would like to tell you more about this constitution of the Waldorf school—about how it is run, about what the relationship should be between teachers and students, as well as the interrelationships of pupils among themselves, and teachers among themselves. Furthermore, I would like to speak about what, in our way of thinking, are the proper methods of dealing with exams and school reports, so that they reflect knowledge of the human being.
|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture VIII
22 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture VIII
22 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In order to round off, so to speak, what we could only superficially outline during the last few days regarding education based on anthroposophical investigations, I would like to add something today, as an example of how these ideas can be put into practice, about how the Waldorf school is run. What has to emerge clearly from the spirit of this education is that equal consideration be given to everything pertaining to the human body, soul, and spirit. If the actual teaching is carried out as characterized, therefore, it will at the same time become a kind of hygiene in the life of the child and, if necessary, even a therapy. To see this clearly, one has to be able to look at the child's being in the right way. And here it must be understood that everything we have said about the child's development, from birth to the change of teeth, is revealed most of all in the activities of the nerve-sense system. Every organic system naturally extends over the entire human body, but each system is at the same time localized in a definite part of the physical organism. Thus the nervous system is mainly organized in the head. But when speaking about the three main organic systems of the human being—the nerve-sense system, the rhythmic system, and the metabolic-motor system—we do not imply that they are confined only to the head, the chest, and the metabolic-limb systems, because this would be completely inaccurate. It is impossible to divide the human organization into three separate spatial regions. It can only be said that these three systems interpenetrate one another, that they work and weave into each other everywhere. The nerve-sense system is, nevertheless, localized primarily in the region of the head. The rhythmic system, which includes everything of a rhythmic nature in the human being, is mainly organized in the chest organs, in the organs of breathing and blood circulation. Here one must not ignore the fact that everything that furthers the rhythms of digestion—and ultimately those of sleeping and waking—also belongs to the rhythmic system, insofar as digesting, and sleeping and waking are based physically within the human organism. The actual chemical-physiological process of digestion is closely connected with all that forms the human motor system. As for movement itself, a reciprocal activity occurs between the nutritional and digestive system on the one hand, and the actual physical movement on the other. All of this means that, although the three systems work naturally into each other during the child's early years until the change of teeth, the formative and malleable shaping forces involved in the child's growth and nourishing processes work mainly downward from the head, the center of the senses and the nervous system. Consequently, if a young child becomes ill, that illness is due primarily to the influences of the nerve-sense system. That is why young children before their second dentition are especially likely to suffer from illnesses that originate from within—those called childhood illnesses. The influences that emanate from the environment, those that reach children through their urge to imitate, have a very powerful effect on this vulnerability to childhood illnesses, more than is commonly realized by the medical profession within the current materialistic climate. Thus, a sudden outburst of anger by an adult, when witnessed by a young child, can be responsible in many cases for an attack of measles. I am not referring to the psychopathic outburst of a psychopath, but to a less violent form of temper that can very often be seen among people. The shock that follows, together with its moral and spiritual implications, must certainly be seen as a contributing factor for measles. Furthermore, all these influences that work on the child will remain as after-effects until almost the ninth year. If a teacher happens to become very angry in school (for example, if a child accidentally spills some ink, and the teacher reacts by shouting, “If you do that again, I'll pour the entire inkwell over your head!” or “I'll throw it at your head!”), then we shouldn't be surprised when this has a very damaging effect on the child's physical health. Of course, I have chosen a fairly drastic example, but this kind of thing can happen too easily in a classroom. Inner dishonesty in teachers also has a very harmful effect on children, even after their second dentition. Falsehoods can take on many different guises, such as insincerity or hypocritical piety, or establishing a moral code for the children that the adults would not dream of applying to themselves. In such cases the element of untruth weaves and lives in the words spoken, and in what unfolds in front of the child. An adult may remain totally oblivious to it, but children will take it in through the teachers' gestures. Through the nerve-sense system, dishonesty and hypocrisy have an extremely powerful effect on the organic structure of the child's digestive tract, and especially on the development of the gall bladder, which can then play a very significant role for the rest of the child's life. All pedagogical interactions have to be permeated by this intensive awareness of how spirit, soul, and body constantly interweave and affect each other, even though it is unnecessary for teachers to speak of it all the time. And since the human organism, from the head downward, is so active during these early years—that is, from the polarity of the nerve-sense system—and because abnormal conditions can easily override socalled normal conditions in the head region, the child is particularly vulnerable to childhood diseases at just this age. The years between the change of teeth and puberty, strangely enough (and yet, true to the nature of the human organism) are the child's healthiest years, although this is not really surprising to anyone with insight into human development. This is because the child's entire organic structure at this age radiates from the rhythmic system. This is the very system that never becomes tired or overstimulated on its own. Symptoms of illness that occur during these years are due to outer circumstances, although this statement must not be taken too strictly, of course, and only within the context of actual life situations. The child who is subject to illness at this particular age, when the rhythmic system plays such a dominant part has been treated improperly, one way or another, in outer life. When puberty is left behind, the occurrence of illness radiates outward from within—that is, from the metabolic-motor system. That is the time of life when the causes of illness, to which young people are exposed, arise from within. Because the method of teaching the actual lessons plays a large part in the physical well-being of the students, we must always allow a certain physical and soul hygiene to be carried, as if on wings, by our educational ideas and methods. This must always be part of whatever we do with our classes, particularly during the second period of childhood. Here certain details can be indicated. Let us take, for example, a child with a melancholic disposition. If you give that child sugar—an appropriate amount, of course—you will find that the sugar has a totally different effect than it would have on a predominantly sanguine child. In a melancholic child the sugar will have a suppressive effect on liver activity. This gradual lessening of liver activity, in radiating out into the entire being of the child, effectively curbs the melancholic tendencies from the physical side. It is a useful expedient, but one has to understand it. Using it as an aid does not mean the denial of soul and spirit, because anyone who knows that spirit is working in all physical or material processes—as anthroposophy reveals—will not view the effect of an increased sugar-intake on the activity of the liver as something merely physical, but as the working of soul and spirit brought about by physical means. (Naturally, the result always depends on the correct dosage.) In the case of a sanguine child it can be beneficial to stimulate liver activity by withholding sugar. This is an example of how knowledge of the interaction and mutual working of body, soul, and spirit can greatly benefit the three systems of the human being. It definitely allows one to say as well that, contrary to frequently held opinions, Waldorf pedagogy (which arises from spiritual foundations) certainly does not neglect the physical aspects of education. On the other hand, you will find that other forms of pedagogy, bent on developing the physical part of the child according to fixed, abstract rules indeed serve it least, because their adherents do not realize that every soul and spiritual stirring within a child has a direct effect on his or her physical nature. Because of all this, I felt it necessary to give a seminar course before the opening of the Waldorf school, for the benefit of those who had been chosen to become its first teachers.1 One of the primary aims of this course was to bring the fundamental and comprehensive thought of the working together of soul, body, and spirit into the new pedagogy before its actual launching; for knowledge of this has been lost gradually during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries—more so than is generally realized. During the years after the Waldorf school founding, shorter supplementary courses were also given.2 It goes without saying that anyone who seriously considers taking an active role in Waldorf education must live in the spirit of these courses. This is what really matters. If one wants to treat a certain subject in a living way, the details are not as important, because they can always be worked out of the spiritual background. The details will then also appear in proper perspective. You may already have seen, through talks given by Waldorf teachers such as Dr. von Baravalle3 and Dr. von Heydebrand,4 how the attempt was made to let the spirit living in this education flow into the ways of teaching various subjects. Something like lifeblood will pulse through the lessons when the human structure is comprehended in terms of an all-comprising spiritual entity. In this respect, of course, much of what can be said today will have to remain brief and superficial. I mentioned yesterday that a united faculty of teachers, functioning like the soul and spirit of the entire school organism, is absolutely fundamental to running a Waldorf school. According to one of its pedagogical impulses, it is not so much a statistical collection of the teachers' observations expressed during the meetings that is important, but that a living and individualizing psychology should be jointly developed from out of the actual experience of teaching lessons. I would like to give you an example. In our school, boys and girls sit next to each other. When we started, there were just over one hundred students in the Waldorf school. But our numbers have grown so quickly that we had seven hundred pupils last year, which necessitated opening parallel classes, especially in the lower grades of the school. Now we find that there are more girls than boys in some classes, while in others there are more boys. The number of boys and girls more or less even in very few classes. To insist on equal numbers in each class would not only be pedantic, but would not work. First of all, new arrivals do not come neatly paired, and, second, such a scheme would not represent real life. The right way to proceed in such a situation is to make it possible to apply educational impulses whatever the outer circumstances may be. All the same, we soon found that a class with a majority of girls presented a very different psychological picture than those with more boys, aside from outer circumstances—that is, aside from the most obvious. What gives such a class its psychological character is the imponderable element that easily escapes one's notice. Nevertheless, when working together in our meetings, the opportunity was presented to make fruitful investigations in this direction. And it soon became clear that sharing such questions of common interest greatly contributed to the school's becoming a living, ensouled organism. Let's imagine someone who says, “I want to think only thoughts that will be useful to me later in life. I don't want to allow anything to enter my soul that does not have direct value for later life, because this would be uneconomical.” Such a person would become an appalling figure in life! First, because such a person would have nothing to dream about—indeed, could never dream. Of course, people who are inclined in this direction might simply reply, “Dreams are unimportant. One can very well do without them, because they really don't mean anything in life.” True, dreams have little consequence for those who accept only external reality. But what if there were more to dreams than just fantastic images? Naturally, those who believe they see something highly significant and deeply prophetic in every dream, even if it is only caused by the activities of their liver, bladder, or stomach—people who consider dreams more important than events in waking life—they will not draw any benefit from their dreaming. Yet, if one knows that in one's dream life forces are expressed—even if only indistinctly—that have either a health-giving or an illness-inducing effect on the breathing, circulatory, and nerve-sense systems, then one also knows that half of the human being is mirrored in these dreams, either in a hygienic or in a pathological sense. Further, one will recognize that not to dream at all would be similar to undermining the digestion or circulation through taking some form of poison. It is important to realize that much of what may appear unnecessary in a human being for outer life, nevertheless, plays an important part—similar to the way we see outer nature. Just compare the infinite number of herring eggs, distributed all over the seas, with the number of herrings actually born, and you could easily reproach nature for being tremendously wasteful. However, this could only be the opinion of those who do not know of the powerful spiritual effects the dead herring eggs have on the growing herrings. A certain number of eggs have to die so that a certain number of eggs may thrive. These things are all interconnected. If we now relate this thought to the school as a living organism, we have the following situation: In the staff meetings of our teachers such matters as the proportion of boys to girls, and many other problems, are being worked through from a psychological and pneumatological aspect as part of a common study of soul and spirit. Efforts are made continually to effect a new understanding of the psychological and pathological problems facing the school. And, in order to cover every contingency, something else is essential in the life of a school, something we have in the Waldorf school, and that is a school doctor. He is a full-time staff member, who also teaches various classes in the school. This allows the teachers—insofar as they actively take part in all the meetings—to discuss and work through pathological and therapeutic questions, as well as those posed by the specially gifted child. Problems are studied not only for the benefit of individual cases—more or less statistically—but they are worked through in depth. In this way, much can be learned from each individual case, even if it does not always appear to be immediately useful. One could compare this situation with someone who has taken in one thing or another, and declares it to be of no use in life. Nevertheless, life may prove otherwise. Similarly, whatever is worked through by the teachers in these meetings, creating a living psychology, a living physiology, and so on, continues to have an effect, often in very unexpected places. Imagine you had occupied yourself, let's say, with the spiritual functions of a child's gall—forgive this expression, but it is fully justified—and that through this study you had learned to find a way into this kind of thinking. If you were now suddenly called on to deal with a child's nose, you actually would relate very differently to the new situation. Even if you may think, “What is the good of learning all about the gall if now I have to deal with the nose?” Once you find a point of entry, you meet every problem and task differently. In this sense, the teaching faculty must become the spirit and soul of the entire school organism. Only then will each teacher enter the classroom with the proper attitude and in the right soul condition. At the same time, we must also remember that, in just these matters, an intensely religious element can be found. It is unnecessary to have the name of the Lord constantly on one's lips or to call on the name of Christ all the time. It is better to adhere to the command: “Thou shalt not take the name of the Lord God in vain.” Nevertheless, it is possible to permeate one's entire life with a fundamental religious impulse, with an intensely Christian impulse. Certain experiences of old, no longer known to the modern mind, will then begin to stir in one's soul, experiences deeply rooted in human evolution, in the Christian development of humankind. For example, teachers who in the depths of their souls are seeking the proper stimulation for finding appropriate forms of pedagogy (especially in these pathological-physiological areas) would do well to allow themselves to be inspired, time and again, by what radiates from the Gospel of Saint Luke. (To modern ears such a statement must sound bizarre.) On the other hand, teachers who want to instill the necessary idealism for life in their students, would do well to find a source of inspiration by reading again and again the Gospel of Saint John. If teachers do not want their pupils to grow up into cowards, but into the kind of people who will tackle life's tasks with exuberant energy, they should look for inspiration in the Gospel of Saint Mark. And those who are enthusiastic to educate the young to grow into perceptive adults, rather than into people who go through life with unseeing eyes, may find the necessary stimulation in the Gospel of Saint Matthew. These are the qualities that, in ancient times, were felt to live in the different Gospels. If our contemporaries were to read that in past ages the Gospel of Saint Luke was felt to radiate a healing element in a medical sense, they could not make anything of it. On the other hand, if they entered life as real pedagogues, they would begin to understand such matters again. This is one way one can speak about these things. It is just as possible to speak of them in an entirely different way, no less religious or Christian. For instance, the main theme during a seminar course could well be the four temperaments of the human being—that is, the psychic, physical, and spiritual natures of the choleric, melancholic, sanguine, and phlegmatic temperaments. First, one would give a description of these four temperaments and then one could discuss how they must be treated in class. For example, it has a salutary effect if one seats choleric children together in one corner of the classroom, giving a certain relief in this way to the rest of the class, because the teacher is freed from having to constantly discipline them. Choleric children can't help pushing and hitting each other. If they now find themselves suddenly at the receiving end, this in itself produces a thoroughly pedagogical effect, because the ones who do the pushing and shoving, goading others into retaliating, are being “shaped up” in a very direct way. And if, by seating the phlegmatics together, one lets them “phlegmatize” each other, this also has a wonderfully pedagogical effect. However, all this needs to be done with the appropriate tact. One really has to know how to handle the situation in each individual case. You will find a detailed treatment of the children's various temperaments in the published version of the first training course, given to the teachers of the Waldorf school.5 What I have said about the four Gospels, fundamentally speaking, is exactly the same when seen from a spiritual perspective, because it leads one into the same element of life. Today it is ordinarily felt that, if one wants to learn something, the relevant elements have to be put neatly side by side. But this is a procedure that will not lead to fundamental principles, as they have to be dealt with in actual life. For example, one cannot understand the human gall or liver system unless one also has an understanding of the human head, because every organ in the digestive tract has a complementary organ in the brain. One does not know anything about the liver unless one also knows its correlative function in the brain. Likewise, one does not have an inner understanding of the immense inspiration that can flow into the human soul from the Gospels, unless one can also transform these into the ways that character and temperament are imprinted into the human individuality here on Earth. To livingly comprehend the world is very different from comprehending it through dead concepts. This will also help one to see that if children are raised in light of the education spoken of here, one allows something to grow in them that will outlast their childhood days, something that will continue to affect them throughout their lives; for what do you have to do when you grow old? People who do not understand human nature cannot assess how important certain impulses, which can be implanted only during childhood, are for life. At that tender age it is still possible for these impulses to be immersed into the soft and pliable organism of the child, still very open to the musical-formative forces. In later years the organism becomes harder, not necessarily physically, but in any case, tending toward psycho-bodily hardening. What one has absorbed through one's upbringing and education, however, does not grow old. No matter how old one has become, one is still inwardly endowed with the same youthful element that one had from, say, the tenth to the fifteenth year. One always carries this element of youthfulness within, but it has to remain supple and flexible to the degree that the now aged brain—perhaps already covered by a bald head—can use it in the same way that the previously soft brain did. If a person's education has not helped this process, however, the result is a generation gap, which appears so often these days, and is considered unbridgeable. Sometimes people say something that is actually the opposite of what is really happening. For example, one often hears the comment, “The young today don't understand the elderly, because old people no longer know how to be young with the young.” But this is not the truth. Not at all. What really happens is that the young generation expects the old generation to be able to properly use the physical organization which has grown old. In this way, young people recognize something in the old that is different from their own condition, something they do not yet have. This is the quality that leads to the natural respect for old age. When young people meet an old person who can still use an already-bald head in the way children use their tousled heads, they feel that something can be received from the older generation, something that they cannot find in their contemporaries. This is how it should be. We must educate young people so that they know how to grow old properly. It is the malaise of our time that as young people grow up, they do not recognize among the older generation those who have aged properly. They see merely childish individuals, instead, who have remained at the same level of development as the young generation. This is because of the inadequate education of old people who cannot properly use their physical organization, and they remain infantile. The expression “overgrown kids” is really chosen with great ingenuity, for it implies that such persons lost the ability to get hold of their entire organism during the course of their lives.6 They can work only with the head, which is precisely what children or young people are meant to do. So the young respond by saying, “Why should we learn from them? They are no further along than we are; they are just as childish as we are.” The point is not that old age lacks youthfulness, but that it has remained behind, is too infantile, and this causes difficulties today. You see how expressions, sometimes chosen with the most goodwill, mean the opposite of what they intend convey.7 These things must all be seen in the proper light before education can stand on its feet again. This has become more than necessary today. Forgive this somewhat drastic way of saying it, but in our intellectual age education really has been turned upside-down. Thus, one of the characteristic features of Waldorf pedagogy is to learn that it is not the externals that are important. Whether a teacher draws substance to nourish the souls of students from the different qualities of the four Gospels, or whether this is done by using what was presented in the Stuttgart teachers' training course with regard to the four temperaments does not matter at all. What does matter is the spirit that reigns in everything developed there. Because of how superficially these things are often regarded today, it could easily happen that someone, when told that the treatment of the four temperaments could be studied in the fundamental course given in Stuttgart, could also consult a later course where one would find something about the teacher's attitude toward the four Gospels. The reaction of such a person might well be, “In this case, I should study the later course as well.” It certainly is a good thing to approach