| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Sixth Lecture
30 Dec 1917, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Sixth Lecture
30 Dec 1917, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Today I would like to approach the subject from a different angle and consider the connections that exist between the human being as a microcosmic entity and the whole macrocosm of the world, of which the human being is a part, a member, an organ, as it were. These things can be considered from the most diverse points of view, and in doing so, the most diverse relationships will come to light, which sometimes seem to contradict each other; but the contradictions consist in the fact that the matter must always be viewed from different sides. From certain considerations that we have been making in these days, you have seen that actually man, as he relates to the world around him, mixes something of himself into his view of the world, that he actually does not take the world of sense as it is; that, as I have tried to express it drastically, he mixes into his view of the world something that rises from within, that is formed from within and that is actually a kind of transformation of the sense of smell. It is what man combines about the world in the most diverse ways, what comes out when he applies his ordinary acumen, as it is called, which comes to him through his body; one could also call it a sense of intuition. What else would be given to man if he could easily make the attempt at all - he can't even do it easily, because he can't easily switch off his intuition - if man would simply take the sensory world as it presents itself to him, without his mind, his combining mind immediately interfering in all sorts of ways. This touches on a subject that may perhaps present some difficulties for understanding. But you can get an idea of what is actually meant if you consider how nature, the essence of a sense, comes to you. It is the same with the other senses, but the matter does not become apparent with the same clarity to the external observer, not as clearly as when you consider what is actually meant here for the sense of sight, for the eye. Consider that this eye as a physical apparatus is actually located as a fairly independent organ in the human skull and is actually only extended backwards into the human body by the appendages, the appendages of the blood vessels, the appendages of the nerves. One can say: this is the human eye, here is the extension (see drawing); but as an eye it lies here in the bony skull cavity with a great deal of independence, insofar as it is a physical apparatus. Here the lens, the incidence of the light rays, the vitreous body, so everything that is a physical apparatus is actually very independent. Only through the optic nerve, the choroid, which extends into the body, does the eye itself extend into the body, so that one can say that this eye, as a physical apparatus, insofar as it perceives the external sensory world in its visibility, is an independent organism, at least to a certain extent.  It is actually the same for every sense, it is just not so obvious for the other senses. Each sense as a sense is basically something independent, so that one can already speak of a sensory zone. It is actually surprising that the study of the senses is not enough to drive the scholars concerned to some spirituality. Because it is precisely this independence of the senses that could drive the scholars to some spirituality. Why? You see, what is experienced through the optic nerve, through the choroid, that would – and this could easily be proven with ordinary science – that would not be enough to make a person aware of what he experiences in his senses. The remarkable thing about the senses is that the etheric body projects into this purely physical apparatus, and it is a purely physical apparatus. In all our senses we are dealing with something that is outside the organism and is only experienced by the etheric body. You would not be able to unite what is caused in your eye by the incidence of light with your consciousness if you did not permeate the sense of the eye, and thus the other senses too, with your etheric body. A ray of light falls into the eye. This ray of light has exactly the same physical effect in the eye as the ray of light in a camera obscura, in a photographic apparatus. And you only become aware of what is happening in this natural camera of the eye because your etheric body lines the eye and captures what is not captured in the mere physical apparatus by an etheric body. In the mere physical apparatus, in the mere photographic apparatus, only the physical process takes place; so that man, in the totality of his senses, really has a kind of continuation of the external world. As physical apparatus, the receiving senses, at least the majority of the receiving senses, belong more to the external world than to man. Your eye belongs much more to the external world than to your own body. In animals, the eye belongs much more to the body than it does to humans. The fact that humans, as sensory beings, have senses that are less connected to the body than the senses of animals, makes them superior to animals. In certain lower animals, this can be demonstrated anatomically. There are all kinds of organic extensions; for example, the fan is inside in lower animals. These are very complicated formations, partly of the nerve, partly of the blood corpuscles, which the lower animals have more completely than the higher animals and especially than man. The fact that in man the physical body takes so little part in his senses and leaves the part very much to the etheric body, that is what makes man a relatively so perfect being. So that we can say: Man is, first of all, this inner bodily man, considered physically, and the senses are inserted everywhere in him, but they are actually - as I once said in a public lecture in Zurich - like gulfs that extend into the outside world. It would be much more correct to draw it schematically like this. Instead of drawing: there is a sense, and there is a sense, and there is a sense (see drawing), it would be much more correct to draw it like this: there is the human body, and that is where the human world is built, for example the eye or the organ of smell, their continuation into the outside world, and their gulfs through the sense organs. The outer world intrudes through the senses, the eye and so on, and from the inside we only encounter it with the etheric body and permeate what the outer world sends in with our etheric body. It thereby takes part in the outer world. As a result, we are dependent on our etheric body to somehow grasp what the outer world sends in.  The fact that what I have just said is not known has meant that for more than a hundred years philosophy has been talking about nothing more fantastic than the way in which man perceives the outside world through his senses. You can get an overview of all this basically fantastic stuff by reading the chapter “The World as Illusion” in my “Riddles of Philosophy”. Because of the belief that the senses can only be understood from the inside out, from the body out, people do not understand how man can actually know something about the world through his senses. They always talk about it in this way: the world makes an impression on the senses, but then what is caused in the senses must be grasped by the soul. The truth is that the external world itself builds into us, that we therefore grasp the external world at the tip, with our etheric body grasp the external world at the tip, when we perceive the external world as human beings with our senses. Everything that Locke, Hume, Kant, the neo-Kantian philosophers of the 19th century, Schopenhauer, Helmholtz, Wundt and all the rest, everything that people have said about sensory perception, has been said to the exclusion of knowledge of the true conditions. As I said, you can read about it in the chapter 'The World as Illusion' in my book 'Riddles of Philosophy'. There you will see, in philosophical terms, the calamity that has been caused by the fact that, with the exclusion of spiritual knowledge of the matter, a giant cabbage as sense physiology actually took hold in the 19th century. Now it is important to really understand what I just said. If you want to check to some extent the truth of what I just called a giant cabbage, it is interesting that in a certain sense what Locke, Hume, Kant, Helmholtz, Wundt and so on said about the senses is true; but curiously enough it is true for animals. Nineteenth-century man, in his quest to understand the human being through science, cannot go beyond understanding the conditions in the animal world. It is no wonder that he also stops at the animal world when it comes to the origin of man! But this is connected to much more complicated conditions. For, as I said, the etheric body touches what is called the external world of the senses at one corner. But what is the ether body in the last analysis? The ether body is ultimately that which the human being now receives from the cosmos, from the macrocosm. So that, by cutting off its ether body from the macrocosmic relationship, the macrocosm takes hold of itself in the human being through the senses. We can feel ourselves as a son of the macrocosm, in that we are an etheric body, and grasp the earthly sense world with our macrocosmic part. The fact that this only became the case relatively late can, in turn, be proven with external science, I would like to say, with pinpoint accuracy, only that this external science cannot see the real conditions if it is not oriented by spiritual science. I have already pointed out that the Greek language does not actually have the expression that we have when we say: I see a man coming to meet us. We say: I see a man coming. The corresponding Greek expression would be: I see a coming man. In the Greco-Latin era there was still a much stronger sense that one is actually doing something when one sees or hears something, that one is grasping something with one's etheric body when one is in the sensory world. This active element is lacking in the drowsy humanity of modern times. This drowsy humanity of modern times would actually prefer to sleep through world events altogether, that is, to let them approach it as dreams. It does not want to develop the consciousness to participate when sensory perceptions occur. That is why it is so difficult to understand the Greek way of thinking today, because the Greeks had a much more active concept of the human being. They felt much more active even in what we today call the passivity of sensory perception. The Greeks would not have invented the incomplete, one-sided theory that man sleeps because he is tired; but they knew that man becomes tired when he wants to sleep, that sleeping is brought about by essentially different impulses, and that tiredness then arises from the impulse to want to sleep. But it is not only this theory of sleep that was actually invented out of the laziness of modern man. Modern man wants to be as passive as possible, to be an active being as little as possible. He can do that, and in a sense, modern man has trained himself to be a passive being. And it is with this passivity that I presented yesterday, perhaps somewhat abruptly, the superstition, the idolatry of modern times. So the outermost post of the external world enters into us, I would say, the outermost post of this external world. Let us draw this again schematically. Let us assume that we draw the human body here (see drawing), the outermost post of the external world enters into our body; we reach over it with our etheric body (red and blue). You know that we actually have twelve senses; these twelve senses are therefore twelve different ways in which the external world penetrates into our body. What is it that actually penetrates into our body? That is the big question. What actually penetrates into our body? We actually see only one side of what is penetrating; without clairvoyance we cannot turn around and look at it from the other side. With his etheric body, the human being receives the incoming ray of light or the incoming sound vibration. But it does not run from the outside into the ear according to the tone; it does not run from the outside into the eye according to the light ray. If it did, the human being would run with the sound wave, with the light beam, with the heat evolution from the outside into his sensory apparatus, as far as the senses extend from the outside. And this area is the realm of the exusiai, the spirits of form.  So if you could turn around so that you could follow what is entering here through the senses (arrows), you would be in the realm of the exusiai, the spirits of form. You can see how the beings of the world are intimately intertwined. We walk through the world as human beings, opening our senses and actually carrying the exusiai, the spirits of form, within us, which reveal themselves to us as we open our senses to the external world. This world of exusiai, the spiritual world, is thus hidden behind the veil of the sensory world. But this world of the Exusiai, which is hidden behind the veil of the sensory world, the world that reveals itself in man, also has a universal cosmic side, because it permeates the cosmos. That which enters our senses vibrates and undulates throughout the cosmos. So that we can say, this area that projects into our senses is not only there in the senses, but also has its manifestation out in the world. What is it there? There are the planets that belong to our solar system. Truly, the connection of the planets of our solar system forms a body that belongs to a spiritual being, and this spiritual being includes the exusiai, which are manifested in the revelations of our senses and which have their objective side out in the universe, in the planets. And embedded in all that is, embedded in this whole stream of exusiai activity, are other beings. They lie behind these Exusiai. I would like to say that other beings do not penetrate as far as the Exusiai do. They are out there in the same area, but they do not come close to us (see drawing): these are the beings of the hierarchy of the Archai, the Archangeloi, the Angeloi.  They are all already present in that which is revealed in our senses, but man cannot take this up into his consciousness. It has an effect on him, but he cannot take it up into his consciousness. So you can say: Through our senses we encounter a world - the realm of the exusiai with the planetary system (red, blue, orange, see drawing on p. 97), and embedded in this whole realm is also the hierarchy of the archai, the archangeloi, the angeloi. These are, so to speak, the ministers of the exusiai. But the human being perceives only the outer appearance of all this; he perceives only the sensory tapestry spread out before him. This is how it is with what is outside of us. It is different again with what is inside us, now also physically inside us. After hearing what is adjacent to our senses, you can go and ask: What is located directly behind our senses inwards? — We have seen: the eye continues inwards in the optic nerve. All the senses continue inward in their corresponding nerve. When the senses continue inward in this way, you get a wonderful structure from the twelve senses inward. It is very complicated. You could simplify it by saying: twelve strands to the inside, twelve sensory spheres; so on the outside the sensory zone, connected to it what the senses now send inward. This is a very complicated structure. How does it come about when we look at the human being as a macrocosmic being? That which lies behind the senses inwards comes from the Dynamis, from the Spirits of Movement. So that, going further inwards, the deeds of the Dynamis, the Spirits of Movement, join the senses here (see drawing on p. 97). You could not think if the spirits of movement did not work on the thinking apparatus, which is the continuation of the sense apparatus. If you look outward, you see the Exusiai making the natural order. You see these Exusiai approaching people with their servants, the Archai, the Archangeloi, the Angeloi. But when you think of your inner being, you must remember that you owe this inner being to the spirits of the movement, who prepare the thinking apparatus for you as a continuation of your sense apparatus inwards; not the combining apparatus, which is a mere transformation of the sense of smell, but the thinking apparatus, which man does not use at all in ordinary physical life. For man uses the sense of smell, the sense of smell merely transformed. He has already ceased to use the sense sphere; he would think quite differently if he could really use the twelve inward continuations of the sense sphere. In the brain, for example, the visual sphere lies behind the frontal lobe, which is essentially a reworked organ of smell. Man hardly uses it, he only thinks habitually through the olfactory sphere. He uses it in a reworked form by combining. If he were to use it directly, he would switch off his forebrain, this forebrain that is only prepared for the external sensory world, and think with the direct, with the four-hill section, with the visual section, where it enters the brain. Then he would have imaginations. It is the same with the other senses. Man also has imaginations in the physical world, because one world always extends into the other. But man does not recognize these imaginations in the physical world as real imaginations: they are in fact olfactory imaginations. What a person smells is actually the only imaginative realm in the ordinary sensory life. But a much nobler imaginative realm could, for example, come from the sphere of vision and from other sensory spheres. Looking inwards, we find the Spirits of Movement. And going further inwards, we come to the regions which do not dominate thinking but feeling, the organs of feeling, which are mostly glandular organs in reality. These organs are the deeds of the Spirits that we call the Kyriotetes, the Spirits of Wisdom. We are sentient beings because the Spirits of Wisdom work in us. We are volitional beings because the Spirits of Will, the Thrones, work in us. Located even further inward, the Thrones, the Spirits of Will, work on the organs of our will (see diagram on p. 97). Just as the exusiai, the spirits of form, have their macrocosmic body in the planets, which, as it were, present the outer visible side to us for ordinary consciousness, so the spirits of movement have their outer side, strangely enough, but it is so, in the fixed stars. Only the dead person between death and a new birth can see their inner side; this is the spiritual side, seen from the other side. In contrast, the Spirits of Wisdom and the Thrones no longer have external visibility at all; they are spiritual in nature. It can be said that they lie behind the planets and behind the fixed stars. And as the deceased looks down on what affects the person in human feeling and human will, the deceased constantly looks at the Kyriotetes, at the Thrones. What I have told you, that the dead person has a connection with the people with whom he is karmically connected, is conveyed to him by the Kyriotetes and by the thrones. The dead person looks into the sphere that invisibly works outside in the objective world and actually only becomes visible in its creature, in human feeling and in human will. What people feel and will here shines up to the dead, and the dead says: In the body of Dynamis, in the body of Kyriotetes, in the body of the thrones, the thinking, feeling and willing of people shines. Just as we look up at the stars, the dead look down into the earthly sphere, into the human sphere. Only, we look at the mineral aspect of the stars, the external physical; the dead do not see the external physical of the glands, the organs of movement, and thus also of the blood, but instead see the spiritual side, the Kyriotetes, the thrones. Just as we look up at the sky, seeing its visible meaning from the outside, the dead person looks down to see the firmament of humanity. The spiritual of this firmament appears to him. That is the dead person's secret. You see what reciprocity reigns in the universe. When you recognize this reciprocity, the human being takes on a strange countenance! Strangely enough, it takes on the countenance that you say to yourself: We look up at the stars, seek the spirits of form in their exterior in the planets, the spirits of movement in the fixed stars; then that in the distant perspectives fades into the spirit. From this sphere the dead person looks down, looks at that which the human being dreamily oversleeps here. But in that he sees his beyond; there the spirit stars shine up into his world. And the human being is embedded in this being. What is said in the first scenes of the mystery “The Testing of the Soul” is given a peculiar illumination. Read these first scenes of 'The Test of the Soul', the words of Capesius, and you will see that from the ethical point of view everything is said there that is now being said, so to speak, from the point of view of celestial knowledge. The way in which this celestial knowledge can work in the consciousness of man is pointed out in the first scenes of 'The Test of the Soul'. And then come the higher worlds, if one wants to apply the word 'higher', that which lies beyond the human being and this universe. I will try to present this schematically, but I must appeal to your goodwill to understand. We can say that if there is a kind of boundary here (see also the drawing on p. 97, yellow), the world of the planets, the world of the fixed stars, loses itself here into the spiritual – and from the other side it comes again. So that here we have the sphere of human will, the sphere of feeling, there the Spirits of Wisdom appear. There we have this order.  But now you can think of an order that is common to both, where man and the universe are included, where we are embedded in such a way that on the one hand we, who shine up to the dead, and on the other hand the starry sky, which shines down to us, are embedded in it. Then we come to the hierarchies, which, if you want to use the word, are higher than the thrones: to the cherubim and seraphim. You can imagine that from this point of view, which has now been mentioned, one cannot speak of the physical exteriors of the cherubim and seraphim, because they are of course even higher spirits; but they are already so spiritual — here I really must appeal to your very good will to understand — they are already so spiritual, these cherubim and seraphim, that their effect comes from another, quite unknown side. Is it not true that the exusiai, the spirits of form, can be perceived directly by the senses in the planets; that is simply the side they turn towards us. The spirits of movement are directly perceptible in the fixed stars; that is the side they turn towards us. But the cherubim and seraphim are not perceptible to the senses in such a way that they turn their other side towards us, so to speak. But they are so imperceptible that the imperceptibility itself becomes perceptible. So that which lives in the world through cherubim and seraphim is so imperceptible that imperceptibility itself is perceived. It withdraws so strongly from human consciousness that man notices this withdrawal from consciousness. Thus we can say: the cherubim do in fact reappear, even if this is manifested in such a way that they are so deeply hidden that one perceives their hiddenness. The cherubim appear not only symbolically, but quite objectively in what takes place in the thundercloud, in what takes place when a planet is ruled by volcanic forces. And the seraphim truly appear in what flashes as lightning from the cloud, or in what manifests as fire in the volcanic eruptions, in such a way that their very imperceptibility in these gigantic effects of nature becomes perceptible. Therefore, in ancient times, when people saw through such things, they looked up at the starry sky, which revealed the most diverse things to them: the secrets of the Exusiai, the secrets of Dynamis. Then they tried to reveal the higher secrets in what man today ridicules: from the interior of the human body - as one says trivially - from the bowels. But then they were aware that the greatest effects, which are really common to the solar system, announce themselves from a completely opposite side in the effects of fire and thunderstorms, in earthquakes and volcanic effects. The most creative aspect of the seraphim and cherubim is announced through its most destructive side, curiously enough. It is precisely the other side, it is the absolute negative, but the spiritual is so spiritually strong that even its imperceptibility, its non-existence, is perceived by the senses. There you have placed man back into the macrocosm. And at the same time you can see that in this whole macrocosm there is something that begins with the cherubim and goes up to themselves, and that only, I would say, reflects, shadows itself in the gigantic effects that we have just mentioned. This gives you the perspective of a natural science that is at the same time a spiritual science; it gives you the perspective of a science that really sees the whole universe as spirit, that is not content with a vague pantheism and other “pantheisms”, but that really goes into what lies at the basis of the universe as spiritual. These things will also make it clear to you that man must have a dual nature in a certain respect. Let us take man as he lives from waking to sleeping; he lives in his senses, in the sensual environment, if one perceives the outside as I have indicated. But the other part of a person lives between falling asleep and waking up. It is only so imperfect in the present human cycle that a person is not aware of what he experiences during sleep. But during sleep, a person experiences his being with the cosmos, with the extraterrestrial cosmos, just as he experiences his coexistence with the earthly cosmos with his senses while awake. The only difference is that he is unaware of the other coexistence, the coexistence with the extraterrestrial cosmos. The moment you fall asleep, you join in the movements of the cosmos spiritually, you enter into a completely different sphere. You make yourself ready when you wake up; you make yourself flexible in relation to the cosmos by falling asleep. You live the life of the cosmos by falling asleep; you tear yourself out of the cosmos by waking up. So that you can say: Man can recognize in his own nature, in his own being, a part that swims in the cosmos, that lives in the cosmos. If the ancient astrologer, in the sense in which it was meant in the last reflections, explored the cosmos with its secrets, he explored that in which man swims with that part of his being that sleeps. Man swims with that which the astrologer tries to explore, the real astrologer, not the merely calculating, mathematical one of modern times. In the moment when the human being sees what he experiences with the part of his being that sleeps, in that moment he stands before what, roughly until the 15th century, was actually called nature. What the human being experiences there was called nature. The Greeks called the same thing that was called nature in the Middle Ages, Proserpina, Persephone. Of course, the mysteries of Persephone were described differently in Greece and in the Middle Ages. But you can see that the Middle Ages knew these things when you read descriptions of nature and its secrets as found in the works of Bernardus Silvestris. In the work 'De mundi universitate' by Bernardus Silvestris, the description begins of the experiences that man has when he awakens to the part that participates in the cosmos, which is otherwise overslept. These things are particularly well described by Alanus ab Insulis, from the area we have mentioned several times; for in Alanus ab Insulis's 'Island', he means Ireland, Hybernia. In his work 'De planctu naturae' and in his 'Anticlaudianus', you will find parallels to the Proserpina myth and what he has to say about nature. And you will find that everything is resurrected in the great teacher of Dante, whom I once mentioned here, in Brunetto Latini. You will find the teachings of Brunetto Latini incorporated into Dante's own ideas. Read the parts of the Divine Comedy in which Dante describes the Matelda, the part that really resembles the Proserpina myth like two peas in a pod, which even the outer science has already noticed. You will acquire an awareness of it – from Bernardus Silvestris, Alanus ab Insulis, from Brunetto Latini and from Dante, you can acquire an awareness, from many others as well - as until the times when the new era dawned, people had an awareness of that other world of the coexistence of man as a microcosm with the macrocosm. On the one hand, there was nature, the human being's experience of the cosmos, which the Middle Ages called Natura and which antiquity called Proserpina. This was personified and