| 229. The Festivals and Their Meaning IV : Michaelmas: The Michael Inspiration
15 Oct 1923, Stuttgart |
|---|
| 229. The Festivals and Their Meaning IV : Michaelmas: The Michael Inspiration
15 Oct 1923, Stuttgart |
|---|
What I have to say to you to-day will be expressed in the form of pictures drawn from the imaginative life, which is the expression, the revelation, of the spiritual world. The human being is woven with his whole existence and activity into the spiritual world. We know from the many and varied descriptions of it that have been given here, that an abstract manner of speaking, such as is applied to external, sense-perceptible nature, cannot be used in speaking of the spiritual world, if actual manifestations of that world are in question. We know too, however, that the manner of speaking we must then adopt is no unreal one, but, on the contrary, one far more realistic than the logical, abstract speech we employ to express merely natural truths. This I wanted to say about the attitude to be adopted in what I shall now put before you. When man finds, with spiritual vision, the way out beyond the physically sense-perceptible world, there reveals itself to him a world of spirit. In that world he feels led to make use of the phenomena of the physical world as pictures, with which to express what is spiritually revealed to him. So let me now put a picture at the centre of our considerations; a picture which is in truth a deep reality. Mankind, throughout its evolutionary history, has always been guided by impulses from the spiritual world. Those who could see so far found these impulses written as it were in brazen letters in a spiritual light, indicating the direction they should take. What is thus found in the spiritual world might be compared with the signposts of the physical world; not those that have just a pointing hand perhaps, and the name of some place or other, but signposts on which is expressed in powerful words—or at least in powerfully sounding words—what changes are due to take place in human thinking, feeling, willing. I am speaking of spiritual signposts. Such directions in the spiritual world, however, are usually drawn up for human beings in a remarkable manner, and have been so in all epochs—namely, in a kind of riddle-language. One has in a certain way to make an effort to get behind the riddle. In order that one of these signposts in the riddle-language may become a real impulse for life, a great deal of what one knows has to be brought together. And so just at the present time, as something suited to our immediate present and the near future, one finds in the astral light, as I may call it, such directing words as can become impulses for mankind. On the most varied occasions—I might say in the most varied places—there comes before one to-day, if one has the faculties needed to behold it, something that is like a warning, having moreover the quality of a riddle, and it calls forth in man the feeling that he should be guided by it, should take it as a strong impulse into his will, into his whole life of soul. What thus shines out to meet us in the astral light, as one such spiritual milestone, consists approximately of the following words:—
First of all there is a challenge to discover what is actually meant. Some sort of impulse is referred to, something which is already present, something known to man, since otherwise one could not reckon on his finding an answer:
The explanation of these words, which, as has been said, how themselves in the astral light like a directing impulse or human beings, will be the purpose of to-day's lecture. Let us recall a number of things that I have already explained here. Let us recall how the year's course, in its regular sequence through Spring, Summer, Autumn, Winter, has a spiritual content; how spiritual occurrences, superensible occurrences, are revealed in what happens in the course of the year just as a man's super-sensible soul and super-sensible spirit are revealed in what happens in his bodily life between birth and death. Let us reflect how, in what appears outwardly during the year's course, in Winter's snow, Spring's sprouting, waxing life, in Summer's life of blossoming and Autumn's life of ripening and fruiting—how in all this which discloses itself physically to men something spiritual is hidden, something spiritual sustains it. And so let us turn our gaze first to what takes place in this yearly course, from spring to summer and on towards the autumn. In all that Earth reveals, in stone and plant, in everything that has being, spiritual beings live; not a mere washed-out spirituality, but separate spirit-beings, Nature-spirits. These Nature-spirits hide during the winter in the bosom of the Earth; they are breathed in, as it were, by the Earth; they are within the Earth. When spring comes, Earth breathes out, as it were, her spirituality; these Nature-spirits strive upwards. They aspire upwards with the forces of springing, sprouting life; they are active in the life which is felt in the light-radiant, sun-warmed air; within this they aspire upwards. And as we approach St. John's Day and the time of midsummer, then in the heights above us, if we look up to them, we have a picture revealed there, embodied in the forms of clouds, embodied mightily in lightning, too, and thunder, embodied in all the meteoric element above us, all that lived in the form of Nature-spirits during winter in the Earth's dark bosom. During winter we must look down to the Earth and feel, or behold how, hidden beneath the covering of snow, Nature-spirits are working, so that out of winter shall come spring again, and summer, from the productive Earth. But if in summer we look down to the Earth, then the Earth is as if impoverished by the loss of those Nature-spirits. The Nature-spirits have gone out into the wide universe; they have united themselves with the cloud-structures and everything that human sight encounters in the heights above. In all the ways I have mentioned they have streamed up to the heights, these Nature-spirits, and with them they have taken, in an extremely subtle form, extremely fine dilution, that which manifests outwardly as crude and lifeless sulphur. And in fact these Nature-spirits, as they billow and surge in cloud-forms and the like, during summer's height, weave and live pre-eminently in sulphur, the sulphur that is then present there in an extraordinarily subtle way, in the heights of the earthly realm. If we could speed through these high reaches of our earthly world during the height of summer with a sort of tasting-feeling sense, we should be aware of a sulphurous taste and even of a sulphurous smell, though in an extraordinarily dilute, subtle and intimate form. What develops up there, however, under the influence of the Sun's warmth and light, is akin to the process that goes on in the human organism when cravings, wishes, emotions and so on come welling up. Anyone who has the faculty for beholding and feeling such things knows that the Nature-spirits in the heights during midsummer live in an element which is as much saturated with desire as is the desire-life that is bound up with the animal nature of man—that animal part of man wherein he, too, is sulphurised, is permeated with sulphur in a very diluted form. We see, as it were, man's lower aspect, that which is animalised in him, arched as Nature's formation above us at the height of summer, filled with the life of Nature-spirits. What we thus recognise in its sulphurous quality when it weaves and lives in human nature, we call the Ahrimanic; in it the Ahrimanic actually lives. So we can also say: when in high summer-time we turn spiritual vision towards the heights, then in the cosmic sulphurous desires the Ahrimanic is revealed to us. So if we conceive of man in relation to this whole world nexus, we must say to ourselves: the Earth takes up in winter what exists in man as his lower nature and spreads over it crystalline snow, and in so doing the Earth receives the Ahrimanic from it. When in high summer the Ahrimanic is free, it works as cosmic desires out in the wide spaces of the world and is, indeed, subject to laws which proceed from the planetary neighbours of the Earth and are effective on them. And now we see how against this Ahrimanic desire-element, against this animal desire-nature of man turned inside out, as it were, in the cosmos, an opposing force is present. The force which brings the human being into subjection through his emotions, dragging him down below the human to the animal level, and is revealed in full summer high above us—against this a counter-force is provided in the cosmos. This counter-force is seen in those remarkable products which from time to time fall on to the Earth as products of the cosmos and contain meteoric iron. If you look at a piece of meteoric iron, you have in it a remarkable witness of the iron dispersed in the cosmos. In the shooting stars which come so frequently in August and bring iron into special activity, as it were, in the cosmos, we see revealed this counter-force of Nature acting against the desire-element which by that time is out there in the cosmos. And in this cosmic iron, condensed to meteoric stones, we have the arrows which the cosmos sends out against the animal desire element which, as I have just described, is cosmically manifest. So we can look with understanding and reverence upon the wisdom-filled guidance of the cosmos. We know, of course, that man needs this animal desire nature, precisely because in overcoming it, and not otherwise, he can develop the forces that first make him fully human. And man could not have this desire nature, this animalising element, if the same animal desire element were not a part also of the cosmos. The sulphur, then, the sulphurous Ahrimanic element is, as it were, one pole out in the cosmos, and the arrows discharged by the Cosmos through space to combat this sulphurous element are concentrated in meteoric iron—in the meteoric projectiles, so to say, of the universe. Now man is a true microcosm, really a little world. Everything that manifests in the great world outside in gigantic and majestic phenomena such as the phenomena of meteors, manifests also within, in the inward nature of what he is himself as physical being. For this physical being is only an expression, a manifestation, of his spiritual being. And so in a certain way we bear within ourselves, starting from the animal lower nature, the sulphurous element. We must say to ourselves: this sulphurous Ahrimanic element storms through the human organism, stirs up his desire-nature, stirs up his emotions. We feel it within us; we behold it at high summer-time in the cosmic desire-covering above our heads. But we also behold how into this over-arching cosmic desire-covering there shoot the iron arrows of the meteoric phenomena, cleansing and clarifying it, acting as an opposite pole to the animal-like desire-nature. For through this shooting in of the meteoric iron arrows from the cosmos, the animal desire-covering of high summer time above us is purified. And what takes place in majesty and grandeur out there in the great cosmos, goes on continually also in us. We produce tiny iron particles in our blood, in combination with other substances, and while, on the one hand, there pulses through our blood the sulphurising process, there works against it inwardly, meteorically, as the other pole, the iron inside us, bringing about the same process as is effected outside in the cosmos by the meteoric iron. We can then so picture man's relationship to the cosmos that in the flashing meteoric element we find the cosmic counterpart of what within us is a million upon million-fold flashing forth of the meteoric element that sets us free by means of the iron in our blood, cleansing and clarifying us from the sulphurising process which is also active in the blood itself. Thus we are inwardly a copy of the cosmos. In the cosmos this process is accomplished during the height of summer; man, because he stands within Nature as one emancipated from her in regard to time, has continually midsummer as well as the other seasons in himself, just as he has within him in the continuity of memory his former experiences. Outwardly they have vanished, but inwardly they remain. So is it too with what is present in Man as Microcosm in relation to the Macrocosm. What he thus carries in his physical body, however, he must grasp in soul and spirit, must become able to experience it within himself; he must learn to experience this meteoric shag of the blood-iron into the blood-sulphur as freedom, or initiative, as the strength of his will. Otherwise it remains an animal or vegetative process in him at the best. What precisely constitutes our becoming [a] human being in soul and spirit is that we grasp the processes which go on in us, such as this iron-sulphur process, with our soul and spirit, that we send the soul and spirit into them as an impulse. Just as when we have made an instrument and know how to handle it properly, we are able to perform something by means of it, so can we turn to the service of our will what works and lives in us as does this process of iron and sulphur, when once we know how to handle it; when, as human beings, we can handle and make use of what goes on as living processes within our body. Let us now turn again to the cosmos and away from man. You can realise that what takes place out there in the cosmos is an earnest admonition to men. For this meteoric iron-process in the cosmos truly brings to mind our inner physical nature; this nature, however, can be placed at the service of our spiritual inner being. So now we come to the meaning which has to be ascribed to that brazen writing in the astral light:—
If we look round us at modern life, as it has developed in the course of recent centuries, we can see that the chief feature of this materialistic culture is the use of iron in the realm of earthly life. Look in any direction where our form of civilisation has flowered in recent times; it is iron that has planted in the physical world everything which has led to the culmination of this materialistic culture. We look for what it was that in so unparalleled a way has brought people together, and has laid down the paths for the various branches of materialistic culture and made them smooth; and everywhere we see it was iron and what can be developed out of it. When we speak of materialism in the life of thought it is true that the essence of materialism consists in the idea that everything is matter, and Spirit is a kind of vaporous result of the activities of matter. But the materialism of mankind in the last four centuries is shown not merely in the fact that people think materialistically; materialism is manifest also in the way we handle outer things. Out of the cultural impulses of recent times man has applied iron to this material culture, while the meteoric iron which falls from heaven is treated merely as a rarity, or as something one seeks to explain by means of a science that cannot grasp much about it. This meteoric iron, however, which falls to earth from out of the cosmos, which purifies and clarifies the animal-like life, is actually an admonition to us that we should look up from using iron materially for earthly purposes, and see what heavenly service iron performs in its meteoric aspect up above us, and, more especially, within us. For these meteoric processes within us go on all the time. And so the first part of this warning speech, shining forth to meet us in the astral light, takes on the likeness of a word written in brazen letters, saying: O Man, thou hast put iron to thine earthly service.
It is not merely that we should look up in our thoughts from the materialistic world-conception to a spiritual world-conception, but that we should also look up from what we use in the service of material culture to the spiritual and cosmic aspects of what serves us in material form. And so precisely through these words, which have first to be unravelled like a riddle, we are directed to that Spiritual Being who lives in the universe in the revelation of meteoric phenomena, especially in what is revealed by meteoric phenomena at the height of summer. For at that time the Ahrimanic sulphurising process, which is otherwise present only within man, is there as a cosmic process, and the meteoric process is a counter-process to it; we have here the arrows which the cosmos discharges into the animalised cravings in the heights. If one lets all this work upon the soul, one feels how truly man is connected with all that surrounds him in the world, and, within, one feels how one's very blood is permeated with soul, saturated with spirit. One feels in it this opposition between the Ahrimanic and that which purifies the Ahrimanic element, the iron in the blood; one feels the inner meteoric process. One looks up with comprehension to what is accomplished outside when the cosmic spirit-forces send the iron arrows into the animalised desire-world of the cosmos; one feels oneself entirely bound up with the cosmos and surrendered to it. Precisely in these particular phenomena, one feels entirely surrendered to the cosmos. When one feels all this in full earnestness, then from this feeling there takes form a cosmic Imagination; one can indeed do no other than form and picture this cosmic Imagination. Just as animals have a different attitude towards outer Nature, being unable to form concepts or ideas of it, but only general impressions, whereas man forms pictures and ideas, so, when the soul has risen to exact clairvoyance, it is not possible for it to do otherwise, when it experiences such things as this—when its feeling turns inwardly towards its own meteoric process, and when looking outward it beholds in the cosmic meteor-process that rich fullness of life which is thus revealed—than to bring it all together in a comprehensive, inwardly saturated picture form, an Imagination in which is displayed how the human being, the Microcosm, and the Macrocosm are grown together. This does not mean that such an Imagination is merely built up out of fantasy; rather is it a real and true expression of a living process permeating the world and the human being; in this case, of a process that lives in the phenomena of the yearly course. The Imagination which comes before man out of this experience is one that springs out of a living together with the natural processes of the year's course from midsummer on towards autumn, as far as the end of summer, the beginning of the autumn; And from this experience there arises, coming before the soul in living actuality, the figure of Michael. Out of what I have described to you is revealed the figure of Michael in his fight with the Dragon, with the animal nature of Man, the sulphurising process. And when one understands what is actually going on there, then the soul, which takes its own form and origin from the interweaving life forces of the cosmos, cannot but bring forth the fight of Michael with the Dragon. There appears as the outward expression of what is working out there in the cosmos in battle with the animalised desire nature, Michael himself. But he appears with a pointing sword, pointing it towards the higher nature of man. He shines forth with this pointing sword, and we picture Michael rightly when we find in his sword the iron that has been cosmically smelted and forged for this purpose. Thus there comes forth, one might say, out of the spiritual cloud-formations the figure of Michael with positive, searching and directing gaze, his eye like a guiding sign, its gaze sent outwards, never drawn back into himself; and the arm of Michael appears to us in the midst of a sparkling shower of meteor-iron, as though this were molten in cosmic desire forces and fused together again to form the flaming sword of Michael. Rightly do we picture Michael then, quite in accord with reality, when we think of his countenance as woven from the golden light of summer, with a positive gaze which is like a sign, as it were pointing outwards; like a ray of light from within which is sent actively out. We picture Michael rightly when his outstretched arm is flaming with flashing sprays of meteor iron, molten and fused together into the sword wherewith he shows humanity the way from the animal-like to man's higher nature, pointing the way from the summer season, when man most makes himself one with outer Nature, most nearly comes to a Nature-consciousness, to that other season, the time of autumn, when man, were he to continue to live united with Nature, could share only in her dying in the death she brings on herself. But it would be terrible for man, if he could only share with Nature, as autumn comes, this natural path to death, this self-destruction. When we experience Spring, then if we are really fully man, we yield ourselves to Nature in her sprouting, waxing, flourishing. If we are fully man, we blossom with each blossom, sprout with every leaf: with every seed we grow ripe ourselves. It is then that we give ourselves over to Nature's mounting, springing, sprouting