different subjects by using different sources. But there is also another way of looking at it—that is, one may find a common message running through both courses, given in two different places at different times, even though outwardly the subjects may appear very different. This inner correspondence found within different lecture courses can be uncomfortable because of the way their various points are interlinked, instead of fitting into the more conventional patterns of cause and effect. Thus, the educational course given here at the Goetheanum just over a year ago (where some English friends were present, and which was rendered very competently and artistically by Mister Steffen)8 can be compared with what I presented to you again differently in this course.9 You will find that, basically, the substance of both courses is the same as, for example, the head and the stomach; each form a part of one organism. It may be uncomfortable that, because of how various themes mutually support each other, one cannot say: I have read and understood the first course; and because the later one is supposed to carry the same message, there is no need for me to study it as well. The fact is, however, that, if one has studied both courses, the earlier one will be understood in greater depth, because each sheds light on the other. It could even be said that, only when one has digested a later teachers' course, can one fully understand an earlier one because of these reciprocal effects. Mathematics is built on purely causal sequences, so it is possible to understand earlier stages without any knowledge of subsequent stages. But when it comes to teaching in a living way, its subject is affected by mutual interconnections, so that what was given at an earlier date may receive further elucidation by what was presented later. I mention this because it is all part of the living spirit that has to permeate the Waldorf way of teaching. One has to have the good will that wants to know it from all sides, and one must never be satisfied with having comprehended one particular aspect of it. As a Waldorf teacher, one has to be conscious of the necessity for continually widening and deepening one's knowledge, rather than feeling satisfied with one's achievements and, indeed, considering oneself very clever. If one has lived into the Waldorf way of teaching, such delusions are soon overcome! For a real Waldorf teacher, everything that flows from this activity must be permeated with true heart and soul forces. It has to spring from the right kind of self-confidence, which rests on trust in God. When there is awareness of the divine forces working within, one will be fed by a constantly flowing fountain of life, flowing since time beyond memory, and very much apart from what one may or may not have learned externally. It is only the beginning of the way when self-confidence stems from outer achievements. One is in the proper place when self-confidence has led to confidence in the working of God, when it has led to an awareness of the power of the words: Not I, but the Christ in me. When this happens, self-confidence also becomes self-modesty, because one realizes that the divine forces of Christ are reflected in whatever is carried in one's soul. This spirit must reign throughout the school. If it were not present, the school would be like a natural organism whose lifeblood was being drawn out, or that was slowly being asphyxiated. This is the spirit that is most important, and if it is alive, it will engender enthusiasm, regardless of the staff or the leadership of the school. One can then be confident that a somewhat objective spirit will live throughout the school, which is not the same as the sum of the teachers' individual spirits. This, however, can be nurtured only gradually within the life of the teaching staff. As a result of working in this way, something has emerged in the Waldorf school that we call “block periods” or “main lessons.” These main lessons—much longer than the ordinary lessons, which allow one subject to be studied in depth—do not distract children, as often happens because of too many subject changes. For example, students might typically be given a geography lesson from 8 to 8:45 A.M., followed by an entirely different subject, such as Latin, from 8:45 until 9:30 A.M. This might be followed again by math, or some other lesson. Block periods of main lessons, on the other hand, are structured so that the same subject is taught every day for about three or four weeks (depending on the type of subject) during the first half of the morning session. For example, in a main lesson period, geography would be studied for perhaps three or four weeks—not severely or in a heavy-handed way, but in a more relaxed, yet completely serious way. When the same subject is taken up again during one of the following terms, it will build on what was given during the previous block period. In this way, the subject matter covered during one year is taught in block periods instead of during regular weekly lessons. This method is, no doubt, more taxing for teachers than the conventional schedule arrangements would be, because such lengthy geography lessons could easily become boring for the children. This is solved by the teachers' much deeper immersion in the subjects, so that they are equal to their freely-chosen tasks. After a mid-morning break, which is essential for the children, the main lesson is usually followed by language lessons, or by other subjects not taught in main lesson periods. Two foreign languages are introduced to our pupils as soon as they enter the first grade in a Waldorf school. Using our own methods, we teach them French and English—the aim not being so much a widening of their outer horizons, but an enrichment of their soul life. You will ascertain from what was said yesterday that physical movement, practiced most of all in eurythmy and gymnastics, is by no means considered to be less important, but is dealt with so that it can play a proper role within the total curriculum. Similarly, right from the beginning in the first grade, all lessons are permeated by a musical element according to various ages and stages. I have already indicated (with unavoidable briefness, unfortunately) how our pupils are being directed into artistic activities—into singing, music-making, modeling, and so on. It is absolutely necessary to nurture these activities. Simply through practicing them with the children, one will come to realize exactly what it means for their entire lives to be properly guided musically during these younger years, from the change of teeth through the ninth and twelfth years until puberty. Proper introduction to the musical element is fundamental for a human being to overcome any hindrance that impedes, later in life, a sound development of a will permeated with courage. Musical forces effect the human organism by allowing, as smoothly as possible, the nerve fluctuations to become active in the stream of breath. The breath-stream, in turn, works back upon the functions of the nervous system. The breathing rhythms then work over into the rhythms of the blood circulation, which in turn act on the rhythms of sleeping and waking. This insight, afforded by anthroposophical investigation, of how musical forces creatively work within the structure of the human being, is one of the most wonderful things in life. One learns to recognize that we have an extremely sensitive and refined musical instrument in the raying out of the nerves from the spinal marrow, from the entire system of the spinal cord. One also learns to see how this delicate instrument dries up and hardens, whereby, inwardly, the human being can no longer properly develop qualities of courage, if musical instruction and the general musical education do not work harmoniously with this wonderfully fine musical instrument. What constitutes a truly delicate and unique musical instrument is coming into being through the mutual interplay between the organs of the nerves and senses with their functions on the one hand, and on the other hand, the human motor functions with their close affinities to the digestive rhythms and those of sleeping and waking. The upper part of the human being wants to influence the lower part. By directing the child's entire organism toward the realm of music, we enhance the merging of external sounds (from a piano during music lessons, or from the children's singing voices) with the nervous and circulatory systems, in what can be recognized as a divine plan of creation. This is a sublime thing, because in every music lesson there is a meeting between the divine-spiritual and what comes from the earthly realm, rising, as it were, within the child's body. Heaven and Earth truly meet in every achievement of musical culture throughout human earthly evolution, and we should always be aware of this. This awareness, plus the teachers' knowledge that they are instrumental in bringing together the genius of Heaven with the genius of Earth, gives them the enthusiasm they need to face their classes. This same enthusiasm is also carried into the teachers' staff meetings where the music teacher may inspire the art teacher, and so on. Here you can see clearly how essential it is that spirit works through every aspect of Waldorf education. To give another example: not long ago, during one of our teacher meetings, it truly became possible to work out to a large extent what happens to the students' spirit, soul, and body, when first given eurythmy exercises and then directed in doing gymnastics. Such insight into the relationship between gymnastics and eurythmy (which is very important to how these lessons are presented) was really accomplished in one of our teacher meetings the other day. Of course, we will continue our research. But, this is how teacher meetings become like the blood that must flow through the school as a living organism. Everything else will fall into place, as long as that is allowed to happen. Teachers will know also when it is proper to take their classes for a walk or for an outing, and the role of gymnastics will find a natural and appropriate place within the life of the students, regardless of which school they attend. Doubts and anxieties will disappear with regard to the remark: What is done in a Waldorf school may all be very good, but they neglect sports there. Admittedly, it is not yet possible for us to do everything that may be desirable, because the Waldorf school has had to develop from small beginnings. Only by overcoming enormous obstacles and external difficulties was it possible to have gone as far as we have today. But when matters are taken care of with spiritual insight, the whole question of the relationship between physical and spiritual will be handled properly. The following analogy could be used: Just as it is unnecessary to learn how the various larger and smaller muscles of the arm function (according to the laws of dynamics and statics, of vitalism, and so on) so that one can lift it, so it is also unnecessary to know every detail of the ins-and-outs of everything that must be done, as long as we can approach and present lessons out of the spirit that has become transformed into the proper attitude of the teacher—as long as we can penetrate properly to the very essence of all our tasks and duties. I could only give you brief and superficial outlines of the fundamental principles and impulses, flowing from anthroposophical research, according to which the Waldorf school functions. And so we have come to the end of this course—primarily because of your other commitments. At this point I would like to express once more what I already said during one of our discussions: If one lives with heart and soul, with the ideal of allowing education to grow into a blessing for all humankind in its evolution, one is filled with deep gratitude when meeting teachers from so many different places; for you have come to this course to obtain information about the way of teaching that arises from anthroposophical investigation, which I have attempted to place before you. Beyond whether this was received by one or another participant with more or less sympathy, I want to express my deep gratitude and inner satisfaction that it was again possible for a large group of souls to perceive what is intended to work on the most varied branches of life, and what is meant to fructify life in general through anthroposophy. Two thoughts will remain with you, especially with those who dealt with the organization and practical arrangements of this course: the happy memory of the gratitude, and the happy memory of the inner satisfaction as I expressed it just now. And the more intensely these thoughts can be inwardly formed—the thoughts of the work based on such gratitude and satisfaction—the more hope will grow that, in times to come, this way of teaching may yet succeed for the benefit of all of humanity. Such hope will intensify the loving care for this way of teaching in those who already have the will to devote themselves to it with all their human qualities. It should also be said that it was not only the Waldorf teachers who may have given you something of their practical experience, because those of you who have been present here as visitors have certainly given equally to them. By allowing us to witness what lives in us begin to live in other souls as well, you have fanned the glow of love that is both necessary and natural, and just that can engender genuine enthusiasm. And we may hope that out of feelings of gratitude and inner satisfaction, of hope and love that have flowed together during this course, good fruits may ripen, provided we can maintain the necessary interest in these matters, and that we are inwardly active enough to sustain them. Ladies and gentlemen, my dear friends, this is what I want to pour into my farewell, which is not to be taken as formal or abstract, but as very concrete, in which gratitude becomes a firm foundation, and inner satisfaction a source of warmth, from which hope will radiate out, bringing both courage and strength. May the love of putting into practice what is willed to become a way of teaching for all human beings be turned into light that shines for those who feel it their duty to care for the education of all humankind! In this sense, having to bring this course to its conclusion, I wish to give you all my warmest farewell greetings. Question: Would it be possible to implement the Waldorf way of teaching in other countries, in Czechoslovakia, for example? Rudolf Steiner: In principle it is possible to introduce Waldorf education anywhere, because it is based purely on pedagogy. This is the significant difference between Waldorf pedagogy and other educational movements. As you know, there are people today who maintain that if one wants to give pupils a proper education, one must send them to a country school, because they consider an urban environment unsuitable for children's education. Then there are those who hold the opinion that only a boarding school can offer the proper conditions for their children's education, while still others insist that only life at home can provide the proper background for children. All of these things cease to be of real importance in Waldorf education. I do not wish to quarrel about these different attitudes (each of which may have its justification from one or another point of view), but since Waldorf education focuses entirely on the pedagogical aspect, it can be adapted to any outer conditions, whether a city school, a country school or whatever. It is not designed to meet specific external conditions, but is based entirely on observation and insight into the growing human being. This means that Waldorf pedagogy could be implemented in every school. Whether this would be allowed to happen, whether the authorities that oversee education, the establishing of curricula, and so on would ever agree to such a step being taken, is an entirely different question. There is nothing to stop Waldorf pedagogy from being applied anywhere in the world, even tomorrow, but the real question is whether permission for this to happen would be granted. This question can be answered only in terms of the various local government policies. That is really all one can say about it.
|
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture I
21 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture I
21 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
We may take it as obvious that only a very small proportion of what my present hearers probably expect for the future of their professional life can be indicated in this series of lectures; for you will all agree that any confidence in the future among medical workers depends on the reform of the actual medical curriculum. It is impossible to give any direct impetus to such reform by means of a course of lectures. The most that may possibly result is that certain individuals will feel the urge to help and participate in such reform. Any medical subject under discussion today has, as its background, those initial studies in anatomy, physiology and general biology, which are the preliminaries to medicine proper. These preliminaries bias the medical mind in a certain direction from the first; and it is absolutely essential that such bias should be rectified. In this series of lectures I should like, in the first place, to submit to you some facts bearing on the obstacles in the customary curriculum to any really objective recognition of the nature of disease per se. Secondly, I would suggest the direction in which we should seek that knowledge of human nature which can afford a real foundation for medical work. Thirdly, I would indicate the possibilities of a rational therapy based on the knowledge of the relationship between man and the surrounding world. In this section I would include the question whether actual healing were possible and practicable. Today I shall restrict myself to introductory remarks, and to a kind of orientation. My principal aim will be to collect for consideration from Spiritual Science all that can be of value to physicians. It is my wish that this attempt should not be confused with an actual medical course, which it nevertheless will be in a sense. But I shall give special attention to everything that may be of value to the medical worker. A true medical science, or art, if I may call it so, can only be attained by consideration of the factors to which I have referred. Probably you have all, in thinking over the task of the physician, been baffled by the question: “What does sickness mean and what is a sick human being?” The most usual definition or explanation of sickness in general and of sick people, is that the morbid process is a deviation from the normal life process; that certain facts which affect human beings, and for which normal human functions are not in the first place adapted, cause certain changes in the normal life process and in the organisation; and that sickness consists in the functional deficiency of the organs caused by such changes. But you must admit that this is a merely negative definition. It offers no help when we are dealing with actual diseases. It is just this practical help that I shall aim at here, help in dealing with actual diseases. In order to make things clear it seems advisable to refer to certain views, which have developed in the course of time, as to the nature of disease; not as indispensable for the present interpretation of morbid symptoms, but as signposts showing the way. For it is easier to recognise where we are now if we appreciate former points of view which led up to those now current. The accepted version of the origin of medicine derives it from the Greece of the fifth and fourth centuries before the Christian era, when the influence of Hippocrates was supreme. Thus an impression is produced that the system of Hippocrates—which developed into the Humoral pathology accepted until well into the nineteenth century—was the first attempt at medicine in the Occident. But this is a fundamental error, and is still harmful as a hindrance to an unprejudiced view of sickness. We must, to begin with, clear this error away. For an unbiased view the conceptions of Hippocrates which even survived until the time of Rokitansky, that is until the last century—are not a beginning only, but to a very significant degree are a conclusion and summary of older medical conceptions. In the ideas which have come down to us from Hippocrates we meet a final filtered remainder of ancient medical conceptions. These were not reached by contemporary methods, i.e., through anatomy, but by the paths of ancient atavistic vision. The most accurate abstract definition of Hippocratic medicine would be: the conclusion of archaic medicine based on atavistic clairvoyance. From an external point of view, we may say that the followers of Hippocrates attributed all forms of sickness to an incorrect blending of the various humours or fluids which co-operate in the human organism. They pointed out that these fluids bore a certain ratio to one another in a normal organism, and that this ratio was disturbed in the sick human body. They termed the healthy mixture or balance Krasis, the improper mixture Dyskrasis. The latter had to be influenced so that the proper blend might be restored. In the external world, they beheld four substances which constituted all physical existence: Earth, Water, Air and Fire—Fire meaning what we describe simply as warmth. They held that these four elements were specialised in the bodies of man and the animals, as black bile, yellow bile, (gall) mucus (slime), and blood, and that the human organism must therefore function by means of the correct blending of these four fluids. The contemporary man with some kind of scientific grounding, who considers this theory, argues as follows: the blending and interaction of blood, mucus, bile and gall, in due proportion, must produce an effect according to their inherent qualities known to chemistry. And this restricted view is thought to be the essence of Humoral pathology; but erroneously. Only one of the four “humours,” the most Hippocratic of all—as it appears to us today—namely “black bile” was believed to work through its actual chemical attributes on the other “humours.” In the case of the remaining three fluids, it was believed that besides the chemical properties there were certain intrinsic qualities of extra-telluric origin. (I am referring to the human organism for the moment, excluding animals from consideration.) Just as water, air and fire were believed to be dependent on extra-telluric forces, so also these ingredients of the organism were believed to be inter-penetrated with forces emanating from beyond the earth. In the course of evolution, western science has completely lost this reference to extra-terrestrial forces. For the scientist of today, there is something absolutely grotesque in the suggestion that water possesses not only the qualities verifiable by chemical tests, but also, in its action within the human organism, qualities appertaining to it as a part of the extra-terrestrial universe. Thus the Ancients held that the fluids of the human body carried into the organism forces derived from the cosmos itself. Such cosmic forces were regarded less and less as the centuries went on; but nevertheless medical thought was built up on the remains of the fading conceptions of Hippocrates until the fifteenth century. Contemporary scientists therefore have great difficulty in understanding pre-fifteenth century treatises on medical subjects; and we must admit that the writers of these treatises did not, as a rule, themselves fully comprehend what they wrote. They talked of the four elements of the human organism, but their special description of these elements was derived from a body of wisdom that had really perished with Hippocrates. Nevertheless, the qualities of these fluids were still matters of discussion and dispute. In fact, from the time of Galen till the fifteenth century, we find a collection of inherited maxims that become continuously less and less intelligible. Yet there were always isolated individuals able to perceive that there was something beyond what could be physically or chemically verified, or included in the merely terrestrial. Such individuals were opponents of what “humoral pathology” had become in current thought and practice. And chief among them were Paracelsus and Van Helmont, who lived and worked from the end of the fifteenth century into the seventeenth, and contributed something new to medical thought, by their attempts to formulate something their contemporaries no longer troubled to define. But the formulation they gave could only be fully understood with some remainder of clairvoyance, which Paracelsus and Van Helmont certainly possessed. If we ignore these facts, we cannot arrive at any conclusion concerning peculiarities of medical terminology whose origin is no longer recognisable. Paracelsus assumed the existence of the Archaeus, as the foundation for the activity of the organic “humours” in man; and his followers accepted it. He assumed the Archaeus, as we today speak of the “Etheric” body of man. Whether we use the term Archaeus, as Paracelsus did, or our term, the etheric body, we refer to an entity which exists but whose origin we do not trace. If we were to do this, our argument would be as follows: Man possesses a physical organism (see Diagram No. 1) mainly constructed by forces acting out of the sphere of the earth; and also an etheric organism (Diagram No. 1 in Red) mainly constructed by forces acting from the cosmic periphery. Our physical body is a portion as it were of the whole organism of our Earth. Our etheric body—like the Archaeus of Paracelsus—is a portion of that which does not belong to the earth, but which acts on and affects the earth from all parts of the cosmos. Thus Paracelsus viewed what was formerly designated the cosmic element in man—of which the knowledge had perished with Hippocratic medicine—in the form of an etheric body, which is the basis of the physical. But he did not investigate further—though he gave some hints—the extra-terrestrial forces associated with the Archaeus and acting in it. 