distinguished from Urania, who rules over the celestial sphere just as nature rules over what the human being experiences from falling asleep to waking up. And these medieval people believed they saw a deep secret when they spoke of the marriage of nature in man with the nus, with the mind, with the intellect in man. And in a right and wrong way, these people tried to experience in man the marriage of nature with the Nus, with the mind or intellect, as a mystical wedding, which was contrasted with the alchemical wedding, as I described in the essay that is the first about Christian Rosenkreutz. These are things that are not so infinitely far behind us. And Dante's haunting work - which on the one hand describes the world and man, the human secrets, with as much sublimity as humor - is like the work that wanted to preserve what has been known for centuries and millennia about man's connection to the macrocosm. In Brunetto Latini we find the same thing that Dante describes in his own poetic way, from the point of view of initiation, also linked to an external event. The consciousness of the connection between man and these spiritual secrets had to be hidden for a time, so to speak, so that what man can experience when it is separated out from the universe and, as it were, dependent on itself, could be kindled in man. We are now living in the age in which, on the one hand, man is exposed to the radiations that permeate him from Pisces, but on the other hand, he is exposed to the radiations of the differently acting, opposite constellation of Virgo. But this age must find the way out of spiritual infertility. Of course, we can no longer simply take over what humanity once knew, because that knowledge was in a form that was useful for ancient humanity. Dante's “Divine Comedy” is, although a great revelation, more a testament of a bygone era. A new era needs the revelations of the spiritual cosmos from a different source. But one thing is possible. When one considers that, I might say, people knew spiritual secrets until a few centuries ago, this has such an effect on the human mind that it can inspire him to seek the way to these secrets in a new way. Therefore, we can also draw impulses from historical observation; only we must take this historical observation in such a way that we go back to what is really historical. Consider what all the external events related in history are worth – in this history, with which, lamentably, our schoolchildren up to the oldest are pampered – what these stories, which are recorded as history, are worth compared to the facts that people like Bernardus Silvestris, Alanus ab Insulis, Brunetto Latini, Dante and so on, Pico de Mirandola, Fludd , and even Jakob Böhme, Paracelsus, if we take a certain sphere of wisdom, and right up to the 18th century we could cite the disciple of Jakob Böhme, Saint-Martin — what are the usual events recorded in history compared to the facts that there were people who carried such cosmic knowledge within them and worked with such cosmic knowledge! Yes, the present is often proud of what it has achieved. This present-day intelligentsia – I mentioned it in connection with the Christmas plays today – has always been quite dismissive of the spiritual content; even when this intelligentsia, as in Oberufer, where the Christmas plays were performed until the middle of the 19th century, consisted of a single personality, the schoolmaster, who was also the village notary, and thus the legal personality and at the same time the mayor. He was the intellectual, he was the only enemy of all the Christmas plays. In his opinion, they were stupid, foolish. Schröer still experienced this, that the intelligentsia of Oberufer was hostile to what was in the Christmas plays. It is very often the intelligentsia that is hostile to what is actually fruitful in human evolution. It is a matter of encouraging that which may be called the enthusiasm of history by looking at real history, by really immersing oneself in what history is. The spiritual part of the event also belongs to history, and it proceeds differently than the external physical-material part. Especially in the harsh present, we must try again and again to stimulate the spiritual impulses by making ourselves aware of how spirit has ruled in the historical development of humanity. Whether you can count the details on the fingers of one hand: That is how the Dynamis work, that is how the Exusiai work — that is much less important than awakening this overall consciousness, how it wants to bring the individual human being together with the spirit of humanity. For in the awakening of this consciousness lies that which is to bring salvation into the evolution of mankind. Sometimes it is good to realize how far removed what passes as world opinion today is from what moves human souls, or at least seems to move them. As a result, there is often no sense of the weight of the individual facts. The spirit weighs the facts correctly. More important than many other things for the assessment of the present – just think about it with the help of what you have heard here – more important than many other things is the news that came in the last few days that the American state administration has taken the railways into self-government. For this is one of a number of symptoms that clearly point to things that are being prepared in order to divert humanity as far as possible from the path along which it can only be preserved if it becomes fully aware that without spirit reality can only be a dying reality. One can indeed choose to die; then life must flee from the areas for which one chooses to die to other areas. The field of truth already carries the victory. But one looks at a field where, so to speak, those who look deeper into the world are also confronted with such powers of a left and a right, as Dante at the starting point of his description of his “Divine Comedy”, or as Brunetto Latini at the beginning of his initiation. Oh, it would be so necessary for the world to grasp thoughts of spirituality in the broadest sense! Instead of this, it is true, we are only faced with the necessity of having to emphasize again and again that we must look towards the spirit. Again and again we are faced with the longing to be able to emphasize the seriousness of the matter sufficiently. People do not want to see where germs are, but they want to be passive, to let things happen to them if possible, to sleep through the course of the world if possible. If many people did not sleep as they do in the present, oversleeping events, then one would see that behind what is now buzzing through the world in such an untrue way, there is a strange tendency. It may well be said, since Woodrow Wilson, the universal idol of modern times, of the present time, of the present, has boasted of such things himself, that four-fifths of humanity is facing one-fifth. This idol of modern humanity, who has been raised to the altar much more than one might think, has indeed boasted of this himself. It will have to be said that it would be a shame if humanity were to oversleep what lies in such an ideal as the ideal of this idol, whose slogans, even those that are not copied from the brave Don Pedro of 1864 like its last manifestation, but rather grew in its own hollow—pardon me, I mean head—go back to what is actually inherent in it as a tendency. What is it then? The aim is to be able to say one day on earth: centuries ago there was a legendary humanity in the middle of Europe; they managed to wipe it out. They had to be wiped out because they were terribly proud. They descended from the gods and even called the main poet Goethe to suggest that they had received a spirit directly from the gods. Although we shall not express ourselves in such spiritual terms, the germ or tendency of Wilsonianism will be recognizable in this. It will only be a matter of whether this can be the path of humanity, whether this can be the future path of the earth, or whether we should not rather reflect on how the earth can be saved from the so-called ideals of Wilsonianism and similar things. One need not fall into nationalism or anti-nationalism with such things. The phrases of nations and the freedom of nations can also be left to Wilsonianism in modern times. But one cannot point out seriously enough what is actually behind the idol that is meant. I know that present-day humanity will not give much credence to such things, but I also know that in the future many a voice will be raised in agreement with what has been said here. May the voices of the future always be added to those of the past: Humanity allowed itself to be led in all sorts of ways by a strange idol; thank the world spirits that the goals of this strange leader of humanity were not fulfilled, who, after all, also to the world by theoretically proclaiming, in grand words, the republic as the only true form of government and by copying out his own republican manifestos from the Brazilian emperor of 1864. The fact that one is actually standing here before a grotesque phenomenon is something that can be said within closed walls. Outside, truth is not the highest value, but is weighed on the political scales. One must not say what is true or not true, but what is prescribed. Until March 15, one was not allowed to say anything against tsarism in the various countries; since March 15, one is of course allowed to say anything against it. Unfortunately, truth is not the highest standard. But to speak out against it is the only way to touch the conditions that are necessary to write into the soul today. It makes sense to add to the great views into the cosmos the small thoughts that passive, sleepy humanity has today, but which unfortunately have great effects on deeds. For humanity must awaken, and the spirit must be the awakener. |
| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Seventh Lecture
31 Dec 1917, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Seventh Lecture
31 Dec 1917, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
When we gathered here a year ago, we were still, so to speak, occupied with the thoughts that arose from the intention at that time to gain some insight into the foundations, into the underlying forces of the current catastrophic events. Some time ago, several of our friends expressed the wish that more should be said than had been said so far about the specific, deeper forces that have contributed to these catastrophic events. And we occupied ourselves at the time with the intentions, with the aspirations of certain circles, which seek to introduce their intentions, one might say, in a hidden way into the world, and which proceed from certain goals which, as we have seen, are by no means generally human goals, but are the group-egoistic goals of certain narrower circles, which, however, know how to calculate - in the sense that one has to calculate in the world if one wants to carry out certain things - which know how to calculate with large time periods. We have been able to refer back to aspirations that are to be pursued, they are to be pursued even further back, but for the time being they are to be pursued in continuous progression until the 1880s, aspirations that have reckoned with the trends and forces asserting themselves in the present cultural world. And perhaps from these considerations we have been able to gain some understanding of the course of events, some understanding that is independent of what dominates the whole world today, independent of the national and other group-egoistic aspirations that lead to such sad consequences. We may have been able to gain a view that is independent of the narrow perspectives that dominate almost all people today, and we may have been able to form, albeit less frequently expressed, certain inner views of what is necessary for the salvation of humanity in the present time. And it is from what is necessary in the present time that the other endeavors have also emerged, which are currently being tried to be asserted on the basis of our anthroposophically oriented spiritual science. In the last year in particular, my public lectures, as friends may have noticed, had a certain basic character. They had the basic character of drawing attention to certain important hidden sides of human nature. Everywhere I was able to lecture this year, I endeavored to awaken a deeper understanding of the human being from this point of view, insofar as the human being is part of the overall human process of the world order. We need only look back at the public lectures that have been held here in Switzerland over the past few months. The aim everywhere, including the more detailed observations that I was able to make in Zurich, was to show how the human being, as a human personality, as a human individual, carries within himself the forces that actually belong to different states of consciousness. How he not only carries within himself forces that belong to his waking consciousness, but also other forces that remain in the subconscious, but which are by no means meaningless, but play their role in the historical development of humanity, which play their role in social and ethical life. Through such endeavors, the idea should be awakened of how necessary it is in the present to strive for a deeper understanding of human nature. In these lectures, even in the public lectures, the connection between the so-called dead and the living was deliberately mentioned. Although such references must still be subtle in public lectures, they have been tried in a more insistent way, especially in recent times. The underlying tone of these lectures was intended to be one that arises from the, I believe justified, insight that salvation in the development of humanity can only come about in the present if humanity truly takes up certain spiritual-scientific impulses. And in the public lectures, an attempt was made to build a bridge between what humanity now chooses to believe and what leads to deeper truths. The attempt was made to build this bridge in such a way that it can be seen that a way can be found, if good will is applied, from what the individual scientists do not push towards, but what contemporary science as such does. It was attempted to show that actually the scientists of the present time are in discord with the results of their science, that science itself opens up the direct perspective into spiritual-scientific truths. And in particular, it was attempted to show how these spiritual-scientific truths have their significant consequences for practical human life, for all the various branches of this practical human life. The tone of these reflections, including the public ones, was such that, if there was good will for understanding, at least such an understanding could be achieved that one could say: something must happen in terms of human understanding of the world; there must be a kind of reversal of certain directions that have been taken, there must be good will. It has been shown that suggestions have fallen on fertile ground here and there. But today there is still a formidable obstacle in the way of adopting a new direction. And this obstacle comes in particular from the human desire for mental comfort, which is so decisive today, from the self-chosen difficulty that many people find in getting away from old thoughts, in really activating their thinking, to banish certain ingrained prejudices from their souls and to take in certain new concepts that are necessary for the further course of human development, certain concepts, certain ideas, above all, ideas that engage with reality. The tone was set in the reflections of this year in such a way that this necessary turning to reality, to reality steeped in truth, was emphasized and particularly highlighted. One might have thought that outside our circles there would be a larger number of people here and there who, inspired by such reflections, would have come to the question: Which paths should one take in this or that field? - that people would have emerged who feel that contemporary thinking has lost touch with true reality. Admittedly, not much of this has been shown. The thinking, the feeling, the perception of people today is casual, comfortable, lethargic, and also haughty, and self-satisfied with what has been handed down. This can be seen from the fact that few people ask themselves: What can be learned from the events of recent years? How many, many people today still take it for granted that they are building on the same principles, which they call ideals, whose collapse they could clearly see through these catastrophic events. Even today, theories and views are still being expounded that could be known to have been shipwrecked by the events of recent years. Currents continue under the same principles under which they used to work, even though one could see that these currents, in their principles, are far removed from the forces that rule reality and that destroy reality if man does not prepare to include the nature and workings of these forces in his imagination, in his view. Such things are not said for the sake of criticizing. Nor are they said for the sake of creating pessimism, but they are said because it cannot be emphasized often enough that the most necessary thing in the present is an understanding of true reality, a departure from the straw-like, insubstantial abstractions that have plunged the world into misfortune! Such straw-like, insubstantial abstractions dominate the world today. And it is urgently necessary for the human soul to turn to this direction. For example, some people today take it for granted when clever people repeatedly declare that it is not people who matter, but rather the ideas that are spread in the world. Such a statement is therefore dangerous because it is a strong temptation. In the real world, everything depends on people, and the best principles and ideas can have no significance if they are represented by people who do not have the strength within themselves to realize what, according to the nature of time, must be realized, who do not have the strength within themselves to find their way to reality with their own hearts and minds. Remoteness from reality is the word that can be used for almost everything that is often proclaimed with grandiose words as an ideal in the world. And a dawn, as humanity must experience it, can only come when, time and again, New Year's reflections come that, on the one hand, reject the impulse of alienation from reality and, on the other hand, attempt to unite man in his soul with reality. It is almost a truism to say, and yet necessary in the present situation: humanity has come under the influence of insubstantial word sounds, under the influence of insubstantial phrases of principle. People are not very inclined to look into where this or that comes from when they hear it, and so they come into tremendous discord with what is real and essential. For the world is not governed in the right way by the words that are spoken, if these words are not spoken from the heart of reality, if these words are only borrowed from the treasury of words and ideas that now flows on the surface of human existence, the content of which can be repeated without being understood. If one disregards the things that unfortunately have this character and are corrupting the world today, and focuses on something that may be insignificant in the face of great world events but is nonetheless characteristic because it is repeated in great world events, if one wishes to draw attention to something, one can say: It is quite natural in the present cycle of humanity that numerous people make good poems, because such good poems simply arise from the impulses rooted in the languages and the social circumstances of people. One need only, so to speak, put together what is already there, and good things will come out in the old sense. This is the case in the other arts and in the other areas of life. Today, however, it is much more necessary to be able to pay attention to what may emerge as something new, perhaps in a stammering and imperfect way, than to be able to keep an eye out for what is pleasing and beautiful. That which carries future possibilities within it may emerge in a rather imperfect way; but the important thing would be to discover in this imperfection the impulsive germ for the future. If efforts were made in this direction, we would try to make it a general principle, as we have done in particular in the construction of this building here at Dornach: to break with the old, even at the risk of being quite imperfect in the new. If that were to become a general method, then some good would come to humanity from such a thing. Above all, it is necessary to break away from the fixed, because the fixed is dying. There is something dying and something coming to life in the historical life of humanity. And it was not without reason that I said in those days: There is something dangerous even in the use of words themselves. One need not go as far as Fritz Mauthner, who in his “Criticism of Language,” in his “Philosophical Dictionary,” enumerates countless sins that people commit by pursuing the cult of the word everywhere. Certainly, Fritz Mauthner carries a correct thought to the point of absurdity when, for example, he asserts that Christianity in Europe is actually essentially a collection of twenty to thirty loan words, that is, it has developed in such a way that people have fallen in love with twenty to thirty words, to which they cling and consider them realities. Of course, we need not go that far. Nor can we entirely agree with Fritz Mauthner when he actually sees the most essential thing in the bringing about of these catastrophic events as being that people have practised idolatry with words, although it is absolutely true that idolatry with words has been practised. This is something that must stop. The word has gradually become something that floats on the surface of human life and to which one clings. The word has gradually become something that is taken for granted. When you try to get to know more intimately what dominates thinking and thought habits today, then, for example, when I see this, I remember an argument that I often encountered during my childhood and up to the age of twenty-five of youth, of boyhood friends, often encountered: I was often asked by this or that person – please excuse the perhaps somewhat offensive topic that comes up – what the actual difference is between love and friendship when it comes to relationships between young men and young women. And a great deal of emphasis was placed on defining the terms “love” and “friendship” as precisely as possible. These were supposed to be well-nested terms. I really did have – I can say this without being silly – the aspiration not to look at such abstractions, but to look at reality. I always said: in case A I see a relationship between a male and a female individual, and the same in case B; these are all concrete relationships of the most diverse kinds. Whether you call it “love” or “friendship” is all the same to me, because what matters is the objective. In contrast to what must be lived out in a social relationship between people, another interest does indeed arise. The interest of codification arises, and then, of course, nested concepts and nested words are needed. How could laws be made without adhering to words! But the alternative cannot be to say: no nested words, but direct human life! Such an alternative would be about as clever as it is clever to raise the ideal of establishing a paradise on the physical plane. But the physical plane is not suitable for establishing a paradise. One can raise the demand, but one can never fulfill it. One can also raise other demands. In recent times, the demand for an international organization has been raised many times. You can make the demand; you can also codify such demands; it can of course come about. But what reality will have to say about that after ten years is another question! Reality takes the paths that you only recognize when you also want to engage with reality in your recognition. Establishing principles, representing principles, these are soon brought together. Founding associations, having programs in these associations, people-pleasing programs, beautiful, admirable programs that cannot be objected to - you can set them up. It is even a thankless task to have to point out that it is so easy to do so. In some cases, you may even - let me say this in parenthesis - come into rather harsh collisions if you have no inclination towards such codification. For example, the Berlin branch of the Anthroposophical Society, in which I myself am involved, has not yet managed to draw up statutes for fifteen years because we have always considered real life to be more important than statutes, than codified life. You can have the most beautiful statutes, wonderful statutes. They may be quite good, but only for the purpose of enabling one to deal with certain outside powers. They have no significance for the inner life of a matter. A truly living thing actually resists statutes and principles. I am not criticizing the making of statutes, but nevertheless, the making of statutes and the founding of associations often seems to me to be just as clever as when a father and a mother have a baby of a few months and draw up a detailed program for this little child. There you have the clash of life with codification, the clash of life with abstract principles. The world will not cease to be a living being, even if a number of idealists — let us say, in order not to hurt them — are now setting up all kinds of world-blessing programs from intergovernmental organizations. Spiritual science does not seek abstract ideals, unreal ideas, but spiritual science strives to seek the real impulses from the realm of life, to recognize that which is, because social principles can only be truly put into practice on the basis of what is. To do that, it takes discomfort to even take such things into one's heart, discomfort is necessary. It is convenient for seven or eight people to sit down together today and establish a world-blessing association with magnificent statutes. You can do that. The statutes will always be right if people are reasonably sensible. You can then also win followers, and there is no objection to such things, because the things are of course right. But it would be necessary for the people who often gather under such flags to first sit down for a few months and study the subject for which they want to achieve something. They do not do that. Instead of people spending a few months familiarizing themselves with the issues at hand, one finds that such associations have made a global impact, have gained thousands and thousands of followers, but that after twenty years there are not five among these thousands of followers have in the meantime taken the trouble to study the subject matter of the weekly journal published by the association, in which the same phrases are repeated over and over again, when the readers, who quickly forget and have forgotten history, which has already been so often. Breaking away from the idolatry of words, breaking away from the idolatry of abstractions, is an essential part of what anthroposophically oriented spiritual science should bring to people. “With words one can argue excellently, with words one can prepare a system.” And one could add: And then one can live comfortably with the system. But life is complicated, and complicated life needs to be considered. And it is perhaps a very good time to point out such a contemplation of life when we are at the end of a year that concludes a series of such sad years for humanity. In such times, we should turn our gaze again to what the basic ideas of spiritual science can inspire in us. These basic ideas of spiritual science admonish us again and again to really study the character of our time. We try to do many things to study the character of our time. Yesterday I referred to the great teacher and friend of Dante, to Brunetto Latini. In Brunetto Latini we have at the same time a man who, in the age of Dante, pointed in a penetrating way to what was to come for humanity. The initiation writing, one can already call it such, which comes from Brunetto Latini, contains approximately the following: He returns from his mission to Alfonso of Castile. On his way back, he learns that events have taken place in Florence, in his city, which, in his opinion, must end the old splendor and glory of Florence. Brunetto Latini senses, in expressing this, the approach of the fifth post-Atlantic period. After all, this initiation writing was still written at a time when there was still an awareness of the connection between man and the spiritual world in the furthest reaches, at a time when numerous human secrets about the spiritual world were still known, and therefore at a time when there was not yet the tendency towards such insubstantial abstractions as there is today. For in an age in which intellectual life is