life. For it is then her will to live, and we feel this impulse of life in experiencing hers. And we do well to devote ourselves to Nature at this season. But in autumn we cannot unfold this nature-consciousness in ourselves, for if we did that onesidedly we should have to share in the experience of the paralysis and death which she makes her own. Man dare not go with her in that direction; in the face of that he must rather increase his strength. Just as he must accompany living Nature in his own life, so must he set against dying Nature, against death, the Self. Nature-consciousness must be transformed into self-consciousness. This is the great and powerful picture given us in the approach of autumn, so that from out of what happens in the cosmos we read the admonition: Nature consciousness must change in man into consciousness of self. But for this he needs the strength to overcome with his qualities of soul and spirit the inwardly death-bringing quality of animal-like Nature. For this he is given guidance when he looks out into the phenomena of the cosmos; to this he is guided by what is revealed in the figure of Michael, with his positive gaze and the flaming meteor-sword in his right hand. And Michael appears to us in that fight with the animalised desire-nature of which, also, a picture emerges from the loom of life. If we wish to paint this whole Imagination, we cannot paint it in any humanly arbitrary way; it can be painted only out of what is given by the cosmos. And the only way to picture the sulphurous element in it, rising into the heights with the elemental spirits in yellowish reddish shades, is in the figure of the Dragon, which takes shape from out of the sulphur. So that above the sulphurous Dragon, in whose burning head, as I might call it, is exhibited the desire-like process, above this Ahrimanised and sulphurised Dragon, we have Michael in the form I have described to you. He who understands the world can describe it in Imaginations. And whosoever believes that one can paint the fight of Michael with the Dragon in any way one chooses, sins against the inner reality of the world. For the interplay of forces in the world has a definite ordering in relation to human beings. And all the great paintings and other works of art in the world have not come into existence out of arbitrary human choice. If that were so, they would scarcely have continued to appeal to man for centuries, even thousands of years. They have sprung from a real understanding of what weaves and lives out there in the cosmos, and also within the human being. And when out of the living and weaving in Nature and in man, in their mutual connection, there is created the substance of Imaginations, with all that is revealed from the mysteries of Nature, even to the colours and the way the colours gleam and shine, and the details of the forms—when all this is given artistic form, then it is that the great, genuine works of art arise, the great works that were created by the seers, that are imitated by the imitators and are decked out by the bunglers with all kinds of frippery till the real greatness that should go forth from these works, born out of the creative weaving of the cosmos, is no longer recognised. This is what gives these works of art the power to influence humanity through long periods of time. The great artistic motifs of painting and sculpture never would have become what they are had they not been created out of impulses seen to arise from the life of Nature and the life of man. So we are able to direct our vision to what appears if Michael and the Dragon are painted in the spiritual sense of to-day (for older ways of apprehending it had to paint it according to their own knowledge); the countenance pictured in golden sun-gleam, the gaze positive, outward-looking, the sword of flame, molten and shaped anew out of the meteor-iron of the cosmos; and below, the Dragon, tormentor of human nature, the Dragon who manifests at high summertime, the sulphurous Dragon revealed in the weaving of flames rising up and at once fading again. This Dragon moving below in his own sulphurous element, taking form as the tormentor of humanity and the opponent of the higher hierarchies—this gives the necessary contrast over against the war-waging Michael, who compels the meteoric iron to his spiritual service. Here you have an example of how the true iron passes over into art, must always pass over into art, since with abstract concepts one cannot compass the whole of reality. And this is the admonition to our times—that we should grasp just such a picture as this, for the awakening of strength, for the awakening of mankind. Therefore one would like to inscribe this picture in particular, this modernised picture of the fight of Michael with the Dragon, deep, deep into the human soul, the human heart, so that it may exert its influence in human forces of will and thought in the present time and in the future. And one can know that if a part of mankind were to take this picture in earnest, if a part of mankind were to understand how this picture takes shape from Nature's very self, and from the directive admonitions in the astral light, then to the material use of iron in the last few centuries, especially the 19th century, there would be added a spiritual element penetrated with the meaning and sense of iron. Then this picturing would kindle in man the force of soul and spirit which makes him able to take hold of the purpose of the meteoric iron within him, the iron that shoots into his blood, warring against sulphur. We must learn not to let this process go on in the subconsciousness, merely shaping the lower nature of Man; we must learn to place this process, this iron process in human blood, in the service of the soul-and-spiritual. That it is, that Michael wills in us. This is what calls on us from the astral light—to celebrate worthily once more the Michael Festival when autumn is beginning. When now we speak of this Michael Festival which should take its place with the Easter and Christmas festivals and that of St. John, it must truly not be understood as meaning that here or there one celebrates a festival in an external way; the point is that we can celebrate such a festival only when we know how to link it with something really significant. The festival of Christmas has not arisen through any arbitrary convenient resolve, but because it is linked with the birth of Christ Jesus; the Easter Festival is linked with the Mystery of Golgotha; and these are very important events in the historical life of mankind. The Michael Festival must be linked with a great and sustaining inner experience of man, with that inner force which summons him to develop self-consciousness out of Nature-consciousness through the strength of his thoughts, the strength of his will, so that he may be able to master the meteoric iron process in his blood, the opponent of the sulphurising process. To be sure, sulphur and iron have flowed in human blood ever since there was a human race. What takes its course there between sulphur and iron determines the unconscious nature of man. It must be lifted into consciousness. We must learn to know this process as the expression of the inner conflict of Michael with the Dragon; we must learn to raise this process into consciousness. Something has then come about to which the Michael Festival may be linked. But it must first be there, be fully understood, inwardly, deeply understood. Then it will be possible to celebrate the Michael Festival in the way a festival drawn from the cosmos can be celebrated by men. Then we shall have the knowledge which is really able to see something in iron other than what the chemist of to-day or the mechanic sees in it. Then we shall have what teaches us how to take in hand the iron in our own organism, in the inner part of our human nature. Then we shall have the majestic picture of Michael in battle with the sulphurous Dragon, of Michael with the flaming sword of iron, as an inspiring impulse to what man must become, if he is to develop the forces of his evolution for progress and not for decline. This it is, which shows itself to us as an admonition from the spiritual world in the brazen letters that grow into enigmatic words but that can be understood precisely out of the conditions of our present time:—
That is Iron. Let us learn to know iron, and equally all other substances, not merely in terms of material value; let us learn to know them in their majestic spirit power! Then there will be human progress once again, progress for the Earth; and that is what we must will, if we want to be man in the true sense of the word. |
| 118. The Reappearance of Christ in the Etheric: Mysteries of the Universe: Comets and the Moon
05 Mar 1910, Stuttgart Translated by Barbara Betteridge, Ruth Pusch, Diane Tatum, Alice Wuslin, Margaret Ingram de Ris |
|---|
| 118. The Reappearance of Christ in the Etheric: Mysteries of the Universe: Comets and the Moon
05 Mar 1910, Stuttgart Translated by Barbara Betteridge, Ruth Pusch, Diane Tatum, Alice Wuslin, Margaret Ingram de Ris |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
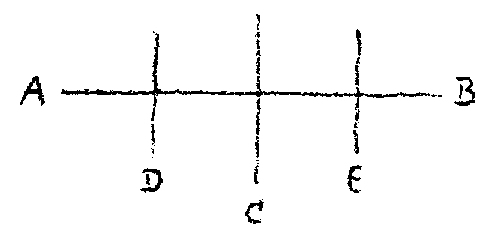
On a night when the stars are clear and we gaze at the expanse of the heavens, it is a feeling of sublimity that first flows through our souls as we let the innumerable wonders of the stars work upon us. This feeling of sublimity will be stronger in one person, less strong in another, according to his particular individual character. When faced with the appearance of the starry heavens, however, a person will soon be aware of his longing to understand something of these wonders of cosmic space. Least of all in regard to the starry heavens will he be deterred by the thought that this direct feeling of sublimity and grandeur might disappear if he wishes to penetrate the mystery of the starry world with his comprehension. We are justified in feeling that understanding and comprehension in this sphere cannot injure the direct feeling that arises in us. Just as in other spheres it soon becomes evident to a greater or lesser degree that spiritual scientific knowledge enhances and strengthens our feelings and experiences if only we have a healthy understanding (Sinn), so will a person become more and more convinced that, regarding these sublime cosmic facts, his life of feeling will not wither in the least when he learns to grasp what is really passing through space or remaining, in appearance, at rest. In any presentation it is, of course, possible to deal only with a tiny corner of the world, and we must take time to learn to grasp, step by step, the facts of the world. Today we will concern ourselves with a part, a small, trifling part, of the world of space in connection with the life of man. Although a person may dimly divine it, he will learn with greater and greater precision through spiritual science that he is born out of the totality of the universe and that the mysteries of the universe are connected with his own special mysteries. This becomes particularly evident when we enter with exactitude into certain mysteries of existence. A contrast is manifest in human life as it evolves on this earth—a contrast to be found everywhere and at all times. It is the contrast between the masculine and the feminine. We know that this contrast in the human race has existed since the time of ancient Lemuria; we know, too, that it will last for a certain period in our earthly existence and ultimately resolve itself again into a higher unity. If we recollect that all human life is born out of cosmic life, we may then ask, if it is indeed true that what has shown itself in human life since the old Lemurian time as the contrast between man and woman has to a certain extent accompanied evolution on the earth, can we find something in the universe that in a higher sense represents this contrast? Can we find in the cosmos that which comes to birth in the masculine and feminine on earth? This question can be answered. If we stand on the ground of spiritual science, we cannot proceed according to the maxims of a present-day materialist. A materialist can visualize nothing apart from what lives in his immediate environment and is therefore prone to seek for this contrast of masculine and feminine in everything, whereas it now applies only to human and animal life on earth. This is an offense of our time. We must bear clearly in mind that the designations “masculine” and “feminine” in the human kingdom hold good in the strict sense only since the Lemurian epoch and up to a certain moment in earthly evolution and, in so far as animals and plants are concerned, only during the ancient Moon evolution and the earth evolution. The question remains, however: are masculine and feminine as they exist on earth born out of a higher, cosmic contrast? If we were able to find this contrast, a wonderful and at first mysterious connection would emerge between this phenomenon and a phenomenon in the cosmos. There are, of course, contrasts everywhere in the cosmos, but one must understand how to discover them in the right way. The first contrast in the cosmos whose significance for human life we can mention is that between sun and earth. In our various studies of earthly evolution we have seen how the sun separated from our earth, how both became independent bodies in space, but we may also ask: how does the contrast between sun and earth in the macrocosm, in the great world, repeat itself in man, the microcosm? Is there in the human being himself a contrast that corresponds to the contrast between sun and earth in our planetary system? Yes, there is. In the human organism—the whole organism, bodily and spiritual—it occurs between all that expresses itself externally in the organ of the head and all that expresses itself externally in the organs of movement, the hands and feet. All that is expressed in the human being in this contrast between the head and the organs of movement corresponds to the contrast or polarity that arises in the cosmos between sun and earth. We shall soon see how this is consistent with the correspondence between the sun and the heart. The point here, however, is that in the human being there is on the one hand the head and on the other what we call the organs of movement. You can readily understand that, in so far as his limbs were concerned, man was a totally different being during the ancient Moon evolution. It was the earth that made him into an upright being, one who uses hands and feet as he does today; again, it was only on the earth that his head was enabled to gaze freely out into cosmic space, because the forces of the sun raised him upright, whereas during the ancient Moon evolution his spine was parallel with the surface of the moon. We may say that the earth is responsible for man being able to use his legs and feet as he does today. The sun, working upon the earth from outside and forming the contrast with the earth, is responsible for the fact that the human head, with its countenance, has in a sense torn itself free from bondage to the earth and is able to gaze freely out into space. That which in the planetary system is the contrast between sun and earth appears within the human being as the contrast between head and limbs. We find this contrast of head and limbs in every human being, whether man or woman, and we also find that here, in all essentials, men and women are alike, so that we can say that the contrast corresponding to that between sun and earth expresses itself in the same way in men and in women. The earth works to the same extent upon woman as upon man; woman is bound to the earth in the same way as man, and the sun frees the head of woman and of man alike from bondage to the earth. We shall be able to gauge the profundity of this contrast if we remember that those beings, for example, who fell into dense matter too early, as it were—the mammals—were not able to attain free sight into cosmic space; their countenance is bound to earthly existence. For the mammals, the contrast between sun and earth did not become, in the same sense, a contrast in their own being. For this reason we may not speak of a mammal as a microcosm, but we can call the human being a microcosm, and in the contrast between head and limbs we have evidence of the microcosmic nature of man. Here we have an example that at the same time shows how infinitely important it is not to become one-sided in our studies. One can count the bones of man and the bones of the higher mammals and also the muscles of man and of the mammals, and the connection that one can draw from this has led in modern times to a world view that places man in closest proximity to the higher mammals. That this can happen proceeds simply from the fact that people have yet to learn through spiritual science how important it is not merely to have truths but to add something to them. Be conscious, my dear friends, that in this moment something of great importance is being said, something that the anthroposophist should inscribe in his memory and in his heart: many things are true, but merely to know that a thing is true is not enough! For example, what modern natural science says about the kinship of man with the apes is undoubtedly true. With a truth, however, the point is not merely to possess it as a truth but to know the importance of it in the explanation of existence as a whole. A seemingly quite ordinary, everyday truth may fail to be regarded as decisive only because its importance is not recognized. A certain familiar truth, known to everyone, becomes deeply significant for our whole doctrine of earthly evolution if its real importance is only understood: the truth that man is the only being on earth who can direct his countenance with real freedom out into cosmic space. If we compare the human being in this respect with the apes who stand near to him, we must say that, although the ape has tried to raise himself into the upright posture, he has somehow made a hash of it ... and that is the point. One must have insight into the relative weight of a truth! We must feel the importance of the fact that man has this advantage, and then we shall also be able to relate it to the other cosmic fact just characterized: it is not the earth alone but the sun in contrast to the earth—something beyond the earth—that above all makes man a citizen of heavenly space and tears him away from earthly existence. In a sense we may say that this whole cosmic adjustment that we know today as the contrast between sun and earth had to be made in order that man might be given this place of precedence in our universe. This constellation of sun and earth had to be brought about for the sake of man, that he might be raised from the posture of the animals. In the human being we thus have the same contrast that we see when we look out into heavenly space and behold the sun with its counterpart, the earth. Now the question arises: can we discover in the cosmos the other contrast that is found on earth, that between masculine and feminine? Is there perhaps something in our solar system that brings about, as a kind of mirror-image on earth, the contrast between man and woman? Yes, this higher polarity can be designated as the contrast between the cometary and lunar natures, between comets and the moon. Just as the contrast of sun-earth is reflected in our head and limbs, so in feminine and masculine is reflected the contrast of comet-moon. This leads us into certain deep cosmic mysteries. Strange as it may sound to you, it is true that the different members of human nature that can confront us in the physical body are in different degrees an expression of the spiritual that lies behind them. In the physical body of man, it is the head, and in a certain other sense the limbs, that correspond most closely in outer form to their underlying, inner, spiritual forces. Let us be clear about this: everything that confronts us externally in the physical world is an image of the spiritual; the spiritual has formed it. If the spiritual is forming something physical, it can form it in such a way that at a certain stage of evolution this physical form is either more similar or less similar to it, or is more or less dissimilar from it. Only head and limbs resemble as external structures their spiritual counterparts. The rest of the human body does not at all resemble the spiritual picture. The outer structure of man, with the exception of head and limbs, is in the deepest sense a mirage, and those whose clairvoyant sight is developed always see the human being in such a way that a true impression is made only by the head and limbs. Head and limbs give a clairvoyant the feeling that they are true; they do not deceive. With regard to the rest of the human body, however, clairvoyant consciousness has the feeling that it is untrue form, that it is something that has deteriorated, that it does not at all resemble the spiritual behind it. Moreover, everything that is feminine appears to clairvoyant consciousness as if it had not advanced beyond a certain stage of evolution but had remained behind.