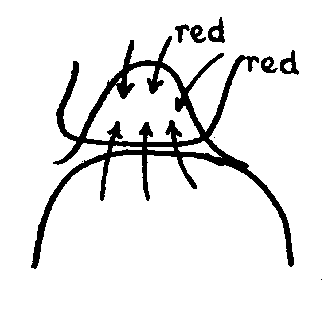 The exact significance of such facts grew more and more obscure, especially with the advent of Stahl's medical school in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Stahl's school has wholly ceased to comprehend this working of cosmic forces into terrestrial occurrences; it grasps instead at vague concepts such as “vital force” and “spirits of life.” Paracelsus and Van Helmont were consciously aware of the reality at work between the soul and spirit of man and his physical organisation. Stahl and his followers talk as though the conscious soul-element was at work, though in another form, upon the structure of man's body. This naturally provoked a vehement reaction. For if one proceeds like this and founds a sort of hypothetic vitalism one comes to purely arbitrary assertions, and the nineteenth century opposed these assertions. Only a very great mind, like Johannes Müller (the teacher of Ernst Haeckel), who died in 1858, was able to overcome the noxious effects of this confusion, a confusion of soul forces with “vital forces” which were supposed to work in the human organism, although how they operated was not very clear. Meanwhile a quite new current made its appearance. We have followed up the other current which faded out; the new current in the nineteenth century had a rather different bearing upon medical thought. It was set in motion by one extremely influential piece of work dating from the preceding century: the De sedibus et causis morborum per anatomen indugatis by Morgagni. Morgagni was a physician of Padua, who introduced an essentially materialistic trend into medicine; the term materialism is used here, of course, as an objective description, without sympathies and antipathies. The new trend initiated by Morgagni's work consisted in turning the interest to the after-effect of disease upon the organism. Post-mortem dissections were regarded as decisive; they revealed that whatever the disease may have been, typical effects could be studied in certain organs, and the changes of the organs by disease were studied from the autopsy. With Morgagni, pathological anatomy begins, whereas the former content of medicine still retained some traces of the ancient element of clairvoyance. It is of interest to observe the suddenness with which this great change finally occurred. The volte-face took place within two decades. The ancient inheritance was abandoned and the atomistic-materialistic conception in modern medicine was founded. Rokitansky's Pathological Anatomy (published in 1842) still contains some traces of the “Humoral” tradition; of the conception that illnesses are due to the abnormal interaction of the fluids. Rokitansky achieved a brilliant combination of the study of organic change, with a belief in the importance of the fluid (humours); but it is impossible to consider these bodily fluids adequately without some recognition of their extra-terrestrial qualities. Rokitansky referred the degenerative changes revealed in autopsies to the effect of the abnormal mixture of the bodily fluids. Thus the last visible trace of the ancient tradition of “Humoral pathology” was in the year 1842. The interlocking of this perishing heritage of the past with attempts such as Hahnemann's—attempts forecasting future trends of dealing with more comprehensive concepts of disease—we shall consider in the next few days, for this subject is far too important to be relegated to an introduction. Similar experiments must be discussed in their general connection and then in detail. The two decades immediately following the appearance of Rokitansky's book were decisive for the growth of the atomistic-materialistic conception in medicine. In the first half of the nineteenth century there were curious echoes of the ancient conceptions. Thus, for example, Schwann may be termed the discoverer of the vegetable cell; and he believed that cells were formed out of a formless fluid substance to which he gave the name Blastem, by a process of solidification, so that the nucleus emerges together with the surrounding protoplasm. Schwann derived cells from a fluid with the special property of differentiation, and believed that the cell was the result of such differentiation. Later on the view gradually develops that the human frame is “built up” of cells; this view is still held today; the cell is the “elementary organism,” and from the combination of cells, the body of man is built up. This conception of Schwann's, which can be read “between the lines” and even quite obviously, is the last remainder of ancient medical thought, because it is not concerned with atomism. It regards the atomistic element, the cell, as the product of a fluid which can never properly be considered as being atomistic—a fluid which contains forces and only differentiates the atomistic from itself. Thus in these two decades, the forties and fifties of the nineteenth century, the older, more universal view approaches its final end, and the atomistic medical view shows its faint beginnings. And it has fully arrived when, in 1858, appeared the Zellular Pathologie (Cellular Pathology) of Virchow. Between Pathologischen Anatomie, 1842, by Rokitansky and Zellular Pathologie, 1858, by Virchow one must actually see an immense revolution—proceeding in leaps and bounds—in the newer medical thinking. Cellular Pathology derives all the manifestations of the human organism from cellular changes. The official ideal henceforth consists in tracing every phenomenon to changes in the cells. From the change in the cell the disease is supposed to be understood. The appeal of this atomism is its simplicity. It makes everything so easy, so evident. In spite of all the progress of modern science, the aim is to make everything quickly and easily understood, regardless of the fact that nature and the universe are essentially extremely complex. For example: It is easy to demonstrate through a microscope that an Amoeba, in a drop of water, changes form continuously, extending and retracting its limb-like projections. It is easy to raise the temperature of the water, and to observe the greater rapidity with which the pseudo-podia protrude and retract, until the temperature reaches a certain point. The amoeba contracts and becomes immobile, unable to meet the change in its environment. Now, an electric current can be sent through the water, the amoeba swells like a balloon, and finally bursts if the voltage becomes too high. Thus it is possible to observe and record the changes of a single cell, under the influence of its environment; and it is possible to construct a theory of the origin and causation of disease, through cumulative cellular change. What is the essential result of this revolution which took place in two decades? It lives on in everything that permeates the acknowledged medical science of today. It is the general tendency to interpret the world atomistically which has gradually arisen in the age of materialistic thought. As I stated at the beginning of this address, the medical worker today must of necessity inquire: What sort of processes are those we term diseased? What is the essential difference between the diseased and the so-called normal processes in the human organism? Only a positive representation of this deviation is practicable, not the official and generally accepted definitions, which are merely negative. These deviations from normality are stated to exist, and then there are attempts to find how they may be removed. But there is no penetrating conception of the nature of the human being. And from the lack of such a conception our whole medical science is suffering. For what, indeed, are morbid processes? It cannot be denied that they are natural processes, for you cannot make an abstract distinction between any external natural process, whose stages can be observed, and a morbid process within the body. The natural process is called normal, the morbid one abnormal, without showing why the process in the human organism differs from normality. No practical treatment can be attained without finding out. Only then can we investigate how to counter-balance it. Only then can we find out from what angle of universal existence the removal of such a process is possible. Moreover, the term “abnormal” is an obstacle to understanding; why should such-and-such a process in man be termed abnormal? Even a lesion, such as a wound or deep cut with a knife, in the finger, is only relatively “abnormal,” for to cut a piece of wood is “normal.” That we are accustomed to other processes than the cutting of a finger says nothing; it is only playing with words. For what happens through the cutting of my finger is, when viewed from a certain angle, as normal as any other natural process. The task before us is to investigate the actual difference between the so-called diseased processes, which are after all quite normal processes of nature, but must be occasioned by definite causes, and the other processes, which we call healthy and which occur every day. We must ascertain this essential difference; it cannot, however, be ascertained without a knowledge of man which leads to his essential being. I shall give you, in this introduction, the first elements; we shall later on proceed to the details. As these lectures are limited in number, you will understand that I am principally giving things which you cannot find in books or lectures and am assuming the knowledge presented in those sources. It would not seem to me worth while to put a theory before you, which you could find stated and illustrated elsewhere. Let us therefore begin here with a simple visual comparison which you can all make: the difference between a human skeleton and that of a gorilla, an ape of so-called high grade. Compare the visible outlines and proportions of these two bony frameworks. The most conspicuous feature of the gorilla, in point of size, is the development of the lower jaw and its appurtenances. This enormous jaw seems to weight down, to overload, the whole bony structure of the head (see Diagram 2), so that the gorilla appears to stand upright only with an effort. But there is the same weightiness in comparison with the human skeleton, if you examine the forearms and hands and fingers. They are heavy and clumsy in the gorilla; whereas in man they are delicate and frail; there the mass is less obvious. Just in these parts, the system of the lower jaws and forearms with the fingers, the mass recedes in man, whereas it is very obvious in the gorilla. The same comparative peculiarities of structure can be traced in the lower limbs and feet of the two skeletons. There, too, we find a certain weight pressing in a definite direction. I should like to denote the force which one can see in the systems of underjaw, arm, leg, foot—by means of this [e.Ed: down and left slanting arrow.] line in the diagram. (See Diagram 3).   These differences in structure suggest to the observer that in human beings, where the weight of the jaws recede and the arms and finger bones are delicate, the downward pressing forces are countered everywhere by a force directed upwards and away from the earth. The formative forces in man must be represented in a certain parallelogram of forces which results from the same force which is directed upwards and which the gorilla appropriates externally only, standing upright with difficulty. I then arrive at a parallelogram of forces that is formed by this line and by this one. (See Diagram 4).  As a rule nowadays we are content to compare the bones and muscles of the higher animals with our own, but to ignore the changes in form and posture. Yet the contemplation of the formative changes is of essential significance. There must be certain forces acting against those other forces which mould the typical gorilla frame. They must exist. They must operate. In seeking them we shall find that which has been lost inasmuch as the ancient medical wisdom has been filtered from the system of Hippocrates. The first set of forces in the parallelogram are of a terrestrial nature, while the other set of forces which unite with the terrestrial forces so as to form a resultant which is not of terrestrial origin, must be sought outside the terrestrial sphere. We must search for tractive forces which bring man into the upright posture, not merely on occasion, as among the higher mammals, but so that these forces are at the same time formative. The difference is obvious: the ape if he walks upright has to counteract forces which oppose the erection with their mass; whereas man forms his very skeleton in accordance with forces of a non-terrestrial nature. If one not only compares the particular bones of the man with those of the animal, but examines the dynamic principle in the human skeleton, one finds that there is something unique and not to be found in the other kingdoms of nature. Forces emerge that we have to combine with the others to make the parallelogram. We find resultants not to be found among the forces of extra-human nature. Our task will be to follow up systematically this “jump” leading from animal to man. Then we can find the origin and essence of “sickness” in animals as well as in man. I can only indicate little by little these lines of inquiry; we shall find much of importance from these elements as we continue further. Now let me mention another fact, which concerns the muscular system. There is a remarkable difference in muscular reactions; when in repose, the chemical reactions of the muscles are alkaline, though very slightly so in comparison with most other alkaline reactions. When in action, the muscular reactions are acid, though also faint. Now consider that from the point of view of metabolism the muscle is formed out of assimilated material, that is, it is a result of the forces present in terrestrial substances. But when man passes to action the normal properties of the muscle, as a substance affected by ordinary metabolism, are overcome. This is quite evident. Changes take place in the muscle itself, which are different from ordinary metabolic processes, and can only be compared with the forces active in the human bone-system. Just as these formative forces in man transcend what he has from outside, inter-penetrating terrestrial forces and uniting with them so that a resultant arises, so we must recognise the force that is manifested through the altered metabolism of muscles in action, as something working chemically from outside the earth into terrestrial chemistry. Here we have something of an extra-terrestrial nature, which works into earthly mechanics and dynamics. In metabolism there is something active beyond terrestrial chemistry, and capable of other results than those caused by terrestrial chemistry alone. Those considerations, which are concerned both with forms and qualities, must be the starting point in our quest for what really lies in the nature of man. Thus we may also find the way back to what we have lost, yet sorely need if we are not to stop at formal definitions of disease that cannot be of much use in actual practice. An important question arises here. Our materia medica contains only terrestrial substances taken from man's environment, for the treatment of the human organism which has suffered changes. But there are non-terrestrial processes active in him—or at least forces which cause his processes to become non-terrestrial—and so the question arises: how can we provoke an interaction leading from sickness to health, by methods affecting the sick organism through its physical earthly environment? How can we initiate an interaction which shall include those other forces, which work in the human organism, yet are not limited to the scope of the processes from which we take our remedies, even when they take effect through certain forms of diet, etc.? You will realise the close connection between a correct conception of human nature and the methods that may lead to a certain therapy. I have intentionally chosen these first elements which are to lead us to an answer, from the differences between animals and men, although well aware of the objection that animals, like men, are subject to diseases, that even plants may become diseased, and that morbid states have recently been spoken of even among minerals; and that there should therefore be no distinction between sickness in animals and in the human race. The difference will become obvious when it will be apparent how little value in the long run, adheres to the results of animal experimentation undertaken solely to gain knowledge for use in human medicine. We shall consider why it is undoubtedly possible to attain some help for mankind through experiments on animals, but only if and when we understand the radical differences, even to the smallest detail, between animal and human organisms. I want to emphasise that in referring to cosmic forces, far greater demands are made on man's personality than if we merely refer to so-called objective rules and laws of nature. The aim must be set before us to make medical diagnosis more and more a practice of intuition; the gift of basing conclusions on the formative phenomena of the individual human organism (which may be healthy or sick) can show how this training in intuitive observation of form will play an ever-increasing part in the future development of medicine. These suggestions are only intended to serve as a sort of introductory orientation. Our concern today was to show that medicine must once more turn its attention to realms not accessible through chemistry or Comparative Anatomy as usually understood, realms only to be reached by consideration of the facts in the light of Spiritual Science. There are still many errors on this subject. Some hold the main essential for the spiritualising of medicine to be the substitution of spiritual means for material. This is quite justifiable in certain departments, but absolutely wrong in general. For there is a spiritual method of knowing the therapeutic properties of material remedies; spiritual science can be applied to evaluate material remedies. This will be the theme of that portion of our subject matter which I have termed the possibilities of healing through recognition of the inter-relationships between mankind and the external world. I shall hope to base what I have to say about special methods of healing on as firm a foundation as possible, and to indicate that in every individual case of sickness it is possible to form a picture of the connection between the so-called “abnormal” process, which must also be a process of nature, and those “normal” processes which again are nothing else than nature processes. This primary problem of how the disease process can be regarded as a natural process has often cropped up. But the issue has been evaded again and again. I find certain facts about Troxler of great interest in this connection. Troxler taught medicine at the University of Berne and in the first half of the last century he devoted much energy to maintaining that the “normality of disease” should be investigated; that such investigation would finally lead to the recognition of a certain world connected with our own, and impinging on our world, as it were, through illegitimate gaps; and that this would be the key to something bearing on morbid phenomena. Please imagine such a diagrammatic picture; a world in the background whose laws, in themselves justified, could cause morbid phenomena amongst the human race. Then, if this world meets and interpenetrates our own, through certain “gaps,” its laws, which are adapted to another world, could do mischief here. Troxler wanted to work in this direction. And however obscure and difficult his expressions on many subjects may be, one notes that he had struck out a path for himself in medicine, with the purpose of working towards a certain restoration of medical science. A friend and I once had the opportunity of inquiry into Troxler's standing amongst his Bernese colleagues and into the results of his initiative. The detailed History of the University had only one thing to say about Troxler: that he had caused much disturbance in the university! That had been remembered and recorded, but we could find nothing about his significance for science. |
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture II
22 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture II
22 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Let us now continue our inquiry on the lines already laid down, and attempt to elucidate the nature of man by observing certain Polarities governing the human organism. Yesterday we found ourselves obliged to combine the weighing down forces found in the animal with certain vertical forces to form a parallelogram, and to consider an analogous phenomenon in the chemical reactions of the muscle. If these ideas are followed up in the study of the bone and muscular system and are supported by all the resources of practical experience, we might make Osteology and Muscular Pathology of greater value for medicine than has hitherto been the case. Special difficulties arise, however, if we try to connect the knowledge of man with the needs of medicine today, in our consideration of the heart. What in Osteology and Myology is only a slight defect becomes an evident defect in Cardiology. For, what is the common belief about the nature of the human heart? It is regarded as a kind of Pump, to send the blood into the various organs. There have been intricate mechanical analogies, in explanation of the heart's action—analogies totally at variance with embryology, be it noted!—but no one has begun to doubt the mechanical explanation, or to test it, at least in orthodox scientific circles. My outline of the subjects for consideration in the next few days will afford piecemeal proof of my general point of view. The most important fact about the heart is that its activity is not a cause but an effect. You will understand this if you consider the polarity between all the organic activities centering round nutrition, digestion, absorption into the blood, and so on: follow, passing upwards through the human frame, the process of digestion up to the interaction between the blood that has absorbed the food, and the breathing that receives air. An unbiased observation will show a certain contrast and opposition between the process of respiration and the process of digestion. Something is seeking for equipoise; it is as though there were an urge towards mutual saturation. Other words, of course, could be chosen for description, but we shall understand each other more and more. There is an interaction in the first place between the liquefied foodstuffs and the air absorbed into the organism by breathing. This process is intricate and worth attention. There is an interplay of forces, and each force before reaching the point of interplay accumulates in the heart. The heart originates as a “damming up” organ (Stauorgan) between the lower activities of the organism, the intake and working up of food, and the upper activities, the lowest of which is the respiratory. A damming up organ is inserted and its action is therefore a product of the interplay between the liquefied foodstuffs and the air absorbed from the outside. All that can be observed in the heart must be looked upon as an effect, not a cause, as a mechanical effect, to begin with. The only hopeful investigations on these lines, so far, have been those of Dr. Karl Schmidt, an Austrian medical man, practising in North Styria, who published a contribution to the Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift (1892, No. 15), “The Heart Action and Curve of the Pulse.” The content of this article is comparatively small, but it proves that his medical practice had enlightened the author on the fact that the heart in no way resembled the ordinary pump but rather must be considered a dam-like organ. Schmidt compares cardiac action to that of the hydraulic ram, set in motion by the currents. This is the kernel of truth in his work. But we need not stop short at the mechanical aspect if we consider the heart action as a result of these symbolic inter-penetrating currents, the watery and the airy. For what is the heart after all? It is a sense organ, and even if its sensory function is not directly present in the consciousness, if its processes are subconscious, nevertheless it serves to enable the “upper” activities to feel and perceive the “lower.” As you perceive external colours through your eyes, so do you perceive, dimly and subconsciously through your heart, what goes on in the lower abdomen. The heart is an organ for inner perception. The polarity in man is only comprehensible if we know that his structure is a dual one and that the upper portion perceives the lower. The following too must be considered: the lower functions—one pole of the whole human being—are considered through the study of nutrition and digestion in the widest sense, up to their interaction with respiration The interaction goes on in a rhythmic activity; we shall have to consider the significance of our rhythmic system later. But linked up with and belonging to the respiratory activity there is the sensory and nervous activity, which includes all that appertains to external perception and its continuation and its being worked up in the nervous activity. Thus, respiration and sensory and nervous activity form one pole of the human organism. Nutrition, digestion, and metabolism in its usual sense, form the other pole of our organisation. The heart is primarily that organ whose perceptible motion expresses the equilibrium between the upper and lower processes; in relation to the soul (or perhaps more accurately in the sub-conscious) it is the perceptive organ that mediates between these two poles of the total human organisation. Anatomy, physiology, biology can all be studied in the light of this principle; and thus light is thrown, and only thus, upon the human organisation. As long as you do not differentiate between these two poles, superior and inferior, and their mediator the heart, you will not be able to understand man, for there is a fundamental difference between the two groups of functional activity in man, according to whether they pertain to the upper or the lower polarity. The difference amounts to this: all the processes of the lower sphere have their “negative” so to speak, their negative counter-image in the upper. The important point, however, is