vibrant, in an age in which the life of feeling is truly present, there is no inclination towards insubstantial abstractions. Insubstantial abstractions are always related to the tendency towards materialism. Brunetto Latini has this age, in which we now live, before him. He is approaching Florence. He knows that what Florence has become under the impulse of direct human life, of direct intellectual impulses, is to be buried under the advent of institutions that arise from abstraction. He is approaching Florence. He describes how the pain causes him to lose his way in a forest, a desolate forest. When he comes to his senses, he notices a path and a giant female figure in the middle of a magnificent world creation - which is his imagination. We hear that under this giant female figure he addresses “true nature”, not the nature that today's science describes, but “true nature”. This “true nature” teaches him about what lives in man, about the secrets of the human soul, about the secrets of the four human temperaments, about the secrets of the human senses, about the secrets of the elements, about the secrets of the planets. He is then led out beyond the planetary realm into the ocean of world existence as far as the Pillars of Hercules, mind you, at a time when Copernicanism had not yet been discovered, at a time when America had not yet been rediscovered. Then he is made aware that he has to leave all this, that is, the whole visible world. Only then would he recognize the secrets of good and evil; only then would he recognize the God of love and so on. One is tempted to say that this approach by Brunetto Latini is a proper New Year's reflection on the fourth post-Atlantic period in the cosmic New Year season of the approach of the fifth post-Atlantic period. In the circles from which Brunetto Latini and others had grown, it was known that man has a connection with the spiritual world, and that the mere literal grasping of the spiritual world must lead to disaster. A preliminary climax has also been reached in science in the 19th century by mere literalness. Everything was prepared, but in the 19th century the matter reached its peak. And from science, the corresponding tendencies have spread to the rest of human experience. But now the time has come to find the courage to break with the old idolatry of words, with the old idolatry of even some word contexts and word combinations regarded as natural laws. The mere fact that a word exists does not accomplish very much in itself. At the beginning of the new era, the Mystery of Golgotha took place. Since that time, Christianity has existed. There were, however, centuries in which this Christianity was sought to be grasped with the whole human soul. But then came other times. Then came the times when human comprehension became weak and was no longer sufficient to understand the Mystery of Golgotha. And now, in the broadest circumference of the Mystery of Golgotha, almost nothing remains but the name of Christ Jesus. But I have shown in these considerations that what is associated with the name of Christ Jesus is, in the light of spiritual science, not much more than an angelic being. And the fact that this is not noticed is due only to the idolatry of words. This idolatry of words has a suggestive power. Anyone who has felt this suggestive power - without becoming an idolater - could experience it in the most diverse fields. Sometimes it is good to make a personal connection without becoming maudlin. In this case, allow me to set an example. I often think, when I try to characterize the tenor of the present time, of the lectures I once heard on constitutional law. Let me pick out just a very small part of these lectures on constitutional law: Now, gentlemen, what is judicial sovereignty? Judicial sovereignty is the sovereign right that lies within the omnipotence of the state. And now followed that which all falls within this state omnipotence. Gentlemen! What is financial sovereignty? Financial sovereignty is the sovereign right that lies within the omnipotence of the state. What is political sovereignty? Political sovereignty is the right inherent in state omnipotence... - and now followed again that which lies in state omnipotence. What is cultural sovereignty? Cultural sovereignty is the right inherent in state omnipotence. Now imagine the human soul, made out of straw, presented with these contrived concepts and developing social efficacy – what do you have then? What you see around you now and what you close your eyes to, so that you can consider it something quite sensible, that has only slipped somewhat in recent years, but that is good and must be continued! But truth is not recognized by words, truth is recognized by realities. One can speak beautifully, and of course also truly, about the excellence of a democratic state administration, about the exemplary nature of a democratic state administration. But the insight into whether this is right or wrong is not shown by reality; rather, reality is shown by the fact that such a democratic state administration brings a Mr. Wilson to the head of almost the whole world. That is where reality is to be found. And talking about reality is not very popular. It was not without reason that I pointed out the hollowness of Mr. Wilson's personality in my Helsingfors cycle before this war. You can read about it in the cycle that was held on the Bhagavad Gita and its occult foundations. One of our friends found himself saying at the end of the lecture that it was terrible that something like that comes to influence and power. Nothing happens in the world with principles. In the world, things happen through realities. In social life, the realities are the personalities. This is something to which spiritual science, in particular, must strongly and vigorously point out, because spiritual science honestly and sincerely wants to help the development of humanity, because it does not want to join in the parade of phrases that dominates the world today. And by this phraseology I do not mean merely that people utter phrases, but I mean something much worse: that people try to realize phrases, that they make phrases into institutions, that they do not decide to call things by their real names. A great deal would be done in the world if people wanted to call things by their right name. It would lead to many things, as I have often pointed out: that one should not give so much importance to outward appearances, as if the most essential thing about the current catastrophic events were that the so-called Entente is at war with the so-called Central Powers, and that peace must be achieved again! I have often pointed out that this is not the most essential thing, this is not the most important thing, because appearances are often deceptive. What is being fought over in the world is something essentially different. The battle of the reality-seeking phrase against the living reality is fundamentally something much more universal. Only by reflecting on oneself can one see how attached one is to the comfort of the phrase. There are already some opportunities for this here in this place. For us, who are connected by love to this building and to what is connected with it, for us, to a certain extent, what lies in time is symbolically expressed by the fact that this building has been started like one of the centers from which what humanity must transfer into a future according to the demands of the present, and how this building was interrupted, stands interrupted by that which now stands in the background of all human contemplation and all human works: the great collapse of the institutions of humanity, which, out of a love of phrase, have been growing for centuries. Not without reason, during the weeks in which we were once again able to be together, until now, at the turn of the year, I have maintained a serious tone in our deliberations here at the building site itself and have repeatedly emphasized the necessity, at least in what is left to our discretion, to seek the necessary seriousness of life; in what is left to our discretion in our understanding, in the unprejudiced pursuit of events. That this structure, too, has been delayed for an indefinite period of time is perhaps a small event within the catastrophic events of the present, but it is symptomatic, it is symbolic in a certain respect; symbolic the reason that one could draw a line between what is loved for humanity from the intention of this building and what is loved from the word “idolatry” and what is associated with it. At the present time, at this turn of the year, the great catastrophic event still looms in the background of everything that can be observed and done. And at this turn of the year we must think back to the turn of the year before. One month after that turn of the year we parted. I still think of the contrast that my words, often harshly characterizing the situation, have found even in our circle. Anyone who knows from what impulse the catastrophic events arose could not have imagined a year before that 1917 would not be even worse than the previous one. That was what people said at the time. Although on the one hand one had to say and could say how infinitely sad it was that a well-intentioned proposal - as I said at the time in my Christmas and New Year's reflection - was shouted down by what calls itself “four-fifths of humanity”, and how, under this shouting down, there was no right mood to look optimistically into this year 1917, so it is, when looking back again, only an unbiased look when one says to oneself: Is there anything that there is a prospect of this or that being achieved out of his or her selfish group interest? Is there anything that can be achieved by such interests and for which the prospect has increased after another year of terrible bloodshed? No! The world situation at the end of 1916 was exactly the same as it is today; for this world situation will only change when reason comes into thinking. Anyone who believes that anything essential has changed in the past year is mistaken, mistaking the external for the internal. This is not to say that this or that, which a comfortable view of life may initially label as something favorable – until after a few months people see that it is not favorable – cannot be done. But the things lie much deeper; they lie so deep that, according to the experiences that have been made, it is not even possible, especially with regard to the events of the present, to speak the decisive word here either. Humanity has a task at the present time. And after a year like this, one can say a few words about this task. That these catastrophic events have occurred was certainly not a task for humanity. That these catastrophic events are continuing is certainly not a task for humanity either. This is a task for humanity: to get out of these catastrophic events; to really get out of these catastrophic events and to recognize that it is a task to get out of them. It does not matter if one wants to continue in the old way in this or that respect. It can already be said: if some socialists believe that what they believed seventeen years ago for the good of humanity can now be used as a universal remedy to get out of the great human calamity, then that is a mistake, a mistake that stems from being out of touch with reality. These catastrophic events are composed of two things that we are not able to truly understand today in everything that exists outside of anthroposophically oriented spiritual science. On the one hand, these catastrophic events have only been made possible by the way in which certain goals have been used to exploit the great antagonism that has developed in humanity over the last three to four centuries between everything that is industrial, commercial and so on imperialism, and socialism, which is opposed to it. That is one thing. The other is that which has emerged through the psychology of nations, which plays a particularly important role in Eastern and Central Europe. Both issues contain problems of the most comprehensive kind for humanity. We must start where we are least disturbed by the outside world today, where external codification still has the least say, in science and art. Or we could establish a bank based on our principles. Many things could be mentioned that would show, alongside this wood and concrete construction, a kind of ideal building, but one that is taken from life and from friendship with reality. This wood and concrete construction stands unfinished today; that is a symptom, that is a symbol. These things, neither the real nor the ideal building or buildings, can be completed if there is only understanding in the world for the opposite, for that which must extinguish all individualism, all personality impulses, from humanity. If man must reconquer that which is lost in abstract institutions, in the tyranny of abstract institutions, then much time will be necessary. Some things must be spoken of only in a roundabout way, if I may put it that way; everyone may try to draw from the things what he can draw. But above all, we should draw the conclusion that, if certain things have been repeated again and again this time, it is not without reason: the admonition to turn away from all that is empty words, even if these empty words have gained an external semblance of reality, and to turn to the truth, to true reality. For it is this true reality that we seek through our anthroposophically oriented spiritual science. Through it, we want to penetrate into the understanding of what is, of that which must work. And we want to free ourselves from that false idealism - false idealism because it is an abstract idealism - that believes it can work in the world without study, without knowledge and without love for reality. In the times when one year follows the other, it is so close to the human soul to have more serious thoughts about how one's own soul relates to life and the essence of being. Today, one cannot think of more serious thoughts than those that come from the contrast between a world that is alien to reality and so proud of its friendship with reality, and between what should be striven for through a real friendship with reality, as it strives for anthroposophically oriented spiritual science. Let us assume that, in addition to what we can so easily develop, we have a certain inclination to take in spiritual truths because they present our relationship to eternity and the like to our soul in a pleasant way. Let us assume that what is a kind of inclination to deal with spiritual-scientific truths, we also carry a real, inner, strong, devoted impulse: to look at life, at all life in the light of this spiritual science. Let us try to carry over from one year, which was truly not easy to live through, into the next, which will also not be easy to live through, let us try to carry over the will to look at life in the sense of spiritual science, the will to become free from the mere phrase that dominates the world today. For something has already been done if there is at least a small group of people in the world who can make a New Year's reflection to not join in the idolatry of the phrase in their thoughts. This is something. Let us get used to new words, new concepts, new ideas for many things that need them! This is said – since we could have another New Year's Eve reflection within this unfinished building, with whose forms, with whose reality we associate so many thoughts for the future – so that we can grasp the idea of living over into this New Year in such a way that, like a burning impulse, like a fire within us, so that this spiritual science is not just a theory that we cultivate in the privacy of our own rooms, but becomes something that passes into our head, into our heart, into our hands, into everything that is to become and happen in our lives. In view of the words that may have sounded harsh but that were nevertheless spoken only out of love for humanity, I would like to give you the impulse, I would like to point you to the impulse, to think through this turning point of two years in such a way that the thought can be the starting point for a truly unbiased examination of what is real and what is unreal. For more than humanity thinks today depends on this. And one would truly like to have something other than weak words for a small circle at a time when so much more would be needed in New Year's reflections than what is so often spoken as New Year's reflections today. But let us be aware that spiritual science has a certain right to demand such a desire for otherness from us! |
| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Fifteenth Lecture
14 Jan 1918, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Fifteenth Lecture
14 Jan 1918, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Today I would like to present something that is purely historical, as it were. I believe that the ninth century and the fifteenth century, which I will speak about in a future lecture, can indeed be considered in such a way that important things can be seen from the consideration of the cultural content of precisely these two centuries, from which much can be learned for the present, for the assessment of current conditions. We are dealing in the 9th century with a significant historical period of European life, in that in this 9th century, so to speak, the Occident is already approaching us in the sense that it has become Christianized. The earlier centuries are actually centuries in which Christianity is only just being integrated into Western life. And in the 9th century, that is, in the period that followed the century of, for example, Charlemagne, we see that Europe has a Christian character, that Christian character that has then been working through the centuries in the lives of the people of Europe. But the fact that Europe has become so Christian, as it actually appears to us in the 9th century, has many prerequisites. And one can only judge how Christianity has become established if one considers these manifold prerequisites. We know, of course, that at the time of the emergence of Christianity, the Roman Empire was just beginning its imperial period, that it was beginning to encompass, in a unified administrative form, basically the whole world known at that time, or to assert this encompassing, to really experience it. We know that this is the time when Hellenism as an external political form of existence is already declining, that Hellenism has long since penetrated into Romanism as a ferment of education and culture, and we then have to direct our attention primarily to the fact that from the beginnings of Christianity, which we do know, this Christianity gradually settled into the entire form of the Roman Empire, into all the administrative and constitutional forms of the Roman Empire. And we see then how Christianity, developing under the most diverse conditions in Europe, in the first, second, and third centuries, becomes established in what is there as the Roman way of life. But then we see how this assimilation of Christianity is initially connected with a complete anarchization of European life. We know how the Roman Empire, from the moment in world history when it was at its most widespread, clearly showed the seeds of its decline. The question will always occupy the mind of anyone who contemplates these things: how did this Roman Empire, which rose to such glory, actually perish in the first three or four centuries of the Christian era? One can believe that the onslaught of the northern, Germanic peoples alone was responsible for the fall of the Roman Empire. One can then find some of this guilt in the spread of Christianity itself. One will misinterpret the deeper basis for the downfall of the Western Roman Empire if one seeks the only motives for this downfall in these factors. For the Western Roman Empire shows, if one looks at it more thoroughly, that such structures do have a life of their own, that they have, so to speak, a birth, a youth, a certain age of maturity, and that they then gradually die, and that the causes of this dying-off must be sought within the state itself, just as, in the case of an individual organism, the causes of its aging and physical dying-off must be sought within the organism itself and not in external conditions. However, it is possible to discern from external appearances how this gradual aging and eventual dying-off of such a thing as the Roman Empire took place. What must be taken into account when considering European development into the 9th century is that two phenomena clearly emerge before the eye that looks at history. One is the gradual decline of the Roman Empire and all that was connected with it; the other, however, is that at the same time the oriental way of life flourishes. We see that in the East, far beyond the areas bordering the Roman Empire to the East, a cultural flowering develops, albeit an external, material cultural flowering. In other words, these countries, to which the Roman Empire, one cannot even say that it bordered them in its cultural flowering, but which it nominally included, these countries develop a brilliant material cultural flowering. Without this material cultural flowering, which formed on the periphery of the Roman Empire, it would have been impossible for Islam to flourish and for the Arabs to assert themselves in the historical development later on, when they were able to lay claim to a large part of the world in such a brilliant way until the 8th or 9th century. We see that up to the 8th or 9th century the Arab domination spread under the spiritual banner of Mohammed as far as Spain, but that in other directions, too, European life came into clear contact with all the cultural blossoms that arose all around. What the Arabs achieved in Spain and Sicily and in the East, before they became the enemies of Europe, must have been rooted in a rich and splendid material civilization. Only on such a foundation was it possible for the Arabs to accomplish such brilliant conquests. Where does this phenomenon come from, which is more closely connected than one might think with what happened in Europe up to the ninth century? How did this phenomenon come about, that on the one hand the Roman Empire was declining, and on the other hand the oriental character was taking a brilliant upswing and had an extraordinary effect on the Occident? For it did not only work through its conquest, it worked in an extraordinary way spiritually. One cannot believe how much of what the Arabs, partly through the Greek education that they themselves had only recently adopted and interwoven with their own nature, has influenced the European Occident. This European Occident, through the way it has developed until the 9th century, does not have just one current in itself. All of us, insofar as we have participated in the formation of the Occident, have two distinct currents within us. It is a great mistake to believe that only the Christian current has spread in the Occident; spiritually, what has come from the Arabs has spread throughout the Occident. The way of thinking, the way of imagining, has been deeply influenced by the Arabs in European conditions. In what today's man - I do not mean the man who is intellectually ill, but the man of general education - thinks about fate, about the natural order, about life in general, the most diverse Arab thoughts are found in it, right down to the peasant's head. And if you take much of what dominates minds today, you will find that Arab thoughts are in them. What, among many other things, can be said to be characteristic of this Arab way of thinking that spread to Europe? It can be said to be particularly characteristic that this Arab way of thinking is, first of all, subtle and abstract, does not like the concrete, and therefore prefers to view all world and natural conditions in abstractions. Alongside this is a development of fantasy that cannot be called merely flourishing, but voluptuous. Just think, what develops alongside the sober, abstract way of thinking, which even shows itself in the artistic in Arabdom, what develops in fantasy about a kind of paradise, about a kind of afterlife with all the pleasures transferred from the sensual into this afterlife. These two parallel things: sober, materialistic observation of natural and world conditions, on the other hand, a lush fantasy life, which of course then becomes dulled and becomes intelligent, is something that has been passed down to the present day. For if today you want to present something of the spiritual world, yes, if it is in the form of fantasy, then people still respond to it. Then they do not need to believe in it, but can accept it as a figment of the imagination. They put up with that, because alongside it they want to have what they call genuine, real. But that must be sober, that must be dry, that must be abstract. These two things, which live as a second current in the soul-life of Europe, came essentially with the Arab element. Although the Arab influence has been pushed back in many respects, this way of thinking has penetrated deeply into European life, especially into southern, western and central European life, less so into eastern European life; but even there, at least into what is called “education”, it has partially penetrated. So that Christianity, which is quite different in relation to these things, had to struggle with these opposing ideas. If we want to understand Europe's development up to the 9th century, we must not forget that such Arab ideas have penetrated into Europe. It is hard to believe how much in Europe is actually close to Turkishness, to Muslim culture in the thoughts that the European has about life, destiny and so on. But how did it come about that something could arise, or rather take root, on the periphery of the Roman Empire that caused Europe so much trouble? This is connected with the ever-increasing expansion of the Roman Empire. This Roman Empire, as it spread more and more, was obliged to obtain many, many products from the Orient to meet the needs that arose in this vast empire, and all of them had to be paid for. And we see with the development of the Roman Empire, precisely from the beginning of our calendar year, that a significant phenomenon in the development of the Roman Empire is that the Romans have to pay so much for what they obtain from the Orient. In other words, we see that during this period there is an enormous outflow of gold from the Roman Empire to the periphery. The gold flows out. And curiously enough, no new sources of gold open up. And the consequence of this is that the wealth conditions of the Roman Empire change completely, that with the development of Christianity the Roman Empire becomes poor in money, that is, poor in gold and silver. This is a phenomenon of fundamental significance. So that Christianity spread throughout the Roman Empire in a region that increasingly tended towards primitive conditions in terms of its economy. For wherever there is a lack of money, wherever there is a lack of gold – on the physical plane that is the case – there the necessity very soon arises to return to primitive forms of natural economy, to primitive forms of a kind of bartering by merely exchanging goods. But that is not even the significant thing. The significant thing is that when such a scarcity of gold occurs, it becomes impossible to create extensive and meaningful human connections. As a result, people are dependent on the exploitation of much closer relationships; they are enclosed within much narrower limits in their needs in the exchange and in their coexistence. And so it came about that the Roman economy gradually grew more and more into a way that it was not accustomed to as an empire. The institutions in the Roman Empire were all affected, all kinds of administrative institutions, administration and so on, everything that is referred to as the connection between the regions and their authorities and so on, was set up so that one had money. And now the money was getting less and less. You can clearly observe it in a particular area. Of course, as the empire grew larger and larger, the Romans needed more and more legions, especially in the outer parts of the empire; they needed soldiers. They had to be paid. You could not always transport infinite masses of things produced in Italy itself to the periphery. The soldiers wanted to be paid in gold, so that they could then trade for it from the others. But gradually the gold was no longer there. The soldiers could no longer be paid. This was the case in many areas. The Roman Empire thus died, so to speak, of its own greatness. And in its periphery, a very special wealth developed, which then of course also resulted in a certain basis for a spiritual life. Now something else is added to this: the Romans had gradually come to be unable to live according to their old habits. Of course, one must not look at the individual people, but at the whole institutions. In the north, however, fresh peoples were there; they were organized according