We can also say that evolution has advanced forward from point A to B. If C were a kind of normal development, then we would be at point C as far as the human head and limbs are concerned. What appears in the form of the female body has remained as if it were at D, not advancing to a further point of development. If it will not be misunderstood, we can say that the female body, as it is today, has remained behind at a more spiritual stage; in its form it has not descended so deeply into matter as to be in accord with the average stage of evolution. The male body, however, has advanced beyond the average stage—apart from head and limbs. He has overshot this average stage, arriving at point E. A male body, therefore, has deteriorated, because it is more material than its spiritual archetype, because it has descended more deeply into the material than is called for today by the average stage of evolution. In the female body we thus have something that has remained behind normal evolution and in the male body something that has descended more deeply into the material than have the head and limbs. This same contrast is also to be found in our solar cosmos. If we take our earth and the sun as representing normal evolutionary stages, the comet has not advanced to this normal stage. It corresponds in our cosmos to the feminine in the human being. Hence, we must see cometary existence as the cosmic archetype of the feminine organism. Lunar existence is the counterpart of masculine existence. This will be clear to you from what has been said before. We know from before that the moon is a piece of the earth that had to be separated off. If it had remained in the earth, the earth could not have gone forward in its evolution. The moon had to be separated off on account of its density. The contrast between comet and moon out in the cosmos is therefore the archetype of feminine and masculine in the human being. This matter is exceedingly interesting, because it shows us that whether we are considering an earthly being, such as man, or the whole universe, we must not simply think of one member side by side with others as they appear to us in space; if we do this we give ourselves up to a dreadful illusion. The various members of a human organism are, of course, beside one another, and the ordinary materialistic anatomist will regard them as being at equal stages of development. For one who studies the truth of things, however, there are differences, inasmuch as one thing has reached a certain point of evolution, another has not—although it has made some progress—and another has passed beyond this point. A time will come when the whole human organism will be studied along these lines; only then will an occult anatomy exist in the real sense. As I have told you, things that lie side by side can be at different stages of evolution, and the organs in the human body are only to be understood when one knows that each of them has reached a quite different stage of evolution. If you recall that the ancient Moon evolution preceded that of our earth, you will realize from what has just been said that although the present moon is certainly part of the ancient Moon evolution, it is not now at that stage of evolution and does not represent it. The moon has not only advanced to the earth stage but has even gone beyond this; it was not able to wait until the earth becomes a Jupiter, and it has therefore fallen into torpor in so far as its material side is concerned—not, of course, in its spiritual relationships. The comets represent the relationship of the ancient Moon to the sun that prevailed at a certain time in the ancient Moon evolution. The comet has remained at this stage, but now it must express this somewhat differently. The comet has not advanced to the point of normal earthly existence. Just as in the present moon we have a portion of a later Jupiter that was born much too early and is therefore torpid, incapable of life, so in our comets we have a portion of the ancient Moon existence projecting into our present earthly evolution. I would like to mention here parenthetically a noteworthy point, through which our spiritual scientific ways of studying have won a little triumph. Those who were present at the eighteen lectures on cosmogony that I gave in Paris in 1906 (see Note 2) will remember that I spoke then of certain things that were not touched upon in my book, An Outline Of Occult Science (see Note 3) (one cannot always present everything; one must not write one book but endless books if one wishes to develop everything). In Paris I developed a point bearing more upon the material, chemical aspect of the subject, as it were. I said that the ancient Moon evolution—which projects itself in present cometary existence, because the comet has remained at this stage and, as far as present conditions allow, expresses those old relationships in its laws—I said that this ancient Moon evolution differs from that of the earth in that nitrogen and certain nitrogenous compounds—cyanide, prussic acid compounds—were as necessary to the beings on the ancient Moon as oxygen is necessary to the beings of our present earth. Cyanide and similar substances are compounds that are deadly to the life of higher beings, leading to their destruction. Yet compounds of carbon and nitrogen, compounds of prussic acid and the like, played an entirely similar role to that of oxygen on the earth. These matters were developed at that time in Paris out of the whole scope of spiritual science, and those who inscribed them in their memories will have had to say to themselves that, if this is true, there must be proof of something like compounds of carbon and nitrogen in today's comets. You may recall (the information was brought to me during the lecture course on St. John and the other three Gospels in Stockholm) that the newspapers have now been saying that the existence of cyanide compounds has actually been proved in the spectrum of the comet. This is a brilliant confirmation of what spiritual research was able to say earlier, and it has at last been confirmed by physical science. As proofs of this kind are always being demanded of us, it is quoted here. When such a striking case is available, it is important for anthroposophists to point it out and—without pride—to remind ourselves of this little triumph of spiritual science. So you see, we can truly say that the contrast between masculine and feminine has its cosmic archetype in the contrast between comet and moon. If we could proceed from this (it is not, of course, possible to go into all the ramifications) and could demonstrate the full effect of the body of the moon and of the comets, you would realize how great and powerful it is for the soul—how it surpasses all general feelings of sublimity—to experience that here on earth we see something reflected and that this, in its functioning, is an exact expression of the contrast between comet and moon in the universe. It is possible to indicate only a few of these matters. A few are very important, and to these we will allude. Above all, we must become conscious of how the contrast expressed in comet and moon works upon the human being. We must not think that this contrast expresses itself only in what constitutes man and woman in humanity, because we must be clear that masculine characteristics exist in every woman and feminine characteristics in every man. We also know that the etheric body of man is female and that of the woman, male, and this at once makes the matter extremely complicated. We must realize that the masculine-feminine contrast is thus reversed for the etheric bodies of man and woman, and so are the cometary and lunar effects. These effects are also there in relation to the astral body and the I. Hence the contrast between comet and moon is of deep, incisive significance for the evolution of humanity on earth. The fact that the Moon evolution has a mysterious connection with the relationship of the sexes, a connection that eludes exoteric ways of thinking, you can recognize in something that might seem entirely accidental, namely, that the product of the union of male and female, the child, needs ten lunar months for its development from conception to birth. Even modern science reckons not with solar but with lunar months, because there the relation between the moon, representing the masculine in the universe and the earth, and the cometary nature, representing the feminine in the universe, is decisive, reflecting itself in the product of the sexes. If we now regard this from the other side, from the comets, we have another important consequence for the evolution of humanity. The cometary nature is as though feminine, and in the movements of the comets, in the whole style of their appearance from time to time, we have a kind of projection of the archetype of the feminine nature in the cosmos. It is something that really gives the impression of having come to a halt before reaching the normal, average stage of evolution. This cosmic feminine—the expression is not quite apt, but we lack suitable terms—shoots in from time to time like something that stirs up our existence from the depths of a nature existing before the dawn of history. In the mode of its appearance, a comet resembles the feminine. We can also express it this way: as what is done by a woman more out of passion, out of feeling, is related to the dry, reasonable, masculine judgment, so is the regular, reasonable course of the moon related to the cometary phenomenon that projects apparently irregularly into our existence. This is the peculiarity of feminine spiritual life. Mark well—I do not mean the spiritual life of woman but the feminine spiritual life. There is a difference. The spiritual life of a woman naturally includes masculine characteristics. Feminine spiritual life, whether in a man or a woman, projects into our existence something of the primitive, something elemental, and this is also what a comet does. Wherever this contrast between man and woman confronts us, we can see it, because it expresses itself with uncommon clarity. People who judge everything by externals criticize spiritual science because many women are drawn to it at the present time. They do not comprehend that this is quite understandable simply because the average brain of a man has overstepped a certain average point of evolution; it has become drier, more wooden, and therefore clings more rigidly to traditional concepts; it cannot free itself of the prejudices in which it is stuck. Someone who is studying spiritual science may at times feel it difficult that in this incarnation he must use this masculine brain! The masculine brain is stiff, resistant, and more difficult to manipulate than the feminine brain, which can easily overcome obstacles that the masculine brain, with its density, erects. Hence the feminine brain can more readily follow what is new in our way of looking at the world. To the extent to which the masculine and feminine principles come to expression in the structure of the human brain, it can even be said that for our present time it is most uncomfortable and unpleasant to be obliged to use a masculine brain. The masculine brain must be trained much more carefully, much more radically, than a feminine brain. You can thus see that it is not really so extraordinary that women today find their bearings more easily in something as eminently new as spiritual science. These matters are of the greatest importance in the history of culture, but one can hardly discuss them anywhere today except in anthroposophical circles. Except in our circles, who will take seriously the fact that to have a masculine brain is not so comfortable as to have a feminine brain? This, naturally, does not imply by any means that many a brain in a woman's body has not thoroughly masculine traits. These things are not as simple as we suppose with our modern notions. The cometary nature is something elemental; it stirs things up and in a certain sense is necessary in order that the advancing course of evolution may be supported in the right way from the cosmos. People have always had a premonition that this cometary nature is connected in some way with earthly existence. It is only in our day that they reject any such idea. Only think what a face the average scholar of today would make if the same thing happened to him as happened between Professor Bode and Hegel. Hegel once stated bluntly to an orthodox German professor that good wine years followed comets, and he tried to prove this by pointing to the years 1811 and 1819, good wine years that were preceded by comets. This made a fine commotion! But Hegel said that his statement was as well founded as many calculations concerning the courses of stars, that it was an empirical matter that was verified in these two cases. Even apart from such comical episodes, however, we can say that people have always conjectured something in this connection. It is not possible to enter into details now, since that would be an endless task, but we wish to shed some light on one main influence related to human evolution. The comets appear at great intervals of time. Let us ask: when they appear, is their relation to human evolution as a whole such that they stimulate, as it were, the feminine principle in human nature? There is, for example, Halley's Comet, which now again has a certain actuality. (see Note 4) The same could be said of many other comets. Halley's Comet has a quite definite task, and everything else that it brings with it stands in a particular connection to this task. Halley's Comet—we are speaking here of its spiritual aspect—has the task of impressing on human nature its own special being in such a way that this human nature and essence take a further step in the development of the I when the comet comes near the earth. It is that step which leads the I out to concepts on the physical plane. To begin with, the comet has its special influence on the two lower members of human nature, on what is masculine and feminine; there it joins company with the workings of the moon. When the comet is not there, the workings of the moon are one-sided; the workings change when the comet is present. This is how the working of the comet now expresses itself: when the human I takes a step forward, then, in order that the whole man can advance, the physical and etheric or life bodies must be correspondingly transformed. If the I is to think differently in the nineteenth century from the way it thought in the eighteenth, there must also be something that changes the outer expression of the I in the physical and etheric bodies—and this something is the comet! The comet works upon the physical and etheric or life bodies of man in such a way that they actually create organs, delicate organs that are suitable for the further development of the I—the I-consciousness as it has developed especially since the imbedding of the Christ impulse in the earth. Since that time the significance of the comet's appearance is that the I, as it develops from stage to stage, receives physical and etheric organs it can use. Just think of it—strange as it may sound and crazy as our contemporaries will find it—it is nonetheless true that if the I of a Büchner, of a Moleschott, (see Note 5) and of other materialists had not possessed, around the years 1850–60, suitable physical and etheric brains, their thinking could not have been as materialistic as it was. Then, perhaps, the worthy Büchner would have made a good, average clergyman. For him to be able to arrive at the thoughts expressed in his Kraft und Stoff, it was necessary not only for his I to evolve in this way but for the corresponding organization to be present in the physical and etheric bodies. If we are searching for the evolution of the I itself, we need only look around at the spiritual-cultural life of the period. If we wish, however, to know how it was that these people of the nineteenth century had a physical brain and an etheric body suitable for materialistic thinking, we must say that in 1835 Halley's Comet appeared. In the eighteenth century there was the so-called Enlightenment, which was also a certain stage in the development of the I. In the second half of the eighteenth century the average human being had in his brain this spiritual configuration that is called “Enlightenment.” What made Goethe so angry was that a few ideas were thrown out and people declared themselves satisfied. What was it that created the brain for this “Age of Enlightenment?” Halley's Comet of the year 1759 created this brain. That was one of its central effects. Every cometary body thus has a definite task. Human spiritual life takes its course with a certain cosmic regularity, as it were—a bourgeois regularity one could say. Just as a man undertakes with an earthly bourgeois regularity certain activities day by day, like lunch and dinner, so does human spiritual life take its course with cosmic regularity. Into this regularity there come other events, events that in ordinary, bourgeois life are also unlike those of every day and through which a certain noticeable advance occurs. So it is, for example, when a child is born into a family. The cosmic regularity manifesting in the whole of human evolution takes its course under the influence of the moon, of the lunar body. In contrast to these events, there are things that always bring about a step forward, that are naturally distributed over wider spans of time; these events occur under the influence of the comets. The various comets have here their different tasks, and when a comet has served its purpose it splinters. Thus we find that from a certain point of time onward, some comets appear as two and then splinter. They dissolve when they have completed their tasks. Regularity, all that belongs to the common round, is connected with the lunar influence; the entry of an elemental impulse, always incorporating something new, is connected with the influence of the comets. So we see that these apparently erratic wanderers in the heavens have their rightful place and significance in the whole structure of our universe. You can well imagine that when something new, like a product of the cosmic feminine, breaks into the evolution of humanity, it can cause tumults that are obvious enough but that people prefer not to notice! It is possible, however, to make people conscious that certain events of earthly existence are connected with the existence of comets. Just as something new, a gift from the woman, may enter into the everyday bustle of the family, so it is with the comets. As when a new little child is born, so it is when, through the return of a comet, something quite new is produced. We must remember, however, that with certain comets the I is always driven out more and more into the physical world, and this is something we must resist. If the influence of Halley's Comet were to continue, a new appearance of it might bring about a great enhancement of Büchnerian thought, and that would be a terrible misfortune. A reappearance of Halley's Comet should therefore give us warning that it might prove to be an evil guest if we were simply to give ourselves up to it, if we were not to resist its influence. It is a matter of holding fast to higher, more significant workings and influences of the cosmos than those of Halley's Comet. It is necessary, however, that human beings should regard this comet as an omen; they should realize that things are no longer as they were in earlier times, when in a sense it was fruitful for humanity that it should come under these influences. This influence is no longer fruitful. Human beings must now unite themselves with different powers in order to balance this dangerous influence from Halley's Comet. When it is said that Halley's Comet can be a warning; that its influence, working alone, might make people superficial and lead the I more and more onto the physical plane; and that precisely in our days this must be resisted—this truly is said not for the sake of reviving an old superstition. The resistance can occur only through a spiritual view of the world, such as that of anthroposophy, replacing the evolutionary trend caused by Halley's Comet. It could be said that once again the Lord is displaying His rod out there in the heavens in order to say to human beings through this omen: now is the time to kindle the spiritual life! On the other hand, is it not wonderful that cometary existence takes hold of the depths of life, including the animal and plant life that is bound up with human life? Those who pay close enough attention to such things would observe how there is actually something altogether different in the blossoming of flowers from what is usually the case. These things are there, but they are easily overlooked, just as people so often overlook the spirit, do not wish to see the spirit. We may now ask: is there something in the cosmos that corresponds to the ascent to a spiritual life that has just been indicated? We have seen that head and limbs and masculine and feminine have polar contrasts in the cosmos. Is there something in the cosmos that corresponds to this welling up of the spiritual, to this advance of man beyond himself, from the lower to the higher I? We will ask ourselves this question tomorrow in connection with the greatest tasks of spiritual life in—our time. Today I wished to give the preliminaries, in order that tomorrow we may understand through greater relationships an important question of the present time. Much that has been said today is admittedly remote, but we are living in a cometary year. It is therefore good to say something about the mysterious relationship of cometary existence to our earthly existence. Beginning with this, we will speak tomorrow about the great spiritual meaning of our time. |
| 118. The Reappearance of Christ in the Etheric: The Reappearance of Christ in the Etheric
06 Mar 1910, Stuttgart Translated by Barbara Betteridge, Ruth Pusch, Diane Tatum, Alice Wuslin, Margaret Ingram de Ris |
|---|
| 118. The Reappearance of Christ in the Etheric: The Reappearance of Christ in the Etheric
06 Mar 1910, Stuttgart Translated by Barbara Betteridge, Ruth Pusch, Diane Tatum, Alice Wuslin, Margaret Ingram de Ris |
|---|
There is a certain connection between the past and the future in the evolution of humanity. When one considers this connection, it throws much light on the question that we can perhaps express in this way: what is our task as human beings in any particular period? When we came together here some time ago, we said various things about the past in the evolution of humanity. Today, something will be said about the connection in the evolution of humanity between the past and the immediate future. In concluding yesterday's lecture, we were able to point to an important indication that says, as if speaking from heaven, that humanity needs a spiritual impulse, something like a new impulse of the age. We can understand how this new impulse must work only if we consider the last millennia before the founding of Christianity in a certain connection with the millennia following Christ, in which we ourselves live. There is a law according to which certain events are repeated in the evolution of humanity, and we spoke of such repetitions in human evolution in the last Stuttgart lectures. Today I wish to point out particularly that when such regular repetitions are referred to by spiritual science, one should not believe that such repetitions can be constructed intellectually, because the repetitions must be examined, after all, in detail; they must be established in detail through spiritual research. One can go far astray if one uses one or another of these repetitions as a pattern for constructing new ones. There is one repetition that, as a matter of fact, resembles another, that repetition in which fundamental events, important events that were effective before the founding of Christianity, recur in a certain way after the founding of Christianity. If one observes the last three millennia before the founding of Christianity, it is seen that these three millennia belong to an epoch in the history of the evolution of humanity that is designated as the so-called Dark Age—the lesser Dark Age—Kali Yuga. This Kali Yuga began in the year 3101 before the founding of Christianity. All that we at the present time designate as the great achievements of humanity, what we call the characteristic feature of present human culture, is bound up with this Dark Age. Before this Dark Age, or Kali Yuga, the whole of human thinking, all human soul forces, were still ordered differently in a certain respect. In the period before the year 3101 BC—this is an approximate date, since evolution moved gradually from one kind of character to another—there existed what one can designate as the last residue of the old clairvoyance. In the course of human evolution these periods follow one another: Krita Yuga, Treta Yuga, Dvapara Yuga, Kali Yuga. The last interests us today most particularly. With the earlier periods we come back to old Atlantis. In ancient times there still existed remnants of the old clairvoyance, so that before the Dark Age man still had an immediate consciousness of the existence of a spiritual world, because he could see into that spiritual world. This consciousness of the spiritual world gradually withdrew from human view, and we may say that, on the average, the faculties and forces began to be cultivated that confine human judgment to the world of the senses and yet that also cultivate human self-consciousness. These forces all began during Kali Yuga. While man was not in a position to look into the spiritual worlds during this period, that firm point increasingly developed itself within the physical, sensible world, the point that we call knowledge of self-consciousness. Do not suppose, however, that this knowledge of self-consciousness has already been cultivated to a high degree. It must cultivate itself further. It could never have entered human consciousness, however, had there not been this Dark Age. In the 3,000 years before the founding of Christianity, therefore, man gradually lost his connection with the spiritual world. He no longer had this connection through his direct observation. During my last visit here, we saw how, at the end of the first millennium, a kind of compensation occurred for the lost vision into the spiritual worlds. This was given to man through the fact that a particular individuality, Abraham, was selected, possessing in special degree that organization of the physical brain through which it was possible to attain consciousness of the spiritual world without the ancient faculties. In spiritual science, therefore, we call the first part of Kali Yuga pre-eminently the period of Abraham—that period in which man loses, to be sure, the direct view into the higher spiritual worlds but in which something like a consciousness of God awakens in him. This gradually grows into his I, so that he increasingly conceives this God as being related to the I-consciousness, the human I-consciousness. The Godhead appears as the World-I to that age, the first millennium in Kali Yuga, which we may call, at its conclusion, the age of Abraham. This age of Abraham was followed by the age of Moses, in which the God Jahve, the World-I, no longer manifested Itself as a mysterious guiding power in human destinies, as a god of one people alone. As we know, this Godhead revealed itself in the age of Moses in the burning bush as the God of the elements. It was a great advance when the World-I, as the Godhead, was experienced in such a way through the teachings of Moses that one said to oneself: the elements of existence—what we see with physical eyes, lightning, thunder, etc.