that there is no material connection between these upper and lower spheres, but a correspondence. The correspondence must be correctly apprehended. without search for or insistence on direct material connection. Let us take a very simple example: the tickling irritation which causes coughing, and the actual cough itself. In so far as they belong to the upper sphere their complementary counterpart in the lower sphere is diarrhea. There is always a counterpart to every such activity. And the key to the understanding of man consists in the correct apprehension of these correspondences with several of which we shall deal in the course of our study. Furthermore, there is not only a theoretical correspondence, but, in the healthy organism, an actual close contact between upper and lower spheres. In a healthy organism this contact is so close, that any upper function, whether it be associated with respiration or with the nerves and senses, must somehow govern a function of the lower sphere and proceed in harmony with it. This will provide us later on with the key to the process of disease: there immediately arises an organic irregularity, whenever there is a predominance of either the upper or the lower function, which destroys its complementary equilibrium. There must always be a certain proportion and correspondence between these two sets of activities, so that they complete one another, master one another, proceed harmoniously as they are mutually orientated. For there is this definite orientation. It is individually different in individual human beings, but nevertheless it governs and relates the whole of the upper processes to the whole of the lower. Now we must be able to find the bridge leading from the healthily functioning organism, (in which the upper spheres correspond harmoniously with the lower) to the diseased organism. In describing a disease one may start from the indications in what Paracelsus called the “Archaeus” and we call the “Etheric body”—or, if to avoid offending people who do not like these terms, you can also say you will speak in the first place of indications of disease in the functional or dynamic, i.e. of the first signs of a morbid condition. And if we speak of what is first indicated in the etheric body or in the purely functional, one can also speak of a polarity, but a polarity which bears within it a non-correspondence, an irregularity, arising in the following manner. Let us assume that within the lower sphere, that is to say, the apparatus of nutrition and digestion in the widest sense, there is a preponderance of the inner chemical or organic forces of the food which has been eaten. In the healthy organism it is essential that all the forces active and immanent in the foodstuffs themselves, which we examine and test in our laboratory work on these foodstuffs, should be overcome by the upper sphere, so that they do not in any way interfere with the efficiency of the inner sphere of the organism and that all activity from external chemistry and dynamics has been entirely overcome. But the upper sphere may be inadequate to the task of penetrating the lower, of thoroughly brewing, or I might say, etherising it—which is more exact—all through. The result is the transference into the human organism of a preponderant process which is foreign to the organism, a process such as normally takes place outside the human body and should not operate within that body. As the physical body does not at once bear the brunt of these irregularities, the first symptoms appear on the functional side, in the etheric body (Archaeus). If we wish to find a current term to designate certain aspects of this irregular function, we must call it Hysteria. We shall use the term Hysteria for the too great autonomy of the processes of Metabolism; and we shall learn later on that the name is not inappropriate. Specific manifestations of hysteria in its narrower sense are nothing but this irregular metabolism raised to its culmination. In essence, the hysterical process, even in it's sexual symptoms, consists of metabolic irregularities, which are external processes having no rightful place in the human body. That is, they are processes which the upper sphere has been too weak to master and control. This is one pole of disease. If such morbid manifestations as are hysterical in character appear, we have to deal with an excess of an activity that belongs to the external world, but is operating in the lower sphere of the human organism. But the same irregularity of reciprocal action can also arise if the upper process does not take place in the proper way and occurs in such a way as to overstrain the upper organisation. This is the opposite, and in some sense, the negative of the lower processes. It is not that the upper processes are over-stimulated; they cease, as it were, before the mediating action of the heart transmits them to the lower sphere. This type of irregularity is too strong spiritually, too organically-intellectual, if I may use such a term, and shows itself as Neurasthenia. This is the other pole. We must keep these two irregularities of the human organism clearly before us—they remain still in the realm of mere functions, they are two defects, expressed respectively in the upper and the lower sphere. And we shall gradually have to learn that the human polarity tends towards either the one or the other deficiency. Neurasthenia is a functional excess of the upper sphere. The organs of that sphere are too much occupied, so that processes which should be transferred and conducted downwards through the heart, take place in the upper sphere and do not pass into the lower organic currents (harmoniously mediated by the damming up in the heart). You will observe that it is much more important to become aware, so to speak, of the specific physiognomy of the disease than to study by post-mortems the organs which have become defective. For post-mortems reveal only the results and symptoms. The essential thing is to form a comprehensive picture of the whole morbid condition; to visualise its physiognomy. This physiognomy will always reveal a tendency in one or the other direction towards the Neurasthenic or the Hysterical Type. But of course, we must use these terms in a wider sense than that usually accepted. If one has acquired an adequate picture of the interaction of the upper and lower spheres, one will gradually learn that irregularity manifesting functionally only in its initial stages—and therefore, as we should say in the etheric sphere—becomes denser in its forces and takes hold of the physical organism. Thus, what was at first merely a tendency to hysteria, may take physical form in various abdominal diseases. And conversely, neurasthenia may develop into diseases of the throat or head. The study of this imprint of what were originally only functional irregularities of neurasthenia and hysteria, will be of the utmost significance for the medicine of the future. If hysteria has become organic, there will be disturbances of the whole digestive process and all the other processes of the abdominal sphere. Such processes have their repercussions on the whole organism; we must be careful to bear these repercussions and reactions in mind. Now let us suppose that a manifestation which would be undoubtedly hysterical, if it were manifested functionally, does not come to expression at all as a disturbance of function. It does not appear in the functional sphere, the etheric body imprints it immediately into the physical body. It is there, but it is not evident in any definite disease of the lower organs. We may say indeed that the organs bear the signature of hysteria. It has been driven into the physical organism, and therefore does not manifest by hysterical symptoms on the psychological plane; and it is not yet sufficiently pronounced to become an appreciable physical affliction. But it is strong enough to work within the whole organism. Thus we have this peculiar condition: something on the borderland, so to speak, between sickness and health influences the upper organic sphere from the lower. It reacts on the upper sphere and in some sense infects it, appearing in its own negative. This phenomenon, in which so to speak, the first physical effects of hysteria affect those regions which are subject to neurasthenia in their own typical irregularities, gives a tendency to Tuberculosis. This is an interesting connection. The tuberculous tendency is a repercussion of the abnormal action of the lower body sphere on the upper, as has just been outlined. The whole of this remarkable interaction is set in motion by an uncompleted process which reacts on the upper sphere, and produces a tendency to tuberculosis. And it is necessary to recognise this primary tendency of the human organism before any rational antidote to tuberculosis can be discovered. For the invasion of the human body by pathogenic bacteria is only a result of primary tendencies such as I have described. This does not contradict the fact that tuberculosis is infectious under certain conditions. Of course these conditions are a necessary prerequisite. But unfortunately this predominance of the activity of the lower organic sphere is alarmingly prevalent in present-day humanity, and this implies a disastrously frequent predisposition to tuberculosis. The concept of infection, however, is none the less valid here. For any highly tuberculous individual affects his fellow beings: and if any person is exposed to the sphere in which the tuberculous patient lives, then it may happen that the effect turns again into a cause. I have often tried to illustrate the relationship between primary causes of a disease and infection in the following analogy. Suppose that I meet a friend of mine, whose relations with other people do not in general touch me. He is sad and has reason to be so, for he has lost one of his friends by death. I have no direct relationship with this friend who has died, but I become sad with him at his sad news. His sadness is, so to speak, first hand and direct; mine arises indirectly, communicated through him. Nevertheless, the fact remains that the mutual relationship between me and my friend provides the pre-condition for this “infection.” Thus both concepts—of primary origin and of infection—are justified, and are so especially in the case of tuberculosis. But they should be applied in a rational manner. Institutions for the treatment of tuberculous persons are often breeding grounds for tuberculosis. If tuberculous persons are to be collected and crowded together in special institutions, then these institutions should be dissolved and replaced by others as often as possible. There should, in fact, be a time limit for their dispersion and removal. For this disease has the peculiarity that its victims are extremely liable to secondary infections. A case which may be by no means hopeless, becomes serious if it is surrounded by severe cases of tuberculosis. For the present, however, I am referring to the specific nature of tuberculosis. And it offers a striking example of the interaction of various processes in the human organism. As you will observe, such processes are dominated by the polarity of the upper and lower spheres, which correspond to one another as positive and negative images. The particularly striking phenomena which lead to tuberculosis following the special organic constitution which I have indicated, may be followed up; and they reveal in their future development a general concept of the true nature of disease. Let us take the most frequent symptoms of an individual who is an incipient tuberculous case. Tuberculosis is in his future, and his present state prepares for it. We find perhaps that he coughs, feels pain in the throat and chest, and perhaps also in his limbs; there will be certain states of exhaustion and fatigue; and there will be profuse sweating at night. If we take all these symptoms together what do they mean? They are, first of all, the effect of those internal irregular interactions to which I have referred. And at the same time, they represent the resistance offered by the organism, its struggles against the deeper foundation of the disease. Let us take the simpler manifestations first. It is certainly not always and under all circumstances beneficial to attempt to stop a cough. It may even sometimes be necessary to stimulate coughing by artificial means. If the lower organic sphere cannot be controlled by the upper, the healthy reaction manifests as the irritation leading to coughing, in order to prevent the invasion of certain things which are undesirable. To suppress coughing as an invariable rule, may be deleterious, for the body will then absorb injurious substances. Coughing is the attempt to get rid of such substances, which cannot be tolerated under the prevailing conditions. Thus the tickling irritation which provokes coughing is a danger signal of something which is wrong in the organism, so that the need arises to repel the invaders, which could otherwise easily effect an entry. What of the other symptoms, enumerated above? They too are forms of organic defence, ways of doing battle with the dangers which approach as the tubercular tendency. The pains in the throat and limbs simply proclaim the obstruction of those processes in the lower sphere, which are not adequately controlled by the upper. If the tubercular tendency is perceived in good time, it may be beneficial to support the resistant organism by moderate stimulation of the coughing, by stimulating the resultant phenomena—as will be indicated in the subsequent lectures—by appropriate diet, and even by stimulating the typical fatigue. Again, if there is marked emaciation, this too is only a form of organic defence. For if this emaciation does not take place, the process which develops is perhaps that activity of the lower sphere which the upper cannot control. The organism dwindles and loses weight, in order to defend itself by getting rid of those elements which cannot be controlled by the upper sphere. Thus it becomes exceedingly important to study symptoms and cases in detail, but not in order immediately to prescribe a corpulency treatment for any one suffering from emaciation. For this emaciation may be highly beneficial, in relation to the actual organic conditions at the time. An especially instructive characteristic of the incipient tuberculous subject, is the heavy loss of perspiration at night. This is a form of organic activity taking place during sleep, which should really take place during working hours, during full physico-spiritual awakeness. But it does not do so, and is obliged to find expression during sleep. This is both a symptom and a method of defence. When the organism is relieved from spiritual occupation, it has recourse to the form of activity manifest in “night sweats.” To evaluate this fact properly, we must know something of the close connection between all the excretory processes and those activities which include soul and spirit. The constructive processes, the vital processes proper, are the foundation of the mere unconscious. Corresponding to the conscious soul and organic functions of our waking hours, are always processes of excretion. Even our thinking does not correspond to constructive cerebral processes, but to processes of excretion, i.e. destruction. And night sweats are an excretory phenomenon which should be concurrent with a spirit and soul activity in normal life. But as the upper and lower spheres are not in correct interaction with one another, the excretory process accumulates and then takes place at night, when the organism is relieved from spirit and soul activity. Thus you will see that a careful study of all the processes connected with growth and development in the healthy and the diseased human organism leads to the conclusion that there is an interaction between the phenomena of disease. Emaciation is one phenomenon. But in its relation to the tubercular tendency, it is part of the disease. Indeed I would say that the phenomena of disease are organically linked up. They constitute an ideal organisation. One such phenomenon belongs in a sense to another. Therefore it is entirely reasonable to come to the help of an organism—keeping to the example of incipient tuberculosis—which has not the strength to react adequately and to provoke from outside the necessary reaction, viz. that one form of disease is made to follow on another. The doctors of old enunciated this truth as a significant educational rule of medicine. They said: The danger of being a physician is that he must not only be able to cure sicknesses but must also provoke them. And in the same measure in which the physician is able to heal diseases he can also provoke them. The ancient world was more aware of these subtle inter-relationships (through the atavistic power of clairvoyance) and they beheld in the physician a double power, who could smite with sickness, if he were of evil will, as well as cure. This aspect of medicine is associated with the need to provoke certain states of disease, in order to put them into a certain relation to others. Such conditions as coughing, pains in the throat and chest, emaciation, persistent fatigue, profuse nocturnal perspiration, all are symptoms of disease, yet they must sometimes be provoked, even though they are diseased. This will naturally lead to the duty not to abandon the sick person when only half-healed, i.e. when the necessary phenomena have been provoked for then the second stage of the healing process begins. We must not only see to it that the appropriate counter-reactions have taken place, but that these reactions are now cured and the whole organism restored to its proper way of functioning. Thus in tubercular cases, having stimulated coughing and pains in the throat, for example, we must then pay heed to the processes of elimination; for there will then be always a tendency to constipation and stasis. It will be necessary to quicken the digestive function into a function of evacuation, even to the extent of stimulating diarrhea. It is always necessary to stimulate diarrhtic action, following the provoked coughing, pains in the throat and similar symptoms. For we must not consider or treat manifestations of the upper sphere, as though confined to that sphere alone. We must often seek a cure through the processes of the lower sphere, even where there is no direct material connection but merely a correspondence. These correspondences deserve the most careful consideration. Let us take as an example the typical fatigue and exhaustion. I should prefer not to regard this fatigue as purely subjective, but as organically determined, as emerging always when the metabolic processes are not fully controlled by the upper sphere. Now if these conditions of fatigue have to be stimulated in the treatment of tuberculosis, they must be subsequently countered, at the appropriate moment, by means of a diet which activates the digestion. (We shall deal later with the special requisites of such a diet). Thus the person in question will digest his food better and more easily than usual. Emaciation, similarly, should receive a dietary treatment, leading to a degree of fat formation which cushions the organs and their tissues. And the subsequent treatment of night sweating, after powerful stimulation, must be through the suggestion of activities in which there are spiritual efforts to be made; the patient makes efforts bound up with thoughts, which make him sweat until a normal perspiration is gradually regained. It is obvious that if we first realise the correspondence between the upper and lower sphere in man, by a correct understanding of the cardiac function, then we can understand the first fore-shadowing of the disease on the functional plane in the etheric body, as we have done in the case of Neurasthenia and Hysteria. Then we can pass on to an understanding of its imprints on the organic and physical structure, and finally to the physiognomy of the disease as a whole. This comprehensive image will enable us to stimulate the course of sickness in the direction of a more or less secondary disease, in order, when the time has come, to lead the whole process back to health. Of course the worst obstacles to these therapeutic methods are external and social conditions; therefore medicine is to a large extent a social problem. On the other hand, the patients themselves offer grave difficulties, for they expect their doctors to “get rid of something”, as they often express themselves. But if we simply “get rid of” some existent condition, it may well be that we make their state worse than before. This must be taken into account; often one does make them worse than before, but they must then wait till the opportunity arises to restore them to health once more. Before that can happen, however, as many of you can testify, they have only too often fled and ceased treatment! So the proper study of both the sick and the sound human being convinces us that the physician must have a hand in the after-treatment if the whole treatment is to be of real value. And you must direct your efforts publicly to this goal. We live in a time of belief in authority and it should not be difficult to initiate such public efforts and emphasise their necessity. I must, however, beg your permission to observe that neither the individual patients of the medical profession find it inopportune to follow up all the ultimate ramifications of disease, and are more or less satisfied if they have “got rid of” something. You will observe that this correct perception of the role of the heart in the human organism is able to lead us gradually into the essence of the state of disease. It is, however, vital to note the radical difference between the activities of the lower organic sphere, which have to some degree overcome external chemical processes (but are yet at the same time somewhat like the upper activities)—and the upper activities which are opposed and polar to them. It is extraordinarily difficulty to define this organic dualism adequately, for our language has hardly any terms to indicate processes contrary to the physical and the organic. But perhaps you will understand clearly—and I shall not hesitate to come up against possible prejudices amongst you—if I try to elucidate this dualism with the following analogy. We shall deal in detail with the subject later on.  Let us think of the qualities proper to any sort of material substance, that is, the qualities essential to its working when absorbed into the lower sphere of the organism, e.g. through the digestion. But if I may use the expression—we can homeopathise, we can dilute the aggregate states of the substances in question. This is what happens if one dilutes in the way of homeopathic doses. Here something occurs which does not receive due attention in the Natural Science of today, for mankind has a strong tendency to abstractions. They say, for example, that from a source of light—for example, the sun—the light radiates in all directions, and finally disappears into infinity. But this is not true. No such form of activity vanishes into infinite space, but it extends within a certain limited orb and then rebounds elastically, returning to its source, although the quality of this return is often different from its centrifugal quality. (See Diagram 5). In Nature there are only rhythmical processes, there are none which continue into infinity. They revert rhythmically upon themselves. That is not only the case in quantitative dispersion, but also in qualitative. If you subdivide any substance, it has at first certain distinctive qualities. These qualities do not decrease and diminish ad infinitum; at a certain point, they are reversed and become their opposites. And this intrinsic rhythm is also the foundation of the contrast between the upper and lower organisation. Our upper organisation works in a homeopathic way. In a certain sense it is diametrically opposed to the process of ordinary digestion, its opposite and negative. Therefore we might say that when the homeopathic chemist manufactures his minute dilutions, he thereby transfers the qualities which are otherwise linked with the lower organic sphere, into those which belong to the upper sphere. This is a most significant inner relationship and we shall discuss it in the ensuing lectures. |
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture III
23 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture III
23 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