to their customs and habits precisely for natural economy. Among them, the tendency and urge towards natural economy had gradually developed. They were organized for such conditions, also through their deeply rooted, elementary inclinations and sympathies. These Germanic peoples – that is what they are called in their entirety, as they spread in Western and Central Europe, in the north of the Roman Empire – had gradually become, over the centuries, both at the time of complete anarchy in the 3rd and 4th centuries and up to the time of complete consolidation in the 9th century, they had gradually come to prefer a natural economy to the Roman one, because it corresponded to their customs and habits, as well as to their sympathies and inclinations. Above all, however, the natural economy corresponded in a certain sense to the institutions, the way people in these northern regions lived together. We must now take a look at these northern regions. In general, we say: in the first Christian centuries, Germanic peoples were there. We call what spread in the north Germanic peoples only because, when something is far away, it appears uniform. When a swarm of mosquitoes is very far away, it looks like a uniform gray mass. If you were to look at each individual mosquito, it would look different. And so what spread in the north while the Roman Empire was falling apart due to the conditions described above, should not be generally referred to as “Germanic peoples”, as it appears now in the temporal distance. Above all, we must consider how it actually came about that what came from the north collided with the Roman Empire in the 3rd, 4th and 5th centuries. That must be borne in mind. Yes, even when Tacitus, in the first Christian century, saw these northern regions, it was the case that the process that had taken place there, when there was still little contact with the Roman Empire, had emerged from the fact that in all these areas there was originally a kind of native population that, if you go back in the development of Europe, leads straight back to Celtic culture, at least for Western Europe and Central Europe. Everything that was cultivated in Europe in ancient times, of course before the emergence of Christianity, belongs to a certain Celtic indigenous population. This Celtic indigenous population can basically be found as the basis of the entire European population. The descendants of Celtic blood flow everywhere in Europe, not only in Western Europe, but above all in Central Europe. There are very many people in Bavaria, Austria, Thuringia, in whom, if one may be imprecise in describing these things, the succession of Celtic blood flows, quite apart from Western Europe. It is even highly probable that less Celtic blood flows in Western Europe than in Central Europe. Into these primeval Celtic conditions something has been pushed which is actually rather unclear in its origin to external history. All kinds of theories have been advanced about this, but the truth is this: through what is usually called the migration of peoples, which also took place somewhat differently than it is usually described in the history books, a people element – one cannot even say a people element, but rather a larger number of people from the most diverse regions, also from Asia via Northern Europe – has pushed its way into the Celtic original population. And through the mingling of this new element with the old Celtic element, through the manifold minglingsome were stronger, some weaker, some in which the Celtic element remained in the foreground, some in which it receded into the background, the various shades of the European population came into being. And from these shades developed, on the one hand, those conditions that then became the folk conditions of Western and Central Europe, but also those conditions that led to the forms of life, to the forms of constitution and administration. There was a time when the Celtic element of the indigenous population lived relatively comfortably, perhaps even very frugally in some areas, but comfortably from year to year, not caring much about any innovations and the like, but lived along not much differently than you can see today, though less and less, in some abandoned area, where people live just from year to year without taking on any innovations. So this Celtic element lived in a certain comfortable calm, which was actually not at all appropriate for the national character of the Celts, but had gradually occurred. Then came these other masses of people, who actually only created Germanic culture by mixing with the Celts. The next thing that emerged was that, as I have already indicated, in one area the old element retained the upper hand, while the new element receded – in some areas it was the other way around – and as a result, different shades of blood emerged. But on the other hand, the result was that the habitual residents were flooded by the intruders. The intruders became the masters. They were the ones who disturbed the peace and thus became the masters. And from this relationship between the conquering immigrant masters and the remaining original inhabitants, the relationship between the free, the semi-free and the unfree emerged. The original inhabitants were gradually pushed down into slavery. Those who had immigrated gradually formed the master class, and that determined the living conditions. Thus Europe was settled by a population that arose in the way I have characterized it, but within which the distinct configuration of a master caste and a kind of serf or slave caste emerged. And on this basis, all the other conditions then developed. Through the nuances of which I have spoken, the various Germanic branches formed, especially towards the west, but also as far as the areas of present-day northern Bavaria, even into the areas of present-day Hesse and so on. What we call the Franks were, in some respects, the most active population, in some respects, in terms of external intellect, the most understanding, active, and in some respects, the most domineering group of the various groups that emerged as nations. This was the population group that spread more towards the west, the element of the Franks. The word is still present today in the word combination “frank und frei”; everyone knows what “frank und frei” means in its composition, and “Franken” is related to the word “frank”, which has a close relationship with the word: to want to feel free, independent, outwardly free, independent. In the middle remained the population that could be described – if one wants a summarizing name – as the Saxon population, which spread into Thuringia, into the northern areas opposite Thuringia, down the Elbe, to the coast. This was the population that was more stubborn in terms of its older national character, that particularly held on to its original identity, that, so to speak, embodied the human-personal-conservative feeling. And so there were other groups. It would be too much to list all these groups. What is important is that the British population developed from the Saxon group, through a variety of mixtures but with a strong predominance of the Saxon group, and that the British population, if one may say so, belongs to the Saxon tribe in its essential origin, leading back to these centuries. Now we have to consider what the life of this population, which has developed in this way, actually was. This population, which lived there, was a youthful, childlike population in relation to the southern population, to the Roman and Greek population. What had become old in Celtic culture had not become very old at all, but had become old early on. A rejuvenation process did take place, however, in that certain ethnic groups pushed in from northern Europe and also indirectly from Asia. Above all, the population had sympathies for the southern element, for the natural economy, for the economy of barter, which placed little value on the money economy, which only comes into play when an empire is at an advanced stage. Those who, despite the migration of peoples – which is, after all, somewhat different than presented in the history books – developed within these newly emerging European conditions, were actually basically only connected to their neighbors, to their closest neighbors. But there was also a very specific peculiarity in the intellectual relationship. All these nations still had something that the Greek and Roman populations had long since lost. Even well into the 6th, 7th, and 8th centuries, they all had, to a much greater extent than the most uneducated Greek and Roman populations, an original atavistic clairvoyance. These people all lived in connection with certain spiritual beings. For them, there was not only an external material nature, there were not only seasons and wind and weather, but for them there was, because they saw it in those states that were more than a dream, the god Wotan, whom the people knew. Many at least knew: they themselves saw the god Wotan, who moved with the wind, on wings of wind. The people knew that. They also knew, for example, the god Saxnot, who helped them in their battles when they had to fight. When they had fought the battles, or before they fought them, their god Saxnot appeared to them, and much more. They were also familiar with the rapidly changing weather conditions not only in a material way, but they were spiritually familiar with the elements, with the god Thor, with his hammer, and the like. These were real experiences for these people, they still knew that. And besides, these people had a belief in guidance from the spiritual world because they knew from their own experience that there is a spiritual world. They believed that everything that happens in the days, in the seasons, is guided by spiritual forces and beings. If any tribe was victorious, it knew that the tribal god had stood by and guided it. You could say of the tribal god: He led. You cannot say of a general human god that he is the god of battle. You can say that of a tribal god just fine. The people were right when they said of their tribal deities that they were led by them. Of course, any tribe can say that it has been protected and cared for by a tribal god, but the same cannot be said of a god to whom the whole of humanity is attributed in the same sense. The priesthoods, which developed – there were also mysteries in these areas, we have often spoken about such things – in order to have, so to speak, the leadership in this whole context of people with the divine spiritual powers. But this leadership was a very specific one because the people knew that there are spiritual powers, that there are spiritual forces and entities. So outwardly these people lived in a certain primitive way with a natural economy; inwardly, one can say, they lived a kind of spiritual life. There were no educated people in the sense that there were in Greece and Rome. The priests were leaders; they organized the life that the others also knew. But they were not educated in the sense that the Greek philosophers or the Roman philosophers, or the Roman poets or those who could read and write in Greece and Rome and were educated in this sense; because the people did not know all this. Of course there was no reading and writing. So you are dealing with a population that lived in primitive natural conditions and that led a spiritual life in a certain way. There was a certain inner strength due to the revitalization that had come into this Celtic culture; it was suitable for the primitive conditions. The southern part was not suitable for the primitive conditions. In certain points, what was a new, young element there clashed with what was present in the south, was present in such a way that in an empire perishing from lack of money, Christianity took root, was adopted in the way you know things. And it was particularly at such points, where the two areas, the old dying and the young emerging, collided, that the Romans still founded their cities, their border cities on the periphery of their empire. Cologne, Trier, Mainz, Strasbourg, Basel, Constance, Salzburg, Augsburg, these were urban structures that had existed since Roman times. Now it should be clear to you: the Romans thought of these urban structures of Cologne, Trier, Mainz, Strasbourg, Constance, Basel, Salzburg and so on as a kind of protective fort against the onslaughing people. But when Romanism - not through anything else, but through itself - gradually disintegrated, the cities were in a very special situation. In the countryside it was good for primitive conditions. In the cities it was nothing special under primitive conditions. And the consequence of this was that the cities would have been deserted if they had not been used in some other way. But the emerging church, which had taken hold of Christianity, was a good observer that knew: one must hold to the cities. And so the dioceses were transferred to the cities, which would otherwise have been deserted. But as a result, the cities gradually became a point of concentration for the surrounding people, who were unfree, over the centuries towards the 9th century, because the dioceses were transferred there, because education came into them – for the bishop initially came from the southern regions. The free had no particular reason to move into the cities, which would gradually have become deserted; so they followed the bishops and clergy into the cities only to a limited extent. But those who were unfree followed the calls from the church to move into the cities. And if you now look at the basic conditions, you will easily understand: the unfree were, after all, the stragglers, the descendants of the original population. There was a great deal of Celtic blood in them. What flocked together in the cities was basically an element that wanted to free itself from those who had become the masters there. This gave the cities, little by little, the character of medieval free enterprise. This was essentially due to the fact that it was often the seething of the Celtic blood in the cities that the cities flourished in the Middle Ages, in the early Middle Ages up to the 9th or 10th century. Then we must realize that all these conditions were real historical necessities. It is hard to believe how little man's character could be guided by external abstract means, especially in earlier times. But it could be guided if one first studied the conditions and then linked them to the concrete. Thus we see – and we could cite many examples, but I can only give a sketch – how a new element arises and how the old element in the south gradually dies out due to its own nature. This dying out can be seen from the fact that, on the one hand, in the south, ancient science and the ancient element of education gradually reach their particular height but then come to a dead end, freeze; they can no longer advance. In the sixth century, Emperor Justinian abolished the office of consul in Rome, helped to condemn the teachings of Origen and closed the last remnants of the Athenian schools of philosophy. The old Athenian schools of philosophy were transferred to Persia. There, Gondishapur was founded as an academy. The Athenian philosophers follow the paths that gold has taken, settling where a spiritual life can develop on the basis of a certain wealth. In Europe, it is necessary to take into account the primitive conditions that have arisen. And two factors initially knew how to deal with these primitive conditions. It can be said that the other factors knew little how to deal with them. But two factors knew well how to reckon with these primitive conditions, namely, the papacy, which was a good observer, not only of the bad, but also of the good, because in those days the papacy had very many good qualities, and those - they were basically nothing more than large landowners - who gradually asserted themselves within the Frankish tribe as Merovingians, Carolingians and so on. What did the papacy need? The papacy could not easily spread Christianity as a doctrine. It did make a thorough, even very thorough attempt to spread Christianity as a doctrine; but in such matters one must always take into account the concrete, real conditions. Pope Gregory the Great sent fifty emissaries to England and Ireland, and from there the emissaries went to Central Europe, Gallus, who is connected with St. Gallen, and many others. But here you could count on people who came from a peoplehood and had a great gift of persuasion. This was a current through which Christianity was spread in a certain spiritual way, spread in such a way that it also went among the rural population, who lived under the characterized conditions, built churches. And around these churches, Christianity gradually took hold in such a way that the people who, as Franks, Saxons, Alemanni and so on, populated these northern regions did not significantly change their concept of God. They still had this concept of God from their atavistic clairvoyance. They did not particularly change it; but, take any area, some messenger came, built a small church - in Alsace, for example, this has happened over and over again in many areas - near a place where there was an image, a statue of the god Saxnot or something like that. He builds a small church, and he knows how to take the people. After he has built his church with his comrades – they did everything themselves, they were hardworking people, not just book writers – he goes to the people and says: Now you have your god, it is the rain god; praying to him will achieve nothing! Such a messenger knows how to make it plausible to them that the God for whom he built the church is better. Now, this required persuasion, because, of course, the God whom he called the Christ had not shown any direct influence on the rain either. But this was mixed up with the fact that the ideas about the gods that had emerged from the military campaigns were gradually brought into contact with Christianity. When some tribe was defeated by another that had already converted to Christianity, it turned out that the people said, “Our god did not help us; their god helped them.” I am only trying to express that the Christian God was equated with the individual tribal deities. But people did not arrive at any other concept of God than that which they had from their atavistic clairvoyance. From this arose the necessity, when the Roman Church naturalized Christianity by using this, that the old tribal deities had to be gradually eradicated, root and branch. For they wanted, as it were, to replace the name of God with the other deities. As I said, attempts were made to spread Christianity as a doctrine, as a spiritual way of life. But it may be said that, owing to the most diverse circumstances, another element was more successful at first, and that was the warlike element of the Franks, who were the most enterprising tribe, the most active, who, through their intellect, through their understanding, really knew: they could make something out of the adoption of what was bound to perish in the Roman Empire, through this adoption of institutions and so on. Through these and similar circumstances a connection arose between the Frankish folk element and the shadow of the Roman Empire, with the institutions and the views of the Roman Empire. This began in the 8th century, continued into the 9th century, and the result was that Christianity was associated with the conquering element. The Saxon tribe, which was conservative and stubborn, was indeed overcome in a conquering manner; and from the West spread that which arose initially from a combination of the old customs and habits with regard to the judiciary and human coexistence with Christianity. This combining of the original customs with the southern element, which came from Christianity but in which Romanism lived, is evident in everything. Today we no longer realize how much it is evident in everything. For example, people believe that a count is a particularly Germanic institution, while the word 'count' is nothing more than something related to graph, stylus, and writing. Writing and administration were taken from the south. The one who administered was the count. And in the event of war, he also led the district, the area. The word “count” has the same root as graphology and stylus and is related to writing. But everything that concerns writing, pen-pushing, everything that concerns education, that came from the southern areas, and which has its real life in dying. So that these two elements interacted well into the 9th century. The most powerful element had just become the Frankish element through Charlemagne, whose power was based primarily on the fact that it had absorbed ecclesiastical Christianity and was now renewing the shadow of the Roman Empire. Charlemagne was indeed crowned in Rome; the old Caesaranity was to rise again. These things, however, had only an artificial supporting power in themselves, not a natural one. We know then: after Charlemagne, the wide areas that Charlemagne supposedly held together initially still followed, and which were also still ruled like a kind of empire by Louis the Dumb - that is to say, the Pious. And when the power of the original conditions became more pronounced, when the Germanic-Frankish breakthrough came – because this Frankish element emerged, as I said, from a large part of what is now called Germany – when that breakthrough came, then the Treaty of Verdun, 843, had to divide. Why did it actually have to be divided? It had to be divided because it was unnatural to hold together. The real cement was Romance, but it was actually effective through the chancellery and through what developed as the first primitive schools and the like, and through what the clergy did, which asserted itself as such. The cement was Romance, but life was not Romance, life was Germanic. The people were organized in small groups. At the head of such small groups stood a duke – not by law. The laws only came into being when what was the custom of the Ripuarian Franks was written down in the Lex Ripuaria or the Ripuarium, in the Salic Law, Lex Salica, and so on. In small communities, the duke was originally the one who brought in the strangers, who led the army that made the settled population into serfs. He gradually disappeared. The count was appointed where there was a duke. You can say that the dukes survived as far as Bavaria and Thuringia. But the count is placed there; he is placed there, judges, administers, where the duke used to be, whom the people called that because he was there before they came to the area. The count is installed and gradually becomes a landowner, gathering the unfree around him and making them his serfs. The feudal system comes into being, the development of which would be very interesting to observe, but we do not have the time. And we see that it is actually through the interaction of such details that those great landowners come into being. Because that is what they are, namely those great landowners that we see in the Merovingians and Carolingians. They are great landowners; and they were now sitting inside, far removed from following Roman law, because according to Roman law one could not have divided up the land as in the Treaty of Verdun! So you divide when you are the owner and divide among your sons. That was an old custom where the personality was involved. That was right according to ancient custom. Roman law could not have allowed that in reality. These were such disintegrating elements. They were everywhere, these disintegrating elements, so that one can only properly understand this 9th century, which is crucial, if one knows that all of Western and Central Europe was flooded by the Romanic element, the popular nature. This was even more pronounced later, as we will discuss in the 14th and 15th centuries, when it will become even more apparent. Of course, educated people are placed in the form of clergy and so on, but it is the Romanic element that overflows these areas. But the Germanic element lives in the people - throughout Europe from the 9th century onwards, yes, even in England, in the British Empire. And this Germanic element is first expressed particularly in the element of the Franks. It was only through this division of the heritage, which actually took place according to purely private, arbitrary circumstances, that this tripartite structure came into being, so that one received this middle long strip along the Rhine and Italy, the other received what was to the west of it, and the third received what was to the east of it. And this then became the basis for the later division of the German and French characters, as a result of the Treaty of Verdun. And what Lothar got in the intermediate line created the happy basis for Central and Western Europe to fight with each other forever! But these things are connected in this way. Now we must bear in mind that there are various and variously important factors at work: the Germanic element, particularly in this period, finding expression in the Frankish element; but the Romance element, which, as a shadow of ancient times, flits across the scene like a ghost, an old inheritance. And into this development, according to the corresponding conditions given by this nature – whereby the Germanic nature, always arising out of the strength of the people, thus out of reality, wanted to shatter the Romanic semblance – into this development, Christianity had to be spread from Rome. One had to take into account all these conditions, one had to reckon with the urban elements, with the rural elements, and one had to try to introduce Christianity in such a way that people could understand it. In spite of Constantine and his successors, it could not be introduced in Rome, because education, although it had reached a high level, had reached a dead end. It had to be introduced into popular elements that had original, youthful vigor in them. Therefore, one had to push back to the East what had just frozen into dogmas, what wanted to remain at a certain point of view. And in the West, one had to reckon with a popular element that wanted to develop out of the ecclesiastical, out of all the elements that I have indicated. The papacy in particular could already count on these elements. There was already active calculation on the part of the papacy when Charlemagne was crowned; for one simply reckoned with this large landowner, who also let himself be reckoned with. And then it was always the policy of the papacy, first and foremost, to introduce Christianity in such a way that it was suitable for seizing the souls of those who had just outgrown the old atavistic clairvoyance. It is of particular importance that from the ninth century onwards, and influenced by the separation from Oriental Christianity, the Roman Church began to take the European ethnic elements and conditions into account in an eminent way, when under Nicholas I, the great Pope, the Orient began to separate from the Occident within the Christian element. The underlying reason for this separation was the necessity to take into account what was rooted in European conditions, as I have outlined in very sketchy fashion. If we now consider the 14th and 15th centuries in terms of their basic character, we will see that the period from the 8th to the 14th century is characterized by the interaction of the papal element, the interaction of the Central European element, and the development of that European configuration, which then changed again when the great discoveries and the Reformation and the like came. I just wanted to show you the factors that culminated in the ninth century in purely historical terms. In the development of Europe, one can clearly distinguish the first three Christian centuries, which led to a kind of anarchy. Everything is topsy-turvy. In the third century, everything is mixed up. But then, through the natural conditions, the situation developed over the next five or six centuries, into the ninth century, in such a way that one can say that Christianity was carried into the circumstances in the way I have indicated, but that these circumstances were actually given by the way people lived. |
| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Sixteenth Lecture
17 Jan 1918, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 180. Mysterious Truths and Christmas Impulses: Sixteenth Lecture