—are, in the last analysis, emanations, deeds of the World-I, of the single World-I. We must understand quite clearly to what extent this was an advance. When we go back beyond the age of Abraham and beyond Kali Yuga, we find that, through their direct vision into the spiritual worlds resulting from remnants of the old clairvoyance, human beings see the spiritual. They see this spiritual in all ancient times, however. We must go a long way back if we wish to find something different. Human beings see the spiritual during Dvapara Yuga, Treta Yuga, Krita Yuga. They see the spiritual in such a way that it manifests itself as a multiplicity of beings. You know, of course, that when we ascend to the spiritual worlds we find there the hierarchies of spiritual beings. These stand, naturally, under spiritual guidance, a unified spiritual guidance. In those ancient times, however, consciousness did not reach as far as this unified spiritual guidance. One saw single members of the hierarchies, one saw a multiplicity of divine beings. Only the initiates were able to bring them together as a unity. Now, however, the World-I, which man first perceived with the physical instrument of the brain that was especially marked in Abraham, confronted the human being. Man now perceived this World-I as manifesting itself in the various kingdoms of nature, in the various elements. Then a further advance was accomplished for the last millennium prior to the founding of Christianity, in the age of Solomon. We thus can distinguish the three millennia before the founding of Christianity in this way: we call the first millennium the age of Abraham, after that individuality who appears in it and who affects the second. From the beginning of Kali Yuga until Abraham, human beings prepare themselves to recognize the single Godhead behind the appearances of nature, and this possibility emerges with Abraham. In the age of Moses, the One God becomes the ruler of natural phenomena and is sought behind the phenomena of nature. All of this undergoes an intensification in the age of Solomon. We are led through this latter age up to the point of evolution at which the same divine being who was regarded as Jahve in the ages of Abraham and Moses takes on human form. In a spiritual scientific contemplation of this matter, one must adhere strictly to the fact that in this respect the Gospels are right: we may not distinguish Christ from Jahve other than as we distinguish the direct light of the sun from that sunlight reflected back to us by the moon. What kind of light do we have on a moonlit night? It is real sunlight, except that it is reflected to us from the moon. We thus can have this sunlight directly during the day or sent back from the moon on moonlit nights. What we see occurring here in space presents itself also in time in the way in which what finally appeared as a Spirit Sun, in Christ, manifested itself beforehand as though reflected. Jahve is the reflection that precedes Christ in time. Just as moonlight is reflected sunlight, so did the Christ being reflect Himself for Abraham, Moses, and Solomon. It was always the same being. Then He Himself appeared as the Christ Sun with the founding of Christianity. We thus have the preparation for this great event in the ages of Abraham, Moses, and Solomon. A repetition of these three ages, as they were before the founding of Christianity, now takes place during the time following Christ, but in reverse order. The repetition occurs in such a way that the essential feature of the age of Solomon is repeated in the first millennium after Christ, and, indeed, the spirit of Solomon lives and weaves in the most outstanding spirits of the first Christian millennium. It was fundamentally the wisdom of Solomon, that which had spread abroad as the wisdom of Solomon, through which man sought to grasp the nature and essential character of the Christ event. It was by means of what man had learned through the wisdom of Solomon that he sought to understand the significance of the Christ event. Then followed the age that can be called the revival of the age of Moses. The age of Solomon after Christ was followed by the age of Moses. When we come to the second millennium after Christ, it is the spirit of Moses that now permeates the best human beings of this time. Indeed, we can find this spirit of Moses revived in a new form. In pre-Christian times the spirit of Moses directed its glance out into the world, toward outer physical nature, in order to find the World-I, to find the World-God as Jahve, as World-I, to find Him in thunder and lightning, to find Him in what can stream in from without as the great law of human action. Just as the World-I streams in from without to Moses, just as the World-I is revealed, as it were, from without, so we find that, in the second age following Christ, the same being proclaims Himself inwardly within the human soul. The impression that was for Moses an outer event, as when he withdrew from his people to receive the Decalogue—this significant event repeats itself. It repeats itself in the second millennium after Christ through a mighty inner revelation. Things are not repeated in the same way but in such a way that what occurs successively appears as a kind of polarity. If, therefore, God revealed Himself to Moses out of the elements of nature, He revealed Himself now, in the second millennium after Christ, out of the deepest foundations of the human soul. How, then, could this come before us in a more sublime way than when we hear how a remarkable man of lofty talents preached in such a way that one heard: he proclaims mighty things out of the depths of his soul? One can assume that this preacher was deeply permeated with what one can call Christian mysticism. Then a seemingly insignificant layman came to the locality where he preached and at first listened to his sermons; it afterward turned out, however, that rather than layman he became the preacher's—that is, Tauler's—instructor. Even though he had reached such a lofty level, the preacher Tauler suspending his preaching until he felt himself permeated by what lived in the layman. When, after having opened himself to this inspiration, Tauler once again ascended the pulpit, the powerful impression of his sermon is made clear to us symbolically when we are told that many of his listeners fell to the ground as if dead. This means that everything of a lower nature in them was killed. It was a revelation of the World-I working just as powerfully from within as it had worked out of the elements, with Moses, during the second pre-Christian age. We thus see the age of Moses coming to life again and in such a way that the spirit of Moses permeates and radiates life into the whole spirit of Christian mysticism, from Master Eckhart to the later Christian mystics. It truly lived in these Christian mystics, the spirit of Moses! It was present in such a way that it entered livingly into their souls. That was the second age following Christ. In it, the whole character of the age of Moses was resurrected. During the first millennium after the Christian era, the second age of Solomon brought shape to the Christian mystery conception, to all that we know as the hierarchies, for example, in the Christian sense; it formed in detail the wisdom, so to speak, of the higher worlds. In the same way, the second age of Moses particularly formed what constituted German mysticism: the deep, mystical consciousness of the One God, Who can be called to life again in the human soul, Who can be resurrected in the human soul. This age of Moses has remained effective in all striving since that time to investigate ever more exactly the World-I, the One God. According to the course of human evolution, however, a renewal of the age of Abraham will take place, beginning with our times, during which we shall slowly pass into the third millennium. Just as the age of Abraham and the age of Solomon followed each other in pre-Christian times, so they follow each other in the Christian era in reverse order: age of Solomon, age of Moses, and age of Abraham. We are moving toward this age of Abraham, and it must and will bring us mighty things. Let us call to mind the significance of the age of Abraham. It was then that the old clairvoyance vanished, that a consciousness of God was given to man that is closely connected with human faculties. Everything that humanity could acquire from this consciousness of God that is bound to the human brain has gradually been drained off, and only a little still remains for human beings to acquire by means of these human faculties—indeed, little more. On the contrary, we are going in exactly the opposite direction in the new age of Abraham. We are taking the path that will lead humanity away once more from merely physical, sensible contemplation, away from the combining of physical, sensible signs. We are going along the path that will lead human beings back again into those regions in which they once were before the age of Abraham. We are going along the path that allows human beings to enter into conditions of natural clairvoyance, of natural clairvoyant powers. In the age of Kali Yuga, only initiation could lead upward into the spiritual worlds in the right way. Naturally, initiation leads up to high stages to which human beings will be able to ascend only in the distant future, but the first traces of a renewed clairvoyance, which will appear as a natural human faculty, will become manifest relatively soon as we pass into the renewal of the age of Abraham. After we have won I-consciousness for ourselves, after human beings have learned to know that the I is a firm central point in the inner being, human beings shall again be guided outward, in order again to be able to look more deeply into the spiritual worlds. This is still connected with that age in which Kali Yuga came to its end. Kali Yuga lasted 5,000 years, until the year 1899 AD. The year 1899 was, indeed, an important year for the evolution of humanity. This is once more an approximate year, of course, for these things happen gradually. Just as the year 3101 BC, however, can be designated as the year when humanity was led down from the old clairvoyance to sense perception and intellectual judgment, so was 1899 AD the year when humanity received another sudden thrust forward, so that it could ascend to the first beginnings of a future human clairvoyance. It is allotted to humanity even in this twentieth century, before the next millennium—indeed, for a few human beings during the first half of the twentieth century—to develop the first elements of a new clairvoyance, a clairvoyance that will most certainly appear in humanity when human beings prove themselves capable of understanding it. We must make clear to ourselves that two things might occur. It is inherent in the fundamental nature of the human soul that such clairvoyant faculties, as natural faculties (we must differentiate between cultivated clairvoyance and what will come into being as a natural clairvoyance), will come into existence for a few human beings even in the first half of the twentieth century, and for more and more human beings during the next 2,500 years, until at last there will be a sufficiently large number of persons who will attain it—that is, the new, natural clairvoyance—if only they win it. There are two different possibilities of what might happen, however. One is that human beings will have the aptitude for this clairvoyance but, during the coming decades, materialism will triumph and humanity will sink into a materialistic swamp. Isolated human beings will appear who will say that it seems to them as if they saw something in physical man like a second man; yet, if materialistic consciousness goes so far as to declare that spiritual science is folly and to stamp out all consciousness of the spiritual world, people simply will not understand these first capacities. It will depend upon humanity itself whether what then takes place turns out to be a blessing or a curse, since what is really to occur might pass by unnoticed. The other situation might arise in which spiritual science will not be trampled. Then one will understand that such qualities are not only to be cultivated in the secret schools of initiation but also to be cherished, when they appear toward the middle of our century, as delicate saplings of human soul life in this or that person. Such a person will say, as if from an awakened soul force, “I see something like a reality, just as it is described in anthroposophy as the second man within physical man.” Still other faculties will appear, for instance, a faculty that human beings will notice in themselves. They will perform some deed. When they look up from this action, something like a dream picture will stand before their souls, from which they will know, “This has some connection with my action.” People will know on the basis of spiritual science, “If such an after-image of my deed appears before me—which is essentially different, however, from this deed—it can have no other meaning than to show me the karmic effect of my action that is to appear in the future.” A few individuals will come to have such karmic understanding in the middle of our century, because Kali Yuga has run its course and because from epoch to epoch ever-new faculties appear in human beings. If understanding is not created, however, if this faculty is trampled to death, so to speak, if one who talks about these faculties is locked up as a fool, it will prove disastrous for humanity. Human beings will decay in the swamp of materialism. All of this will depend upon whether an understanding is awakened for spiritual science or whether the materialistic counter-current succeeds—whether Ahriman succeeds—in repelling what spiritual science does with good purpose. Then, to be sure, those people who are mired and choking in this materialistic swamp may say jeeringly, “Yes, indeed, those were fine prophets who said human beings would see a second man beside the physical man!” Certainly, nothing will manifest itself if the necessary faculties have been trampled to death. If these faculties do not become apparent in the middle of the twentieth century, however, it will be no proof that the human being is not so endowed but will only prove that human beings have crushed under foot the budding young shoots. What has been described today is there and can develop if only humanity wills it. We stand, therefore, directly before such an evolution. We are retracing our steps, so to speak, along the path of evolution. With Abraham, consciousness of God was led into the brain; as we enter into a new age of Abraham, this consciousness of God is in turn led out of the brain and, during the next 2,500 years, we shall come gradually to know human beings who will have what the exalted secrets of initiation yield as the great spiritual teachings about the mysteries of the universe. Just as the spirit of Moses ruled in the age that has run its course up to our time, so does the spirit of Abraham now begin to reign in order that, having led humanity into a consciousness of God within the world of the senses, he may now lead humanity out again. It is an eternal cosmic law that each individual must perform a particular deed repeatedly. He must, above all, perform the deed twice—one time as though doing the opposite of the other time. What Abraham brought down for humanity into physical consciousness he will carry up again for humanity into the spiritual world. We thus see that we are living in important, essential conditions in this age, and we understand that to disseminate spiritual science today is not something one does by preference but something demanded by our times. To prepare humanity for great moments in evolution is one of the tasks of spiritual research. Spiritual science exists in order that human beings shall know what they see. Whoever is true to the age in which he lives cannot help thinking that knowledge of the spirit must come into the world so as not to allow what will come in the future to go unnoticed by humanity. These things are bound up with still others. In certain other respects, everything renews itself in such similar repetitions. We are approaching a time when ever more of what existed in the pre-Christian centuries will be renewed for humanity, but everything will be immersed in what humanity has been able to win through the great Christ event. We have seen that humanity has now experienced again in Christian inwardness the great moment that Moses experienced through his impressions of the burning bush and the lightning-fire on Sinai. Now, the Taulers and the Eckharts know clearly that, when there arises within them what Moses called Jahve, it is the Christ. It is, however, no longer the reflected Christ being but the Christ Himself who rises from the depths of the heart. What had been experienced by Moses was actually experienced again by the Christian mystics but in a Christianized form—in a form altered through the Christ impulse. What was experienced in the pre-Christian age of Abraham will be experienced in a completely altered, new form. What will this be? All things and events that appear normally in human evolution cast their lights ahead, as it were. (I do not wish to repeat the triviality that is often uttered, that events “cast their shadows,” but that they cast their lights.) Thus, in a certain respect, something connected with events of the future is cast ahead in light in what we call the conversion of Saul to Paul—the event of Damascus. Let us make it clear to ourselves what this event had to signify for Paul. Until this event took place, Paul was acquainted with all that was inherent in the old Hebraic esoteric doctrine. What did Paul know? Paul knew, through his ancient Hebraic esoteric doctrine, that some day an individuality would descend to earth representing for humanity the one who would overcome death. He knew that an individuality would appear once in the flesh. Through His life He would show that the spirit lives beyond death in such a way that death would mean nothing other than another physical event for this individuality, within His incarnation on earth. This Paul knew. He also knew from his ancient Hebraic esoteric doctrine that when the Christ, the Messiah Who was to come, had been present in the flesh, when He had risen from the dead and had won a victory over death, as it were, the spiritual sphere of the earth would be transformed; clairvoyance would experience a transformation. Whereas previously a clairvoyant could not see the Christ being in the spiritual atmosphere of the earth but only when looking up to the Sun Spirit, Paul knew that, through the Christ impulse, such a transformation in earthly existence must occur that after the victory over death the Christ would be found, for clairvoyant consciousness, in the earthly sphere. When, therefore, the human being becomes clairvoyant, he must behold the Christ in the earthly sphere as the active Earth Spirit. What Paul could not convince himself of while he was still Saul, however, was that the one Who had lived in Palestine, Who had died on the cross, about Whom His disciples said that He had risen from the dead, was really the one about Whom the ancient Hebraic esoteric doctrine had spoken. The significant thing is that Paul was not convinced of what is related in the Gospels through what he had seen physically. He began to have the conviction that Christ was the predicted Messiah only when that forward-cast light manifested itself in him, when he became clairvoyant as though through grace and discovered the Christ in the earthly sphere. “He has, then, already been here; he has already risen from the dead,” he must have said to himself. After Paul himself saw the Christ clairvoyantly in the spiritual sphere of the earth, he knew: now He is here. From that moment on, he felt completely convinced regarding Christ Jesus. The fundamental event was therefore that, through the event of Damascus, he discovered Christ Jesus clairvoyantly in the earthly sphere. If Paul had not been able to hear the accounts in Palestine of the deeds of Christ Jesus, if he had not been able to have the personal experience of hearing the Gospels but had lived somewhat later, it might have happened that he would simply have experienced at a later time this Christ event of Damascus. He would then have arrived, however, at the same conviction, because this event revealed to him the fact that the Christ was there! He who reveals Himself there in the earthly sphere is the one about whom the ancient Hebraic esoteric doctrine speaks! This Christ event is not limited to one point in time. In the case of Paul, it simply followed quickly in order that Christianity would be able to pursue its course through Paul. Now, to be sure, during the ensuing time of Kali Yuga until 1899, the development of humanity was not such that a person could, without further ado, experience an event such as Paul's; human faculties had not ripened to this extent. It could therefore be experienced by grace, and others also experienced similar events by grace. We are now living, however, in the age in which that mighty, revolutionary change is to occur in which the first seeds of a natural clairvoyance will evolve. We are coming into the age of Abraham; we are being led out into the spiritual world. Through this, the possibility is given that a certain number of human beings, and then more and more, shall experience during the next 2,500 years a repetition of the event of Damascus. The greatness and power of the next age will consist in the fact that for many people the event of Damascus will come to life; that through these faculties of which I have just spoken the Christ will become perceptible in the spiritual sphere of the earth. He will radiate into these faculties. As human beings become capable of seeing the etheric body, they will learn to see the etheric body of Christ Jesus, even as Paul saw it. This is what is beginning as the characteristic of a new age, and it will become manifest between 1930 and 1940 to 1945 in the first forerunners among human beings who have these faculties. If human beings are attentive, they will experience this event of Damascus through direct spiritual observation, and with it clarity and truth about the Christ event. A striking parallelism of events will take place, because in the next two decades human beings will gradually fall away from the letter of the Gospels and will no longer understand them. We see even today how trivial scholars “prove” to people everywhere that the Gospels are not historical documents, that one cannot refer at all to a historic Christ. The historical documents will lose their value for humanity; the number of those who deny Christ Jesus will become greater and greater. Those human beings are shortsighted who will still be able to believe that one can preserve Christianity by means of the mere story. Those whose intentions are honest regarding Christianity are not the ones who reject an understanding of the spiritual proof of Christ Jesus. The spiritual proof of Christ Jesus will be provided through nurturing the faculties of human beings, through the fact that they shall behold the truly existing Christ in His etheric body. After all, no matter how much those persons who wish to rely only on documents call themselves good Christians, they destroy Christianity; no matter how much they raise a hue and cry and how loudly they proclaim what they know about Christianity through the documents, they destroy Christianity. They destroy it because they reject a spiritual teaching according to which Christ in our century will become truth for human beings through vision. When our era began, human beings had been descending into the Dark Age for more than three millennia and were dependent upon their outer faculties. At that time Christ could have revealed Himself to the faculties that were necessary for human evolution in no other way than through physical incarnation. At that time the physical faculties had reached the peak of their development, and Christ had to appear in a physical body. Humanity would not have advanced a single step, however, if it could not become capable of finding the reality of Christ in higher worlds through higher faculties. Just as Christ had to be found with purely physical faculties at that time, so will human beings with the newly developed faculties find Christ in that world in which only etheric bodies are seen, for there is no second physical incarnation of Christ. Only once did He appear in the flesh, for only once were human faculties dependent upon having Christ in a physical body. Now, however, with the higher faculties, human beings will be able to perceive the much more real etheric body of the Christ. This is what one can call the mighty event that lies ahead of us—the reappearance of Christ Jesus—taking place gradually, at first only for a few, then for more and more human beings. It is an event that has significance not only for those human beings who will then still be incarnated in the flesh. A number of human beings who are incarnated today will still be incarnated at the time when this Christ event takes place. They will experience it as it has been described. Others will have gone through the portal of death. Just as we once learned here that the event of Golgotha was not only an event for the physical world but carried its effect over into all spiritual worlds—just as the descent of Christ into the underworld was a real fact—so will the Christ event, which will present itself in our century, have its effect also in the world between death and a new birth, though in a different form from the one man will find here on earth. One thing will be necessary, however. Those faculties through which one will be able to perceive the Christ event between death and a new birth cannot be acquired between death and a new birth; they must be acquired here on the physical plane and must be carried with one into the life between death and a new birth. There are faculties that must be acquired on earth, as it is not for nothing that we are placed on the physical earth. Anyone who believes that we have been put on the physical earth for nothing is on the wrong track. We must acquire faculties here that we cannot acquire in any other world. The faculties for an understanding of the Christ event, of which we have spoken, and of the following events, must be acquired here on earth. Those human beings who acquire these faculties now, here on this earth, through the teachings of spiritual science, will carry these faculties through the portal of death. Not merely through initiation but through the understanding acceptance of the teachings of spiritual science one acquires these faculties, the possibility of perceiving the Christ event also in the spiritual world between death and a new birth. Anyone who has deaf ears, however, must wait until a subsequent incarnation to acquire the faculties that one must acquire here, in order to be able to experience the Christ event there, in the spiritual world. No one, therefore, should harbor the belief that the revelation of the Christ event, which can be understood only through the whole of spiritual scientific teaching, will not bear fruit for him if he has already passed through the portal of death at the time when it takes place. It will bear fruit for him. We thus see that spiritual research is a preparation for a new Christ event. Those, however, who absorb the essence of the teaching of the spirit as the content of their whole soul life—as vital life—should then really grow upward to a spiritual understanding of the matter. They should then make it clear to themselves that they must learn through spiritual science to understand our newly awakening age thoroughly. We must learn to understand that in the future we are not to look on the physical plane for the most important events but outside it, just as we shall have to look for Christ on His return as etheric form in the spiritual world. What has been said now will be said again and again in the next decades. There will be human beings who will misunderstand this, however, and they will say, “The Christ is to come again!” Since they will carry into this idea the belief that it is a physical return, they will supply nourishment to all those who will appear as false messiahs. There will be many such persons in the middle of the twentieth century who will use the materialistic beliefs of human beings, who will use the materialistic thinking and feeling of human beings to pass themselves off as the Christ. There have always been false messiahs. There was, for instance, the age before the Crusades when a false messiah appeared in the south of France, in whom his followers saw something like a Christ incarnated in a physical body. Before that, a false messiah had appeared in Spain and found many followers. In North Africa one who presented himself as the Christ created a great sensation. In the seventeenth century a man appeared as Christ in Smyrna and gained a huge following. He was called Shabattai Tzevi. People from Poland, Hungary, Austria, Spain, Germany, France—from the whole of Europe and from a large part of Africa and Asia—made pilgrimages to see him. In the past centuries this was not so terrible, because the demand had not yet been made of humanity to distinguish the true from the false. Only now have we come to the age when it could be disastrous if human beings should fail to pass the spiritual test. Those will pass it who know that human faculties go through a further evolution; that those faculties for seeing Christ in the physical were limited to seeing Him thus only to the time of the founding of Christianity but that humanity would not advance if it did not find the Christ again in our century in a higher form. Those who strive after spiritual science will have to prove themselves to be the ones who can distinguish the false messiahs from the one Messiah, Who will appear, not in the flesh but as a spiritual being for the newly awakened faculties. The time will come when human beings will again look into the spiritual world and will see the land there from which those streams flow down that give true spiritual nourishment to everything that happens in the physical world. We have, indeed, always seen that it was possible for human beings with the old clairvoyance to look into the spiritual world. The Oriental writings contain in their traditions something like a record handed down about an ancient spiritual land that human beings were once able to behold, from which they could draw all that could flow into the physical world from the super-sensible. Many descriptions of that land, which human beings were once able to reach and which seems to have withdrawn, are full of melancholy. This land was, indeed, once accessible to human beings, and it will now be accessible to them again, since Kali Yuga, the Dark Age, has run its course. Initiation, however, always led into that mysterious land, which is spoken of as a country that seemed to have vanished out of the sphere of human experience. It withdrew during Kali Yuga, but for those who had received initiation there was always the possibility of guiding their steps into it. The accounts of this ancient country are touching. It is the same land to which the initiates again and again repair in order to fetch from it the new streams and impulses for all that is to be given to humanity from century to century. Again and again those who stand in this relationship with the spiritual world enter this mysterious land, which is called Shamballa. It is the primal fountainhead, into which clairvoyant sight once reached but which withdrew during Kali Yuga. It is spoken of as one would speak of an ancient fairyland, one that will return, however, into the realm of human beings. There will be Shamballa again after Kali Yuga has run its course. Humanity, through normal human faculties, will again grow into the land of Shamballa, from which the initiates bring strength and wisdom for their mission. There is Shamballa; there was Shamballa; Shamballa will come to be again for humanity. Among the first visions that human beings will have when Shamballa shows itself again will be Christ in His etheric form. Humanity has no other leader than the Christ to take it into the land that Oriental writings declare to have vanished. Christ will lead humanity to Shamballa. It is this that we must inscribe into our souls. It can come to pass for humanity if we interpret in the right sense the omen of Halley's Comet that we mentioned yesterday. If humanity understands that it must not sink deeper into matter, that it must reverse its course, that a spiritual life must begin, there will arise, at first only for a few, then—in the next 2,500 years—for more and more human beings, the light-woven, light-gleaming Shamballa, abounding in infinite fullness of life and filling our hearts with wisdom. For those who wish to understand, for those who have ears to hear and eyes to see, this must be described as the event that signifies the greatest turning point in the evolution of humanity, at the dawn of the age of Abraham following the founding of Christianity. It will be the event through which human beings will understand to a higher degree the Christ impulse. For the peculiar thing will be that, through this, wisdom will suffer no loss. The more visions human beings win for themselves, the greater Christ will appear to them, the mightier He will appear! When once human beings are able to immerse their gaze into Shamballa, then only will they be able to understand various things that are indeed contained in the Gospels. To recognize what is given in the Gospels they will need a kind of event of Damascus. Thus, at the time when human beings will be most unbelieving regarding documents, the new profession of faith in Christ Jesus will arise through our growing into the sphere in which we shall encounter Him, through our growing into the mysterious land of Shamballa. |