I propose to incorporate all the inquiries and requests I have received in the course of these lectures. Of course they contain repetitions, so I shall group the answers together, as far as possible. For it makes a difference whether we discuss what has been asked or suggested, before or after a certain basis has been laid down. Therefore, I shall try, in today's address, to establish such a basis for every future consideration, taking into account what I have had from you in the way of requests and suggestions. You will remember that we first considered the form and inner forces of the osseous and muscular systems, that yesterday we reviewed illustrative examples of the process of disease, and the requisites of curative treatment; and that we took as our starting point on that occasion, the circulation in the cardiac system. Today I shall describe the introductory principles of a conception that may be derived from a deeper study of human nature regarding the possibility and the essentials of healing in general. Special points will be dealt with in subsequent comments, but it is my intention to begin with these basic principles. If we examine the medical curriculum of today we shall find, roughly speaking, that therapeutics are dealt with concurrently with pathology, although there is no clear and evident connection between the two. And in therapeutics at the present time, purely empirical methods generally prevail. It is hardly possible to discover a rational cure, combining practice with sound principles, in the domain of therapeutics. We are also aware that in the course of the nineteenth century, these deficiencies in the medical conception led to what was termed the Nihilist School. This Nihilism laid all stress on diagnosis, was content to recognise disease, and on the whole, was sceptical as regards any rationale of healing. But in a purely rational approach to medicine, we might surely expect something suggesting lines of treatment to be given together with diagnosis? The connection between therapeutics and pathology must not be external only. The nature of disease must be recognised to such a degree that some idea can be formed from it as to the appropriate methods of the curative process. And thus the question arises: How far does the whole intricate web of natural processes admit of curative Media and curative processes? An interesting axiom of Paracelsus has often been quoted, to this effect: the medical man must pass Nature's examination. But it cannot be maintained that the more recent literature dealing with Paracelsus has made much use of this axiom; for, if it had, there would be definite attempts made to unravel the curative processes from Nature herself. Of course, there are such attempts, in those processes of disease in which Nature herself gives counsel. But these examples are more or less exceptions, for there have already been injuries of one kind or another; whereas a genuine study of Nature would be a study of normal processes. This leads to a further inquiry. Is there really any possibility of observing normal processes—in the current sense of the term—in Nature, in order to gather from them some conception of the healing method? You will immediately perceive the serious difficulty in this connection. We can of course, only observe curative processes in Nature in a normal way, if diseased processes are normally present in Nature. So we are confronted with this: Are there processes of disease in Nature itself, so that we can pass Nature's examination and thus learn how to heal them? We shall try today to advance somewhat nearer to the answering of this question, which will be fully dealt with in the course of these lectures. But one can say at once in this connection that the path here indicated has been made impassable by the natural scientific basis of medicine as practised today. This means very “heavy going,” in the face of prevailing assumptions, for curiously enough, the materialistic tendency of the nineteenth century has led to a complete misconception of the functions of that system of the human organism with which we must now deal in sequence to the osseous, muscular and cardiac systems, viz. the nervous system. It has gradually become the fashion to burden the nervous system with all the soul functions and to resolve all that man accomplishes of a soul and spirt nature into parallel processes which are then supposed to be found in the nervous system. As you are aware, I have felt bound to protest against this kind of nature study in my book Concerning the Problems of the Soul. In this work, I first of all tried (and many empirical data confirm this truth, as we shall see) to prove, that only the processes proper to the formation of images are connected with the nervous system, whilst all the processes of feeling are linked—not indirectly but directly—with the rhythmic processes of the organism. The Natural Scientist of today assumes—as a rule—that the feeling processes are not directly connected with the rhythmic system, but that these bodily rhythms are transmitted to the nervous system, and thus indirectly, the feeling life is expressed through the nerve system. Further I have tried to show that the whole life of our will depends directly on the metabolic system and not through the intermediary of the nerves. Thus the nervous system does nothing more than perceive will processes. The nervous system does not put into action the “will” but that which takes place through will within us, is perceived. All the views maintained in that book can be thoroughly corroborated by biological facts, whereas the contrary assumption of the exclusive relation of the nerve system to the soul, cannot be proved at all. I should like to put this question to healthy unbiased reason: how can the fact that a so-called motor nerve and a sensory nerve can be cut, and subsequently grown together, so that they form one nerve, be harmonised with the assumption that there are two kinds of nerves: motor and sensory? There are not two kinds of nerves. What are termed “motor” nerves are those sensory nerves that perceive the movements of our limbs, that is, the process of metabolism in our limbs when we will. Thus in the motor nerves we have sensory nerves that merely perceive processes in ourselves, while the sensory nerves proper perceive the external world. There is much here of enormous significance to medicine, but it can only be appreciated if the true facts are faced. For it is particularly difficult to preserve the distinction between motor and sensory nerves, in respect of the symptoms enumerated yesterday, as appertaining to tuberculosis. Therefore reasonable scientists have for some time assumed that every nerve has in itself a double conduction, one from the centre to the periphery, and also one from the periphery to the centre. Thus each motor nerve would have a complete double “circuit,” and if the explanation of any condition—such as hysteria—is to be based on the nervous system, one has to assume the existence of two nerve currents running in opposite directions. You see: as soon as one gets down to the facts, one must postulate qualities of the nervous system directly contrary to the accepted theories. Inasmuch as these conceptions about the nervous system have arisen, access has actually been barred to all knowledge of what goes on in the organism below the nervous system as in hysteria for example. In the preceding lecture, we defined this as caused by metabolic changes; and these are only perceived and registered by the nerves. All this should have received attention. But instead of such attentive study, there has been a wholesale attribution of symptoms and conditions to “nerves” alone, and hysteria was diagnosed as a kind of vulnerability and disequilibrium of the nervous system. This has led further. It is undeniable that among the more remote causes of hysteria are some that originate in the soul: grief, disappointment, disillusion, or deep-seated desires which cannot be fulfilled and may lead to hysterical manifestations. But those who have, so to speak, detached all the rest of the human organism from the life of the soul, and only admit a genuine direct connection between that life and the nervous system, have been compelled to attribute everything to “nerves.” Thus there has arisen a view which does not correspond in the least with the facts, and furthermore offers no available link between the soul and the human organism. The soul-forces are only admitted to contact with the nervous system, and are excluded from the human organism as a whole. Or, alternatively, motor nerves are invented, and expected to exercise an influence on the circulation, etc., an influence which is entirely hypothetical. These errors helped to mislead the best brains, when hypnotism and “suggestion” came into the field of scientific discussion. Extraordinary cases have been experienced and recorded, though certainly some time ago. Thus, ladies afflicted with hysteria completely mystified and misled the most capable physicians, who swallowed wholesale all that these patients told them, instead of inquiring into the causes within the organism. In this connection, it is perhaps of interest to remind you of the mistake made by Schleich, in the case of a male hysteric. Schleich was fated to fall into this error, although he was quite well accustomed to think over matters thoroughly. A man who had pricked his finger with an inky pen, came to him and said that the accident would certainly prove fatal that same night, for blood poisoning would develop, unless the arm was amputated. Schleich, not being a surgeon, could not amputate. He could only seek to calm the man's fears, and carry out the customary precautions, suction of the wound, etc., but not remove an arm on the mere assertion of the patient himself. The patient then went to a specialist, who also declined to amputate. But Schleich felt uncomfortable about the case, and inquired early the next morning, and found that the patient had died in the night. And Schleich's verdict was: Death through Suggestion. And that is an obvious—terribly obvious explanation. But an insight into the nature of man forbids us to suppose that this death was due to suggestion in the manner assumed. If death through suggestion is the diagnosis, there had been a thorough confusion of cause and effect. For there was no blood poisoning—the autopsy proved this; but the man died, to all appearance, from a cause which was not understood by the physicians, but which must obviously have been deep-seated and organic. And this deep-seated organic cause had already—on the previous day—made the man somewhat awkward and clumsy, so that he stuck an inky pen into his finger, which is an action most people avoid. This was a result of his awkwardness. But this external and physical clumsiness was concurrent with an increased inner power of vision, and under the influence of disease, he foresaw that his death would occur that night. His death had not the least connection with the fact that he hurt his finger with an ink-stained pen, although this was the cause of his sensations, owing to the cause of death which he carried within him. Thus the whole course of events is merely externally linked with the internal processes which caused the death. There is no question of “death through suggestion” here. He foresaw his own death, however, and interpreted everything that happened, so as to fit into this sentiment This one example will show you how extremely cautious we must be, if we are to reach an objective judgment of the complicated processes of nature. In these matters one cannot take the simplest facts as a starting point. Now we must pose this question: Does sensory perception, and all that resembles such perception, offer us any basis on which to estimate the somewhat dissimilar influences which are expected to affect the human constitution, through materia medica? We have three kinds of influence upon the human organism in its normal state: the influences through sense perception, which then extend to the nervous system; the influences working through the rhythmic system, breathing and blood circulation; and those working through metabolism. These three normal relationships must have some sort of analogies in the abnormal relationships which we establish between the curative media—which we must after all take in some way from the external world of nature—and the human organism. Undoubtedly the most evident and definite results of this interaction between the external world and the human organism, are those affecting the nervous system. So we must ask ourselves this question: How can we rationally conceive a connection between man himself and that which is external nature; a connection of which we wish to avail ourselves, whether through processes, or substances with medicinal properties for human healing? We must form a view of the exact nature of this interaction between man and the external world, from which we take our means of healing. For even if we apply cold water treatment, we apply something external. All that we apply is applied from outside to the processes peculiar to man, and we must therefore form a rational concept of the nature of this connection between man and the external process. Here we come to a chapter where again there is in the orthodox study of medicine a sheer aggregate instead of an organic connection. Granted that the medical student hears preliminary lectures on natural science; and that on this preparatory natural science, general and special pathology, general therapeutics and so forth, are then built up, but once lectures on medicine proper have begun, not much more is heard of the relationship between the processes discussed in these lectures, and the activities of external nature, especially in connection with healing methods. I believe that medical men who have passed through the professional curriculum of today, will not only find this a defect on the theoretical and intellectual side, but will even have a strong feeling of uncertainty when they come to the practical aspect, as to whether this or that remedy should be applied to influence the diseased process. A real knowledge of the relationship between the remedy indicated and what happens in the human body is actually extremely rare. So the very nature of the subject makes a major reform of the medical curriculum imperative. I shall now try to illustrate the extent of the difference between certain external processes and human processes, by means of examples drawn from the former category. I propose to begin with what we can observe in plants and lower forms of animals, passing on from these to processes that can be activated through agencies derived from the vegetable, animal and especially the mineral kingdoms. But we can only approach a characterisation of pure mineral substances, if we start from the most elementary conceptions of natural science, and then go on to the results, let us say, of the introduction of arsenic or tin into the human organism. But, first and foremost, we must emphasise the complete difference between the metamorphoses of growth in the human organism, and in external objects. We shall not be able to escape forming some notion of the actual principle of growth, of the vital growth of and in mankind, and conceiving the same principle in external entities as well. But the difference is of fundamental significance. For instance, I would ask you to observe a very common natural object: the so-called locust tree, Robina pseudacacia. If the leaves of this plant are cut off where they join the petioles, there occurs an interesting metamorphosis; the truncated leaf stalk becomes blunt and knobby, and takes over the functions of the leaves. Here we find a high degree of activity on the part of something inherent in the whole plant; something that we will provisionally and by hypothesis term a “force,” which manifests itself if we prevent the plant from using its normally developed organ. Now, observe, further, there is still a trace in mankind of what is so conspicuously present in the simple growing plant. For instance, if a man is prevented for one reason or another, from using one of his arms or hands for any purpose, the other arm or hand grows more powerful, stronger, and also physically larger. We must bring together facts like these. This is the path that leads to the cognition of remedial possibilities. In external nature these trends develop to extremes. For instance, this has been observed: A plant has grown on the slope of a mountain; certain of its stems develop in such a way that the leaves remain undeveloped; on the other hand the stem curves round and becomes an organ of support. The leaves are dwarfed; the stem twists round, becomes a supporting organ, and finds its base. These are plants with transformed stems, whose leaves have atrophied. (See Diagram 6).  Such facts point to inherent formative forces in the plant itself enabling it to adapt itself, within wide limits, to its environment. The same forces, active and constructive from within, are also revealed among lower organisms in an interesting way. Take, for example, any embryo which has reached the gastrula stage of development. You can cut up this gastrula, dividing it through the middle, and each half rounds out and evolves the potentiality within itself of growing its own three portions of the intestine—the fore, middle and hind portion, independently. This means that if the gastrula is cut in two, we find that each half behaves just as the whole gastrula would have behaved. You know that this experiment can even be applied to forms of animal life as high in the scale as earthworms; that when portions are removed from these creatures, they are restored, the animal drawing on its internal formative forces to rebuild out of its own body the portion of which it has been deprived. We must point to these formative forces objectively; not as hypotheses, assuming the existence of some sort of vital force, but as matters of fact. For if we observe exactly what occurs here, and follow its various stages, we have this result. For instance, take a frog, and remove a portion in a very early stage of development, the bulk of the mutilated organism replaces the amputated portion by growing it again. A critic of a materialistic turn of mind, will say; Oh yes, the wound is the seat of tonic forces, and through these the new growth is added. But this cannot be assumed.  Suppose that it were the case, and I were to remove a part of an organism, and a new part grows on the site of the injury (b) (See Diagram 7) through the tonic force (c) located here; then the new growth should strictly speaking be the immediately adjacent part, its neighbour in the intact and perfect organism. Actually, however, this does not happen; if portions of the larval frog are amputated, what grows from the site of the injury are extremities, tails or even heads; and in other creatures antennae. Not, that is to say, the strictly adjacent parts, but those of most use to the organism. Therefore, it is quite impossible that the normally adjacent structure develops at the point of amputation through the specially localised tonic forces; instead, we are obliged to assume that, in these re-growths or repairs, the whole organism takes part in some way. And so it is really possible to trace what happens in lower organisms. As I have indicated the path to follow you can extend its application to all the cases recorded, and see in all of them, that one can only achieve a conception of the matter along this line of thought. And in man, you will have to conclude, however, that things do not happen in this way. It would be extremely pleasant and convenient to be able to cut off a finger or an arm, in the certainty that it would be grown again! But this simply does not happen. And the question is: what becomes of those forces, growth forces, which show themselves unmistakably in the case of animals, when it comes to the human organism? Are they lost in it? or are they non-existent? Anyone who can observe Nature objectively knows that only by this line of inquiry can we arrive at a sound conception of the link between physical and spiritual in man. For the forces we learnt to know as plastic formative forces, which mould forms straight from the living substance, are simply lifted out of the organs, and exist entirely in the soul and spiritual functions. Because they have been so lifted, and are no longer within the organs as formative forces, man has them as separate forces, in the functions of soul and spirit. If I think or feel, I think and feel by virtue of the same forces that work plastically in the lower animals or the vegetable world. Indeed I could not think if I did not perform my thinking, feeling and willing with these same forces, which I have drawn out of matter. So, when I contemplate the lower organisms, I must say to myself; the power inherent in them, which manifests as a formative force, is the same as I carry within me; but I have drawn it out from my organs and hold it apart. I think and feel and will with the same powers that are formative and active plastically, in the lower organisms. Anyone wishing to be a sound psychologist, whose statements have substance, and not mere words, as is usual today, would have so to follow up the processes of thinking, feeling and willing, as to show that the very same activities in the regions of soul and spirit manifest themselves on the lower level as plastic formative forces. Observe for yourselves how we can achieve within the soul things we can no longer achieve within our organism. We can complete trains of thought that have escaped us by producing them out of others. Our activity here is quite similar to organic production; what appears first is not the immediately neighboring, but one lying far removed. There is a complete parallelism between what we experience inwardly through the soul, and the external formative forces and principles of Nature. There is a perfect correspondence between them. We must emphasise this correspondence, and show that man faces the same formative principles in the external world, as he has drawn from his own organism for the life of his soul and spirit, and which therefore in his own organism no longer underlie the substance. Moreover, we have not drawn these elements in equal proportions from all parts. We can only approach the human organism properly, if we have first armed ourselves with the preliminary knowledge outlined here. For if you observe all the components of our nervous system, you will find the following peculiarity: what we are accustomed to term nerve-cells (neurons) and the nerve tissue, and so forth, develop comparatively slowly in the early stages of growth; they are not very advanced cellular formations. So that we might reasonably expect these so-called nerve-cells to display the characteristics of earlier primitive cellular structures yet, they do not do so at all. For instance, they are not capable of reproducing themselves; nerve-cells, like the cells of the blood, are indivisible. Thus we find that in a relatively early stage of evolution, they have been deprived of a capacity that belongs to cells external to man. They remain at an earlier stage of evolution; they are, so to speak, paralysed at this stage. What has been paralysed in them, separates off and becomes the soul and spirit element. So that, in fact, with our soul and spiritual processes we return to what was once formative in organic substance. And we are only able to attain to this because we bear in us the nervous substances which we destroy or at least cripple in a relatively early stage of growth. In this way we can approach the inherent nature of the nerve substance. The result explains why this substance has the peculiarity both of resembling primitive forms, even in its later developments; and yet of serving what is usually termed the highest faculty of mankind, the activity of the spirit. I will interpolate here a suggestion rather outside the subject we are at present considering. In my opinion, even a superficial observation of the human head with its various enclosed nerve centres, reminds one rather of lower forms than highly developed species of animal life, in that the nerve centres are enclosed in a firm armour of bone. The human head actually reminds us of prehistoric animals. It is only somewhat transformed. And if we describe the lower animal forms, we generally do so by referring to their external skeleton, whereas the higher animals and man have their bony structure inside. Nevertheless our head, our most highly evolved and specialised part, has an external skeleton. This resemblance is at least a sort of leit-motif for our preceding considerations. Now let us suppose that we have occasion, because of some condition that we term disease, (I shall deal with this in more detail later) to bring back into our organism what has thus been removed. If we replace or restore these formative forces of external nature—of which we have deprived our organism because we use them for the soul and spirit—by means of a plant product or some other substance used as a remedy—we thereby reunite with the organism something that was lacking. We help the organism by adding and returning what we first took away in order to become human. Here you see the dawn of what can be termed the process of healing: the employment of those external forces of nature, not normally present in man, to strengthen some faculty or function. Take as an example—purely by way of illustration—a lung. Here too we shall find that we have drawn away formative principles to augment our soul and spiritual powers. If we discover among the products of the vegetable kingdom, the exact forces thus drawn from the lung and re-introduce them in a case of disturbance of the lung system, we help to restore that organ's activity. So the question arises; which forces of external nature are similar to the forces that underlie the human organs and have been extracted in the service of soul and spirit? Here you will find the path, leading from the method of trial and error in therapy, to a sort of “rationale” of therapy. In addition to the errors fostered in respect of the nervous system—which refers to the inner human being—there is another very considerable error, regarding extra-human nature. This I will just touch on today and explain more fully later. During the age of materialism, people accustomed themselves to think of a sort of evolution of natural objects, from the so-called simplest to the most complex. The lower organisms were first studied in their structural evolution, then the more complex; and then attention was directed to structures outside the organic realm, that is in the mineral kingdom. The mineral kingdom was envisaged merely as being simpler than the vegetable. This has led to all those strange questions and speculations, concerning the origin of life from the mineral kingdom, a changing over of substance occurring at some unknown point in time, from a merely inorganic to an organic activity. This was the Generation Aequivoca or spontaneous generation, which provoked so many controversies. However an unbiased examination certainly does not confirm this view. On the contrary, we must put the following proposition to ourselves. In a way, just as we can conceive of a sort of evolution from plant life on through animal life to man, so it is not possible to conceive of another evolution, from organisms, in this case, plants, to the minerals, inasmuch as the latter are deprived of life. As I have said, this is only a hint which will be made clearer in later lectures. But we shall only avoid going astray here, if we do not think of evolution as ascending from the mineral through the vegetable and animal forms to mankind, but if we postulate a starting point in the center, as it were, with our evolutionary sequence ascending from plant through animal life to man, and another, descending to the mineral kingdom. Thus the central point of departure would lie not in the mineral kingdom, but somewhere in the middle kingdoms of nature. There would be two trends of evolution, an upward