17 Jan 1918, Dornach Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The things I am now presenting in a somewhat prosaic way in this last lecture, in contrast to the great vistas we have been accustomed to in these meditations, do, however, have a certain inner connection with our entire meditations and also with the present time. And in a sense it was important to me, even if it can only be done in aphoristic form for these things, and again in the form of remarks, perhaps even without further context (otherwise one would have to talk for days on the subject). Just as we tried to penetrate the period that culminated in the 8th century with a few remarks, so we want to consider today the following period, which then culminated in a certain sense in the 15th century for European life. This 15th century is extraordinarily interesting to consider in the most diverse respects, especially to see how it emerges from the European living conditions of the preceding centuries. This century is significant for the reason that it was only in the 15th century that the conditions in Europe were formed within which we are currently living. People think, one might say – we have mentioned this from other points of view – in the short term; they imagine that the way they experience the circumstances around them is constant. But it is not. Living conditions are subject to metamorphoses. And if one does not look at everything from the present-day point of view, as unfortunately happens so often in modern history, but tries to understand the nature of earlier times, which can only be done through spiritual science, especially in practical matters, one comes to the conclusion that times have changed quite considerably. I think I already mentioned in the course of these lectures that, when I recently presented something similar in a lecture, a gentleman said to me at the end: Yes, but spiritual science assumes that these epochs, as they developed, were different from one another; and history shows us that people have actually always been the same, that they have always had the same vices, the same jealousies and so on, that people have not changed significantly; what causes conflict today also caused conflict in the past. I replied to the gentleman at the time: You can go even further with this approach, you can simply take certain very obvious sources of conflict in the present and look for them among the Greek gods, who certainly have very different conditions of existence from all earthly men, and you will find that the things you are looking at can even be found among the Greek gods. Of course, certain human conditions that have been the same everywhere can be found if you look at things abstractly. Indeed, there are even some scientific observations at present that find very similar conditions, family relationships and the like in these or those animal species. Why not! If you just apply enough abstractions, you will find such similarities. But that is not the point. Such a way of looking at things is eminently impractical. Above all, people today, and truly not only people in the broader circles, but precisely influential, very influential circles, look at what national conditions are in Europe and in the educated world in general, as if these national conditions were eternal things. They are not eternal things; but precisely that form of feeling that arises from the national, for example, for today's man, is entirely dependent on what emerged in the 15th century, because before that, especially with regard to these things, Europe was something completely different. What the national structures are today, crystallizing into states, only dates back to the 15th century. And what Europe was before that has nothing to do with the national formations of today. This should be clear from a historical study of the past. If, however, the past does not go back further than the 15th century, then it might happen that someone might express the judgments that can be made about the present as if they were eternal conditions. If, for example, a state structure such as did not exist in Europe before the 15th century could only be established according to European ideas in a territory that became known for European conditions only after the 15th century, which therefore does not have a past in the sense of Europe, where one therefore only thinks in terms of a few centuries and then considers this thinking to be eternal conditions, if one were to think up state ideas or even ideas of nations with such thinking, then at least the judgments that one can make about the present would have to be expressed as if they were eternal conditions. past in the same sense as Europe has, where one thinks only in terms of a few centuries and then mistakes this way of thinking for eternal conditions. If, with such thinking, one were to conceive of state ideas or even ideas of nations, then at least the Europeans should know that such ideas of nations must necessarily have very short legs. In the 15th century, something else occurred that is connected with what I had to mention about the beginnings of Christian development in Europe, especially in the vast Roman Empire. I stated at the time that the Roman Empire had found its downfall through various forces, but that among these forces there was also the fact that there was an incredibly strong outflow of gold to the Orient, that the vast Roman Empire became poor in gold. Now this did not benefit the Romans, who were accustomed to needing gold in the institutions of their empire, and now they had none. This led to decadence. But it benefited the peoples storming in from the north. Due to the various circumstances we mentioned last time, they were organized precisely for direct natural economy. And the strange thing is that – despite the fact that certain conquerors, of whom we have already spoken, laid hold of the lands that had previously been at peace – a certain settledness emerged from the coexistence of the conquered people and the conquerors. Those who were already there in Europe loved their land in a certain sense, and those who had been drawn to it sought a plot of land. And so, out of that event which is usually called the migration of peoples, favorable living conditions arose that can be called: natural economy versus monetary economy. Europe had gradually become such that the Carolingians were forced to take into account the need to set up the conditions in such a way that, to a certain extent, the generous circulation of money could be dispensed with. The Carolingians, and even the Merovingians, these dynasties of rulers, often only meant something for the inner course of events – if you want to look at it objectively – what is called the hour and minute hands of the clock. You are also convinced, aren't you, that it is not the hour and minute hand that forces you to do this or that, and yet you do it; or when you tell the story, you say: I did this at twelve o'clock or one o'clock. - So in the historical account, it depends on the intention that one associates with it. When I say this, I mean the time, the living conditions in this time. But one must be aware that a person like Charlemagne meant something in Europe through his personality, through his outward appearance; because things are concretely different. Louis the Pious, of course, meant nothing more. And when playwrights find themselves dressing up Louis the Pious's family quarrels as grand state affairs, it's nonsense that may interest childish minds sitting in the theater; but it has nothing to do with any “history,” it is worlds away from any real history. It is different when you take the tone-setting Charlemagne and then look away from the lesser ones who came after him; sometimes they are already strangely characterized by the epithets popular in such circles; history has some strange epithets for them: “the Simple,” “the Fat,” which, well, doesn't exactly seem meaningful for something that made a world-historical epoch. But there was a certain tone, a certain tendency in Carolingian life, and this tendency had a much broader effect than perhaps the tendency of any personal center since the 15th century has been able to have. In the Middle Ages, people lived in a time when personality still had a far greater value, a far greater significance, than it had later. Now, these Carolingians had to take into account that, out of the conglomeration of the migration of peoples, settled humanity had gradually emerged over Europe. This settled way of life, which was particularly characteristic of the Saxons in Central Europe and of their descendants who then came to England, to the British Isles, was a general characteristic of the Germanic peoples – I mean in this period, in the Carolingian period, after the migration of peoples had subsided. Settledness, combined with dependence on what is produced directly on the land, thus a farming population, administered by the count in the way I have recently discussed, administered by the clergy, a population in the vicinity of the cities, administered by the bishoprics in the cities; but a population that was settled in terms of agricultural production, in terms of commercial production, and that held something dear to the place with which it was associated, because the conditions of life kept them connected to that place. Of course, trade relations were beginning to develop, but these were more towards the coastal areas. In the areas that were of primary importance for medieval life, people were settled. And the consequence of this was that they were not able to administer and manage as they were accustomed to in the Roman Empire. They had adopted the traditional practices of the educated people who knew what was customary in the Roman Empire. They had adopted this or that practice, and administered it in the Roman Empire in a certain way, and it had proved to be correct. But that was not applicable to the conditions that had developed throughout Europe. It was not applicable because the entire Roman Empire, after it had once reached a certain size, was actually built on the military system of the Roman Empire, on the military system of the Roman Empire. The Roman Empire is inconceivable in its size without the possibility of sending soldiers everywhere, right into the periphery. The soldiers had to be paid. I already mentioned last time that this required the circulation of gold. And when the gold circulation slowed down, it was no longer possible. And while these conditions were developing, while an empire was developing that was entirely dependent on its internal support, the possibility of its internal expansion, the possibility of developing itself, all views were formed in such a way that everything in these views was based on the military. So one could have said in the Carolingian period: I hire someone who is familiar with the administrative and legal techniques of the Roman Empire. For that had remained with them. But it did not help much, because what was built on the legion system of administrative art could not be applied where it was supposed to be applied across the whole of Europe and now also into Italy, because these conditions had developed for everything, where one had to deal with settled farmers. For at that moment, when one would have forced the peasants, or those who settled down as landlords and were only large farmers, to form legions, as was the case in the Roman Empire, then one would have deprived them of their living conditions. Under such a monetary economy as that of the Roman Empire, the legions could be sent anywhere. But conditions had gradually developed within Europe in such a way that if one had wanted to do it exactly the same way as in the Roman Empire, if the farmer had to go to war or the lord of the manor as a count had to lead the farmers in war, they would have had to take all their fields with them on their backs – which, as is well known, they cannot. The consequence of this was that, since movement was needed among the peoples, something quite different had to gradually develop, an element that is not now like the legion system in the Roman Empire. And this element that emerged came about in the following way. It came about in the following way: I am now talking about the centuries that followed the Carolingian period, because what I am telling you happened over the course of centuries. Gradually, some of the landowners attracted people who entered into their special service and became dependent on them. These were mostly those who were now surplus to requirements in the wide field of natural economy. And these people, who were redundant in the field of natural economy, could be gathered around them when they wanted to undertake military campaigns and military expeditions. These people, who were either redundant due to overpopulation there or there, or who were redundant because they had others do their work for them, these were now the people from whom, gradually, all over Europe, what is now from the Middle Ages onwards as knighthood; knighthood - essentially what one might call “quality warriors”, people who made war their trade, who thus carried out what they did in the service of this or that lord for the sake of this trade. With knighthood, then, a special people of war developed at the same time, which became a special class throughout Europe. And from this arose another necessary consequence: there existed, as it were, two circles of interests. Without realizing these two circles of interests, one does not understand the Middle Ages. There were the wide interests of those to whom it was actually absolutely indifferent whether these knights or their leaders undertook this or that, who wanted nothing more than to cultivate their soil and trade in the immediate vicinity, to pursue their trade. This interest gradually gave rise to the sentiment in Europe that was not yet present at the time of the migration of peoples, which later appeared particularly in the crafts of the cities: the bourgeois sentiment. This spread within one class of the population, and the chivalrous sentiment, which was based on the quality warrior, went parallel to it, but quite apart from the other sentiment. In this way you have given an example – if you look at world history correctly, you will find such things everywhere, only in a different form – but you have given an example of how different classes develop out of certain concrete necessities that arise over time. But that was where a discrepancy occurred. Those who gradually rose through the ranks – isn't that right? I can't tell the whole story, I can only make aphoristic comments – rose from being a landed gentry, by gradually making their surroundings dependent. The whole essence of the Merovingians came about in no other way than that large estate owners extended their networks further, making more people dependent; for when we speak of a Merovingian “state” in history today, it is almost a cliché in comparison! What we call a state today only begins after the 15th century. The Merovingians, who rose to power, initially had to deal only with the people who had joined them as a knightly population, so to speak, the supernumeraries who shared their adventures. Because the territory was a common one, they continually had the other interest groups either against them or had them beside them in such a way that they did not know how to deal with them properly. At that time there was no question of any real organization, such as a state administration, that would have reached into all aspects of life. If one speaks of princes for that time, then these princes basically only had some influence over those who had joined them. Those who sat on their own little plot of land regarded themselves as the independent lords of their own little plot and, if I may use the trivial expression, cared little about those who wanted to rule with them. They did as they pleased. When going back to the time of Louis the Pious, one should not read history today as if what is attributed to him as the “empire” could be attributed to him in such a relationship, so-called to his government, as a state is to its government today. That is not the case at all. These things must be considered in concrete terms. And so one can say that it has been shown that there were constant, diverse, and strongly differentiated interests. This must be taken into account in particular because the historical life of the Middle Ages emerges from these things. Now I said: the 15th century is remarkable for the reason that in the 15th century, again, especially through the natural development of mines and the like, gold appeared in Europe, later through the voyages of discovery; so that since the 15th century, circumstances have arisen that are fundamentally different from the previous ones in that gold has appeared again. And this 15th century, which we can also call the age of the Christian Rosenkreuz, is therefore the one through which we again sailed into the monetary economy in Europe. There is also a mighty turning point in this respect. The last times of the fourth post-Atlantic period in Europe were the moneyless ones, those of the natural economy. That is what we have to bear in mind. And now, during this time, through all the holes in that, what I have described developed, which then, from the 15th century onwards, brought about the gradual change in circumstances so that we can now speak of compact nationalities separated into states. To speak of such a contrast between Germans and French, as one can do since the 15th century, is still quite impossible for the period up to the 15th century, and is even meaningless. What can be called the French nation has only formed very slowly and gradually. Of course, the Franks were distinct from the Saxons; but the Frankish character was no more distinct from the Saxon character than I described it last time. There were tribal differences, not ethnic or national differences, no greater differences than there are today between Prussians and Bavarians, perhaps even smaller in many respects. But everything that had developed there is still connected with the circumstances we have just described. For that which then became the French kingship really emerged from landowning circumstances. And the great difference in the formation of the closed French nationality and the so-called German nationality, which was open in every direction, in the center of Europe is essentially due to the fact that the French members of the Merovingians, Carolingians and so on could more easily smooth over the differences between themselves and the others due to the tribal character; they got along better with the opposing elements. For from all that I have described, it emerged that, initially, the people who were settled on the land, the settled people in general, did not want to go along with anything, did not greet the Gessler's hat anywhere. That was already the custom throughout Europe: nowhere to greet the Gessler's hat. But even those who had become knights gradually sought to settle here and there. Of course, after they had first attained a certain position under the protection of this or that feudal lord, that is, prince, they were very inclined to become independent again. Why should one not be as powerful as the one under whose protection one had become powerful? But this meant that the one who was something like a ruler soon had to deal with unruly elements. And the period of the 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th, 13th, and 14th centuries essentially developed in such a way that there was a continuous struggle between the opposing elements and those who wanted to rule over them. What had emerged from the consequences of the migration of peoples could not easily be reduced to some abstract form. One wonders how it actually came about that in what later became France a unified nationality was able to develop relatively early on? For the historical observer, this is in a sense a kind of puzzle that immediately presents itself, and one must try to solve such a puzzle. For one cannot get away from the general saying: nations develop in this or that way. In every corner of the earth, what is a nation develops differently, even if it is later called the same in each case. One asks oneself: how did it happen that from the Merovingian period until the 15th century this compact French nation was able to develop? Now, this is still connected with somewhat earlier conditions. Even when the Roman Empire was still powerful, fewer inhabitants and personalities of the Roman Empire were transferred to Central Germany than to what later became France. The western regions of Europe were actually already very, very much permeated with Romance elements at the time of the Roman Empire. And I said that many things penetrated through the gaps in these conditions. Otherwise, in principle, present-day France is no different from what it was in those centuries, but there is one difference: intermingled with the other population were many Romance elements, Romance personalities with Romance views, interests, inclinations, remnants of the old Roman Empire. And on the wings of the old Roman Empire, one might say, Christianity had gradually spread throughout Europe. Christianity came to France with the Roman element, and came in the same way as it had made its entry into the Roman Empire itself. And it was therefore of some advantage in this area if those who wanted to rule adhered to what was left of the Roman element. Because the settled people and the knights all had a characteristic that made them appear well suited for administration when there were others who were different. If, as in Central Europe, there had been no one as such for a long time, then of course these people had to be used. Right? In Central Europe they did it like this: The people of a certain area came together through purely oral agreements and from time to time they organized what was called a thing. And there, with ideas that were all from the atavistic Hell, they discussed how to punish one or the other who had done something wrong. This was arranged orally, and it was actually quite common in the areas of Central Europe to arrange these things orally. Little was written because the sedentary farmers and knights had the peculiarity that none of them could read or write. You may know that Wolfram von Eschenbach, the famous poet of the Middle Ages, could not read or write a single letter. But the Romance elements that had flooded into Western Europe could. They were also, in the sense that we call it today, educated people. The consequence of this was that, of course, those who wanted to rule made use of these “educated” people, apart from the fact that the clergy were of course taken first from this class. This also led to the connection of the administrative civil service with the spiritual element, which consisted to a large extent of the influx of the Romanic element. But with this and with the church at the same time, which was thus drawn from the Romanic, it came about that the linguistic element began to play an enormous role. And the puzzle that I have hinted at cannot be solved otherwise than by gaining an idea of the tremendous suggestive power of language. With the language that was transformed from Romance in Western Europe, but which retained the Romance style, if I may say so, with this language not only a language but an entire spirit was transferred. For a spirit lives in language with tremendous suggestive power. And this spirit had an overwhelming effect. And the arrival of the Romance spirit on the wings of the Romance language, from the Carolingian period to the 15th century, was a fact. And now the peculiar thing happens: Western Europe is now quite different from the conditions in Central Europe. In Western Europe, what language, which had gradually developed from a Romance element, has suggestively achieved in people's souls, as if from below, is complete. What lay in the broad popular consciousness, in what I have just described as the settled farmers, this settled peasantry with its ancient atavistic clairvoyance - even if these people had become Christians - with the bringing up of their, not faith, but direct insight into what was in the spiritual worlds, that did not emerge everywhere for the people who ruled or administered there above. But in Western Europe, an upper class emerged that, by shaping the language, also had a suggestive effect on the lower classes. We do not need to consider this upper class in terms of how it administered and what legal and administrative conditions emerged; but we do need to consider it as a class of civil servants, as a class of language that into the lower class and with the language the whole suggestive element, which spread as a uniform over a certain territory, before the people from below reacted against what had formed as a ruling class. Because we see until the 15th century what had formed as a ruling class, making its various manipulations; and what is below, does not care about it, remains free, until clashes occur. What rules has the tendency, after all, to draw more and more to itself. By the time the country had reached the point where the peasantry, the original folklore, reacted, the linguistic element with its suggestive power had already been vigorously effective. And you can find it particularly significant in Western Europe, you can see how the broad masses of the people react, who were still within their old spirituality, in their atavistic spirituality. The messenger, the genius of this mass of people, is the Maid of Orleans. With the Maid of Orleans, there arises that which, after language has worked through its suggestive power, is the reaction of the people from below, which forces the French monarchy to take the people into account. You see, until the 15th century, until the appearance of the Maid of Orleans, who actually made France as France, Romanesque flooding, then the appearance of the people's messenger. So that even in this way of the appearance of the folk through the shear science of Joan of Arc, it shows how what was naturally alive everywhere in this folk reacts upwards and only then actually becomes “history” for external history. There were such Maidens of Orleans throughout Europe in those centuries, not with the power of action but with the power of vision. And the foundation on which the Maid of Orleans built was the element spread over the broad peasantry and the broad masses of the people. In the Maid it only came to the surface. It is not described for the people. You have to codify Louis as stupid – no, pious – and his councils and all the stuff that is in the chronicles, what they wrote together, as “history” and you have to make people believe that these great landowners were rulers of states and the like. But basically that is outside of real concrete life. But real life was permeated with what then came to the surface in the genius of the Maid of Orleans and entered into the French character at a time when the suggestive power of language was being exercised. And thus, from below, what was national strength was poured into the French character. That is how it came about. This was not the case in Central Europe. There was no language that exercised such suggestive power. All other conditions were similar, but there was nothing that welded a larger tribal group into a national force through the suggestive power of language. Therefore, in national terms, what exists in Central Europe remains a fluid mass, and – peculiarly – can easily be used for colonization. But the colonization that is done with the population of Central Europe is different from what it is today. When colonization is done today, it is usually to acquire foreign territories. But in the past, people were sent to foreign lands – and in large numbers they were called, the colonizers – and what they then understood from their homeland, they carried into foreign lands. This is what happened in the eastern part of Europe in the broadest sense. But it remained a fluid mass. And while in the West, in particular, the suggestive power of language was effective, in Central Europe there remained the brawls, the quarrels, the differentiated interests that I have described, insubordination above all against those who wanted to rule, which then had the consequence that a widespread, uniform nationality could not develop as it could in the West. There was nothing to suggest the power of language. Therefore, in many cases, those who were the stronger as a result of the circumstances arose. Hence the territorial principalities, which had remained even beyond the 15th century, and which essentially arose because there was no such suggestive power as the power of language in the West. The other element, which now really understood how to deal with some of these circumstances, had to take them into account: the ecclesiastical element, which gradually emerged in Rome from the perished Roman Empire. This ecclesiastical element is called in occult circles the grey shadow of the Roman Empire, because it took over everything that was the way of thinking about administration and the like from the Roman Empire, but applied it to ecclesiastical conditions. This striving of the church had to go in the direction of differentiating itself into what was developing in Europe. And I have already hinted to you a few times about how they in Rome knew how to deal with the situation. From the 9th century to the end of the 10th century and the beginning of the 11th century, they knew how to deal with the situation perfectly well, in that they in Rome now actually endeavored to force what they called Christianity into all these situations in an administrative