| 337a. Threefold Order of the Body Social II: On Propaganda of the Threefold Social Order
09 Jun 1920, Stuttgart Translated by Ethel Bowen-Wedgwood |
|---|
| 337a. Threefold Order of the Body Social II: On Propaganda of the Threefold Social Order
09 Jun 1920, Stuttgart Translated by Ethel Bowen-Wedgwood |
|---|
It will be more in keeping with the character of a study-evening, such as this, if I do not deliver a regular lecture, but begin simply by offering a few remarks, which may lead on to as wide a discussion as possible of the particular subjects which the different members of the audience may have more especially at heart, and which may seem needful for the further work of propagating the Threefold Social Order. It has been intimated to me, that an important question at this moment is that of propaganda; a how and through what means the idea of the Threefold Order can best be propagated during the coming months. Since I was not present at the last study-evenings, it is possible that what I say to-day may be apart from the general context; but this question of propaganda was represented to me as being of particular importance. Well, it is hardly very profitable, to-day, to discuss the ways and means in which the propaganda of the Threefold Order should be carried on, unless one is prepared to base anything one may propose to do upon the experiences we have actually had up till now. In discussing a subject of this kind, I must really point out once more, that, in face of the general situation throughout the world to-day, it can really not be a question of how one thinks of arranging every detail in one particular concern,—especially not in the economic field. From any measures on a small scale, one can truly no longer hope for much to-day. To-day we should after all be learning to see, that at bottom nothing is to be accomplished except by treating things on a big scale, as I might say. As regards our propaganda,—I spoke of it last time at one of these very study-evenings, and called attention to the fact, that with our propaganda we have met with very interesting experiences. And the dominant note of our repeated experiences was always this: how very difficult it is really today, even in these times of need, to approach men's souls at all with the very thing which in all respects,—spiritual, political, economical,—one must feel to be absolutely needful. I pointed out last time, how certain proposed plans had failed, and how we were therefore obliged to fall back upon more or less individual enterprises, which, as you know finally concentrated in our business-undertaking, the Kommender Tag. We are quite well aware, that if our propaganda for the Threefold idea does not succeed in making its way through as a whole, this single undertaking can at best be but a very unsatisfying substitute in every respect. For the thing, above all, which is of importance to-day,—and it cannot be too often repeated,—is, that an understanding of the threefold idea, as an active onward-bearing force, should make its way into as many heads as possible. Unless we have a sufficiently large number of people who really understand this Threefold idea, there is no getting on. This understanding applies to many things, let me say. And here I should like to point to a concrete instance. When we first started our propaganda here, we began, as you know, by working in the way I have just indicated: by trying to win over as large a number as possible of souls with understanding. And the actual questions of economic life too were practically discussed. There is one very definite question of economic life for instance, which was discussed by me not once but many times: and that was the question of price-adjustment. I have often pointed out, that this question of price-adjustment is a cardinal one; that the fact of the matter is simply, that in the economic process there are of course other questions, but that even such questions as wages, and the like, are not the primary ones to be settled; but that these also must be settled on the basis of the price-question; that a quite definite price for any particular article is the only state of things which can be regarded as a healthy one in economic life. In other words: a definite article must be obtainable for a definite price within any particular set of economic combinations; and this must be the standard to which economic relations are adjusted. There can be nothing more unsound that to look upon prices as something that can be put up and down at convenience; and then begins the endless screw, of adjusting the rate of wages to suit the prices, and then putting up the prices again at convenience to suit the wages; if prices rise, then wages rise, and so on ad infinitum. This is laying hold of the whole matter by the wrong end. In those days I used to take for discussion a concrete question of this kind from the bed-rock of general economics. What was the result? In those days we used to have meetings which were attended for the greater part by working men only. The middle-class circles held aloof, for they thought that we arranged things only to suit the working classes. Well, in short, we met with some understanding amongst the particular circles who, in those days, listened to us. But this understanding completely dried up. The people gradually left off coming. They produced all their old stock-in-trade of questions from the regulation party shibboleths; and then they gradually stayed away; and one of the cardinal questions simply dried up in this way. I am just picking out one example; there are many others that might be quoted. And I cannot help thinking, in comparison, of an occasion I had, not long ago, to talk with a thoroughly practical business man, who is in the thick of business-life under a state-system which is not the German one; and in the course of our conversation it came out, that, simply from his own experience as a practical businessman, he had arrived at the view, that the most important thing to be dealt with is the problem of price-adjustment. Yes! of this—let me say—I am convinced: with people, who are business people, and at the same time can think, one finds no difficulty. I must confess that, so far, I have met with remarkably few people of this description. I have met with business-people who did not think, but who are under the habit of thought, even today, of regarding it as the all-important matter that one is ‘a practical man,’ and that one is ‘a practical man’ when one takes care that the State—or some other institution—thinks for one: one can leave it to them.—This was the way things were done too in Germany during the war; It must be left to the people above, at headquarters; they must know all about it!—And so, as I was saying, I have not met with many as yet, but when one does meet with such people to-day, who are business-men and at the same time can think, they arrive quite infallibly, through their own practical thinking on business matters, to the same results as you find in my Roots of the Social Question.1 You must not compare my Roots of the Social Question, and test what you find there, with the crazy things in the party-programmes. The party-programmes of the fourteen parties just elected to this impossible Reichstag (it will be a quite impossible conglomeration!) are all alike equally impracticable and impossible. The point about what you find in the Roots of the Social Question is, that it must be compared with a real practice of life, with what the actual facts of life require,—that is to say if one really thinks about actual life, and does not merely go crying the old stock-in-trade and the regulation shibboleths. But this method of propaganda, as we have seen, makes no headway: the method of really examining what, of course, had to be said on a limited number of pages. For one can't write a whole library off-hand; and it would be only less read than The Roots of the Social Question! But instead of people comparing what is said in The Roots of Social Question with the things one can learn in the factory as a business-man or a practical technician, they go hawking about the old, old party shibboleths and party-programmes; and the real practical thing of which the book is talking, instead of being compared with real practice, is compared with some bee or other, that is buzzing in some particular bonnet, and is supposed to be ‘the practical thing.’ This, then, is the first thing we have to achieve. We must decide to direct our efforts to making people see, that it is really not so easy to settle public affairs. I must say that for me it is a bitter pill, a bitter experience in this respect, that after I tried to write this book at that time from the actual needs of the time, people should now come and demand, that what is written in The Roots of the Social Question should be boiled down into a general mess, and drained off onto a page or two. That is what these people want! They want to have everything laid before them in a couple of pages,—which already in the book is stated as shortly as ever is possible! Or perhaps they would like to have it on a single leaflet for distribution! If you ask me to-day: In what does the trouble lie in our present age? I can only answer: The trouble lies just in this fact, that people can still to-day make such a demand as this; and that they are not willing, even now, to go to the bottom of things. Things that require careful study, they want to have crammed together anyhow on a couple of printed sheets,—such as already have appeared as an abstract of the Roots of the Social Question. So long as this is people's attitude of mind, nothing will be accomplished in the only way in which anything can be accomplished to-day. It is true that I propose very soon to issue a new edition of the Roots of the Social Question, with a special introduction, in which I shall shortly summarise in a couple of pages the contents discussed in the book.2 But this is only intended to be used as a sort of preparatory introduction, printed as the beginning, by way of preparation for reading the book in full. But if anyone imagines that he can learn from still fewer pages what it is necessary to understand to-day, it simply means that he has no feeling for the things that have actually to be done to-day. This is the very first thing we have to consider, if we are really in earnest about what we may term the propaganda-question. Just take this concrete fact, that our weekly paper, the Threefold Social Order,3 has already brought out 49 numbers:—49 numbers. Take these 49 numbers, read them through in succession, and you will see what an amount we have collected together in them of practically all the things which it is more immediately necessary for mankind to know about the Threefold question. We have already issued 49 numbers; and really there is to be found in them all that is more immediately necessary to know. Yet what can we only tell ourselves to-day? People still come to us, asking for information about some point or other. They are always asking for information about this point or that. As a matter of fact we have written these 49 numbers of the Threefold Order, and the whole of the material is for the time being flung away. Doesn't it look as though we should be almost obliged to begin over again from the beginning; to give out No. 1 again just as before, and then all the following numbers, just as they appeared before! Having said really a great deal here, which was thrown to the winds, which never made its way into people's heads at all, are we always expected to find something new to say! Well, they can't after all expect too much—the people outside;—they can't expect us always to be finding something new. What is wanted now, would be to set to work and actually propagate the Threefold idea, as it is. Of course there are any number of things in the way of this; but they all reside entirely in the human will. They reside in the fact, that it is necessary that people's souls to-day should wake up; and that they should take the things seriously which are really in question. There is one question, for instance, which people to-day invariably seek to evade. But it is the one from which the Roots of the Social Question sets out from the very first, and upon which, practically speaking, the whole of the Threefold propaganda must be based, not in substance, but as regards the way of propaganda: namely, the recognition, that in the so-called ‘social question’ to-day, we most certainly are not dealing with what most people talk about under that name. Most people, in talking about the social question, talk about what should be done with this or that institution, about the systems to be adopted in one or other department. Anyone who talks in this way has absolutely no understanding of what is going on in our present age; for the simple reason, that he does not see, that to-day you might make the most splendid institutions—if that were possible!—and that afterwards, when you have made them, you will soon have exactly the same agitation going on as before. As mankind is constituted at the present day, you may have a party, which for a long while has been in opposition;—take for example the Majority Socialists at the present time: the moment these Majority Socialists come into power, another party forms, of the socalled Independent Socialists. If these were to come into power, a new party again would form in opposition,—the Communists. And if these were to come into power, another new opposition party would soon be in the field. The fact we have to recognise is, that we are not dealing to-day with anything that can be touched by any sort of projects for particular institutions, but that the social question to-day is a human question, a question strictly of human worth and human consciousness. And one sees, what the social question really is, if one looks about one in countries, where everything has not yet crashed, but where the crash is still to come. There one may see, on the one side, the classes who formerly held the reins. These people see so far as that all business is coming to a stand-still: that enormous stocks of goods are piling up in the business-houses; that they have difficulty in making enough to pay their workmen, and are beginning to think, that if things go on in the same way, they soon won't be able to pay them at all; that they also won't be able to get rid of the stock in the warehouses. All this they see so far quite well; but they fancy, that some miracle will come about, and then, in a little while, things will be different. And so they sit waiting for the miracle, in order not to have to use their own brains, and think what ought really to be done. And, standing over on the other side, one sees those people who talk a very different language: namely the broad masses of the working class throughout the civilised world. Of what is going on amongst these broad masses, the first description of people have, nevertheless, not the faintest notion. But in these working-classes there exists a will: a will, that clothes its problems in conceptions, in ideas, which, the moment they are actually realised, will mean the destruction of everything we possess in the form of human civilisation:—ideas that destroy everything, everything,—that sweep everything away. And the leading classes imagine, that in a little while maybe things will have gone back again to the year 1913, or the Spring of 1914, and they will begin again whore they left off at that time;—and that then, amongst these broad masses, they will still find people to come quite willingly, and work again as they used to work in those days. No! to-day it is no question of institutions with which we have to deal, but a question of human beings. And we have to recognise, that amongst the leading classes for a very long time past there has not been the faintest sign of understanding for the task they had to perform. And do you think, then, that from the masses anything could possibly come, except what we experienced to our horror here in Stuttgart, when we started with our Threefold propaganda? You must consider, that there were two conditions under which the beginning we made, in April last year, might quite well have been carried further. Under two conditions:—the one would have been, that we should have succeeded, regardless of their leaders, in winning over the broad masses of the working classes to a really understanding conception of life. That was on a very fair road to success. And the next thing would have been, on the other side, if the people with some influence amongst the middle-classes—the bourgeoisie—would have held out a hand, would have shown us some confidence; if they had said to themselves: ‘Here is at least an attempt being made to construct a bridge between the working classes and the others.’—And what actually happened? As you can think, the matter is no easy one to-day; for as to the sort of thing which Stresemann talks, and the like,—or which bears the least odour of any leanings in that direction,—in nothing of this sort will the working classes ever, under any circumstances, place the slightest confidence. But, for all that, we were really in a fair way to appeal to the working classes simply on common-sense grounds; and all that was needed, would have been, that the bourgeoisie on their side should have met us with so much understanding as to say: ‘Alright: we will do our best, and wait and see what you can do. We will admit that amongst ourselves, there are a large number of people who cannot hope to win the necessary confidence, for they have trifled this confidence away; but, by this line of proceeding, it will be possible to bridge the gap.’ But, instead of this, what happened? The people who should have met us with this much understanding, planted themselves down across the path, and declared:iThese people are leading us straight into Bolshevism,—or not far short of it! They are hand-in-glove with the proletariatell Not the least understanding was to be met with on that side. And under these circumstances it then grew too late; so that the leaders of the working class, who should have been left out of it, found it easy to step in and alienate the workers from us again. That is what spoilt the matter for us, and why it came to grief at that time. But, in the same way, anything we might now do in respect of propaganda, would also inevitably come to grief, if the general kind of view were to be, for instance, as regards the paper: “Yes; but the articles in the Threefold Order are so difficult to understand!”—When anybody says that to me, I look upon it as my duty to tell him, with all politeness (politeness is necessary with such people as a rule); so I politely explain to him, that it is just for this reason,—that people have so long had a tendency to think everything un-understandable which comes from the real practice of life, and have always demanded that one should descend to a lower level when it comes to writing,—that now we find ourselves in trouble. And you—I say—are a representative of the people who have brought us into trouble. And when you demand, that one should write to suit the kind of understanding which passes current with you, you simply show yourself to be a specimen of the detrimentals who have brought us to this present pass. And so long as we are not in a position, (with all due politeness, of course, for the individual instance!),—so long as we cannot find a sufficient number of people with the courage at last to say, ‘A new day will have to come, with new people! There must be a clean sweep of everything to do with these horrible old parties; something quite new must come to life!’—until we can do this, all discussion as to the most effective ways of propaganda is so much talk for the cat! We are not living to-day in an age when anything whatever can be done by little measures; we are living in an age when it is an urgent necessity, that a sufficiently large number of people, holding the same language and the same ideas, should be capable of throwing themselves actively into the thing,—not merely of being ‘quite enthusiastic’ about it. I think that many of you must be asking himself, why there should be this continual crescendo in the way of speaking; why the words that I myself use, for instance, should grow ever stronger and stronger? Well, for a very simple reason. Only think for a moment: when one has been trying to induce a part of mankind to wake up; when one has taken the practical steps to enable a part of mankind to wake up; and one sees people falling ever more softly and soundly asleep,—then one's voice too grows louder in proportion, then everything one has to say grows proportionately louder, because one feels the instinctive necessity of overcoming the sleepiness of one's fellow-men! And as regards their conceptions of the urgent social questions of the day, we truly cannot say that the sleepiness of our fellow-humanity has grown any less of late. Things are taken up, even in our own movement, from an utterly wrong end. I delivered a lecture recently on the idea of the Threefold Order, and the necessity of placing the spiritual life upon its own footing. And in reply, somebody said in the most good-natured, well-meaning way: ‘Here, amongst us, there is really no occasion to complain of the lack of freedom in spiritual life. We possess a very considerable degree of freedom in our spiritual life. Amongst us, the State really interferes very little in anything we may choose to do as regards our school-system.’—Let me say to you, that people who talk in this way are the very best testimony to the necessity of emancipating our spiritual life. People who still have some sense of how unfree they are, are people for whom one can find much more use. But the people, who no longer have even a sense of their own lack of freedom, who take the State-educational ideas, that have been pumped into their heads, to come from their own inner freedom, and have not the faintest notion of how far this public-educational slavery extends,—these are the people really, who are the drag upon everything. It is a question of taking hold of things by the right end. And people who, without knowing it, take slavery for freedom, are the people who, naturally, hinder us from getting forwards. One may say, therefore, that the first matter above all, is to recognise, that all mutual understanding has been lost between the broad masses and those other people, whose special task for long years past it should have been, to hold such a language in the world, that these broad masses should not to-day be advocating, in their newspapers and everywhere, the kind of views which they are advocating. I read lately—in another country—the Whitsuntide number of a socialist newspaper. They were the queerest Whitsun articles, that were in it! Everything to do with ‘Spirit’ was rejected altogether, and it was pointed out instead, that the only kind of Spirit is the one which proceeds from the broad masses. Well, one really feels oneself wrought into such a state of mind by such Whitsun articles in a socialist paper of bolshevist tendencies, that one begins to say to oneself: ‘Where can I catch it? where can I hold of it, this “Spirit,” which is coming up like a smoke out of the broad masses?’ And then, when one really sets to work to try and form even some conception, let alone to grasp this Spirit of the broad masses,—then I can only say that one has after all the feeling: It is a far worse superstition, than the kind of superstition which sees a hobgoblin or a fairy in every bush and tree. The men of modern times have no notion really, under what forms of superstition they are living as a matter of fact. And what does it all amount to? Well, you know, it amounts after all to this: that people are much too easy-going to give their minds to the necessity of really building up a new spiritual life. This is an experience which one has had very thorough opportunities of learning for many years past. Directly one approaches people with any appeal for the necessity of building up a new spiritual life, one finds a certain number of people no doubt, who, in addition to their other occupations in life, can make up their minds,—on Sunday afternoons, or Branch-evenings, or for the time they spend on anthroposophical reading,—to devote themselves to this new spiritual movement. But, as to trying to make any connection between this new spiritual movement and their other occupations in life,—this is something which they cannot make up their minds to do. But there are numbers and numbers of other people, who come to one and say: ‘After all, what you want, is really what the better sort of Catholics, or the better sort of Protestants, want too. Why there was some clergyman, again, whose sermon from the pulpit was quite in the anthroposophical direction! More or less everything that you are aiming at is to be found in this or the other quarter as well.’