and a downward. In this way we should come to perceive, in passing downwards from plant to mineral, and especially—as we shall see—to that particularly important mineral group, the metals, that in this descending evolutionary sequence, forces are manifest which have peculiar relationships to their opposites in the ascending trend of evolution. In short: what are those special forces inherent in mineral substances, which we can only study if we consider here the formative forces which we have studied in lower organic forms, and apply the same methods? In mineral substances such formative forces manifest themselves in crystallisation. Crystallisation reveals quite definitely a factor in operation on the descending line of evolution that is in some manner interrelated—but not identical—with that which manifests as formative forces on the ascending line. Then if we bring to the living organism that force which inheres in mineral substances, a new question arises. We have already been able to answer a previous and similar inquiry: if we restore the formative forces that we have absorbed from our organism by our soul and spiritual activities by means of vegetable and animal substances, we help the organism thus treated. But what would be the effect of applying these other, different, forces coming from the descending evolutionary line, that is from the mineral world, to the human organism? This is the question which I will put to you today, and which will be answered in detail, in the course of our considerations. But with all this, we have not yet been able to contribute anything of real help to the question at the forefront of our programme for today, viz: Can we gather by careful listening a healing process straight from nature itself? Here it depends on whether we approach nature with real insight—and we have attempted to get at least an outline of such understanding—whether certain processes will reveal their inherent secret. There are two processes in the human organism—as also among animals, which are of less interest to us at the moment—which appear in a certain sense directly contrary to one another, when looked at in the light of the concepts with which we are now equipped. Moreover these two processes are to a great extent polar to one another; but not wholly so, and I lay special stress on this not wholly, so please bear it in mind to avoid misconstruction of my present line of argument. They are the formation of blood, and the formation of milk, as they take place in the human body. Even externally and superficially these processes differ greatly. The formation of blood, is, so to speak, very deep seated and hidden in the recesses of the human organism. The formation of milk finally tends towards the surface. But the most fundamental difference is that the formation of blood is a process bearing very strong potentialities of itself, producing formative forces. The blood has the formative power in the whole domestic economy of the human organism, to use a commonplace expression. It has retained in some measure the formative forces we have observed in lower organisms. And modern science could base itself on something of immense significance, in the observation and study of the blood; but it has not yet done so in a rational manner. Modern science could base itself on the fact that the main constituents of blood are the red corpuscles, and that these again are not capable of reproducing themselves. They share this limitation of potentiality with the nerve-cells. But, in emphasising this attribute held in common, all depends on the cause; is the cause the same in both cases? It is not, for we have not extracted the formative forces from our blood to anything like the same extent as from our nerve substance. Our nerve substance is the basis of our mental life, and is greatly lacking in internal formative force. During the whole span of life from birth, the nerve substance of man is worked upon by or is dependent on external impressions. The internal formative force is superseded by the faculty of simple adaptation to external influences. Conditions are different in the blood, which has kept to a great extent its internal formative force. This internal formative force, as the facts show, is also present in a certain sense in milk; for if this were not so, we could not give milk to young babies, as the most wholesome form of nourishment. It contains a similar formative potentiality as the blood; in this respect both vital fluids have something in common. But there is also a considerable difference. Milk has formative potentiality; but lacks a constituent that is most essential to blood, or has it only in the smallest quantity. This is iron, fundamentally the only metal in the human organism that forms such compounds within the organism as display the true phenomenon of crystallisation. Thus, even if milk also contains other metals in minute amounts, there is this difference: that blood essentially requires iron, which is a typical metal. Milk, although also potentially formative, does not require iron as a constituent. Why does the blood need iron? This is one of the crucial questions of the whole science of medicine. The blood actually needs iron (we shall sift and collect the material evidence for the facts I have sketched today). Blood is that substance of the human organism, which is diseased through its own nature, and must be continuously healed by iron. This is not the case with milk. Were it so, milk could not be a formative medium for mankind, as it actually is; a formative medium administered from outside. When we study the human blood, we study something that is constantly sick, from the very nature of our constitution and organism. Blood by its very nature is sick and needs to be continuously cured by the addition of iron. This means that a continuous healing process is carried on within us, in the essential process of our blood. If the medical man is “a candidate for Nature's examination,” he must study first of all, not an abnormal but a normal process of nature. And the process essential to the blood is certainly “normal,” and at the same time a process in which nature itself must continually heal, and must heal by means of the administration of the requisite mineral, iron. To depict what happens to our blood by means of a graph, we must show the inherent constitution of blood itself, without any admixture of iron, as a curve or line sloping downwards, and finally arriving at the point of complete dissolution of the blood. (See Diagram 8, red). whereas the effect of iron in the blood is to raise the line continuously upwards as it heals. (yellow line).  There indeed we have a process which is both normal and a standard pattern to be followed if we want to think of the processes of healing. Here we can really pass Nature's examination, for we see how nature works, bringing the metal and its forces which are external to mankind, into the human frame. And at the same time, we learn how the blood, which needs must remain inside the human organism, must be healed and how what flows out of the human organism, namely milk does not need to be healed, but which if it has formative forces, can wholesomely transmit them to another organism. Here we have a certain polarity—and mark well, a certain, not a complete polarity—between blood and milk, which must have attention and observation, for we can learn very much from it. |
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture IV
24 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture IV
24 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The discussion yesterday was certainly of absorbing interest, but I must enter a caveat in connection with a question that has just been handed to me. I must again—as on a previous occasion—emphasise that we shall only reach an adequate method of ascertaining the relationship between individual remedies and individual phenomena of disease, after having answered in these lectures certain preliminary questions. Only these can enable us to judge the significance of every fact we discover about the connection between man and that external nature from which our remedies are derived. In particular, until we have settled these preliminaries, we shall not find it possible to deal with the connection between specific remedies and specific organs, for the simple reason that the connection is a complicated one, and we can only appreciate its real point when we have answered certain preliminary questions. This we shall try to do today and perhaps also in part tomorrow. Then we shall be in a position to point out a definite connection between particular remedies and the disease of particular organs. I want to make an introductory remark today and at once; and to ask you to accept it provisionally, because it throws light on many things. Regarding what was said in yesterday's lecture, [Ed: A lecture on the Ritter treatment of disease given by one of those attending the course.] I should like to ask you to face the reverse side of the matter. In that lecture, many very instructive cases were cited of undoubted cures—and certainly we must feel deeply gratified at this result. But I can suggest a very simple means whereby these cures would become more and more infrequent, and of course, I only make this suggestion so that you do not use this means although one might be led to use it. And I can, of course, only mention this amongst persons who have acquired a certain knowledge of Anthroposophy. The method referred to would consist in making every possible effort to make the Ritter therapy universally accepted. In face of successes of this treatment, you forget that you work as individual physicians. Possibly individuals among you may be aware of the struggle you have to wage against the majority of other doctors; and you may be aware that the moment you make Ritter's treatment into an accepted university institution, you would cease to be a minority in opposition and that treatment would then be practised by many others—I will not go so far as to say by all. You would then find the number of your successful cures appreciably diminished. So strangely do things befall in real life; they are often quite different from what we have imagined. As individual medical men you have the greatest interest in healing the individual patient, and modern materialistic medicine has even—one might say—sought in this way a legal justification for its aim of healing the individual. But this justification really consists in the claim that there are no diseases; there are only sick, diseased people! Now, this justification would be valid if patients were really so isolated regarding their sickness, as appears to be the case today. But in actual fact, individual patients are not so isolated. The fact that certain dispositions of disease spread over a wide region, as was mentioned yesterday by Dr. E., is of great importance. After curing one case, you can never be sure of the number of other individuals to whom you have brought the disease. The single case of disease is not viewed as part of a general process, and therefore, taken one by one, the individual result may be most striking. But one who aims at the benefit of mankind as a whole must speak—if I may say so—from a different angle. This is the factor which requires not only a one-sided purely therapeutic orientation, but a completely worked out therapy on the basis of pathology. This is precisely what we here attempt to provide, bringing a certain rationale into what is otherwise merely an empirical thinking on a basis of statistics. We will start our inquiry today from a fact that is common knowledge, and can fundamentally help us to judge the relationship of man to external nature, but has not been given anything like due attention, in ordinary medical and biological thinking. This is that man as a threefold being, in his nerves and senses system, in his circulatory system (as a being living in rhythms) and finally in his metabolic system, has a certain negative relationship to the events of external nature, especially in the plant world. Please give your consideration to this: in external nature (let us consider only plants to begin with) there is in the flora a tendency at work to concentrate carbon; to make this substance the base of all vegetation. Inasmuch as we are surrounded with plants, we are surrounded with organic structures whose essential nature consists of carbon concentration. Do not forget that the same substance is also present in the human organism, but that it is essential to the organism to arrest this formation, to keep it, as it were, in a permanent status nascendi, of dissolution, and to replace it by the opposite substance. We have the initial stages of this process in what I have recently termed the lower human organism. We deposit the carbon and, begin, as it were, out of our own forces, the process of plant formation, and at the same time, we are compelled to fight against this process, at the urge of our upper organism. We cancel the plant formation by opposing carbon with oxygen, by changing it into carbon dioxide, and thus we develop in ourselves the process directly opposite to plant formation. I recommend you to give heed wherever these processes contrary to external nature are found. You will thereby reach a more fundamental comprehension of what man actually is. You do not understand man's nature by weighing him—to take a symbolic example for all investigations by means of the methods proper to physics; but you will understand something about the mechanics of man immediately if you consider that the brain, as is well known, has an average weight of about 1,300 grammes, but that this full weight cannot press upon the lower interior surface of the cranium, for if it did, all the delicate network of minute veins in that region would be crushed and obliterated. The pressure of the brain on its base does not exceed twenty grammes. The cause is the well known hydraulic principle enunciated by Archimedes, that the brain becomes buoyant as it floats in the cerebro-spinal fluid, so that its total mass and weight are not effective but are counteracted by the surrounding liquid. And just as the weight of the brain is neutralised and we do not live within the physical weight of our organism, but within the buoyancy which is the force opposed to material weight—so is it with other human processes. In fact we do not live in what physics would make of us, but in that part of the physical that is neutralised or counteracted in us. And similarly we do not live in the processes observable as operative in external nature, which reach their final manifestations in the vegetable world, but we live in the cancelation of the plant formation process. This fact is of course an essential in building the bridge between the human organism in disease and remedies drawn from the vegetable world. This theme could be treated—so to speak—in the style of a poetical story. We could say: if we take in all the beauty of the vegetable world that surrounds us in external nature, we are entranced and rightly so. But it is otherwise if we cut open a sheep's body and forthwith become aware of another kind of flora which certainly originated in a similar way to the flora of the external world. If we open the body of a freshly killed sheep and encounter the full force of the odour of putrefaction from its entrails, we most certainly feel far less pleasure in the existence of the intestinal flora. We must carefully note and consider this fact; for it is simply self-evident that the same causes which favour the growth of vegetation in external nature, must be counteracted in man, and that the intestinal flora ought not to develop in us. Here we have a remarkably extensive field of research, and I would venture to recommend, as a theme for doctoral theses for younger students, to make use of this subject matter, and especially of comparative anatomical research, on the intestinal structures of various animal groups, through mammals up to man. As I say, a remarkably rich source, for much that is most significant here has not yet been investigated. Try particularly to find out why the opened sheep exhales so foul an odour of putrefacation by reason of its intestinal flora, whereas this is far from being the case in birds, even in carrion birds, whose bodies when opened smell comparatively pleasant. There is very much in these matters that has received no scientific study and research up till now. And the same is true of the comparative anatomy of the intestines. Think for a moment of the considerable difference in all birds from both the Mammalia and mankind. (It is just here that materialists, for instance the Paris expert, Metchnikoff, have perpetrated the greatest errors). In birds there is a remarkably poor development of both bladder and large intestine. Only in those groups which form the Ratites (the Ostrich and its relatives) does the colon begin to enlarge, and certain approximations to the bladder appear. So that we are led to the important fact that birds are unable to accumulate their excretions, retain them for a while within their bodies and then evacuate them as occasion offers; but on the contrary, there is a continuous equipoise between what is taken into their bodies and what is evacuated from them. It is one of the most superficial views to regard the flora of the human intestines—and, as we shall see later, also the microscopic fauna found there and elsewhere in the human organism—as anything to be called the cause of sickness. It is really quite appalling, in the course of examining and collating the literature pathology today, to find in every chapter the refrain: In cases of this disease we have discovered such and such a bacillus, in cases of that disease, another bacillus and so forth. Such facts are of great interest to the study of the botany and zoology of the human organisms, but as regards the condition of disease they have at best only the significance of indicators, indicators enabling one to conclude that if this or that form of disease is present, the human organism thus affected offers appropriate soil for the growth of this or that interesting vegetable or animal micro-organism. They mean this and nothing more. With the disease as such, this development of microscopic flora and fauna has only very little to do; and that little, only indirectly. For, I ask you to observe that the logic displayed in contemporary medicine today on these themes, is quite remarkable. Suppose for example you discover a landscape, in which you find a number of extremely well fed and healthy looking cattle. Would it occur to you to say: all that you behold in this countryside is as it is, because the cattle have somehow descended from the air and have infected the district? Such an idea would hardly occur to you; rather will you be obliged to inquire, why there are industrious people in this district, why the soil is specially propitious for this or that form of pasturage, and so on. You will probably exhaust all the possible reasons for well-fed and cared for livestock, in your mental review; but you would never dream of propounding the theory that the countryside has been infected by an immigration of well fed cows! This however is exactly the train of reasoning displayed by Medical Science today, in respect of microbes, etc.... These remarkable creatures simply prove, by their presence, that there is a certain type of medium or substratum favourable to them, and attention should accordingly be directed to the study of this substratum. Of this substratum, of course there may be indirect causes and effects. For instance, in the country-side we spoke of, someone might say; “Here are a lot of fine, well-cared for cattle; if we send a few more, perhaps some more people will put their backs into it and join the others.” Thus it is, of course, possible, that a well prepared substratum is incited by the invasion of bacteria to develop some disease on its own part. But with the study of disease as such this concentration on the nature of bacilli has nothing whatever to do. If only care were taken to build up a sound logical line of thought, nothing of what is perpetrated by official science to the ruin of sound thinking, could occur. The really decisive factor is a certain unbalanced interaction of what I have recently termed the upper and lower spheres in man, which may disturb or destroy their correct and normal relationship. So that a defective counter-activity of the upper sphere may set free in the lower sphere forces which cannot cope with the process of plant formation; a process which is there as an inborn tendency and requires to be checked. Then there is opportunity for the growth of abundant intestinal flora, and such intestinal flora becomes a symptom of defective abdominal functions in man. Now there is this peculiarity: the activities which normally proceed from the upper sphere to the lower, are dammed up, as it were, if they cannot fulfill their downward course. Therefore, if there are obstacles which prevent the performance of the functions for which the lower part of the body is organised, those functions are pushed backwards. That may seem to some people an unscientific expression, but it is more scientifically accurate than much that is written in the usual text books on Pathology. These processes, normally proper to the lower sphere of man, are pushed back into the upper, and we have to observe and follow this up as a cause of discharges from the lungs and other parts of the upper body, such as the pleura and so on, and inquire into the state of the normal or abnormal secretory processes of the lower sphere of man It is very important to get a clear view of this reversal of organic processes from and through the lower sphere into the upper again, so that much that manifests in the upper parts are simply abdominal processes pushed back. And this reversal of processes does occur if the correct interaction between the two spheres is disturbed. Here is another circumstance for your consideration. You all know it as a fact; but it has not received adequate attention, although a healthy scientific view would lay great stress on it. At the very moment that you have thoughts about any organ of your bodies, or to express it better, thoughts that are connected with any organ, there is a certain degree of activity in that part. Here is, I suggest to you another wide field for future doctoral theses! Just study the association of certain trains of thought with, for example, the flow of saliva, the flow of mucoid substance from the intestines, the flow of milk, of urine, of seminal secretion; all these are the accompaniment of thoughts which arise and proceed concurrently with these organic phenomena. What is the fact before us? In your soul life certain thoughts arise; organic phenomena appear concurrently; the two processes run parallel. What does it mean? What arises in your thoughts is entirely within the organs. If you have thoughts synchronising with a glandular secretion, you have drawn the activity which is the basis of the thought, the thinking out of the gland itself. You perform the activity apart from the gland, leaving the gland to its own fate, and the gland performs its proper activity; it secretes. The secretion is held up, that is to say what otherwise is set free from the gland, remains within it, because thought unites it with the gland. Here then, you have so to speak, in a tangible form, the passing of plastic activity from out of the organ into the thought. You can say to yourselves: if I had not thought thus, my gland would not have secreted. That is: I have drawn a force out of the gland, transferred it into my soul life, and the gland has given forth its secretion. The human organism supplies the most obvious proof of my argument in our previous considerations, that what we experience in soul and spirit is simply the operation of those formative forces, separated in us, but working in the rest of Nature's order. The external natural processes take place, by virtue of the same forces that develop the flora of fields and woods, corresponding to our intestinal flora; in the external flora are the same formative forces that we extract in the case of our own flora. If you look at the flora of the mountains and meadows, you must recognise in them the same forces that you evolve in your thoughts, when you live in representation and feeling. And the humble vegetation of your intestines differs from the external flora, because the latter do not have to be deprived of the thoughts. Thoughts are inherent in the external vegetable world, as much parts of the plants as their stems and leaves and blossoms. Here you get an idea of the kinship between what holds sway in flowers and foliage and that which works within yourselves when you develop an intestinal vegetation, which you deprive of formative powers, taking those powers away for your own use. For indeed, if you did not do this you would not be a thinking being. You take away from your intestinal flora what the flora out in nature still retain. This is equally true of the fauna. It is impossible to correlate the nature of man with remedies from the vegetable world, without understanding what I have just said. Similarly until we realise that mankind has drawn away from his intestinal fauna the forces formative of animal life in external nature, we can get no right concept of the use of sera. So you can see that a system, a rationale in these matters, is only obtainable when we envisage the relationship of man to his environment. And I would draw your attention to another point that is curiously significant. I do not know how many of you some time ago noticed the most preposterous placards forbidding people to spit. As you know the purpose behind them was to combat tuberculosis. These prohibitory placards are abjured for the reason—which ought to be common knowledge—that the daily diffused light of the sun destroys the bacilli of tuberculosis in a very short time. If you examine a sputum specimen after a short time, it contains no more such bacilli. So that even if the assumption of current medicine were valid—this prohibition would be extremely absurd. Such prohibitions have significance for the elementary observance of cleanliness, but not for the widest aspects of hygiene. For the student