form. If it was possible to convert a city into a bishop's see, then that was done; if there was a peasantry somewhere that one wanted to win over, one built a church for them so that they would gather around it; if there was a lord of the manor somewhere, one tried little by little to replace this lord of the manor by training his son or the like to become a clergyman. The church used all circumstances. And indeed: as never later was the church within these centuries put into the possibility of becoming a universal European power. This process, how the church worked in the 9th, 10th, 11th centuries, is tremendously significant because it really aims to take into account all the concrete circumstances. One must only consider this. The people who were Catholic clergy or priests at the time were not so foolish as to believe that the spirits that people spoke of in atavistic clairvoyance were not spirits; they reckoned that these were real powers, but they sought the appropriate means to fight them. While the princes were not at all able to cope with them, the church was actually able to gradually provide the ideas - which were quite justified for them - with a nomenclature. It is true that in Rome they knew very well that the atavistic clairvoyance is not all about devils, but that these demons are our opponents and we must fight them. One weapon in this fight was to label them as devils, to ascribe them to a particular category. This was a very real fight against the spiritual world that was waged in those days. It was only from the 15th century onwards that people no longer had any awareness of the spiritual powers at work. The strength of the spreading ecclesiastical Christianity lies in the fact that one knew how to deal with what is real: with the spiritual powers. And in the 11th and 12th centuries the process was actually completed to a certain extent. You will only be able to judge the history of the Middle Ages correctly if you bear in mind that all the ecclesiastical arts that were effectively applied and which were great and meaningful arts, had actually been developed in the church from the 9th century, when it was shown, for example, under Pope Nicholas I, how one reckoned strongly with the spiritual powers, how one had to reckon with everything that the people knew through atavistic clairvoyance. And the art of working in the spiritual realm is what actually made the Church great. But by the 11th and 12th centuries these arts had been exhausted. Of course, the old arts were still practiced, but new ones had not been invented, so that one can say: everything else that happens is actually in the service of this mighty spiritual struggle. For even that which appears to set the tone, the establishment of the German-Roman Empire, which passes, not truly, from the West to Central Europe under the Saxon emperors, this coupling of Central Europe with Italy, this recedes more or less in the face of the tremendous power that lies in the fact that the church in these times is pouring an international over Europe that only from the 15th century onwards becomes a national. It is only from the 15th century onwards that the conditions under which people in Europe live at present have developed, also with regard to the peoples of Central Europe. It must be emphasized again and again, for what was actually the basis of what constantly took place between the so-called Roman-German emperors and the popes? You can study this especially if you read the accounts of Henry IV, who may have been distorted in history but was very clever politically. What was at the root of it was always that it was necessary for those who wanted to rule, who should rule for my sake, to tame the unruly. The spreading church was, of course, a good means of combating the unruly - if the church helped. Hence the perpetual binding together of secular power with ecclesiastical power, which in that time could only be achieved through a certain relationship between those who were elected in Central Europe and who, precisely because of what they achieved through this election in Central Europe, had little of their rule but the powers over the unruly, the powers over those whom they actually did not want at all. Just think about it: we are dealing with an elective monarchy. The kings were elected. They were elected by the so-called seven electors. Of these seven electors, however, three were the ecclesiastical princes. The ecclesiastical princes, with the help of the ecclesiastical means, as I have just indicated, were powerful. The archbishops of Mainz, Cologne and Trier had three of the seven votes, and they were powerful. The only other powerful figure was the Count Palatine of the Rhine, who was still in a position to deal with his vassals – as they were later called, subjects – under the circumstances that had developed. But the other three electors, so-called electors, one of whom, for example, was the King of Bohemia, who was unruly himself; the other two ruled over what were then still entirely Slavic regions, along the Elbe and so on, with a strong Slavic population. Kingship really meant nothing more than what the Carolingian Empire meant. The only difference was that Carolingianism had an easier time dealing with what was striving to the surface because the suggestive power of language was there. That was not the case in Central Europe. There is much more I could tell you about how these differences developed in detail, but you can read about it in any history book. If you follow the same points of view that we are applying here, you will read history with different eyes. When the relations that had gradually developed between the papacy and the empire had died down a little, the ecclesiastical element had become so strong that it wanted to pursue independent policies. This was essentially the case in the 11th and 12th centuries. And it is interesting that Pope Innocent III now administered the affairs of Italy, which had been anarchic until then - in a sense, the clergy were the most difficult there - from Rome. Actually, Innocent III is now, as a human and spiritual power, the creator of a national consciousness of the so-called Italians with what came from him. Innocent III is a Lombard offspring, but one can say that what came from him basically made the Italian nation, which actually also became a nation through the impulses that Innocent III laid. The nationalization process was also completed by the 15th century. So it is essentially the church itself that created the national element. Thus, in the formation of the French nation, one must look for the suggestive power of language, and in the Italian nation, directly, the ecclesiastical element. These things only confirm what is obtained in a concrete way from spiritual science, which we have already considered for the various nations. It is quite characteristic of Innocent III that he actually set very specific tasks for the Catholic Church. And one might ask: What then is the task that the papacy set itself after the great period of which I have spoken, from about the 10th, 11th or 12th century onwards, and what has been the mission of the papacy since those centuries? The mission of the papacy, in the Catholic Church in general, consists essentially in keeping Europe from recognizing what the Christ Impulse actually is. More or less consciously, the aim is to establish a church that sets itself the task of completely misunderstanding the actual Christian impulse, not to let the people know what the actual impulse of Christianity is. For wherever an attempt is made to place in the foreground some element that wants to approach the Christian impulse more closely - let us say the element of Francis of Assisi or something similar - it is consumed, but not incorporated into the actual structure of the church's power. The situation in Europe has developed in such a way that the people of Europe have gradually accepted a Christianity that is not Christianity at all. Christianity must first become known again through the spiritual-scientific discovery of Christianity. The fact that the Europeans have accepted a Christianity that is not Christianity has contributed significantly to the fact that talking about the Christian mysteries is an absolute impossibility today. Nothing can be done about this; first, long preparations are needed. For what matters is not that one uses the name of Christ, but that one would be able to properly grasp the essence of what Christianity is. But that was precisely what was to be concealed, what was to be suppressed by what popes like Innocent III did. The external circumstances were already strange, as Innocent III shaped them. For one must not forget that at that time a remarkable victory had been won by the papal side. There was – as you will know from external history – a twofold current in Central Europe, Southern Europe, Western Europe: a more papal-friendly current, the so-called Guelph, and an anti-papal current, the Hohenstaufen. The Hohenstaufen were, after all, more or less always in conflict with the popes. But that did not prevent Innocent III from joining forces with the French and the Hohenstaufen to defeat the English and the Guelphs. For it had already come to the point that on the papal side they were now reckoning with the circumstances that subsequently became political. In its better times, the Church could not yet reckon with political circumstances; it had to reckon with concrete circumstances. This gives you a picture of the configuration of Europe and of the gradual insertion, insertion of the universal church into this configuration of Europe. Now, we must not forget that it was essentially a overcoming of the old clairvoyant element by the church. That was one side of it. But the old clairvoyant element continued to develop nevertheless, and you see everywhere where secular and ecclesiastical powers make their compromises that there or there the talk is of the princes or the popes having to lead the fight against the heretics. Just think of the Waldensians and so on, of the Cathars; there are heretical elements everywhere. But they also had their continuation, their development. Gradually something emerged from them, and these were the people who, little by little, looked at Christianity on its own merits. And the strange thing is that, from among the heretics, people gradually emerged who looked at Christianity on its own merits and were able to recognize that what comes from Rome is something different from Christianity. This was a new element in the struggle, which, if you follow it, can be particularly strong for you to face, as the kings of France, who were allied with the Pope, had to wage war against the Count of Toulouse, who was a protector of the heretics of southern France. And you can find something like that in all fields. But these heretics looked at Christianity and could not agree with the political Christianity that came from Rome. So while the conditions I have described were forming, there were also such heretics everywhere, who were actually Christians, who were violently opposed, who often kept quiet, founded all kinds of communities, spread secrets about it. The others were powerful; but they strove for a special Christianity. It would be interesting to study how, on the one hand, the continuous advances from Asia became occasions for what are called the Crusades. But for the papacy, at the same time, the call that was made by Peser of Amiens and others 'on behalf of the pope to the Crusades' was a kind of means of information. Even in those days, the papacy needed some kind of improvement. What had become purely political needed to create an artificial enthusiasm, and essentially the way the papacy conducted the crusades was designed to instill new enthusiasm in the people. But now there were people who actually emerged from the ranks of the heretics, who were the direct development of the heretics. Gottfried von Bouillon was particularly characteristic of these heretical people, who had, however, looked at Christianity; for Gottfried von Bouillon is always distorted in history. It is always presented in history as if Peter of Amiens and Walter of Habenichts went first, could not accomplish anything right, and then, under the same tendency, Gottfried von Bouillon went to Asia Minor with others, and they wanted to continue what Peter of Amiens and Walter of Habenichts should have done. But that cannot be the case. Because this so-called first regulated crusade is something completely different. Gottfried von Bouillon and the others associated with him were essentially - even if they did not outwardly show it - emerged from the ranks of the heretics, for the reasons that I have discussed. And for these, the goal was initially a Christian one: with the help of the Crusades, they wanted to establish a new center against Rome by founding a new center in Jerusalem, and to replace the Christianity of Rome with a true Christianity. The Crusades were directed against Rome by those who were, as it were, initiated into their real secrets. And the secret password of the crusaders was: Jerusalem against Rome. - That is what is little touched upon in external history, but it is so. What was wanted from heretical Christianity in contrast to Roman political Christianity was to be achieved indirectly through the Crusades. But that did not work. The papacy was still too powerful. But what came about was that people's horizons were broadened. One need only remember how narrow they had become in Europe since the time of Augustine. In my book, “Christianity as Mystical Fact,” you will find that Augustine is quoted as saying, and Gregory of Nazianzus and others have also said: Yes, certain things cannot, of course, be reconciled with reason, but the Church, the Catholic Church, prescribes them, so I believe it. - This version, this disastrous information, which was necessary for Europe in many respects, had, however, brought with it the fact that great points of view, which were capable of linking to great sensations, to great worldviews, were avoided. Read the Confessions of Augustine, how he flees from the Manicheans. And actually it is that in the Manichean doctrine he has a world view. One is afraid of it, one is afraid of it, one shies away from it. But over there in Asia, on the basis of what I have described in a very material way as the influx of gold into the Orient, the old Persian doctrine had blossomed and taken a great upswing. The Crusaders broadened their horizons considerably, were able to take up what had actually been buried, and thus many secrets were revealed to them, which they carefully guarded. The consequence of this was that, because they did not have enough power to carry out “Jerusalem against Rome,” they had to keep things secret. Hence, orders and all kinds of associations arose, which preserved certain Christian things under a different guise, because the Church was powerful, in orders and the like, but which are precisely opposed to the Church. At that time, the difference actually emerged that now only comes up when you have visited a church somewhere, let's say in Italy, and someone inside has just preached against the Freemasons: you see people standing there who, of course, couldn't care less about the Freemasons; they don't know any names, but the pastor rants against the Freemasons from the pulpit. This antagonism between the Church and Freemasonry, which nevertheless developed out of heresy, essentially took shape in those days. These and many other phenomena could be cited if one really wants to understand in detail what actually happened in reality back then. And you will have gathered from the whole that life was partly a very varied one, but that the most diverse spiritual interests played havoc with each other. People were confronted with such contradictions as those between the heretics, many of whom were actually Christians in the best sense of the word, and the church Christians. One could cite many other things that then led to the Reformation in Germany, for example, and the like. One could mention that the politicization of the church has led to the church losing more and more of its power, while in earlier times it would have been unthinkable that the church would not have found a way to get what it wanted. In certain areas, one must say, despite the fact that the church was able to burn Hus at the Council of Constance: Husitism has survived and as a power it actually had quite a significance. But what is the actual timbre of these medieval scholars? It is true that a religious movement spread that ultimately took on a purely political form. It's a shame that time is so short; there would be many more interesting things to be said. A religious movement spread that takes on a universal character. Due to the different circumstances, the nationalities in Europe are gradually developing. If you consider that Christianity has brought with it ideas that have become so ingrained in Europe, such as the Fall of Man, then it is possible to create plays like the “Paradeisspiel”, which was performed in large parts of Europe, especially in the 12th century. It has penetrated into the most individual, most elementary circumstances. Ideas that go deep into the heart and soul have become widespread, ideas about what man could actually have been according to – if one may say so – God's original plan and what he has become. This created an atmosphere in which, perhaps never before, and certainly not in our time, has a question been raised again and again and again, emotionally, in so wide a range, the question that is based on the difference between this world here and the world of paradise, between the world that can make people happy. This question, in the most diverse variants, already dominated wide circles. And people who were intelligent, people whose longings were intellectual, often came to direct their striving in a naive, but often also in a matter-of-fact way, towards such riddles. Just look at the whole configuration of the time. With the Roman Empire, Europe became poor in gold. The economy of nature came. Under the natural economy, conditions gradually arose that did not appear paradisiacal to the people. You only have to think of the medieval law of the jungle, of the intermarriage of the ruling families, and so on. The church had spread, for many to such an extent that they said to themselves: It is not Christianity, it is rather there to conceal Christianity, gives rather a false idea of the Christ mystery than a right one. But all this has indeed had the effect that we are not happy. The question: Why is man on earth not happy? Yes, one can say that, more than eating and drinking, this question gradually occupied people in the 13th, 14th and 15th centuries, especially those who felt something in the right way about the Mystery of Golgotha. Which, of course, has a deep meaning and another meaning, that connected itself with the question for people: Why are we not happy? Under what conditions can a person be happy on earth? Something emerged as a result – in the form it took, it can be traced back to the cause I am about to mention – which will be clear to you from the descriptions I have given. Europe was without gold; natural economy was the basis on which unhappy humanity developed. The Roman papacy veiled Christianity. 'But people should strive for something that is a real human goal. And so, to put it briefly, it sounds paradoxical, but in wider circles, especially in those that emerged from the heresy circle, the mood has developed: Yes, we have become poor in Europe, Romanism has gradually made us poor. And it was realized that only those work their way out who work their way out in the same way that the Roman Empire became great, who had come to gold. How can you paralyze that? How can you paralyze the power of gold? If you can make gold! Thus, the widespread art of experimenting and trying to make gold is connected with the very specific circumstances of the time when there was little gold and only a few individuals came into gold who could use it to tyrannize over others. People strove to balance this out. Because they knew that If everyone can make gold, then gold has no value. Therefore, the ideal became to be able to make gold. They said to themselves: In any case, you can only be happy in a world in which you can make gold. And it is similar with the quest for the “philosopher's stone”, even with the quest for the “homunculus”. Where interests arise as they did from family circumstances - as seen in the divisions of the Carolingians and so on - people cannot be happy. But this is connected with the natural reproduction of man. In any case, if a paradise is possible, it is more likely to be possible if homunculi are created than if ordinary reproduction with all its family relationships continues. Such things, which today sound quite paradoxical and twisted, were something that moved countless minds in those days. And you don't understand the time if you don't know that it was moved by such questions. And then came the 15th century, and that put an end to gold-seeking, of course, in that they discovered America and brought the gold back from there. And then the phenomenon I have just characterized subsided. Universally summarizing all those elements that were active in the Crusades, deepening during the Crusades, summarizing all the longings that lay in the Middle Ages - the art of making gold, of creating the homunculus , to summarize all this in a truly spiritual way so that it could become an active impulse, that was essentially what the companions of Christian Rosenkreutz set out to do. To do this, it was first necessary to come to terms with all the things that had developed up to the 15th century. The time had not yet come to draw new truths from the spirit, and so the impulses of Christian Rosenkreutz, like the efforts of Johann Valentin Andreae, ultimately remained unsuccessful. What did they lead to? They led to the emergence of what I am about to say now, and I would ask you to please pay attention and take it into consideration: Europe is differentiating itself; differentiated structures have emerged from what used to prevail there. It would be interesting, but there is no more time, for me to also tell how the British nation formed in a similar way. Even in the east, the Russian-Slavic nation formed in a corresponding way. All of this could be described. Everywhere it has happened with a reaction from below, only in France it is so significant because the genius from below had a direct character in that it appeared in Joan of Arc. In the face of this differentiation, to do something truly universalistic – for that Romanism is not suitable for being universalistic had just been shown by Innocent III, who founded the Italian nation; so the church is no longer universalistic – to find a spiritual impulse so strong that it transcends all these differentiations, and truly makes humanity a whole, that was essentially what underlay Rosicrucianism. Of course, humanity was not ripe enough to adopt the means and ways to achieve this. But it has always remained an ideal. And just as it is true that humanity is a whole, a unity, it is also true that, even if it takes some time in different forms, such an ideal must be taken up again. And history itself, the way it tends towards the fifteenth century and the way it develops the peculiar configuration in the fifteenth century, is the most vivid proof of this. There is no need to resurrect the old Rosicrucianism, but the ideal on which it was based must be taken up. These are a few aphoristic remarks that I wanted to make at the end. I really wanted to give more suggestions than anything detailed and exhaustive, now that I will have to say goodbye to you again for some time. Over the years, if I may say so, it has become increasingly difficult to say goodbye because it has always happened under less hopeful circumstances. Now, I do not need to assure you that I view the structure and everything associated with it in an honest and sincere way as something that is essentially a real factor in the aspirations that should actually become the aspirations of our time in the broadest sense. I have never seen this structure as merely the hobby of a few individuals or something similar, but I have always seen in this structure and in what it emerges from, on the basis of which it is built, something that must be the cultural ferment of our time, namely, of the future. Therefore, it can be said that a great deal depends on those who have come to understand the significance of this building to also really understand it emphatically and seriously and to represent it with all dignity. Certainly, the building is a first attempt in every respect. But if humanity is to be redeemed in the human being, if that which is trampled underfoot today is to be cultivated in humanity again, then forces will be needed that are of the same nature as those meant by our building, and that are connected with our building. Today, when old religious beliefs and the like criticize this, it sounds very strange; after all, these old religious beliefs have had quite a long time to take effect. And if humanity has reached an impasse today, then it is perhaps not unfounded to ask: If you are saying the same thing you said before, why hasn't it worked before? If it is considered correctly, this may perhaps lead to an understanding of the necessity of what is actually meant here, and what is intended here. And now, however time may change – every time I left, I asked you: May these or those circumstances arise, to the extent that you are able, hold fast to what has led to this undertaking. It is certainly true that the hostility is growing; but consider that even in this unfavorable time, in the course of the last few years, here and there and even in wider circles, some sympathy has arisen precisely for the nature of this undertaking and what is connected with it. And if one does not consider the great task of our spiritual scientific movement, the difficulties it has, the wide gap between what is to be achieved and what is there, if one finally, without becoming foolish on the one hand, but on the other hand without misjudging things, looks at what is developing - one can also look at the good for once - then it is there! Things are moving forward. If you follow with a finer feeling, for example, how such a detail as the eurythmic art has been developed here over the last few years – I think you can see that – then you can say that there is no standstill in our ranks. And if you were to look at the more intimate progress that is taking place within the creation of this building, you can speak of a certain progress. I can even say this today, when I have to say goodbye to you again for some time, with a certain inner heartfelt emotion. When the first steps were taken to create this structure, the first thing to be done was to draw the larger lines, to ensure that this or that happened. But even though we have to focus our attention with deep pain and sorrow on the way this structure has suffered from the general catastrophic conditions of humanity, something else can be said: the circumstances have led me to work much more intensively on the details that arise here at the building site. And it is precisely for this reason that I can say that I may express it here with an agitated heart: what is being built really does express more and more visibly and intimately what is connected with the greater impulses of humanity. Recently, for example, I was able to tell you about the new legend of Isis, which story is meant to be characteristic of the entire situation of the building, characteristic of what I would like to express with it, in saying that this building is meant to be a kind of – let me use the philistine expression, a landmark that separates the old, which will finally have to recognize that it is old, from the new, which wants to become because it must become if humanity is not to end up in ever more catastrophic circumstances. The time will come when people will regret that what was intended with this building was often seen as folly. For this catastrophe of humanity will also have the consequence that many things will be recognized that would not have been recognized without this catastrophe. For it speaks with very, very clear signs. That humanity can be redeemed from man precisely through such impulses as are connected with this building is really supported by many things that could be observed during its construction. Today, you will be particularly confronted with how many cultural works come about externally. Ask yourself whether wherever a church or something similar is built today - it could also be a department store - it is always built in such a way that those who build it and those who work with them are completely immersed in the purpose for which the things are built. One could build some great cathedrals in which the master builders do not really believe in the symbol that is inside. But here it is already a truth that the one works best who is most deeply connected with the matter at hand, who is able to use not only his art but his whole being, who not only works with the outer forms but who wholeheartedly not only works with this world view but lives this world view. And so I must say: It is of particular importance to me, especially this time, to express not only my outward thanks to all those who dedicate their work, their life forces, their thoughts to this building, to those who want to work with us here to bring this work to fruition, but to tell them that I really feel deeply, deeply, what it means that people have come together who want to work here on this work of culture. And out of this feeling, which indeed binds us even more deeply in times when people are as bound as they are in these, I say to you today, as we come to the end of these lectures, a kind of farewell for the time being, for the external physical circumstances. We will remain together in thought. Physical circumstances cannot separate us. But that which will connect us best will be when the power remains alive in us that wants to be built and formed into that which wants to develop into human peace in the stormy times of humanity. |