—People who would like to make compromises, to the extent of being ready to let Anthroposophy be practically swamped by the sort of thing they are used to,—such people are to be found in plenty. People, who, even in matters that call for resolute will,—such as we spoke of in the public lecture yesterday—nevertheless still follow the principle ‘Wash my fur, but don't wet it by a single drop,’—such people are peculiarly plentiful in these days. And until we find means to put a clear understanding into as many heads as possible, that what is needed before all else is a new spiritual life, a spiritual life that lays hold on everything,—until we find means to do this, we shall get no further. When we have this new spiritual life,—when we no longer have the senselessness of the intellectuals to contend with,—then we shall once more have something that can speak to men in such a way, that the speaking has power to call forth social facts. If people would but form a conception of what can be done by the power of the Word! Look over the whole civilised world today, whereever you may travel, by train or by motor-car; everywhere you see towns and villages, and in all these towns and villages churches: churches, that have been built. These churches were none of them there, not so very long ago. In the first centuries of our present, Christian era, all over this Europe, now strewn with churches, there was something very different. Yet they were but a small Few, who went out amongst the people,—though indeed amongst a fresher age of man, less given to sleep. And these small Few it was, who through the power of their words gave Europe the face it wears to-day. Had the people, who accomplished this, been of the same type of mind as—say the sample-dozen leaders of our collective 14 parties, probably not so many as a dozen of these churches would have been built. It is the inner power of the spirit, after all, which must create social facts. But then, this inner power of the spirit must find its carriers in men, who really have courage to carry it. And today we simply have to face the fact, that everything, which in those days was founded on its own inner grounds, can only now be maintained in place by measures of force, by prejudice, by custom,—and that, at bottom, it is not possible to maintain it, if people's minds are true and honest;—that a new spiritual life must be set in its place;—that there is no other possible way for us to go forwards, except by setting a new spiritual life in place of the old. Every sort of compromise is an impossibility to-day. And until people recognise that it will be inevitably necessary to put something entirely new in the place of all these old things, but something which shall draw from the spirit the power to create a new social order,—till then, we shall get no further.—And therefore I must say to you, that I regard it, in a way, as a matter of very minor importance, whether all the petty measures of propaganda are discussed in this manner or that,—whether it is done in this manner or that; it may all, from a certain point of view, be very good, or miserably bad: that is not the important matter; the really important matter, as I have said over and over again in our paper, The Threefold Order, is this: that we should find a sufficiently large number of people who will make up their minds to stand out courageously for our ideas, who will make up their minds not for ever to be wanting to drift back into the old grooves. At the present moment, as you know, we are busy setting on foot the various businesses, collectively comprised under this Kommender Tag. What strikes me more than anything else about it is, that well-meaning people keep coming and saying: ‘Really, you know, that ought to be done quite differently; you ought to call in a specialist; you ought to call in a practical man.’—It is the most pitiable experience one can gb through, if one does for once give in and follow the suggestion. For such a suggestion really implies, that the person wants to import the old unpractical groove-drifting amongst us again. What we need, is not to import the old so-called practical men into our institutions; on the contrary, what we need, is clearly to recognise, that the people who may happen to-day to have the best reputation in any department, and know best how to handle the old routine, are the worst people for our purpose. And the best people for our purpose are those who are prepared to do new work from their own quite inner and spontaneous initiative, and who do not plume themselves in any way on what they have learnt under the old conditions. Unless we leave off pluming ourselves on anything we have attained to under the old conditions, we shall in no case get any further. This is what we must clearly recognise to-day. And in conclusion I would say to you as regards our propaganda: Let us spread abroad in the first place what we have really been endeavoring to do for more than a year past; and don't let us always try to be over-clever and always want to twist round the attempts that have been made, and give them a different shape again; in order then—excuse the expression!—to lick one's fingers over one's own cleverness, and for ever be repeating: ‘They are so unpractical in everything they start! This ought to be done, and that ought to be done!’ Just reflect for a moment what it means: 49 numbers of the Threefold. Order—of our paper—flung away and come to nothing! And why did they come to nothing? The Threefold Order ought really by now to be so far on, that we could bring it out as a daily paper. Why do I say this? Because as a matter of fact today I can still only take the same standpoint as was expressed in the words I used when we first began this thing, in April and May of last year. Do you imagine that it was a form of speech, that it was a phrase, when I concluded a great number of my speeches in those days with the words: we must make up our minds to do whatever it might be, before it is too late!—For many things it is simply too late to-day. By the paths along which we attempted to do all manner of things in those days, we to-day can obviously get no further. To-day it is not in the least our business to enter into any sort of discussion with the old stock-in-trade arguments whether of the creeds or the parties. Our business today, is to stand firm upon the ground of what we have to say, and to introduce it into as many heads as possible. In no other way shall we get forwards. For as a fact, for many things it is now simply too late. And it may possibly very soon be too late also for other things, which it is still possible to do, namely for the spreading of our ideas,—if we are for ever turning our minds to all sorts of secondary matters, instead of going straight for the main thing, which is to spread our ideas. I said, that this concern we have founded, the Kommender Tag; can after all be only an unsatisfactory substitute. And why? Simply because we are under no delusions that we can possibly be practical without basing ourselves upon practical actions. We are endeavoring to take an active share in practical business-life; and then people come and ask one: ‘How, exactly, ought one to set up a grocery shop, so as to be as much as possible on the lines of the Threefold Commonwealth?’ Of course, we are trying to found business undertakings in the Kommender Tag; but there it is a case of handling them really practically. And how, is one, for instance, to handle the matter really practically to-day, when one can only tell oneself: If I intend to carry on a particular kind of undertaking, then, in order to carry out the thing rationally, I must have another set of undertakings. For a particular set of industrial undertakings, for instance, I must have a particular set of agricultural undertakings. Well, but can you do it? It is all impossible as things are to-day. The State makes it quite impossible for you to make this particular kind of practical arrangement. So great is the external power of the State to-day. It is not a question of any want of practicality; but simply that the thing is made impossible on the other side by external power.—And therefore those persons, who actually now possess a standing in one or other department of economic business-life, should really not spend their time to-day in discussing subordinate questions, but should discuss together instead, how these various ‘business-estates’ of the Body Economic can make themselves free of the political State and everything involved with it,—how they can manage to slip out of it. So long as the technical experts, so long as all these various people are concerned with nothing but how to make arrangements that may best fit in with the life of the existing State, we shall get no step further;—not till they begin to discuss: How can we get free? how can we establish a really free economic life, where things are not ‘organised’ from above downwards, where, instead of ‘organisation,’ there is ‘association,’ in which the different ‘business-estates’ link up together through the actual course of business?—As yet there is not the first, elementary A.B.C. of this in our practical discussions of the Threefold system, but only the same old talk and the same old tinkering round and round, always with a respectful eye on existing conditions. All this roundabout talk leads nowhere to-day. We must be chary of the people who are for ever saying, ‘But how about this, and how about thatl! for the fact of the matter is, that we shall first be able to begin to discuss things sensibly, when we are a bit further on with the separation of the three systems; when we actually have thrown ourselves so completely into the propaganda for the threefolding of the body social, that a sufficiently large number of people in economic life definitely know: ‘Nothing we can say has any sense, so long as we still continue to reckon on the whole of our economic life being arranged for us by the State. Only in proportion as we manage to get free, will discussion begin to have any sense. Until then, everything we may say is nonsense.’—And, in the same way, there is just as little sense in discussing reforms in the spiritual life, until one is clear, that one can't even begin to converse on the subject, before one is actually living in a free spiritual system. One must at least be fully aware, that so long as one is living in a spiritual system which is dependent on the State, all one may say can have no sense,—that, so long as this is the case, one cannot reform anything. This, you see, very clearly marks out the point which is the important one: It is a question, not of little things, but of big things; and the more this comes to be recognised, so much more will it be possible to accomplish in the field of practical life. You will say: ‘What is the use of giving us such a philippic, when what we are asking is, how to carry on our propaganda?’ When you come to think over what I have said however, you will see, that even with what I might call an ‘elevenpence ha'penny propaganda’ (as they say in Austria, where they used to have shops in which every article could be bought for elevenpence halfpenny), that, even so, we shall get no further, so long as, even in our own circles, people discuss every petty detail of ways and means. We shall only begin to get further, when people have hearts and minds for the great motor forces of the world; for it is a question of these great motor forces to-day. Well, I have said a great deal to the same effect before now, and all in vain;—namely that it is a question of the great motor forces of the world. Still, I shall never grow weary of persisting, in general principle, to decline everything which leans towards the making of compromises to-day. I shall never weary of pointing out, again and again, the necessity of bringing the great world-moving questions of the day really to the comprehension of the very broadest masses of the people. And for this reason too, I always feel myself obliged to deliver the public lectures in the style I did yesterday, and to defy all the over-clever people who say, that one ought to talk more intelligibly to the masses,—meaning as a rule themselves only and their own intellectual niveau. I shall always maintain the view, that it is the people who talk in this way, who are the detrimentals; these are the people whom we have to overcome. And we must come so far as to have the courage to say to ourselves: ‘Yes, indeed! The foundations must be laid of something quite new!’ The truth is—as I wrote lately in our paper,—that the old parties, practically speaking, no longer exist; they only exist any longer as lies and phrases, and are made up of people who, knowing of nothing new, drape themselves with the empty catchwords of the old parties; and all the while, the whole business is nonsense (including what has been going on in these last days), and directly proves how radically something new is needed. (At the close of a desultory discussion Dr. Steiner concluded as follows:) It is regrettable that so little has been said about the Threefold idea itself in the course of the discussion, and only about all sorts of other matters. I should like just to bring back the theme a little to the Threefold idea and to the things connected with it. I will therefore pick out several questions that have been raised, and so lead back to the theme of the lecture. One of the questions raised was; What my attitude is—or the attitude of the Threefold idea—towards Syndicalism? Well, as you know, we have endeavoured, really, to find an attitude towards a great many movements of all kinds. I myself could only say the same about Syndicalism to-day, as I have often said about it before: that in certain circles of syndicalist tendencies one undoubtedly finds a consciousness of how much might be done by means of combining the various business-callings, the various branches of business, and that this, the ‘syndicalist’ idea, might lead in a way to certain fruitful results, at any rate in economic life. All this I am quite ready to acknowledge;—as also, for example, that Syndicalism takes up, in a way, a less slavish position towards the idea of the ‘State,’ than Marxian Socialism does for instance. This I am perfectly ready to acknowledge, and have often acknowledged it before. But all such movements in this direction belong, after all, not to the present day, but to a past one; and only project themselves on into the present day, because the people who adopted the name at an earlier date, have since been incapable of learning new conceptions. One might say really, that the whole set of party-shibboleths have lost their meaning for present-day conditions,—only that the people, who in past days belonged to the things these party shibboleths stand for, have not get made up their minds to label themselves with anything else but old party-shibboleths. Down to the end of 1914, you see, there was still a certain sense in people calling themselves by a party-name, such for instance as v.H.... and L.... still do to-day; but to-day there is no longer any sense in it. And yet people still go on calling themselves by the names of these parties. In the same way, to go on clinging to-day to bye-gone things like Syndicalism, has no real meaning any longer. And so, having made the attempt to approach such people as might be hoped to have brains still plastic enough to get beyond these old party-shibboleths,—so long as the attempt could be made, we made it. But one must learn a little wisdom from the circumstances in this case;—and indeed it is urgently necessary to-day to learn wisdom from circumstances. And therefore I must confess, that to-day I no longer feel any force in the question: What is my attitude towards Syndicalism? I can only assure you, that I have also tried to find an attitude towards Syndicalism; that is to say, I have tried to find people amongst the syndicalists who might be able, by means of a still more plastic brain, to understand the idea of the Threefold Order:—but that too was all in vain. And therefore, to-day, it is necessary to speak as I have spoken to-night, and to say, that our business is to take our stand on the firm ground of the Threefold idea, and not to trouble about anything else. For, what we have to do to-day is, to find a sufficiently large number of people who understand the idea of the Threefold Order; and whether they come to us from this camp or that, from the syndicalist camp, or any other, is to us a matter of complete indifference. We no longer trouble ourselves to-day about what is the attitude of the Threefold idea to the syndicalists; we can wait and see, what attitude the syndicalists will adopt towards the Threefold idea. Anything else would be so much wisdom learnt in vain in the course of the last year; and no one can work effectively to-day who is not capable of learning wisdom. And then the question was asked: ‘In what way is it proposed to widen out the organisation of the ‘Kommender Tag,’ so that the Threefold movement may spread?’—Well, here, I must really beg you—especially in the question of an isolated case like this,—to bear in sight, that the Threefold idea, in its whole character, is something eminently practical; that we are dealing with something that is concrete, and not floating in a blue haze. The ‘Kommender Tag’ was founded, because it was recognised that the usual bank-system, as it is to-day, has gradually in the course of the nineteenth century come to be a injurious element in our economic life. I pointed this out when I was here last time, at another of the study-evenings. I showed that, more or less from the first third of the nineteenth century on, money has played a similar role in the economic life of modern civilisation, to that of abstract conceptions in our thinking-process: that it has gradually blotted out all concreteness of aim and effort; that it has spread itself like a cloak over the things that must find their expression in economic energies. And therefore it has become necessary to-day to found something, which is not merely a bank, but makes a centre of concentration for economic forces which are both a bank and, at the same time, engaged in concrete economic activity:—to found, that is, something which combines in itself real, concrete economic activities with the organisation of these special branches of economic activity,—in the same way as is done by a bank, where economic activities are included, but abstractly, without regard to the conditions of actual economy. That is to say, a practical attempt is here being made to overcome the injury done by the money-system. To-day we have seen all sorts of people,—Gesell, [Silvio Gesell, originator of the Free-Money (‘stable money’) movement.—‘Gesell’ in German means ‘fellow.’] and other strange ‘fellows’ in life,—dancing around, and talking about ‘free money.’ Those are the utopians! Those are the abstractionists! What is wanted in reality, is to look at practical life, and learn to see where the centres of injury really lie. And one centre of injury lies in the fact, that the bank-system has taken the economic form that it has to-day. The bank-system in our economic life to-day plays the same part as a man's thoughts in the life of his soul, when he translates everything at once into abstractions, and troubles himself no further about the particular, concrete things which one sees and has to do with, but translates everything into lofty abstractions. A man who translates everything into lofty abstractions,—and that is the majority of people to-day,—never arrives at any real understanding of realities. Abstractions of this kind you can hear today on any Sunday from any pulpit. Abstractions of this kind have no longer anything to do with the actual life of the people who find it so thoroughly happy and comfortable to be lulled away from life in this manner for the space of a Sunday afternoon. And what for the individual souls life this substanceless abstraction is, that flies away to its airy cloud-castles, the same for economic life is the bank-system, that lives in the transaction of money. And so it was possible to make an experiment in little, which, let us hope, will grow into something quite big, and in which things could be so arranged, that the money is brought back as it were into the economic activities, and the economic activities carried up into money; so that money, here, again becomes something which serves to make economic activities more feasible and easier to set in motion. Just as our thoughts are not for the purpose of carrying us aloft into abstract sublimities where we feel happy and comfortable, but of enabling us to set in motion the concrete facts of life; so too, with money, the important thing is to bring it down into actual economic industry, to carry on the different branches of practical economy, and not to sit ourselves down in a bank and transact business, in money:—for money-trasactions in themselves are the most injurious element we have in economic life, in the nineteenth and beginning of the twentieth century. Here we have then simply a practical idea, taken up and also practically conceived. And until people recognise that it is a case here of quite practically conceiving ideas down into every particular, they will not succeed in understanding the League for the Threefold Social Order. And now I should like to direct your attention to something which is not unconnected with the general note which I have been endeavoring to strike to-day: to a quarter, namely, which was alluded to by Mr.D.... (i.e. the Jesuits).—And although the cause is one, with which I, truly, will have nothing to do; yet you certainly find things advocated there in a very forceful manner. You may hear continually from that quarter: ‘Thousands and thousands of our followers may fall away; yet, though we should lose thousands and thousands, this matters nothing to us; the thing alone that could matter to us, would be the loss of a single truth!’ You may hear this over and over again from the quarter to which Mr.D.... alluded: ‘Thousands and thousands of our followers may fall away from us; but not a single truth must be let fall!’ Where people speak in this way on behalf of a cause, with which I, truly, will have nothing to do, it is easy to see, that they have here a very forceful manner of propaganda. And this is the thing which is needed7 to have strength to take up the stand, that it matters nothing to have numbers of followers; but that it matters everything to have strength to take our stand on the truths we possess, with no making of compromises, no sidelong glances to one side or another: "Can I get hold of this person? should I make myself agreeable to that person?" That is not what is needed to-day; but what is needed is, that we should win over as many people as possible to the ideas of the Threefold Order,—really not because one is enamoured of the Threefold Order, or because one is set on one's own notions; but because one sees that there is no other may of carrying on further. Well, it is hardly necessary, I think, to go into the subject raised by Dr.H.... as to the licensed architects,—the State-architects,—and their relations with the legal profession. These are things which were all settled long ago in the most elementary discussions of the League. And you will agree that is quite out of the question, when we are talking on the lines of the Threefold Order, that we should take up a standpoint altogether off Threefold ground. For it would after all, you know, make a curious impression, if when we were talking—say—of the free spiritual life, we were to start a discussion, as to whether it might be advisable, from a certain point of view, to alter the old titles of the heads of the University Colleges and call them "Directors of Studies", or something of that sort! These are all questions which are based on the old forms of the social State. And the same with the State-architects: it really cannot matter, what their relations are with the legal profession; for, the moment one enters upon the Threefold Commonwealth, it is not possible to talk of Government-architects, since one is talking here on the basis of a political State, which is strictly democratic ground, and comprises in its sphere those things in which every full-grown man meets every other full-grown man as an equal; and it really cannot be a question of the line this democratic State would take as regards a person on whom some title is to be conferred, and things of that kind. In short, we must accustom ourselves, altogether, to go rather more into realities. One meets with so many strange things in life, of which one is so often reminded. For instance, I was in company once with a certain socialistic celebrity—a very sound socialist—and we were discussing a very, very exalted Government official. I held this very, very exalted Government official to be totally incompetent, in fact a hopelessly impossible person; and I said, that I thought really the proper profession for this very exalted Government official would be, to give up his job and take to the business of a road-sweeper. You should just have seen the horror which overcame the socialistic gentleman at the suggestion that this person, with whom he was well-acquainted, could possible become a road-sweeper! Well, of course it was only just an idea; but still it seems to me that this idea was more in the direction of reality than—forgive me for saying!—the one put forward just now in this form, that ‘the gentleman should not look askance at the road-sweeper, nor the road-sweeper at the gentleman. Really, we shall not solve the social question simply by not looking askance at each other! The point of the matter really is, that in our present order of society the gentleman needs the road-sweeper, and so forth,—but, if he merely doesn't look askance at him, the social question will hardly be solved. And whether one plumes oneself on something, or whether one doesn't, are, after all, questions that have nothing whatever to do in reality with the actual business-facts and the grave realities of life at the present day. It really is not the important matter for us to-day, merely to demonstrate to people that the gentleman needs the road-sweeper, and the road-sweeper needs the gentleman. For, in the background, we have still, after all, just a little the notion, that the road-sweeper should remain a road-sweeper, and the gentleman should remain a gentleman, in the position where each happens to be placed to-day; only they should not look askance at each other,—which will certainly be an easier matter for the gentleman than for the road-sweeper! But in my opinion, all these things (which savour rather strongly of moralic acid!) will not help us to a blade of grass to-day; for the urgent matter is not, to-day, that we should merely not look askance at each other, but that we should turn our hands to making things different; and, first and foremost, that we should succeed in coming to an understanding, above and beyond classes. And this understanding will lead to a total reconstruction of the forms of life,—not merely to twisting eyes round from skewness to straightness, but to very different things besides. And if you go through the whole tendency that lies in the Threefold idea, you will see that, here, there can be a question of its leading in actual fact to something which mankind cannot but long for today, in so far as they understand anything of the forces that are striving to realisation in world-history. These are the things upon which we must turn our eyes to-day, and not upon something, which is mere moralising, and yet is linked with those forms of social life which happen to be in force at the present day. No! to-day we must be clear, that we take our stand on the ground of a new spiritual life, and that we need something that proceeds from this new spiritual life itself. And though in detail the Threefold Movement may have managed things never so badly, yet, nevertheless again and again we must affirm, that this Threefold Movement takes its stand on the ground, that: Only through a change of thinking, only through a transforming of human thoughts and feelings in their innermost depths, can we ever look to reach a better state of things,—and through nothing else.