who is beginning to estimate facts correctly, this is very important, for it indicates the inability of the kinsman of intestinal fauna or flora, the bacillus, to survive in the sunlight. Sunlight does not suit it. Where can the bacillus survive? In the interior of the human body. And why just there? It is not that the bacillus itself is the noxious agent, it is the forces active within the body that we must consider. And here is another fact that is ignored. We are continually surrounded by light; light—as you will of course remember perfectly from your study of science—has supreme importance for the evolution of the extra-human beings, and especially for the development of all extra-human flora. But at the border line between ourselves and the world outside, something very significant happens to light, that is, to something purely etheric; it becomes transmuted. And it needs must be transmuted. For, consider how the process of plant formation is held up in man, how this process is so to speak broken off and counteracted by the process that manufactures carbon dioxide. In the same way, the process contained in the life of light is interrupted in man. And so, if we seek for light within man, it must be something transformed, it must be a metamorphosis of light. At the moment of crossing the border of man inwards we have a metamorphosis of light. This means that man does not only transform the common, ponderable processes of external nature within himself, but also the imponderable element—Light itself. He changes it into something different. And if the bacillus of tuberculosis thrives in the human interior and perishes in the full sunlight, it is evident—to a sound judgment of the fact—that the product of the light as transmuted within us, must offer a favourable environment to these bacilli, and if they multiply excessively, there must be something wrong with the product of transmutation, and thence we get the insight that amongst the causes of tuberculosis is involved that of the process of transmutation of light within the patient. Something occurs which should not occur, otherwise he would not harbour too many of the tuberculosis bacilli—for they are always present in all of us, but as a rule in insufficient numbers to provoke active tuberculosis. If they are too prolific, their “host” succumbs to the disease. And the tuberculosis bacillus could not be found everywhere, if there were not something abnormal in the development of this transmuted light of the sun. It will again be easy to work out an adequate number of doctorial theses and scientific papers on this. Empirical material gleaned from observation, will pour on you in floods, in corroboration of views which I can only offer here in mere outline. What happens if a human being becomes suitable soil for tuberculosis bacilli is that either he is not constitutionally capable of absorbing sunlight, or he does not get enough sunlight owing to his way of life. Thus there is not an adequate balance between the amount of sunlight he receives from outside, and the amount he can transmute; and this forces him to draw reserves from the already transmuted light stored up within him. Please pay particular attention to this: Man by the very fact of being man, has a continuous supply of stored and transmuted light within. That is necessary to his organisation. If the mutual process, enacted between man and the external sunlight, does not take place properly, his body is deprived of the transmuted light, just as, in cases of emaciation, the body loses fat which it needs. And in such cases, man faces the dilemma of either forcing his upper sphere to become diseased or of depriving his lower sphere of what he needs for the upper: that is of making his lower sphere sick, by depriving it of transmuted light. You will gather from this that the organisation of man needs not only ponderable substances, derived from the external world and transformed, but that imponderable, etheric substances are also present within him, although in metamorphosis. Further you will conclude that these basic principles afford the possibility of building up a correct view, on the one hand, of the healing effect of the sun's light: we can expose the human being directly to the sunlight, in order to regulate his disordered interrelation to the environing light. And, on the other hand, we may administer internally those substances that counteract the irregularity in the deprivation of transmuted light. We must counter-balance the deprivation of transmuted light, by means of what can be drawn from the remedial substances. There is the window through which you can observe the human organisation at work. But now—you must excuse my somewhat undiplomatic expression, it is really objective, detached from sympathy or antipathy—everybody who observes the world must after a time acquire a certain anger against every use of the microscope, against every research on the microscopic scale: because microscopical methods are more apt to lead away from a wholesome view of life and its disturbances, than to lead towards it. All the processes actually affecting us, in our health and sickness, can be much better studied on the macroscopic than on the microscopic scale. We must only seek out the opportunities for such a study in the world of the macrocosm. Let us return to the Birds. As a result of the absence of a bladder and large intestine, these creatures possess a continual balance between nutrition and evacuation. Birds can evacuate their waste matter in flight; they do not retain it; they do not store it in themselves. They have no organs for such a purpose. If a bird were to accumulate and retain excretions, this would be a disease which would destroy it. In so far as we are human beings we have gone further than the birds on the evolutionary path, in the phrase that meets contemporary opinion; or—as would be a more correct statement—we have descended below the level of that order. For birds do not need to wage the vigorous war against intestinal flora which does not exist in them; this war is unavoidable in higher animals and mankind. But let us consider a—shall we say—somewhat more highly placed activity of ours; the metamorphic activity of the etheric element, the metamorphosis of light, as just described. In respect of these functions we are on the same grade as birds. We have a large intestine and a bladder in our physical organism, but in our etheric organism, in these respects, we are birds; these organs are actually absent in the dynamics of the cosmos. Therefore we are obliged to work up light as soon as we receive it, and to give forth the products by excretion. If a disturbance arises here, there is no corresponding organ for its operation. We cannot stand the disturbance without our health suffering accordingly. So when we observe the birds with their miniature brains, it becomes evident that in the macrocosmos they are replicas of our more subtle organisation. And if you want to study man with reference to this finer organisation which separates itself from his coarser organisation which has descended below the birds—then, my friends, you must study the processes of the world of birds macroscopically. Here I should like to interpolate a comment. We human creatures would be in a sad state, if in our etheric organism we had the same superiority over birds as we have in our physical; for the etheric organism cannot be enclosed and sequestrated, in the same way, from the external world. If we possessed organs of smell receptive to the storage of transmuted light, the social life of mankind would be an appalling experience. We should have the same experience we get when we cut open a sheep and inhale the fumes of its entrails. Whereas, in actual fact, the etheric aroma of mankind, as perceived among ourselves, may be compared to the relatively far from disagreeable smell of a freshly killed carrion bird. Contrast this with what we smell if we open the body of a ruminant animal and even of such an animal as the horse, which is not a true ruminant although it has the tendency to become a ruminant in its organisation. So what we have to do is to investigate the analogy between what happens in the external animal and vegetable worlds, and what happens in regard to the intestinal flora and fauna in the human organisation, which has to be combated and counteracted. And in deciding the relationship between any specific organ and any specific remedy, we must pass from the general definitions just given, to the particular definitions and descriptions of the following lectures. Now pass from the reasons compelling us to combat the intestinal flora and fauna, inasmuch as within the circulatory function we find something that attacks the process of plant formation. Let us consider man's nervous and senses system. This aspect of our nature is far more significant for its totality than is generally believed. Science has become so remote an abstraction, that it has not been realised how this nervous and sensory system, which is interpenetrated with light and the warmth inseparable from light, is linked up with the internal life. This is because the imponderable elements that enter the body with the light, must be absorbed and transmuted by our organs, and are forming organs in us, just as do the substances of the ponderable world. The special significance of the nerves and senses system for our human organism has been neglected. But whereas, if we enter more deeply into the lower man we descend out of the formative force of intestinal flora into that of intestinal fauna, we come, if we ascend in man, out of the region where the intestinal flora is combated, into the region where there must be a continual combating of the tendency of man to become mineralised, to become sclerotic. You can observe externally in the greater ossification of the human head how the tendency towards mineralisation increases the more man develops upwards. This tendency towards mineralisation is of great importance for our whole organisation. We must constantly recall—as I have done already in public lectures—that in dividing the human being into three systems, i.e. the head man, the trunk man and the limb man, we must be careful not to imagine that these three are external to one another within external spatial boundaries. Man is of course wholly head man, but qualitatively distributed. That which has its chief focus in the head, also extends over the whole man. The same is true of the other main systems, circulation system, limb and metabolic system; they too, extend throughout man's body. So the tendency to mineralisation, localised chiefly in the head, exists and must be counteracted all through the body. Here is a field of knowledge of which the contemporary student can no longer understand anything when he glances through the ancient treatises written in the light of atavistic clairvoyance. For after all, only the smallest minority of those who trouble to read that Paracelsus writes of the salt-process, get any worth-while idea from it today. But the salt-process belongs to the region that I am now outlining, just as the sulphur process belongs to the region previously described. Man has an inherent tendency to mineralisation; just as the forces fundamental to the development of our internal flora and fauna can get “out of hand,” so also can the mineralising tendency. How is it to be counteracted? Only by shattering it; by, as it were, driving a perpetual succession of minute wedges into it. And here you enter the region where you have to pass from serotherapy through vegetable therapy to mineral therapy. You cannot do without this, as you only reach a starting ground for the support of all that needs support, in man's struggle against mineralisation, against general sclerosis, in the interaction between the minerals and those human substances which tend themselves to become minerals. It does not suffice simply to introduce the mineral, in its crude state as found in the external world, into the human organism. The right method would indicate some form of the homeopathic principle. For it is precisely from the mineral kingdom that we must set free the forces opposed to the action of the external forces of that kingdom. It is a sound comment (and one already made) that we have only to turn our attention to the very slight mineral content of many medicinal springs, which have a remedial effect, in order to observe a conspicuous homeopathic process. This process shows that at the very instant in which we liberate the mineral components from their externally known forces, other forces emerge which can only be fully liberated through homeopathic dosage. This subject shall be given special consideration later on. But I would add the following consideration today, and address my remarks particularly to the younger members of my audience. Let us assume that you are making comparative investigations into the structural changes of the whole intestinal system, let us say from the fishes, through the Amphibia to the reptiles—the conditions in the Amphibia and reptiles in this respect, are most interesting—to the birds on the one side, and the mammals, and finally, man, on the other. You will find that remarkable changes of form occur in the organs. For instance, there are the Caeca the equivalent of what has become the vermiform appendix in man; in the lower mammals, or, in bird groups which deviate from the normal type—the rudiments of the vermiform appendix appear. Or study the quite different way in which the great gut, which does not exist in fishes, evolves through the ascent of so-called more perfect classes, into what we can recognise as the larger intestine (colon). Between this and the manner in which caeca become what we recognise as the appendix in mankind, (certain species of animals have several appendices) you will find a remarkable complementary relationship. A comparative study should bring this interrelationship into sharp relief. Of course you can put the question from the outside, as it were, and you know how often it is so put: why is there such a thing as the vermiform appendix in mankind? Yes, that is often asked. And if the question is raised, it is generally forgotten that man exhibits a duality, so that what originates in the lower sphere has always complementary organ in the upper, and that certain organs of the upper sphere could not evolve without their complementary organs, almost their opposite poles, in the lower. The more the fore-brain approximates to the form which it reaches in mankind, the more evolved does the intestine become in the direction of the process of the depositing of waste material. There is a close correspondence between cerebral and intestinal formation; if the great gut and the caecum did not appear in the course of animal evolution, it would not be possible for men capable of thinking, to arise on a physical basis; for man possesses the brain, the organ of thinking at the expense—I repeat, entirely at the expense of his intestinal organs, and the intestinal organs are the exact reverse side of the brain parts. You are relieved of the need for physical action in order to think; but instead your organism is burdened with the functions of the highly developed larger intestine and bladder. Thus the highest activities of soul and spirit manifested in the physical world through man, so far as they are dependent on a complete brain formation, are also dependent on the equivalent structure of the intestine. This crucially important inter-relationship throws much light on the whole way in which nature works. For, however paradoxical, it is nevertheless permissible to say, that man has a vermiform appendix in order that he may think like a human being. That which shapes and reveals itself in the appendix, has its polar complement in the human brain. All that is in one sphere has its analogies in the other. These are facts which must be acquired once more through new methods of knowledge. We cannot merely echo the physicians of antiquity, who based their doctrine on atavistic perceptions. That road will not lead us to many results. We must reconquer these truths ourselves. And in that reconquest we shall find the purely materialistic achievements of medicine, which are averse from such associations, a real obstacle. For medicine and biology today, the brain is simply an internal organ and so are the contents of the abdomen and pelvis; entrails, all of them. And thus they made the same mistake as if they identified positive with negative electricity; just electricity, what is the difference? The mistake here is quite analogous but is overlooked. For, just as between positive and negative electricity there arise tensions which then seek their equilibrium, there is also perpetual tension within man, between the upper and lower organic spheres. And the control of this tension really comprises what we must search for in the field of medicine. This tension also manifests itself (I will merely indicate this today, but treat it in detail later) through the forces concentrated in two organs: the Pineal Gland and the so-called Pituitary Gland. In the pineal, all those forces are focused and marshaled which are contrary to those of the pituitary, the hypophysis cerebri, that is to those which are of the nature of the lower organic sphere. It is a mutual relation of opposing tensions. And if we were in the habit of forming an opinion of the state of this balance of tensions, from the general health of the individual case, we should have laid a very sound foundation for the remedial treatment to follow. |
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture V
25 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 312. Spiritual Science and Medicine: Lecture V
25 Mar 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
As we go further into that special realm where pathology is to meet therapeutics and where, in a certain sense, we build a bridge between the two, we shall need to mention many things that can only remain a sort of ideal for treatment and cannot be everywhere fully applied. Nevertheless, if we had a comprehensive picture of all that matters in the treatment of disease, we should be able to select one or other particular point, and at least we should know how a fragmentary diagnosis of a given disease can be utilised. First and foremost, we must consider the importance, even in the most special cases, of knowing the whole personality before us. This should include all the main data of the patient's life. Some medical practitioners have given me their confidence, and discussed various topics with me, and I have often been amazed. My first question was: “How old is the patient?” and the practitioner could give no definite answer. He had himself formed no opinion on the patient's age. As we shall see in the next few lectures, it is one of the essentials to know this, for therapeutics depend very much on the age of the person treated. The day before yesterday we heard it said of certain remedies, that while in some cases they were of extraordinary efficacy in others they failed.1 Here arises the question whether there was any connection between the failure and the age of the patient under treatment We must collect and collate very exact records concerning the influence of age upon the effect of remedies. Then there is the factor of stature. We should always pay special attention to the stature and build of the patient—whether he is short and compact or tall and lanky. It is important to be able to judge, from differences in build, the forces inherent in what we term the etheric body of man. I have given much consideration to the possibility of avoiding these terms, which belong to the reality of man's being; but it is impossible to do so, and presumably you would not wish to do so. Of course we could replace them by other terms that find more approval among those who are not Anthroposophists. Perhaps of this course. Here and now, however, we shall retain this vocabulary for the sake of better understanding. We can judge what I might term the intensity of the etheric body's activity by the build and physique of the individual. One should wherever possible find out—(I will mention every factor, although often they cannot be considered for lack of the necessary data) whether in his youth the patient grew slowly or rapidly. All such facts are symptomatic of what we might term the action of the etheric body, or let us say, of the functional manifestations of the man in relation to his physical body. This must be taken into account, if we want to perceive a connection between the man and his medical remedies. Then we must find out the relationship of both physical and etheric bodies to the higher members of the human organisation, to what we call the astral body, (the soul proper) and the ego (the spiritual proper). So for instance we should ask the patient about his dream-life: does he dream much or little? An extensive dream-life is an extremely important constitutional peculiarity, for it testifies to a tendency of the astral body and Ego to unfold an activity of their own, and not to concern themselves very closely with the physical body, so that the formative forces of the soul do not flow down into the organic system. Another question that should be put—although it may be “uncomfortable”—is whether the individual patient is fond of movement and exertion, or inclined to inertia. For personalities with the latter tendency have a powerful internal agility of their astral bodies and egos. This may appear paradoxical, but the activity referred to does not reach our consciousness. And for this very reason the individual is not consciously industrious, but, on the whole, lazy. For what I here define as the opposite of inertia is the organic capacity to grip the lower human sphere by means of the higher members, i.e., to transmit activity from the astral body and from the ego, into the physical and etheric bodies. Lazy people have very slight capacity of this kind. The lazy man is really, from the point of view of spiritual science, a man asleep. Then we should inform ourselves about the patient's eyesight: is he short-sighted or long-sighted? Short-sighted individuals have a certain reluctance of the astral body and ego to permeate the physical body, and short-sight is one of the chief symptoms of this reluctance. I would offer a further suggestion which might some day be feasible. It would be most important in the treatment of disease, and, as I believe, could become valuable in practice if the various professions were to develop more social feeling. My suggestion is this: it would be most useful if dentists and dental surgeons were to use their knowledge of the dental system and all that is connected with it, that is, of the digestive system as well, so as to be able to offer a sort of diagram to their patients on each occasion of treatment or consultation. Of course the patients themselves must be persuaded to co-operate, but, with some social sense, this would perhaps be possible. On such a diagram the dentist would note the efficiency of all factors related to dentition, whether there was any early tendency to dental caries;, whether the teeth have kept in good condition in later life, and so forth. As we shall see during the next lectures, these matters are crucial for the correct judgment of the total human organisation. And if the physician who has to treat an isolated case of illness could obtain a summary of the patient's state of health from the state of his teeth in this way, the document would be an extremely important basis for the treatment. Further, you should learn from the patients themselves their chief physical sympathies and antipathies. It is particularly important to know whether any person you propose to treat, has a keen appetite for salt, for instance. His most pronounced tastes in food should be ascertained. If he has a strong appetite for all saline flavours, we have to deal with a person in whom there is too close a connection between the ego and astral body on the one hand, and the physical and etheric bodies on the other. The affinity between his soul and spirit and his bodily organism is, so to speak too complete. The same conclusion may be drawn from liability to vertigo—fits of dizziness following external mechanical movements, such as rapidly turning round. It should be noted whether a patient becomes dizzy easily following certain bodily movements. Moreover, one ought to acquaint oneself—though this is very generally known—with every disturbance of elimination, with the whole glandular activity of the patient. Where there are irregularities of elimination there are also always disturbances in the interaction of ego and astral body with the etheric and physical bodies. These are a few indications of what must be ascertained in the first consultation with any patient. They are chosen as examples, but you will perceive their general trend, in so far as the individual bodily constitution is concerned. Later on we shall discuss also the indications of habits of life, the access to good air, etc. These are rather matters for consideration under the special headings. But you have had an outline of the way to obtain a view of the sort of person you have to treat. For only when this is known in detail, will it be possible to judge how to administer or compose any remedy. I should like to remind you of the general fact mentioned before that there is an inherent relationship between man and the whole non-human world. In Spiritual Science this relationship is often formulated in this, admittedly abstract, manner in the course of evolution mankind has discarded and released the other natural kingdoms out of his own entity, and therefore external things retain a relationship to him. But in place of this abstract formulation, we shall have to point to repeated specific and concrete instances of the relationship in organo-therapy. Let us be clear, first of all, as to the actual basis of this remedial reaction of man to non-human nature. You know that there is much controversy on this theme. As we shall explain more fully later, different methods of treatment are arranged against one another. One of these disputes is all too well known to the public; that waged by the advocates of homeopathy and of allopathy respectively. It might interest you