| 183. Occult Psychology: Lecture I
17 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 183. Occult Psychology: Lecture I
17 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
You will easily believe what very deep satisfaction it gives me to take up work again among you all on this building of ours. It is a fact that anyone coming into intimate contact with the whole aura of this building today would be able to receive the impression, as a result not only of deep reflection but also of quite superficial thought; that something connected with the most significant, the most weighty tasks of man's future is bound up with this building. And it goes without saying that after long, forced absence one is profoundly satisfied on finding oneself once more at this place where this building stands as a symbol of our cause. To this I would add that particularly for me, my dear friends, it is a matter of infinite gratification every time I now return after long absence to be able to see how beautifully and significantly the work on the building has progressed through the active devotion of the workers. In these months of my recent absence in particular, when work has been carried out under such difficult conditions, part of the artistic work has gone forward in an unprecedented way; it has made progress in the spirit that should permeate the whole. With deep pleasure too, I see, as a consequence of the spirit in our work, as consequence of all that is originating here, the real feeling of solidarity among many of our friends—the genuine feeling towards all that this building incorporates. What reveals itself to the soul when one lets this whole matter renew its effect upon one is that here we have a place with which is united such a true sentiment in a number of the friends of our spiritual movement, so sincere a sentiment that it promises a continuance of the best impulses in this movement for the future of mankind for which they are so necessary. In the work devoted to this building there is already something that could serve as a model for all that, in common with what we call today the Anthroposophical Society, is actually intended. On the other hand, I have a strong feeling that what is favourable, what is so significantly good found here in our building, in the harmony of human work, and human feeling consists in this building being able through its objective nature to free what our movement wills from the subjective interests of individual men. Concerning what we have just touched upon, my dear friends, there have been indeed, and still are, in all similar societies as well as in the Anthroposophical Society, certain remarkable views, that to be more exact, are remarkable illusions. A great deal is preached about selflessness and universal love between men; this is often, however, a mere mask for certain artful egoistic interests of individual human beings. It true that these individuals do not know that this is a question of mere egoistic interest; in face of their own consciousness they are innocent nevertheless, the fact remains. The building itself, however, claims from a relatively large number of our friends a selfless devotion to something objective, to something standing out as a symbol of our cause, and free from all that is personal. And what is connected with our building can to that extent very well be, the model for what is sought in our Movement. My dear friends! When, as today, we greet each other again, we need especially to dwell upon what if fruitful and all-embracing in the spiritual movement of ours. Meeting thus again, we need to reflect upon how earnestly we can believe that however it may happen—and the manner in which it does so depends upon how conditions take their course—man will never find his way out of the appalling blind alley into which he has come today until he decides in some way to seek a starting point for fruitful work, fruitful action, within a spiritual movement such as ours. We shall certainly not insist egoistically that the truth is to be found only in our small confined circle where it is recognised, through the very nature of the matter, that man has landed himself in the present terrible situation by neglecting his own spiritual substance. We should be able to recognise ourselves as men who are united in those ideas that alone can lead mankind out of this blind alley. In the soul of modern men there is indeed very much that is not clear. When it has been possible to renew our knowledge here or there about the needs prevailing in our spiritual movement the following may be said on one hand: Yes indeed, the number of souls of those who are thirsting for spiritual life in our sense has very greatly increased. The longing for such spiritual life can well be said to have become infinitely greater; the attention given to our impulses has recently become undeniably greater, at least in those spheres that have been outwardly accessible to me in these last years and especially in recent months. It is not without meaning that I remark upon this distinct increase and strengthening of man's longing for the spiritual life. It is true that over against this strengthening and sharpening of the desire for spirit life there stands the terrible confusion from which the greater part of mankind is suffering. This terrible confusion among men comes about through the outworn ideas, or it would be better to say the outworn lack of ideas, the easy-going comfort where all keen vigorous thought concerned, the comfort that comes from the laxity, the indolence, with which during many decades, the thought-life on earth has been carried. This laxity, this laziness, leads souls astray in the present yearning after spiritual life. On the one hand, men are immersed in a genuine longing for spirituality, for strong supersensible impulses. On the other hand, these souls are fettered by the old powers that do not wish to withdraw from the scene of human activity, but should be able to see from this very activity how far they are removed from having any further place there. It might be said that one finds everywhere this dark impression, this impression of a cleft. In many places in connection with repeated lectures with lantern slides, I have talked a great deal with our members about the Group that will take the chief place in our building. It could be seen on the one hand what powerful impulses have actually entered those souls who, by reason of the conditions during past years, have not even had a glimpse of what is going on here. A new human understanding is already arising from the very way in which what is ahrimanic and what is luciferic has been thought out in connection with what belongs to the Christ and has been represented and revealed in our Group. It makes a deep impression on souls when they are approached by all that is thus given. On the other hand, however, my dear friends, we find everywhere the obstructive influences of what is widespread among men in the remnants of what is old, rotten, in their so called cultural life. This could be seen particularly in what might be called in a real sense the humorous frame of mind with which the lectures were received that were given at the art centre of our friend Herr von Bernus in Munich, when I tried to show a large audience the inner impulses active here in our conception of art. That did indeed arouse interest in people to an extraordinary degree, for I held lectures of this kind in Munich in February and in May and had to give each of them twice. Herr von Bernus assured me there were so many enquiries that I should have been able to give four times over each of the public lectures dealing with the principles of my conception of art, as they have found expression in the building here. Interest was certainly there, but it goes without saying one could find less reason to be pleased in the agreement shown with what was said by the critic of a Munich newspaper, which might be called a showing of teeth though politely and humorously. It was particularly facetious since inner resentment made itself felt against what could not be understood. It was all—not spoken,—but spat out, if you forgive the inelegant expression. And it was shown up by the very interest aroused by the matter where honesty and sincerity spoke in opposition to what was otherwise noticeable in this artistic centre (that is Munich, it goes without saying; it is a well-known fact). Thus was shown how in this centre of artistic activity the most intelligible as well as the unintelligible stuff was talked... It is just in this sort of discrepancy that we get an example of how today the two streams of which I have been speaking are present, and how we need to stand consciously within what is essential and important, towards which we must struggle for the sake of the world and its future. I am certainly not saying all this because when our matters have publicity anywhere I would strive for what is called a “good press” for the moment we had a “ good press” I should think there must be something wrong, something of ours must have been untrue. All these things are suitable for calling up in us a consciousness that it is very necessary for us to take a decided stand on the grounds of our cause. For nothing could promote greater confusion among us than our wishing to make any kind of compromise with—well with what the external world would consider it right for us to do. In what we do it is only towards the principles for which we stand that must look for guidance. Another example of what we have been discussing, less directly connected with our cause, nevertheless connected inwardly, is the recent increasing interest shown in the most varied places for Eurythmy. And when we who were present remember how Eurythmy was received particularly in one place, where it had scarcely been seen before, it was partly something entirely new to the audience, namely in Hamburg, we have really to remember this reception with the deepest satisfaction. The significance of the impulses going out from even an affair of that kind was especially evident in Hamburg. People were there who to all intents and purposes were witnessing a proper performance of Eurythmy for the first time. And the possibility will yet arise perhaps for Eurythmy to be performed publicly. It is just at this juncture, however, that we must stand on the very firmest ground with our cause and do nothing that is not entirely consistent with it.Otherwise, my dear friends, it would soon be seen that, from a certain point of view, it must not be thought that I shall yield when some particular matter is in question that depends upon me. Most of you already know that where no principle is concerned, when some purely human affair comes to the fore, it goes without saying that I am always in it all with best of you. When it is a question, however, of approaching the boundary where any principle whatever has to be forsworn—even in the smallest degree—I shall show myself inflexible. Therefore, at the present time, when so much dancing can be seen—for there is dancing everywhere, it is quite dreadful, if you live in a town any night you join in a dance evening—when there is show-dancing everywhere, if it should be thought (I do not say all this without good reason; although I do not specify any particular instance, I have good reason to speak) if it should be thought that by giving public performances of Eurythmy, we meant to identify ourselves with any kind of journalistic stunt to put forward some kind of claim for attention, then I should take precautions against this in the most determined manner. A feeling for what is in good taste must be forthcoming solely out of our cause. You see my dear friends, we have sometimes also to remember, especially on meeting again, to conduct according to the standard of spiritual impulses the necessary direct activity resulting from the will. These spiritual impulses will have to fight against a great deal of what today we can no longer call prejudice, for things work too powerfully be described by such a weak term. I do not say in a conceited, egoistical way “We” have to fight, but these impulses will have to fight against many different things. Now over and over again we have to refer to the terrible malady of our age, that consists in lack of control where the life of thinking is concerned. For, rightly conceived, the life of thought is already a spiritual life. It is because men give so little heed to their life of thinking that they seldom find their way into the spiritual worlds. There is one thing upon which I must repeatedly touch from the most varied sides, namely, what an appalling value is put today upon the mere content of thoughts. The content of thoughts, however, is what is of least importance! The content of thoughts—Look! a grain of wheat is a grain of wheat, this cannot be gainsaid. Even though a grain of wheat is a grain of wheat, however, when you put it into suitable, good, fruitful ground you get a juicy ear, and when you, put it into ground that is barren and stony, you get either nothing at all or a rotten ear. But each time you are dealing with a grain of wheat. Let us speak of something other than a grain of wheat. Let us say instead of ‘grain of wheat ’, ‘idea of free man’ which is so much discussed today. Some will say ‘idea of free man’ is the ‘idea of free man.’ It is just the same as a grain of wheat is a grain of wheat. But there is a difference in whether ‘idea of free man’ flourishes in a heart, in soul where this heart and soul is fruitful ground, or whether the ‘idea of free man’, exactly the same idea with the same foundation, flourishes in Woodrow Wilson's head! It matters not in the least if a grain of wheat is sown in stony ground or right into the rock, and it is just true that all the so called beautiful ideas that we are given in the programmes of Woodrow Wilson signify nothing if they come out of his head. But this is something that modern man comes to understand with such infinite difficulty, for he holds the view that it is the content of a programme, the content of the idea, has as little significance as the germinating power of a grain of wheat before it is planted in fertile ground. To think with reality! Man has the greatest need of this. And something else is connected with the present unreality in thinking namely, men are taken unawares by almost all that happens. Indeed one might ask when has that not occurred in these last years?. Men are surprised by everything, and they will go on being more and more surprised. But they will not have anything to do with what is really working in the world, and this today makes it impossible for them to bring any foresight to bear on their affairs. Working merely with ideas, one can from any side base anything upon anything. If one works with the content of ideas alone it is actually possible to base everything on anything. This is also something it is necessary to see into increasingly and ever more deeply; it is necessary but there is little will for it. Generally, when such things are spoken of, and examples of them given, one meets with no real response because the examples seem too grotesque. But our whole life of soul and spirit today fairly hums with these things that give so grotesque an impression on being brought to light—my dear friends, they buzz around us! I know that many of you may feel resentment if I give you a really outstanding idea as an example—I will, however, quote this instance. Now it is a case here of a University professor, an old respected professor at a university, who lit on the fact that Goethe during his long life was attracted by various women. Yes, our professor came up against this idea and took upon himself the task of making a real study of both the life of Goethe and that of the spirits connected with him. And we see how he obviously makes it his business, in spite of not being professor at a European university, to go to work as thoroughly as a mid-European professor usually does, and he made to pass before his soul the whole procession of Goethe's ladies in their relation to Goethe. What did he discover? I can quote this for you almost in his very words. He discovered that each woman Goethe loved momentarily during his life can be said to have been for him a kind of Belgium, the neutrality of which he violated and then bemoaned that his heart bled for having been obliged to assail shining innocence. Neither did he forget to assert, each time, like the German Chancellor, that this sphere of violated neutrality had deserved a better fate but that he, Goethe, could not do otherwise since his destiny and the rights of his spiritual life obliged him to sacrifice the loved one—yes, even to offer up the pain of his very heart on the altar of the duty he owed to his own immortal ego. Now I could give you here many other ideas that come in this book. You might ask for, what purpose? But, my dear friends, there is very good reason. For you find this kind of idea all over the world. The ideas of modern men are like that! And it is not without reason that such ideas should show themselves in literature where the essence of human thinking appears. This conception is upheld by Santayana, a professor at Harvard University in America, a much esteemed Spaniard who is, however, completely Americanised. His book was written during this present catastrophe, or at least Boutroux has translated it into French during the war. Shortly before this Boutroux gave a lecture in Heidelberg in which he eulogised German Philosophy in the most flattering terms! The book is called The Errors of German Philosophy and is entirely characteristic of present-day thinking. The appearance of this book was certainly not just a casual event but is very characteristic of modern thought and compares man with what is very far removed from him, with the same facility we find in Professor Santayana when he compares Belgian neutrality with Goethe's treatment of various women. For, if you have eyes to see it, this kind of thinking meets you in every sphere of so-called modern science. It is a fact; you come across it everywhere. Now it is just the task of the spiritual impulse to which our Anthroposophy is devoted, to make a stand against three fundamental evils in the present so-called culture of mankind. There is nothing for it but to fight against these fundamental evils. One fundamental evil shows itself in the sphere of thinking, another in the sphere of feeling and the third fundamental evil is seen in the sphere of the will. In the sphere of thinking we have gradually reached the point where men can only think in the way the thinking takes its course when it is strictly bound up with the brain. But this thinking, so closely connected with the brain, this thinking that refuses to make a flight to the spiritual, is condemned in all circumstances to be narrow and confined. And the most significant symptom of present scientific thinking in particular is narrowness and limitation. In the field of his narrowness and limitation great things can certainly be done. It is done for example, in modern science. But the thought applied to science today has no need of genius, my dear friends! Thus, narrowness, limitation, is what must be striven against, especially in the intellectual sphere. Today I will simply give these things in outline, but later we shall be describing them more in detail. In the sphere of feeling it is a question of men having gradually arrived at a certain philistinism—we can only call it so—philistinism, lack of generosity, and being bound to a certain confined circle. It is the chief characteristic mark of the philistine that he is incapable of being interested in the big affairs of the world. Village pump politicians are always philistines. Naturally, in the sphere of Spiritual Science this does not suffice, for here one cannot confine oneself to a narrow circle, we have to be interested in what is outside the earth, therefore in a very wide circle indeed. And people get quite annoyed at the mere suggestion that there should be a desire to know something about a circle wide enough to embrace Moon, Sun, Saturn. In all spheres, however, philistinism must soften into non-philistinism if Spiritual Science is to penetrate. Sometimes that is not convenient or comfortable, for it means facing up unreservedly to the matter. It demands a more unprejudiced facing up to the matter. Recently an awkward thing happened in our midst—but I stopped it because otherwise perhaps—well, nothing actually happened but something could have happened. Now you will remember the Zurich lectures of last fear; among various examples I gave then of how Darwinism can be overcome through the growth of natural science itself, I pointed to the excellent book by Oskar Hertwig called Des Werden der Organismen (How Organisms come into Being). Here, and every time the opportunity occurred, I referred to this excellent book. Very soon after this work a shorter book appeared by this same Oskar Hertwig, in which the same Oskar Hertwig spoke about the social, the ethical and the political life. And I then thought to myself: it may happen that some of our members having heard me call Oskar Hertwig's book about organisms an outstanding book will assume that this second volume is excellent also, when it is actually a worthless book, a book written by a man who in this particular sphere—in the sphere of the social life, the ethical life and the political life—cannot put into shape a single orderly thought. I feared lest certain of our members might already have judged that since it came from Hertwig this book too would have some kind of merit. So I had to step in and again whenever I could seize the opportunity I availed myself of it to point out that I considered this second book of the author, who had previously written so well about natural science, to be the worthless and foolish effort of a man who had no ability to speak of the things of which he spoke here. Our Spiritual Science does not admit of one thing conveniently following from another, without each new fact being confronted and judged impartially. Spiritual Science demands from men actual proof of the concrete nature of every single case. Philistinism is something that will vanish when the impulse of Spiritual Science spreads. So much for the sphere of feeling. And in the sphere of the will there is something that recently has particularly and in the widest sense taken hold of mankind, something I can only term lack of skill. As a rule, a man today is very able within the narrow circle of what he learns, but he is considerably inept about everything outside this circle. One comes across people who can't even sew on a button—that is only one example. There are men who are unable to sew on a button! Lack of skill in anything beyond a narrow circle is what is specially prevalent in the sphere of the will. Whoever takes what we call Spiritual Science with his whole soul, and not just with abstract thinking, will see that it makes a man more dexterous and fits him actually to spread his interest over a wider area, to extend his will over a wider world. Naturally it is just where this lack of skill is concerned that spiritual science is still too weak; but the more intensively we take it the more will it contend with unskillfulness. This is what confronts the present-day acceptance of Spiritual Science with what might be called a trinity: narrowness in the intellectual sphere; philistinism, which means a lack of generosity, in the sphere of feeling; unskillfulness in the sphere of will. And the three are loved nowadays even if loved unconsciously. Nothing in the world today is more loved than unskillfulness, philistinism and narrow-mindedness. Because they are loved it will not be easy for men to progress to the wide views to which they must come—to the way in which we must look at all that is connected with the names Ahriman and Lucifer. And it is just here that something important must understood today. For today among many other things there is an important transition from the luciferic to the ahrimanic. And as this transition is shown not simply elsewhere but also here in Switzerland one may well speak of it here. In this region the first has perhaps less significance owing to the very habits of the Swiss. The second, however, shows every prospect of attaining more importance precisely in this country. Where certain things are concerned mankind is indeed in a state of transition from faults that are luciferic to those that are ahrimanic, from luciferic impulses that run counter to human development to ahrimanic counter-impulses. Now certain impulses of earlier days holding good in educational matters were of a thoroughly luciferic nature. Ambition and vanity were counted on in educational matters. (All of us when young, with the exception of the youngest among us, have known this quite well.) Perhaps this applies less to Switzerland but elsewhere it is pretty prevalent—this reckoning on ambition and vanity—orders, titles, and so on and so forth! Some people's whole career was based on the luciferic impulses of vanity and ambition, on the being worth more than other men. Just try to think back to how educational affairs were indeed built up on such luciferic impulses. At the present time there is an endeavour to put ahrimanic impulses in the place of those that are luciferic. Today they hide themselves behind the elegant term “ability tests”. In the ahrimanic sphere this corresponds to what in the luciferic sphere was boasting about vanity and ambition even among children. Today there is an endeavour to seek out those the most gifted, or those who apart from that are most successful in class; out of these again individuals are taken. Among these gifted ones tests are made, intelligence tests, memory tests, perception tests and so on. This is something very suited to the Swiss disposition. And should the luciferic play a very small part here, the ahrimanic shows itself nicely in bud in the understanding for these ability tests. For these ability tests proceed from the intelligence, from science, from the present-day psychology of the learned. Then these gifted ones who are to be tested are made to sit down and are given the written words: murdered, looking-glass, the murderer's victim. And they sit there, poor lambs, in front of the three words murderer, looking-glass, the murderer's victim, and are supposed to look for a connecting link between them. One child finds that the murderer steals upon his victim, but the victim has a looking-glass in which the murderer is reflected so that the victim is able to save himself. So much for the first child. His gift of perception takes him as far as connecting the three words in this way. Now comes another:—A murderer is creeping on his victim and sees himself in a looking-glass. His face appears to him in it as the face of somebody with a bad conscience, so he leaves his victim on account of seeing the reflection of his own face. That is the second child. The third child makes yet another combination. A murderer comes creeping, he finds a mirror and falls against it so that the mirror falls down with a terrible noise, it makes a regular disturbance. The victim hears the noise and is in time to defend himself against the murderer. The last child is the most talented! The first only found the nearest combination of ideas; the second an obvious matter of morals; the third child found a very complicated connection of ideas, and this one is the most talented!