|
| 337a. Threefold Order of the Body Social II: Influence of the human will upon the course of economic life
15 Sep 1920, Stuttgart Translated by Ethel Bowen-Wedgwood |
|---|
| 337a. Threefold Order of the Body Social II: Influence of the human will upon the course of economic life
15 Sep 1920, Stuttgart Translated by Ethel Bowen-Wedgwood |
|---|
If things really went on in political life—or in public life generally—in the way imagined by many people at the present day, one could only give up all hope of any personal action, any direct human intervention, being able to effect anything towards the betterment of social conditions. More particularly, one cannot but remember that there are quite a number of people at the present day, who are under the idea, that the phases of economic life run their course almost like natural phaenomena: that after one set of economic occurrences has played itself out, another set of occurrences will follow, with an inevitability of cause and effect in every way comparable to the inevitability with which a substance, possessing certain properties, will catch fire when brought together in a certain way with another substance. And in the same way many people have the idea in economic life, that when some phase like a ‘favorable business conjuncture’ has been evolved for a while, that then this ‘favorable business conjuncture’ will of itself inevitably evolve a crisis, and that this will then be succeeded for a while by a bad run of business and a declining phase of economic conditions; until again a sort of recovery sets in, and a rise takes place so to speak in economic life. This way of depicting economic processes was one peculiarly favoured in latter times by the theoreticians of economic thought, by political economists, who would have liked to describe everything as part of a chain of external cause and effect, to the exclusion of all intervention from the human will. It has actually been asserted, for instance, that the important economic crisis, which took place towards 1907 and during that year, was one that was bound to follow of necessity, as a consequence of the boom that preceded it. It may be thought perhaps, that a study of processes which cover such a wide range of economic life as favourable or unfavorable conjunctures cannot be of so much concern for the private individual; but this is not the case. And in particular any person, who wants himself to embark on any sort of undertaking, must each time pay good heed to the ‘conjunctural aspect’ into which he is launching. It is of course only too comprehensible, that the whole natural-science way of thinking during the last three to four hundred years should give rise to this belief in an inevitable chain of cause and effect. As you know, it is the Marxian school of social thought more especially, whose devotees indulge in this sort of ideas, and would like to make such ideas too the basis of social action. In the eyes of many persons to-day it seems quite foolish to criticise anything of this kind; for people look upon natural science and its methods of thought as presenting a downright ideal; and they look upon it as a great achievement, that this natural-science method of thought has been extended to the affairs of practical life as well. Here it is, that spiritual science, which, according to the views represented at all times in this place,1 is the only science from which a sound, social way of thinking can proceed ... here it is that spiritual science must come in and rectify errors; and it is able to rectify them through its whole essence, which has nothing whatever in it of that peculiar abstract, theoretic character assumed by materialist, natural-science thought in modern times,—which, on the contrary, educates in a man something which leads him to look plainly at the actual facts of life, and not to let these facts of life be mystified with a fog of theories.—I have pointed out in my "Roots of the Social Question", that it is just the working classes of the day who are peculiarly prone to bow down to a world-conception which from first to last is purely theoretic. The reason of this is simply, that the working classes of the day,—finding no understanding of what they were in search of,—took over from the middle-classes,—who were developing ever more and more materialistically,—the only world-conception that these middle-classes stood for: that of Materialism. And now they believe in this materialist world-conception as in an infallible gospel, and simply cannot free themselves from it. Spiritual science allows of no bowing down to theories, and—above all—of no tendency to phantasies of any sort. For, if one has any latent tendency as a spiritual scientist to be at all fantastical, then everything one may see in the spiritual world will become thereby distorted,—caricatured: one will only get into quite a distorted world. The first, necessary foundation for spiritual science is, that it should train its disciples to realities,—in a certain measure indeed, as I might say, to sober commonplace. But, once anyone has trained himself in the spiritual field, firstly to strict, clear logic, and secondly to the careful consideration of actual facts, then he is in a position to carry this training on into practical every-day life as well, and in every way fitted, there too, to let facts tell their own tale and to allow them their due weight. What do the political economists and theorists do, and the other people who sit at their feet, when they want, for instance, to study something like the economic crisis of 1907? They first begin by studying the economic conditions that went before it, in 1906, and come there to a year of favourable conjuncture. And they then attempt to find in these conditions, that went before, the origin of the economic collapse, that came after. If one follows this procedure, one is apt to confuse one's mind with all sorts of nebulous notions, and becomes in the end altogether incapable of thinking straight in social matters. Whereas, if one has trained oneself in the things such as spiritual science absolutely requires, then one examines the actual economic facts; and then one discovers something of this kind, (we might have chosen any other example), that—as regards the crisis of 1907—there was a powerful combine of finance-magnates in America, who owned 30 banks and over 30 long lines of rail, besides a number of other things. This powerful combine had, on the quiet, bought up big quantities of stock in certain speculative concerns, which were also being traded with on the European exchanges; so that nearly the whole of this stock was in the hands of this combine of financial magnates. They then, through all sorts of business manipulations, induced a number of European banks, and European undertakings generally, to buy stock of this kind ‘for future delivery,’ and succeeded so well at that time as to get quite a large number of people to buy stock of this kind ‘for future delivery.’ Now let us suppose that a business undertaking concluded a purchase ‘for future delivery’ in stock of this kind, in order to sell it again; and that, at the same time with the European undertakings, these banks in America concluded purchases ‘for future delivery’ in the same stock. Suppose then, a European undertaking had bought these stocks, on the one hand, and, on the other, was pledged to sell them again at a specified term,—but didn't possess them, because they had all been bought up again in advance by the Morgan-Combine; so that they had first to buy them back again from over there. The business undertakings in Europe were to a very wide extent under obligations to deliver stock of this kind; but now, in the meantime, during the period which had elapsed between the speculative purchase and the term of delivery, they had succeeded on the American side in screwing up the value of this stock enormously high; and the consequence was an extraordinary drain upon the European money-market; of which the result was this crisis: The crisis, that is, was created by a purely financial speculation brought about by a small number of definite individuals.—Those, who recall it, will remember that the bank discount at that time rose in England as high as 7 per cent, and in Germany at times as high as 8 per cent; and a rise in the bank discount is always a barometer for crises.—This crisis, therefore, was really brought about by the will of these particular persons; and it is to facts, such as these, one must look, that is, to quite specific, concrete facts of actual life, and not to general theories, if one wants to understand actual life in its social manifestations. It may be all very clever, it may seem uncommonly clever and convincing, when Carl Marx, for instance, takes a particular form of economic life, and proceeds to deduce from this with a kind of logical necessity all that people subsequently think. But at bottom this is all a product merely of ‘the study table;’ and it is a most characteristic symptom, that just this purest sample of a ‘study-table’ product,—Carl Marx's ‘Capital,’—should have become so popular a book, and indeed a sort of gospel amongst the working classes. If one would learn to know life, however, one must observe life itself. And one will then find, that spiritual science is the very best training for this decidedly somewhat troublesome observation of life. It is on the whole certainly much less trouble to construct abstract theories, than to consent to examine actual life. And now you will ask: ‘Well, but aren't the things all quite right, which the theorists produce and the agitators carry out amongst the people, and which are so plausible? If one only thinks of the army of figures, of the infallible tables of statistics, with which these things are usually supported! Think of the books we have today, showing the course of social affairs, and especially on the different economic theories,—why, they are simply swarming with data! And what can be more obvious, than that, if a person can support a thing with figures, then his conclusions must be right!’—There are however other statistics also, which, looked at in one way, really seem intended to represent a certain natural course in human life,—or at least a course definable by natural science. For instance, take the insurance statistics, as forming the basis of that eminently practical branch of life, Insurance. One calculates out, how many out of a number of persons, who are now 20 years old, will be still living in 30 years time, and how many will have died. One only needs to take the number large enough, in order to get very constant figures: Out of so and so many persons of 20 years old, only so and so many will be living in 30 years' time. And from this one can then calculate the amount of insurance, the rate of insurance, which the person in question will have to pay. And one may say, that here undoubtedly statistics afford a result with which one can to a certain extent reckon for the practical purposes of life.—You know, I daresay, that there is also a ‘suicide statistics;’ that one need only take a large enough area and a long enough period of time, and one can tell, that during this number of years so and so many people will commit suicide within this area. But would anybody be right in concluding from the necessity—the apparent necessity—of a definite number of suicides occurring every five years within a particular area, that therefore the people are not free; but that just as a stone falls of necessity to the ground, so these human beings are necessarily forced to kill themselves? Most certainly he would not be right in drawing such a conclusion. The existence of certain laws does not mean that man's free will is excluded. There is no question of itl And even it it should happen, that at 50 years old you came to look round you, and saw, that with this solitary exception all the rest were dead, of those who at 20 years old were calculated to die before 50, yet you certainly will not say: Well, now I must die too! Statistics are meant for something quite different; and not to state anything about Man's free will,—not even suicide statistics! Neither are any economic laws whatever in a position to state anything about the free intervention of human initiative in economic affairs. Though here, certainly, there is something besides, which comes into question:— Assume a condition of things such as had come about towards the year 1907: there was a favourable business conjuncture, which had lead to certain habits of life amongst a large number of people. One can tell, that when a number of people have been in comfortable circumstances for a few years, they will acquire certain habits of life; and when such habits of life have become established, those people who care to take advantage of the situation,—whose interest it is to take advantage of these habits of life,—can then do the sort of thing which the Morgan-Combine did in 1907. They may say to themselves: ‘Now is the time when people are inclined to do this and that; it is our chance for a speculation’ It is just the same, for example, as when certain influences are at work in a country; and people succumb to these influences, and a certain number commit suicide. And yet, notwithstanding, these people commit suicide of their own free will,—insofar as one can talk of ‘free will’ in ordinary life. (I have discussed the subject fully in my ‘Philosophy of Freedom’). The real fact of the matter is, then, not that there is a certain constellation in economic life in the first place, and that what happens after, follows as a consequence of this; but what happens, follows solely and simply as a consequence of what people do. And if the people choose to do something which in a way is ‘calculable,’ what does this prove?—Well, here one need only look at a procedure which will be familiar to you all. Suppose, there is the dog ‘Trusty,’ and you hold out a piece of meat to him. You can calculate pretty accurately what he will do: he will snap at it; and the cases will be extremely rare, in which Dog Trusty does not snap at the piece of meat. But when a human being in a given situation does something which is calculable, then it only proves, that the level of the human soul has sunk; and the more one is able to calculate, or determine causally, in social life, the more it indicates that men have sunk towards the level of the animal. And so all these suicide and other statistics, and calculations from favourable or unfavourable business conjunctures, are proofs of nothing except the state of men's souls;—though then, indeed, one must go on to examine the general atmospheric conditions under which certain states of soul are possible; Such a thing as was done by the Morgan Group in 1907, by which any number of human existences in Europe were flung into ruin,—such a thing could only take place in this present age;—such a thing would not have been possible 150 years earlier. How has it come about, that such a thing is possible? It has come about through the emancipation of the money-market from the goods-market. This emancipation dates from about the years 1810 to 1815. It was at this period first, that the earlier, purely economic conditions controlling public life, gave place to a control of public life by the money-market. It was the time when the bank-system first really became the dominant factor in economic life. And for economic situations to be created by transactions solely in the money-market, on the grand scale that was possible by 1907, was something which only came about through money having become what I might call an ‘actual abstraction,’ that spreads through our whole economic life and to all other life as well. We go back in thought to the time, when a man was himself involved with the thing he produced. The money, in those days, was practically no more than a sort of equivalent for the specific article produced. People clung to their specific productions; it was in those days by no means a matter of indifference, what one produced; one grew together with one's specific article of output. By to-day it has already become somewhat fabulous, when one meets with an incident like the following, which I tell as an example: It happened that I was staying in Budapest, and wanted to get my hair cut; and there I discovered a hair-dresser, who still cut hair really with enthusiasm, and declared: ‘My aim is not to make money; my aim is a really handsome cut of hair!’ And he said it in such a tone, as really to give one the impression of inward truth and sincerity. This close association, between the man and the things he puts out, is totally disappearing: all that is aimed at now, is to bring in a sufficient income to satisfy personal needs. And it comes then to be a question of Capital and Wages, and how much these will bring in. Just like abstract principles, which can be extended to cover every sort of thing, so this abstractified money extends over every conceivable thing. It is after all—in the minds of many people to-day—a matter of complete indifference, when the object is to earn a certain number of shillings a day, it is a matter of complete indifference, whether one does so by manufacturing shoes, or by manufacturing text-books. Money is the actual Real Abstraction, just as general principles are abstract; and, like them, it can be applied to every sort of thing. And this abstract money, emancipated from the real reality of life, has made the kind of atmosphere possible, in which transactions can then go on such as went on in 1907; and yet these transactions, nevertheless, proceed absolutely and entirely from the will of human beings. In saying this, I merely wish to point out, that Spirital Science, from the first, is directed to grasping realities in their true shape. Materialistic science—whether it be natural science, or historical—has become altogether divorced from realities; it has run into theorisations. Spiritual Science is obliged to go into realities; and therefore it does not let itself be mystified by theoretical conceptions. For this very reason, though, it arrives at a real understanding of actual life, and therefore will be the only science which is able to help in any way towards building up a new social edifice in the future.—It has gradually come to be the custom in question of national economy altogether, to take only things like ‘supply and demand’ into account, or questions of that kind: conditions of the market, af trade, of exchanges, and so forth. And what is really meant by it always is something purely abstract, which figures as ‘returns’. And when one comes to examine the way in which people to a very large extent think about economic problems to-day, they really think about these things only so far as to take into account the factors of returns. And in consequence, the whole of economic life is left out of account, which has to do with consumption. Consumption is simply left to proceed, I might say, automatically from whatever one may get as returns from anything. What one looks at, in going into any sort of business, is the amount it brings in, not at the kind of consumption that is connected with the particular business. One doesn't take into account in the least any special qualification in the article, insofar as it is an article of consumption; from the national-economy aspect, one considers it solely on the side of returns, not on the side of consumption. People think, that everything is to be found out by studying the returns side; how conjunctures develope, whether favourable or unfavourable; how upward or downward tendencies develope in economic life, and so on. If one altogether neglects however to give any economic thought to the other, to the consumption side, the result is that consumption gradually becomes anarchic; it runs wild; and one gradually loses all possibility of coping with consumption. Now Consumption has a peculiar property. It holds a definite relation, a sort of causative relation, toward man's moral nature, towards men's psychic disposition. It holds an opposite relation as regards man's psychic disposition, to what Production does. The moral, the psychic disposition plays a part too in Production; but here the psychic factor is the causative one. If I produce an article by means of which I defraud other people, this proceeds from a moral defect. But the way people live, that is, what possibilities they have of consumption,—whether they consume one article or the other,—all this acts as a cause upon the disposition of their souls, upon their moral nature; and this factor is the one which is left out of account in the whole of modern national economy. For this reason, national economy got completely out of hand. It is simply impossible for any sane thinking to comprehend, from the conditions of Production (although there were some circumstances of Production too as causes), why the number of strikes went up 87 per cent between the years 1907 and 1919; but one gets a picture of the whole matter, directly one looks at the conditions of Consumption. Now the various things in economic life have all a certain connection with each other; a connection which has of course been considered by the political economists and the business-men; but the real causes have not been studied by these people, because their calculations were directed solely to the paying side. And if one thinks of everything as a natural science, one comes gradually quite away from all economic thinking,—in particular as regards everything that has to do with the consumers. That is why the modern business-man knows so little, and has so very little to say, about the connection between strikes and any particular species of production. He knows—for he is in the habit of thinking of this—what returns one or other species of production will yield. He knows, if he was, for instance, a manufacturer of cri-cris in Paris (to take an extreme case), that this is an article Which is likely to have a very favourable run for a year or two. These cri-cris were quite curious little machines: it was a strip of steel fitted into a little metal case; and if one put it in one's pocket and went into the street, and then pressed on the steel, it made a most excruciating noise, so that the people in the street got horribly cross at the noise. It was last century, somewhere in the 'seventies: the streets were made downright intolerable by these cri-cris. But the ‘returns’ which the inventor of cri-cris got from them were enormous: he became a multi-millionaire. But he didn't in the least take into account the cost on the consumers' side. For of course, as regards human existence, the manufacture of cri-cris might quite well have been dispensed with. And now, just calculate how many people were employed in these cri-cri factories, who all paid their costs of consumption out of these returns. The consumption, that is, of so and so many cri-cri workers, arose out of unnecessary human labour. These things have their effect in social life. Unnecessary human labour has immense significance in social life. I might take a different example again. Even Lichtenberg in his day once said, that 99 per cent more literary works were turned out in one year than was enough for the happiness of the whole of mankind. And, as regards the present day, one might venture to say indeed, that if 99 per cent fewer books were produced it would probably be very much to the happiness of mankind. Just think of the batches of lyrical poems (always emanating of course from unrecognised geniuses!), that are turned out in editions of 3 to 5 hundred strong, of which not 50 copies at most are disposed of: how much unnecessary work is performed there! This unnecessary work might well be saved; and it would have an uncommonly beneficial effect upon the general conditions of consumption. This is to say, that when one merely reckons with returns, one can do so without the very least relation to the actual requirements of life: one may leave these quite out of account in all one's