to hear about the part Spiritual Science should take here. But its intervention is somewhat peculiar. I shall give a general statement regarding it now, but reserve the details for later addresses. Strictly speaking, in the light of the results of Spiritual Science, there are no allopaths. There are in reality no allopaths because even what is described as an allopathic remedy is subjected within the organism to a homeopathic process and heals only through and by virtue of this process, so that, in actual fact, every allopath is supported and helped in his characteristic methods, by the homeopathic processes of the organism under treatment. This carries out what the allopath forgets, the dispersion of the particles of the remedial substances. But, of course, there is a considerable difference, according to whether we relieve the organism of this homeopathic function, or not. This is simply because the curative processes within us are associated with the condition of these remedies after they have been gradually homeopathised, whereas the organism has no curative interaction with the substances of the external world in their usual state. When these are taken into the body, they are “foreign bodies,” causing really awful disturbances and overloading if the body is burdened with the forces contained in allopathic dosages. We shall give special consideration to the cases in which it is impossible to relieve the organism of this homeopathic effort. Homeopathic dosage has really up to a point been very carefully copied from Nature herself, although fanatics have often gone too far and jumped to conclusions. How can we find a way to the relationship between man and his non-human environment? As I pointed out yesterday, in another context, we cannot merely repeat what the physicians of old time have laid down, although an intelligent study of their works can be helpful. But we have also to investigate this interaction between the human and extra-human world with all the resources of modern science. And we must hold steadfastly to the knowledge that we cannot get much further by means of chemical research into various substances, that is, by consideration of the results of laboratory tests on such substances. This is a kind of microscopy; I have already suggested that this should be replaced by macroscopic observation of the Cosmos itself. Today I have to put some significant facts before you which may to some extent show in what way the extra-human world corresponds in a sort of threefold division to the threefold nature of man. First of all, consider all soluble substances. Solubility is the last and latest attribute of special importance in the evolution of our planet, What has been deposited as the solid element is mainly derived from a cosmic process of solution which has been overcome and has deadened and thrown off the solid particles. But it is a purely external view to consider the planetary process as a merely mechanical deposit of sediment, and to construct geognosy and geology on this premise. Rather may we maintain that in the process of solution something is manifested that man has liberated from his own being, in so far as it occurs externally in the extra-human nature. Something that man has set free is at work. So we must inquire what are the relationships between external processes of solution and the internal functions of our organism. It is of fundamental significance, that certain individuals in whom the spirit and soul principle is too closely linked with the etheric and physical bodies, have an organic hunger or thirst for salt; that means that they tend to reverse the process of depositing salt. They want to cancel the process of earth-formation within their own bodies, and restore salt to an earlier, more primitive, state than that in which the earth has solidified. It is very important to include these connections in our view. They afford real insight into the connections between the human organism and external nature. We may conclude that our human nature has inherent in it an organic need to reverse certain processes that take place in the external world, to fight against them. As I pointed out yesterday, there is even a resistance to the force of gravitation, shown by the buoyancy that lifts and suspends the human brain. This resistance is a general tendency. And what does this opposition to earth-solidifying forces mean? It means nothing less, in essence, than the liberation of the lower man from the soul and spirit principle, the expulsion of this principle from the lower sphere into the upper in the first instance. Thus in all cases where there is a pronounced appetite for salt, the lower organic sphere is striving somehow for liberation from the too potent activity of the soul and spirit within it, and trying, so to speak, to cause this activity to flow towards the upper organic sphere. Let us assume disturbances of function in the lower sphere, disturbances that have been recognised as such. Later on we shall see how one can recognise the particular methods of finding out the diseases that result. What can we do about them? Here I must interpolate a comment which may be of use to those who tend to be one-sided towards the use of mineral remedies. This antipathy is not justifiable. As we shall see, purely plant remedies can only be efficacious within very definite limits, and mineral remedies are of great service, particularly in more serious cases. So I ask you not to take offense, if I start from mineral remedies, from the efficacy of mineral remedies, however, which are incorporated within the realm of organic life. You can throw a strong light on certain treatments of the human pelvis and abdomen, in relation to the upper organs, by studying the oyster: there is great significance in the oyster and the formative process of its shell. The oyster is encased in a covering of carbonate of lime, Calcarea Carbonica, and it expels this substance from its body, to form the shell. You must accept a little help from Spiritual Science here; but if you study the oyster with this help, you will become aware that although this mollusk occupies a very low position in the animal world, its position in the Cosmos is relatively high. For this reason: the force that man carries within him which manifests itself as his power of thought, is extruded from the oyster to form the shell. If the oyster could link up the formative forces that are conducted outwards with its actual organic growth, it would become a highly intelligent creature and be put on a very high level in the animal kingdom. The forces which pass outwards from the interior, show the path by which this potentiality is canalised, drained to the exterior. And you can see clearly, and, so to speak, tangibly, in the origin of the oyster shell, the operation of carbonate of lime. It operates to draw the excess activity of the soul and spirit from the organism. Suppose you find a case of superfluous and excessive activity of soul and spirit manifesting within the lower bodily sphere, as happens in certain forms of disease, which we shall describe in due course. You must have recourse to the remedy we owe to the shells of oysters or similar substances, which, through the mysterious forces of carbonate of lime work outwards from within. Something quite crucial in the treatment will therefore depend on comprehending that certain healing forces are active in this centrifugal tendency. All that is associated with the therapeutic properties of Calcarea Carbonica and similar substances can only be rationally understood, if viewed in this context. All the forces inherent in phosphorus, e.g., are polar opposites to those in carbonate of lime. (The expressions I use in this connection are at least no less scientific, in their true significance, than much that today passes for science.) If all “saline substances” behave in such a way as to give themselves up to the environment, the reason is that all salts arise through deprivation and liberation of the corresponding substances from the inner workings of light and other imponderable elements. I might say that all that is saline has so repelled the imponderable elements through its very origin that they are alien to it. Of phosphorus the exact contrary is true. Ancient atavistic knowledge was indeed not without justification in calling phosphorus the Light-bearer. Men saw that phosphorus does carry and contain that imponderable light. What salt repels and holds at bay, phosphorus carries within it. Thus the substances at the opposite pole from salt, are those that appropriate, so to speak, the imponderable entities—principally light, but also others, for instance, warmth—and interiorise them, making them their inner properties. This is the basis of the remedial efficacy of all the qualities of phosphorus, and of all that is allied to phosphorus in its healing effect. Therefore phosphorus, in which the imponderable are internally stored, is especially conducive to bringing the astral body and the ego into closer relationship with the physical organism. Let us suppose that you are consulted by a person suffering from some disease (we shall deal with particular diseases later) in which there are particularly vivid and frequent dreams. This means that the astral body likes to separate from the physical, does so with ease, and goes about its own business. Moreover the patient tells you that he has a constitutional tendency to inflammations affecting the periphery of the organism. This is a further symptom showing that the astral body and ego are not settled properly in the physical. If these symptoms are found, you will be able to employ the force where with phosphorus grips its imponderables to make the astral body and ego occupy themselves more with the physical body. In persons who have restless and disturbed sleep, even in very different cases of disease, one can beneficially employ phosphorus, for it tends to restore and re-unite the astral body and ego to the physical and etheric bodies. Thus we find phosphoric and saline substances, polar opposites in some measure. And I would ask you to bear in mind the cosmic roles played by these two groups, as of far more significance than—if I may say so—the individual names applied in modern chemistry to all the separate substances. In the course of our discussions we shall see how phosphorus can be used for healing purposes, in the form of related substances. Here then you have, in external nature, two states which are polar to one another; that which acts in a saline manner and that which acts in a phosphoric manner. And between them, there is a third group: that which acts Mercurially. Just as man is a threefold being, a creature with nerves and senses, with a circulatory system, and with metabolism; and as circulation is the bridge linking nerves and senses to the metabolic functions: so also there is a mediatory function in external nature. It comprises everything that possesses, to a great degree, neither the saline character nor the character of interiorising the imponderables, but—so to speak—holds the equipoise between these two, by manifesting in the form of drops. For mercurial substances are essentially those which tend to assume the form of drops, by virtue of their inner combination of forces. This is the point which matters in all mercury substances, not whether they are known today under the name of quicksilver. The test of what is mercurial is the combination of forces whereby a substance is poised midway between the liquefying tendency of the saline, and the concentrating tendency in which imponderables are held together. So we must give special heed to the state of the forces that are the most evident in all mercurial substances. You will find accordingly, that these mercurial substances are mainly linked up with all that is calculated to bring about a balance between the activities for which phosphorous and saline substances are best qualified. We shall find that their effects upon the organism are not contradictory to the indications just given, when we deal specially with syphilitic and similar diseases. In this sketch of the three groups: Saline. Mercurial. Phosphoric. I have presented to you the most conspicuous mineral types. But in dealing with the saline group, we have already had to refer to an organic activity, as manifested in the formation of the oyster's shell, which works behind the saline nature. Such an organic process is in a certain sense at work also when imponderables become concentrated in phosphorus. But as in that case, all depends on interiorisation, the process becomes less obvious externally. Now let us turn from the contemplation of these typical forms manifested in the external world, to other processes that have been segregated at a different epoch from man—viz., plant life. As we have already recognised from a somewhat different point of view, the character of the plant represents the opposite of the activity proper to the human organism. But in the plant itself we can clearly differentiate between three kinds of manifestation. This threefold diversity strikes you very plainly, as you observe that which unfolds earthward to form the root and that which springs upward to send forth blossom, fruit and seed. The external direction in space as such indicates the contrast between the plant nature and Man (the animal must be left aside for the moment). This contrast in direction contains something of great significance and value. The plant sinks itself deep into the earth with its roots and stretches its blossom, its reproductive organs, upwards. Man is the direct opposite in his relation to the Cosmos. He sends his roots, so to speak, upwards, with his head, and he strives earthwards with his organs of reproduction. Thus it is not in the least unreasonable to picture our human frame as containing a plant, with its root sent upwards and its blossom opening downwards in the reproductive organs. For in a special way the plant nature is fitted, as it were, into the human. And again, there is a remarkable difference in Man and animal in that the plant hidden in the animal lies horizontally, that is at right angles to the direction of the growing plants, while Man has completely turned round and has executed a semicircle of 180 degrees when compared with the plant. This is one of the most instructive facts for the study [of] man's relationship to the external world. If our students of medicine would investigate such macrocosmic matters more closely, they would learn more of the forces operative, even, for instance, in the living cells, than through the methods of microscopy. For the most important forces that work even in the cells—and quite differently in plant, animal or man—can be observed and studied macroscopically. The human soul can be studied to much better effect, by observing the co-operation of that which extends vertically upwards and downwards, and that which lies in the balance of the horizontal. These forces can be observed in the macrocosm and are operative even down into the cellular tissues. And what is active within the cells, is in fact nothing less than the image of this macrocosmic working. Let us consider the vegetation of the Earth; but not in the usual fashion, by wandering on the Earth's surface to contemplate one plant beside another, examine it minutely in all its parts, invent a title of two or three separate names, and then list the plant in a system of classification. No: you must bear in mind that the whole earth is one single entity, and that the whole vegetable world pertains to the Earth's organism just as your hair belongs to yours—(although with this difference, that hairs resemble each other closely whereas plants are various and differ one from another). You can no more regard the single plant as an independent organism than you can so regard the single hair. The cause of the variety among plants is simply this; the Earth in its interaction with the rest of the Cosmos develops different forces towards the most diverse directions, and in this way gives a different organisation to the plants. But there is a certain basic unity in the constitution of the earth, from which all plant growth derives. The following consideration is therefore important. To give an example; suppose you are studying mushrooms and fungi: for these the earth itself is, so to speak, the support and matrix. Pass higher up the scale to herbs; here, too, the earth supports and nourishes, but forces from outside the earth have also influence in shaping their leaves and flowers: the force of light, for instance. And most interesting of all vegetable forms are the trees. Turn your attention to trees and you will recognise that the formation of their stems or trunks (by virtue of which trees become perennial) represents a continuation of what the whole earth is for the plant that nestles upon it. Please visualise this relationship of earth and plant. The herbal plant springs up out of the earth. This means that we must search in the earth itself for the forces fundamental to growth, which interact with the forces streaming on to our earth out of the Cosmos. But when a tree grows, do not, please, be too much shocked by what I say, for this is really the case—the earth rises up and grows, so to speak to cover over that which formally flowed directly out of the earth into the herb-like plant. That shoots up into the trunk—and all tree trunks are really outgrowths of the earth. If we have forgotten this, it is because of that gruesome materialistic concept of today, that the earth is merely composed of minerals. People do not realise how impossible is the concept of a mineral earth! The earth has other forces as well as those which segregate into the mineral kingdom; it has the forces that sprout into vegetation. These forces rise up out of the soil and become trunks. And all that grows upon the trunks is in a relationship to them comparable with that of the lower plant forms and herbs to the earth itself. Indeed I would say that the soil of earth is itself the trunk, or main stem, of those lesser vegetable growths, and that the trees formed an extra trunk to carry their essential organs—blossoms and seeds. Thus you will observe that there is a certain difference as to whether I take a blossom from a tree or from a herb-like plant. Consider further the formation of parasitic plants, more especially the mistletoe. In it you find the blossoms and seed organs which are normally united to the supporting plant, separated and stuck upon a stem like a process apart. Thus the formative process of the mistletoe represents an intensification of what is active in blossom and seed formation, and at the same time, in some sort, a separation from the terrestrial forces. What is non-terrestrial in the plant emancipates itself in the formation of the mistletoe. We see that upward urge away from the earth, which interacts with extra-terrestrial forces, gradually liberate and separate itself in the efflorescence of blossom and fruit, and arrive at a remarkable individualisation and emancipation, in the mistletoe. Bearing this in mind, together with the varied forms of plants; you will admit that there must be considerable organic difference according as a plant tends most to root-development, its growth forces manifesting principally in the root, but its blossoms small or even atrophied. Such plants tend more towards the earth forces. Those plants which liberate themselves from the earth forces are those that give themselves up to the formation of blossom and seed, or, most of all, those that live as parasites upon others of the vegetable kingdom. All plants tend to make some one organ particularly predominant. Take the pineapple, which tends to make its stem predominant, or indeed any other plant. Every principal organ of the plant, roots, stems, leaves, blossoms, fruit, becomes the chief and most conspicuous organ of this or that plant kind. Take for instance, Equisetum (the horse-tail), and observe the trend to become all stem. Other species, again, tend to become all leaves, There is a certain parallelism between these divergent tendencies in the vegetable growth and those three types of mineral activity in the external world that I have enumerated today. Let us consider the emancipatory tendency in plants—that urge which culminates in the activity of the parasitic species; here is something which tends to the interiorisation of imponderables. That which streams earthward out of the cosmos as imponderables is as definitely collected and conserved in blossoms and fruit, if blossoms and fruit prevail, as in the phosphor substance. So we may maintain that, in a certain sense, blossoms, seeds and all that tends towards mistletoe and other parasite development in plants are “phosphoric.” And on the opposite pole we find that the root process which the plant develops by regarding the earth as its mother-ground is closely related to salt-formation. Thus both these polarities face us in the world of the plant. And further: in the visible linkage between the blossom and fruit process that extends upwards and the downwards anchorage in the earth we have the mediating activity of the mercurial process. Now, take into account the opposite placing of organs, in man and in the plant respectively. You must conclude that all substances tending inwardly towards the formation of flowers and fruit must be closely related to the organs of the hypogastrium and all those organs directed and orientated by them. All phosphoric substance must therefore have close interaction with these lower human organs. We shall presently confirm this. On the other hand, all that tends towards root development will be intimately connected with all organs of the upper organisation. But of course you must bear in mind that we cannot make a simple and external threefold division of man's body. On the contrary, for instance, much that appertains to the lowest organic region, the digestive system, strives for its continuation as it were in the direction of the head. It is a complete, one might say a foolish error to suppose that the substrate substance of thought is mainly given in the grey matter of the brain. This is not so. The grey matter serves principally to conduct nourishment to the brain. It is essentially a colony of the digestive tract, surrounding the brain in order to feed it, whereas the white matter of the brain is of a great importance as substrate substance of thought. You will find something in the anatomical structure of the grey matter which is much more linked with a more general function of the whole body, than with the function usually attributed to it. As you see dealing with digestion, we cannot restrict ourselves to the lower abdominal regions. Nevertheless, in considering what is derived from or connected with roots, we shall find a definite affinity with what can be applied to the upper organic sphere in man. And all those portions of plants that achieve the equipoise between the blossom and fruit process, and the root process, and manifest in the common herbs through the leaves, will as a decoction have special influence on circulatory disturbances, that is on the rhythmic balance between the upper and lower spheres. Here then is the parallel between minerals that absorb and concentrate the imponderables, minerals that repel the imponderables, and the intermediate group, and the whole configuration of the plant. This furnishes you with the first rational method (as indicated by the plant itself, in the respective development of this or that organ) of establishing a mutual relationship with the human organism. We shall see how this basic principle works in detail. We have pointed out these mutual relationships between the vegetable, the mineral and the human. In recent times, there has been a very hopeful addition, in the suggested relationship and interaction between human and animal substances. But not only were the initial ventures in serotherapy carried out by curious methods; there are also objections to customary serotherapy, in principle. For when serotherapy was first introduced, Behring proceeded in a somewhat strange way. Those who merely followed the many speeches that were delivered, and publications that were issued, dealing with the mere fringe of the problem and with the results that were expected to come from the serum, received the impression that a thorough reform of all medical practice was impending. But after careful reading of the description of the actual experiments given in the fundamental scientific papers, they learned—without exaggeration, as some amongst my audience can probably confirm—that this treatment based on tests with guinea pigs (as laboratory material), which it was proposed to extend to human subjects, had proved “successful” with a “remarkably large” number of guinea pigs. Actually, only one amongst the legions of these creatures treated with the serum showed a favourable result. I repeat, one single guinea pig in such a dressed-up test treatment, at a time when the big drum had already begun to beat in the cause of serotherapy. I cite this one fact, and I think some of you already know it well. And if I may so call it, this extraordinary intellectual slovenliness in scientific publicity deserves to be definitely recorded in the history of Science. To state in principle today what will be outlined in detail during the following lectures:—it is not the processes of the extra-human world that are superficially most apparent, that work most effectively in mankind, but those that must be discovered and extracted from the deeper levels of being. Mankind is actually related, in a certain way, to all that he has shed from his being: to the phosphoric process, and saline process, the blossom process, the fruit processes, the root process, the process of leaf formation; but in a reversed sense, bearing within him the tendency to cancel and change into its opposite that which manifests in external nature. It is not the same with animals. For the animal has already gone half the way towards mankind; man is not opposed in the same sense to the animal, but stands rather at right angles to the animal. He has reached an angle of 180 degrees from the plant. This is significant, and demands serious consideration when the question arises of the use of serum and similar remedies of animal origin.
|