schemes for the regulation of life. This is at the back of the great crisis we are going through now; it is at the back of our present down-slide; and it is a thing quite beyond the calculation of the people who reckon in the old economic style, because they make no connection between unnecessary human labour and human suffering. Here is the point where Spiritual Science is able to come in, and to show the great connections; because Spiritual Science never looks to the one side only, but to all sides. I don't mean a kind of spiritual science that soars aloft into abstract, mystical heights, and that sort of thing, but a spiritual science which is bent on giving men an education that will make them of use for practical life. Spiritual Science, rightly applied, is an education for life, for the actual, full-lived up-building of life; and therefore the national economy which it founds will be one that knows the connection between unwillingness to work, unfittedness for work, and the manufacture of particular kinds of products. Such a way of thinking should lead on in the end to practical undertakings; and this was really the idea which lay at the bottom of an undertaking like the "Kommender Tag". It is obviously not possible to put such an undertaking straight away upon a sound basis in respect to every concrete detail; but nevertheless, where an isolated undertaking of this kind is directed solely by people thoroughly imbued with the kind of education which comes from Spiritual Science, then all the practical measures that are taken will of themselves tend towards people not being burdened with unnecessary work, but only with necessary work;—it will have to consider the consumption side of the general economy; and then the kind of arrangements will naturally grow up, which can lead on in the end to economic recovery. To someone who is merely bent upon getting returns, it is a matter of indifference, what he is producing for and what he is paid for, so long as he gets his money; money is abstract in economic life, and for money he can get everything. But what is needed, is to bring our general economy into a form in which it shall depend in an honest way upon the human will,—not depend on it in a dishonest way. How can it be brought to depend in an honest way upon the human will? By means of the Associations. When you have Associations, then all that takes place in economic life proceeds from the direct will of the people joined together in these Associations; the transactions that take place in economic life will then be transacted between the different Associations; then you will have transactions between live people, and what is produced will be the proceeds of this kind of transaction between live people, one with another, in the Associations. When it is a question of starting a factory, people will not consider it merely from the point of view of how much ‘returns’ it will yield under the existing conjuncture; but they will start from a collective insight into what is needed. It requires no government regulations: that would only tie the whole thing up in red tape—what it requires, is the practical knowledge of the people actually engaged in the various businesses and the various branches of business; and this gives the means of finding out whether a particular business-works is needed. If it is needed, then one may go on to production, and the people can make their earnings by it too. It will be done by way of the Associations; and in this way everything will become eliminated which might acquire an unhealthy influence. For then it will not be possible to trade in financial measures, as was done in the case of the Morgan-Combine; people will then work to meet economic needs. This results of itself, when it is a question of men, and not of money-balances. It is curious, how hard many people find it in these days to bring themselves to look at the realities of life. To look at realities! That is the most urgent demand of these days! How does it come about—one might ask—that people in the present day have wandered so wide of real life? It comes precisely from the materialism of the day; for the peculiarity of materialism is, that, at the same time, it trains people's minds to abstractness. Spiritual Science has just the opposite peculiarity: it trains people to concreteness, to actual-mindedness, practicality. That is what I wanted to throw into the discussion to-day. A very great deal, however, will be needed, before habits of thought, habits of feeling, and the actual practices of feeling, will become all that is necessary to enable us fully to overcome the many evils which have thus crept into modern economic life, and into the whole public life of modern times. This matter-of-fact thinking can only come as the result of real penetration into the depths of the spiritual world; and the new rise will come from the depths of the spirit, not from mere continuations, in some form or other, of what people have been used to look upon as ‘the right thing’ for the last tens, one might say indeed, for the last half-hundred of years in the nineteenth century. And anyone in these days, who has not the will to go in quite radically for a move forward in this direction, for a change in old habits of mind, a change of thinking, I could almost say, a change of living,—he will be able to do nothing to help towards a new rise, he will only go on helping to hurry us full steam into the downfall. And then indeed those things will come to pass which people like Oswald Spengler have given us a picture of, in his book ‘The Decline of the West.’ And then, in actual fact, the result will be that Western civilisation will pass over into barbarism. And if one is not willing to have barbarism, then one must actively will the thing that can prevent this barbarism; and the only thing that can prevent it, is a spiritual education of the West; for nothing but a spiritual education can open men's eyes to actual reality. We need this eye-opening;—Let us achieve it,—and then we shall get forwards!
The question is one that may quite well be asked. But in asking it, people have not really quite thought out where the point lies. The point is, not to look at what is taking place at one particular spot in life, but to look at what the results are in the whole context of life. It is quite true that these cri-cri workers would have figured as consumers too, even if they had not made cri-cris, that is to say, if they had not done this unnecessary work. But they would all the same have done something: they would have done necessary work, which is a matter of all essential importance for the general economy; and that is the point. There are a great many people, who esteem themselves very practical;—they read the ‘Roots of the Social Question’ [‘Die Kernpunkte,’ published as The Threefold Commonwealth.], and think it ‘utopian.’ The real fact of the matter is, that these people themselves are the unpractical ones and the ‘Utopians;’ and since these unpractical Utopians are in the main the people who dominate the whole of life—which is just what has brought us to the present state of things!—so it is just these people who have so little perception for what is in the true sense practically conceived; and one is always particularly glad, when the ‘practical men’ interest themselves for what is practical. Only recently, a practical man from the North said to me that the ‘Roots of the Social Question’ [‘Die Kernpunkte,’ published as The Threefold Commonwealth.], takes one to the most important question of all, the question of prices; that people are busying their minds at this moment with every conceivable thing, except the fact, that the price of any commodity is, strictly speaking, something that must not rise above a certain level, and mustn't sink below a certain level. That was a thing which this practical man could see. And directly one sees that the price question is one of such importance, that questions of Capital or Wages really fade into the background, then one has a sound thinking-basis to go upon. No doubt the cri-cri workers would have figured as consumers too; but this is not the connection in which one must consider them; for, what goes to make up the whole life of the general economy, and is ultimately connected with the price of any commodity, is very closely involved with whether necessary work is performed, or unnecessary. Only people do not think out the matter consequently; and this consequential thinking must be carried down into all the details of life. I had a discussion once with an acquaintance at table, over picture post-cards, somewhere in the year 1902–3. I said, I didn't like writing picture post-cards; in fact I never wrote picture post-cards; for I couldn't help thinking that, for every picture post-card, a postman might perhaps have to run up several flights of stairs—just for the sake of a picture post-card; and I would gladly save him the labour,—seeing that picture postcards don't exactly rank among the necessaries of life. The other man's reply was: “I know that I give people pleasure by sending them picture post-cards, and I write a great many: it contributes to the general pleasure. And if it should happen in some place or other, that a single postman isn't enough for all the post-cards, then they will put on an extra one, and that contributes to the possibilities of livelihood.” But in saying so, he didn't think the matter out further and reflect, that when one appoints an extra postman for picture post-cards, it leads to the production of nothing which is needful for life; but that when the needful requirements of life only are produced, the extent of their production means a certain price. And anyone, then, who performs unnecessary work, will undoubtedly be a consumer too; but if he is not employed in delivering unnecessary picture post-cards, he will no longer be increasing the amount of unnecessary work; and in consequence he will then do real proper work that corresponds to requirements; and this will have a very essential influence upon the whole character of our general public economy. As regards the things of practical life, there are two important points in question, of which as a rule people only consider the one. The first is, whether a thing is theoretically right; and the second is, whether it is in accordance with the realities. People think it quite sufficient for an idea to be theoretically right; but it requires also to be in accordance with the realities. And until this reality of thinking has gained general ground, we can not possibly find our way out of the perplexities of actual life. If somebody thinks therefore, that the cri-cri workers would figure as consumers in life too, even though they didn't manufacture cri-cris, he doesn't reflect, that the number of people who are consumers would of course not be diminished, but that the character of the general economy would be changed in respect of necessary or unnecessary work. And that is the point. One must learn to look at those points which are necessary and of importance; this is the thing which we have to acquire in social matters. And this is what it is hoped to inaugurate through the book, thenRoots of the Social Question, and the whole movement for the Threefold Social Order.
In the first place, as to the patent-leather boots, I should like to say, that here too, things have their connections in life; and it would soon be found, if once unnecessary forms of production ceased, that certain wants would disappear too. Of course, when one talks of ‘regulating consumption,’ one is in a way again upon a sort of false track. To try and regulate consumption in any way dictatorially, certainly won't do. But when all the economic arrangements tend towards the gradual disappearance of unnecessary work, this, in the whole context of economic life, will have a certain consequence: the consequence, namely, that a person who wants unnecessarily to have patent-leather boots will not be able to pay for them. And, because one thing is connected with another, it should be obvious that one must not directly attack something which will infallibly disappear with something else. That would make one into a tyrant. The facts of life are such, that if one wants to respect Freedom, one simply can't abolish anything over night; but certain things cease of themselves, through the influence of other determining conditions. When a kind of economic thinking gains ground, under which unnecessary work more or less disappears, then wants of this sort will disappear too:—amongst other things, the money for them will not be forthcoming. One can perceive this, solely through a practical connexion with real life. The conditions of consumption cannot be regulated by any sort of ordinances, but only by a progress, so to speak, in the ways of life. I might say the same thing too with respect to literature. I can only point out, ... and here of course it is a question merely of social conditions; one can quite well have a feeling for somebody who has lyrical poems he would like to print! ... but I might point to the example of our Anthroposophical Press in Berlin. It has never had books that were not sold. It has not got a great many books, which are in great demand; but it has never had batches of books which are just stacked up and don't get sold. It was always carried on on the basis of what one might call a ‘spiritual want.’ A book was not printed before knowing that a certain number of readers were there. The work began by first making people acquainted with the subject-matter, and so creating the readers; it was not done by any sort of ‘dictatorship.’ From the economic point of view, it must be said, that the Anthroposophical Press at any rate did not lead to the performance of unnecessary work. It all depends from which point one starts working in economic life. If one sets out from returns on production, this of itself leads on into unnecessary production. If one starts from understanding of requirements, then a kind of production gradually springs up in the rear, which is not continually piling up: the work goes on ahead; and where the work is of a kind to create requirements, these requirements find their satisfaction subsequently in the rear. In talking solely of work for returns, people are harnessing the cart before the horse as it were. It is a case of looking at life clearly, and knowing from which end to begin working. It is not a case of making ‘regulations’ about anything; but simply of laying hold of actual life in such a manner that things can take their proper course. As regards the present crisis, it is one which is more or less a final consequence. It cannot be examined by quite the same tests as other crises; and yet again it must be examined—not by theories, but by the actual facts. Consider, I beg of you, what has taken place in these last few years; How much has been produced by human labour power since 1914, in order that we might successfully bring it to the point, when from 10 to 12 million men have been shot dead in the course of 5 years, and three times that number disabled for life! How much labour-power has been expended upon this; and labour thereby withdrawn from life, which might have been employed very differently in life's service! I think one may not unjustly take the view, that what was there produced in order that men might be shot dead, was perhaps also unnecessary work, and work that might have been left undone. If one only thinks, what a long time was needed for deliberation, as late as 1912, when a million was required for educational purposes; and how very quickly the money was to hand, when a million was required for turning into powder! And then take what came after. Take this quintessence of abstraction; that money became an abstraction in the course of the 19th century; and now it has reached the perfection of abstraction: Look and see, how many paper-notes the stamp-press turns out every day. One can really only find use for it all, because the usage is artificially provided for! [Spoken during the time of the great inflation in Germany.] And behind it all, is the fact that we are living on the plunder of what is left over from the years 1911–18. That will come to an end at some time: Then the crisis will come! The present crisis has been brought about by men's utter frivolity of mind, in thinking that one could employ people for years in manufacturing unnecessary things, and take them away from doing necessary work. “Whether one can really succeed in building up anything new with the existing generation?”—I have often recurred to this question in the paper of the Threefold Order, and often pointed out, that it Is a sign of unprofitable thinking to put questions of this kind. What I set value upon in this connection is the human will,—not so much the faculty of perceiving the existing state of things, as of firing the will. And when I hear that “one can do nothing with the existing generation,” I still cannot but assume, that those who pass such a criticism on the existing generation are nevertheless of the opinion, that with themselves at any rate something “can be done.” And since I set more value upon the will than upon the observation, I call upon all these people: “Come then! and together we will see what we can do with you!” There would be quite a large enough number of them already. And so we will call together all these people who “can do nothing with the existing generation,” and we will work together with them. There is one more, and a very searching question, which has been put: “What are the spiritual causes underlying the divorce of the money-market from the goods-market?”—We can only find the answer to a question like this, if we are clearly aware, that statements such as I made to-day must be taken in their exact sense, and not as being merely historical remarks, which are relatively exact so far. When one says, “through the emancipation of money a certain atmosphere was created,” one must look exactly at what this atmosphere is. In considering this abstractionising of the money-market,—where it is a matter of indifference, what the money stands for,—one must point out further, that this was necessary for the general progress of evolution. I have often pointed in this connection to the strong impulse which exists amongst the civilised peoples since the middle of the fifteenth century, to detach the individual from the group-spirit; how democracy has come more and more to be the general impulse of mankind; how the individual human being is tending more and more to become a factor of importance; and those things too are ever more gaining in importance, which proceed from a man's own soul. For this whole course of human evolution the abstractionising of economic life through money was a necessity; and we only require to recognise, that everything, which comes into being, will need after a certain time to be put straight,—or must be supplemented by something else which will counteract the mischief. For in actual life it is not possible to find anything which is absolutely good: everything in life is relative only. One can't say, if my boots are in holes to-day, that they are unconditionally bad; only, it is the fate of good boots to wear bad in course of time. It is inherent in the best system of economic life, that, when it has fulfilled certain functions, it should show signs of detriment. And so it is with the money-system too: it was not detrimental from the first. If one studies the historical circumstances of the time, in the middle of the 19th century, they very essentially contributed amongst other things to the rise of democratic conceptions. But then came the time, when this kind of abstraction reached its proper limit. I may rightly say ‘abstraction,’ for the function of money may in every way be compared to the soul's inner process in abstracting. Of this we may see a striking illustration. There exists also a theosophical movement,—with which this anthroposophical movement had a sort of external connection at one time. This theosophical movement is, really, a materialistic one. It talks indeed of the “higher, spiritual” parts of Man; but all it really means in talking of the aether-body for instance, is that it is something thinner and less substantial than the physical body; and so with the astral body, that this is again something still thinner, and so on. That is, they only apply the materialistic notion. And when they wanted for once to be unusually brilliant, they said—these people in the theosophical movement—“Man lives recurrent lives on earth.” But the materialistic notions were terribly fast set in their heads; and so there must now be something, which passed over into the man's next incarnation. These people had been taught by natural science, that Man is made up of atoms. The atoms fall at Man's death into the earth; and now these people had thought out in their own minds a doctrine of the Permanent Atom: this one atom didn't fall into the grave, but passed over beyond death; and round this one permanent atom all the other atoms could then congregate in the next life.—Here, under the semblance of a spiritual movement, we have the crassest materialism. So it is, when one becomes altogether involved in abstractions:—so we have abstractions in the soul's life; and so we have money (when it is an abstract commodity) in economic life. And since what takes place in economic life is only the outer side of the spiritual life, there is a very real connection between the spiritual life and the economic one. For it is quite a mistaken view to think, that down below there are only economic processes going on, and that on the other side there is the spiritual life, which is only ‘ideology.’ The real truth is: that the economic life of a particular time, and the spiritual life of a particular time (the times are not quite identical) hold the same relation as the nut to the nutshell; the economic life is invariably the shell which the spiritual life has thrown out, and which takes its cast from the spiritual life. And therefore, since economic life has become so abstractionised, the spiritual life too can only be abstract. And so we are in an age of abstract thinking, of life-remoteness—unreal conjunctures and such things. These are connections which should be carefully considered. And when one considers them carefully, one is led to a fruitful conception: to the conception of the threefold order of the body social, and comes to see, how the three systems of the whole living organism work one into the other, and combine together to a unity from the very fact that each is allowed its own independent basis of development, in the same way as in the human organism. In the human organism, we distinguish between: the nerve-and-sense system, the rhythmic system, and the metabolic, or digestory, system;—these, functionally considered, make up the whole human being. The three systems work in co-operation; yet each, for itself, is relatively independent. And they must be independent. No good results can come of mixing everything together. Of an abstract unity, such as the modern state aims at, (such as is aimed at in particular by the socialist state to-day in the East), there can be no question; it is a question simply of learning to know the conditions of life in an individual organism, and of recognising that they find expression in this joint threefold system. Anyone who is willing to examine the matter will see, that the three different systems of life are in the first place independent, each for itself; and, again, that they work in cooperation with one another, and work best in co-operation, when they have first developed independently, each on its own basis. The unity is then an outcome from within, instead of being imported from without. An abstract, lifeless unity bears no fruits, and destroys itself. The unity which grows up as the final form of independent parts, becomes a living, life-bearing unity, something of that kind alone which can really live and grow.
|