—That is more or less how it is. When describing things briefly one naturally gives them a little colouring of one's own. But this is how the ability of children is henceforward going to be tested to find out who is the most talented. One thing is certain, my dear friends—if the men who invent these methods would just think of the great people they revere, Helmholtz for instance, and so on, Newton and so on, these great ones would one and all, if given these tests, have been looked upon as the most untalented little rascals. Nothing would have come of it. For Helmholtz who is certainly considered by those who give these tests today as a very great physicist—as I think you will agree—was a hydrocephalic and not at all gifted in his youth, and so on and so forth. What is it that people want to test? Simply the outer organism, entirely what may be counted as the physical instrument of man, what is purely ahrimanic in human nature. If ever the fruits of these ability tests are to come to anything, more ghastly thought-pictures will arise than those that have led to the present human catastrophe. When, however, one speaks today about anything that may lead to catastrophic events in perhaps a hundred years, this does not interest man. For we live now in this transition from a luciferic educational system to an educational system that is ahrimanic; and we must belong to those who understand how to see clearly into such matters: Men must change what is active force for the future into forces of the present. For this is what is demanded from us today—to confront concrete reality in a true, genuine, unprejudiced way. Here one may have very strange experiences. I do not remember if I have already mentioned here a very interesting experience of mine. There are writings of Woodrow Wilson's—one about “Freedom”, another just called “Literature”. These writings have been very much admired—are still very much admired. In the publication called “Literature” an interesting lecture appears again which Woodrow Wilson once gave about the historical evolution of America. And elsewhere, too, interesting lectures by Woodrow Wilson have been repeated having wide historic standpoints. And reading these writings I had an interesting experience. In them one finds isolated sentences which appeared to me extraordinarily familiar yet certainly not copied from anywhere—certainly not copied they nevertheless seemed to me wonderfully familiar. And the idea soon struck me that these sentences of Woodrow Wilson's might just well have been written by Herman Grimm, that quite a number of these sentences indeed are found word for word in Grimm. Herman Grimm I love; Woodrow Wilson—Well, you know by now that I do not exactly love him! Nevertheless I cannot on that account conceal the objective fact that where the content of the subject is concerned one could simply take over whole sentences from Herman Grimm's lectures and articles and transpose them into those of Wilson—and, vice versa, transpose sentences of Wilson's into the works of Herman Grimm. Here are two people who as far as the actual text is concerned are saying just the same thing. We have, however, to learn today that when two people say the same thing it is not the same! For the interesting fact meets us that Herman Grimm's sentences are personally striven for, bit by bit they are wrenched from the soul. The sentences of Woodrow Wilson that sound so similar come from a kind of characteristic frenzy. The man is possessed by a subconscious ego forcing these sentences into the conscious life. Whoever can judge of such things realises that this is the point here! A grain of wheat is a grain of wheat: The difference, however, lies in where it is sown, in what kind of soil. There is a difference in whether an idea becomes so much part of a personality because he has striven for it bit by bit in his own particular way, or whether one gets the idea by being possessed by the subconscious, everything sounding out of a possessed subconscious, out of a consciousness that is possessed by the subconscious. Thus it is a question today of understanding that the content of thoughts, the content of programmes, are not of importance—the important thing is the livingness of the life lived by mankind. My dear friends! We can teach materialistic philosophy, we can teach the philosophy of mere ideas; we can teach a science that is merely materialistic, and in this merely materialistic science become a most excellent European teacher, a credit to the university and a good citizen of the State. The type is not so rare, I fancy you can find them anywhere, these ornaments and lights of science, who at the same time are quite exemplary good citizens; one can well be this, my dear friends! But take some ideas, I should say an idea of a definite kind, let us take as a trivial idea the struggle for existence, for instance, or those ideas that are advocated by more peaceable people such as Oskar Hertwig, and so on, or ideas upheld by Spencer, Mill, Boutroux or Bergson who certainly are not wishing to press forward to the spiritual life, but are confined to the philosophy of mere ideas. But still more, take the materialistic ideas of science, take these ideas! It is true they might be able to spring up in the brain of the good subjects of the State. Very well. But, my dear friends, a grain of wheat is a grain of wheat; nevertheless it makes a difference whether it grows in soil that is fertile for it or in rocky soil, and it makes a difference whether these scientific ideas which can be striven for in Europe as a credit to science, and hold good in the universities, thrive in the brains of the university students, or whether they spring up in the brain of a man whose brother already as a young man at the end of the eighties was counted a shining light in science at the Petersburg laboratory... Such facts certainly like a flash of lightning illumine things that are working at the present time! Take this young man who was there in the Petersburg laboratory about the year already a shining light in science, full of productive ideas in chemistry with a medal—a very rare thing—distinguished by this special medal from all those working with him, and highly esteemed even as a young man—and suddenly he disappears! Even marked out by the university authorities—he is suddenly no longer there! In all manner of roundabout ways his colleagues have to find out that meanwhile he has been hanged for taking part in a conspiracy against the reactionary Alexander III. It makes a difference whether the same idea enters the brain of a worthy university professor of Western Europe, or the brain of the brother of the man who was hanged under such conditions. When it enters the brain of this brother it changes this brother into a Lenin—for the hanged mans brother is Lenin—then this idea becomes the driving force behind all that you now see in Eastern Europe. Idea is idea, as grain of wheat is grain of wheat; one has, however, to realise whether something is the same idea that arises either in the brain of a university professor or in the brain of the brother of this man they hanged. We must have the will to see into the background of existence where lie the actual impulses behind events. And we must have the courage to reject all the empty nonsense about programmes, ideas, sciences, of those who believe in them. Something depends on what they uphold. This or that may be upheld according to its content, nevertheless it is of consequence in what sphere of actual life what is thus upheld lies, just as it is of consequence where the grain of wheat falls, whether in fertile or unfertile ground. In every sphere man must find the way out of the abstraction that in the present grave conditions is everywhere leading to illusion or to chaos; he must find the way to the reality that can be found in spirituality alone! And however long it be, this is the only road by which man can find his way out of the present confusion to what can bless and heal him. This is what should be written on our hearts, my dear friends, something in which we can all be united. this is something with which we should greet each other in earnest, associating ourselves in this knowledge with what must be the cure for man's failings. For it is possible to cure them. But, my dear friends, this may not be done with quack remedies, they must be healed by something the lack of which has brought mankind into this chaos. Leninism would never have taken hold of the East had not materialistic science—not always recognised as such—been taught in the West. For what has been produced in the East is the direct child of materialistic science. It is just a child of materialistic science. Through Karl Marx a changeling has arisen; the real child of materialistic science already exists in the East. But we must have the will really to see into these things. This, my dear friends, is as it were the background against which our building is being erected. And individual men who work here at this building think about it quite apart from the ideas today affecting men in so many lands. We can well imagine that outside, in other countries, there may be people who consider that men are living here who keep aloof from what concerns the world and, as these people believe, should concern it. It is easy to imagine people looking reproachfully at this place. Those who have their whole heart and soul in this building need not worry themselves about being thus reproached. For even if this building does not perhaps fulfil its task, if it never reaches its goal, what works on the building, my dear friends, and what proceeds from those working with devotion on the building, is today the most important thing of all; it is what must rescue men from everything into which they have fallen. And when people outside believe that here men are working with no thought for the task of present-day mankind, the answer must be that here we are working on what is of supreme importance today, on what is preeminently essential, only others know nothing of it, it is something of which as yet they are ignorant. But the important point is that mankind will want to know something of what is happening here. Once again let it be emphasised. It is not important whether this building attains its goal—although it would be good were it to do so. What is important is that this building should be worked upon out of certain ideas that men have discovered for this work. It is not the content of these ideas but the way in which they live that gives them their impulses for the future, whereas the ideas so many believe in today are simply and solely ideas that incline towards the grave, ideas of a former age which are passing into dissolution and are ripe for dissolution. |
| 183. Occult Psychology: Lecture II
18 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 183. Occult Psychology: Lecture II
18 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Today I should like to start by giving a kind of sketch of the human soul, as this human soul stands in relation to the world and to itself. I should like to give this sketch in such a way that it can be said: we are looking at the profile of man as a soul being. So that we understand ourselves just as if we were to look at the physical man—not the soul-being (see Head in diagram 1)—not perhaps seeing him full-face but, let us say, from the right in profile. Let us observe him thus. If we try to sketch in outline anything like this we must naturally always keep in mind that we have to do with imaginative knowledge, that the reality behind the matter therefore is being given in picture form. The picture refers to the matter and is given, too, in such a way that it correctly indicates the matter. Naturally, however, we may not have the same idea of a drawing, a sketch, meant to represent something of a soul and spirit nature as we do of anything that in a naturalistic way is copied from an external perceptible reality. One must be conscious all the time of what I am now saying. I shall therefore omit all that concerns the physical and lower etheric organism of man and try to sketch only what is soul—soul-and-spirit (see diagram 2). As you know from the various descriptions that have been given, the soul-and-spirit stands in a more direct connection with the world of soul-and-spirit than physical man stands in connection with his physical environment. Towards his physical perceptible environment physical man is rather an isolated being; one might even say that physical man of the senses is really shut up within his actual skin. It is not so where what can be called the men of soul-and-spirit is concerned. There we have to think of a continual crossing of the currents pulsating in the inner depths of man's soul-and-spirit—of all the movements and currents existing in the general, universal world of soul-and-spirit. If I want first of all to describe from the one side the kind of relation the human soul-and-spirit has to what is of soul-and-spirit in the cosmic environment, I should have perhaps to do it in this way. I should, first of all, have to paint what enters in a soul-spiritual way from the universal, from the infinity of space, like this. Naturally I should have to paint the whole space in a way... but that is not really necessary. I shall only paint man's immediate environment. Thus it is now what we may understand as the surrounding world. (see blue in diagram 2). Now imagine in this picture form of the soul-spiritual that into which man is placed. Man indeed is not yet there, but indicated in this blue is only the edge of the environment. Imagine this like a surging blue sea filling space. (When I say ‘blue’ sea this must naturally be taken as I have often described it in books available to you, namely, colours are to be grasped in the description of the aura, of the soul-spiritual.) Borne like a wave, swimming, I might say, or hovering, so nothing else is borne up which is of soul-and-spirit. This is what I should now have to represent perhaps in the following way. Thus, if we pass from the cosmic environment to man, we may be able to think of ourselves and what belongs to the human spirit-and-soul as perhaps hovering in this red.   There we should have first of all part of the soul-spiritual; and if we would make the sketch in accordance with reality it is only the upper part we should have to give in a kind of violet, in lilac graduating into red. This could only be given correctly by toning down the red into violet. Thus, you see, with this I have given you first what might be called the one pole of man's spirit-and-soul nature. We get the other pole when we can perhaps incorporate in the following way what, adjoining the universal soul-spiritual here, is swimming and hovering towards the human physical face: yellow, green, orange; green running into the blue.  Here you get from the right side what I might call the side view of the normal aura of man. I say expressly a normal aura seen from the right side. What is presented to the view in this figure shows how man is placed into his environment of soul-and-spirit. But t also describes where man, the soul-and-spirit in man, stands in relation to itself. When everything represented by this figure is studied, it can clearly be seen how man is a being bounded an two sides. These two sides where man has his limits are always observed in life; but they are not indicated correctly nor considered in the right way—at least they are not understood. You know how in external science it is said that when man observes the world, when with his science he wishes to gain knowledge of the world, he comes to definite limits. We have often spoken of these limits, of the famous ignorabimus (“we shall never know”) which holds good with scientists and many philosophers. It is said that man comes indeed to certain limits in his cognition, in his conception, of the external world. I have certainly already quoted to you du Bois-Reymond's famous statement that in his seventieth year he made to the Scientific Congress in Leipzig; Human cognition will never penetrate into the regions haunted by matter—this is roughly what he said at the time. Perhaps the more correct way of speaking about the limits to human knowledge would be the following. In observing the world it is necessary for man to hold fast certain concepts which he penetrates neither with his scientific cognition nor with his ordinary philosophical cognition, we need only consider such concepts as that of the atom. The atom, however naturally has meaning only when we cannot actually speak of it, when we cannot say what it is. For the moment we were to begin describing the atom, it would no—longer be an atom. It is simply something unapproachable. And it is thus already matter, actual substance. Certain concepts have to be maintained that can never be approached. It is the same with knowledge of the external world; inaccessible concepts like matter, force and so on, must be maintained. That they should have to be maintained, depends here simply upon the inner light of man's soul-and-spirit stretching out into the darkness. What is stated to be the limit of knowledge can, I might say, actually be seen clearly in the aura. Here lies a boundary in front of man. His being, what he himself is, is here represented in the aura by what I nave made run from bright green into blue violet (see diagram 2). But by passing over into blue-violet it leaves off being man and becomes the encircling cosmos. There with his being, which is the inner force of his world outlook, man comes to a boundary; there in a sense he reaches nothingness and he has to hold fast to concepts having no content—concepts such as matter, atom, substance, force. This lies in the human organization, it lies in man's connection with the whole cosmos. Man's connection with the whole cosmos actually stands out in front of him. If we describe this boundary in accordance with the ideas of spiritual science, we can do so by saying (diagram 3): this boundary allows man with his soul to come into contact with the universe. If we indicate the direction of the universe in one loop of a lemniscate we can with the other loop show what belongs to man, only what proceeds from man goes out into the universe, into the infinite. Therefore we must make the line of the loop, the lemniscate, open on one side, closed on the other, and draw it like this—here the line of the loop is closed and here it goes out into infinity. It is the same line that I drew there, only here the arm goes out at this end into infinity (see diagram 4 of lemniscate open to the outside). What I have here drawn as an open lemniscate, as an open loop, is not just something thought out, but something you can actually look upon as flashing in and out of a gentle, very slow movement as the expression of man's relation to the universe. The currents of the universe continually approach man; he draws them towards him, they become intermingled in his vicinity and proceed outward again. Thus this kind of thing streams towards man, interweaves and then goes out again; man is permeated by these currents belonging to the universe, which stop short in front of him.  As you may imagine, through this man is surrounded by a kind of wave-like aura; these currents enter from the universe, form a whirlpool here, and by making this whirlpool in front of him, as it were, salute man. So that here he is surrounded by a kind of auric stream. This is essentially an expression of man's relation to the cosmos, to the surrounding world of soul-and-spirit. You can, however, find all that you actually experience as lying in your consciousness represented here as a mixture of blue, green and yellow running into orange towards the inside. But that pushes up against here; within the soul part of man this yellow-orange collides with what waves on the blue sea as the soul-and-spirit of the lower man, of the man below. What I have shown here in red passing into orange, belongs to the subconscious part of man, and corresponds to those processes in the physical that take place principally in the activity of the digestion and so forth, where consciousness plays no part. What is connected with the consciousness would be described, where the aura is concerned, in the bright parts that I have applied here. (see diagram 2) Just as here the soul-spiritual of man meets the soul-spiritual of the surrounding world, so what is within man as his soul and spirit meets his subconscious—that actually also belongs to the universe. I shall have to draw this meeting of the currents so that one of the streams goes out into the infinite; within man I must draw this meeting differently. Here I must also draw a loop line but this must be done so that it runs towards the inside. Now please notice that I am keeping entirely to a looped line but I take the under loop and turn it around so that it goes thus (diagram 6).    Thus, I turn the lower loop around. In contrast to the above diagram 5, where I have made one loop run out to infinity, widen out into the infinite, I now turn back the lower loop; with this I have shown diagrammatically the obstacles, dams, that arise where the spirit and soul here in the inside enter the subconscious spirit-and-soul and therefore also that of the cosmos. I must therefore describe these obstacles if I draw them as corresponding to what arises in man, in the following way; seven lemniscates with turned back loops—those are the obstacles that correspond to an inner wave in man (diagram 7). If you wish actually to follow up this inner wave, its main direction—but only its main direction—would perhaps take the course of running along beside the junction of man's wrongly named but so-called sensory and motor nerves. This is only said by the way for today I am going to describe the matter chiefly in its soul-spiritual aspect. By this you can see the strong contrast existing in man's relation to the spirit and soul environment and to himself, namely, to that bit he takes in out of the spirit-soul environment as his subconscious, and what I have had to sketch as the red wave swimming on the universal blue sea of the spirit-soul universe. We said that this wave here (see right of diagram 2) corresponds to the barrier against which man pushes if he wishes to know about the external world. But there is a limit here too (see left of diagram 2); within men himself there is a barrier. Did this limit, this barrier, not exist you would always be looking down into what is within you, my dear friends. Everyone would look within himself. In the same way that man would look into the external world were the barrier (on the right) not there, if the boundary on the left were not present he would look into himself. If man looked into himself in this present cycle of evolution this would indeed give him little joy, because what he would see there would be a most imperfect, chaotic seething upheaval in man's inner nature—something that certainly could not arouse joy in him. It is, however, that into which imaginative mystics believe they are able to link when they speak of the mysticism that is full of fantasy. All that the mystics of fantasy very largely look upon as a goal worthy of their striving, what, particularly in the case of many such mystics who really believe that in looking within themselves they are able to learn about the universe, what figures with them as mysticism—all that is concealed, entirely concealed, from men by just this dam.1 Man cannot look into himself. what is formed inside this region (left) is dammed up and reflected, it can t be reflected back into itself; and the expression of this, reflection is memory—remembrance. Every time a thought or an impression that you have received comes back in memory it does so because this damming process begins to work. If you had not this stemming wave, every impression received from outside, every thought you grasp and which permeates you, would be unable to remain with you and would go out into the rest of the soul-spiritual universe. It is only because you have this obstructing wave that you can preserve the impressions you receive. Through certain processes still to be described you are in a position to call back your impressions. And this is expressed in the functioning of recollection, of memory. You can therefore picture to yourself that you have in you something that here in this diagram is drawn in profile (for so it is drawn; there is in you just such a flat surface); There we find thrown back what should not penetrate. When you are awake you remain united with the external world, otherwise in the waking condition everything would go through you. You would actually know nothing of impressions; you would nave impressions but be unable to keep them. This is what memory signifies. And the surface of this dam that brings about our memory conceals what the imaginative mystic would like to look at, within himself. One could say of what is underneath that for those who really know these things, the saying holds good that man should never be curious to see what the beneficent Godhead has covered with night and obscurity, but the mystics are fantastic and wish to look down into it. All the same, they cannot do so, however, for they would so bore into and destroy the normal consciousness that the waves of memory would not be thrown back. All that produces our memory, all that is so necessary for external life, conceals from us what the fantastic mystic would like to see but men should not look upon. Beneath recollection, beneath what causes recollection, beneath the surface of recollection, lies an essential part of man. Just like the back of a mirror, the mercury being a mirror, what is in front, what is thus in your consciousness works; it does not go inside but is thrown back and is therefore able to continue there as memory. In this way our whole life is reflected as a memory. And what we call the life of our ego is essentially reflection in memory. Thus you see that we actually live our conscious life between this wave (right of Diagram 2) and this other wave (left). We should be mere funnels, therefore, letting everything flow through us; had we not this dam as the basis of memory, and we should see into the secrets beyond our boundary of knowledge were we not obliged to place ourselves outside the sphere of perceptible concepts for which we have no content. We should be funnels were we not so organised that we could not produce this dam, organised so that we should not be obliged to set up before us concepts as it were without a content, obscure concepts, we should become loveless beings, empty of love, with dry, stony natures. Nothing, in the world would please us and we should be so many Mephistopheles. Because we are organised so that we are unable to approach what is of soul-and-spirit in our environment with our abstract concepts, with our intellectual powers—to this we owe our capacity to love. For we are not meant to approach what we should love by analysing it in the ordinary sense of the term, nor by tearing it to pieces and treating it as chemicals are treated by the chemist in a laboratory. We do not love when we analyse like a chemist or synthesise chemically. The power of memory, the capacity to love—these are two capacities that correspond at the same time to two boundaries of human nature. The boundary towards within, corresponds to the power of memory; what lies beyond the memory zone is the subconscious within man. The other zone corresponds to the power of love, and whet lies beyond this zone corresponds to what is of the nature of soul-and-spirit in the universe. The unconscious part of man's nature lies beyond this zone as far as what is within man reaches; the soul-spiritual of the universe goes out boundlessly from the other zone into the wide space. We can therefore speak of the zone of love and the zone of memory and can include man's soul-and-spirit in these zones. We must however seek beyond the one zone above (see right of diagram 2) whet is unconscious, and because it remains unconscious is on that account very closely connected with the bodily nature of man, with his bodily organisation. Naturally things are not in reality so simple as they must be in any representation, because everything is interwoven. What is red here (diagram 2) runs into things and is changed; again, what is green and blue is also changed. Actually, things all intermix with one another: in spite of this, however, the sketch is correct in the main and corresponds with the facts. But from this we see that for physical life here on earth the spiritual is both strong and conscious. Here (left) the spiritual that actually merges into the universe is unconscious. These two parts of man are very clearly differentiated. The spiritual here (in the middle) is for this reason above all for earthly life a very finely woven spiritual element. Everything here (yellow) is what might be called finely woven light. Were I obliged to show where this finely woven light is in man, I should have to go to what I have been so minutely describing—the human head. What I have thus described, what I have sketched in yellow, yellow-green, yellow-orange, on the other side, is what I might cell the finely woven spirit light. This has no very strong connection with earthly matter; it has as little connection with earthly matter as is possible. And because it has so little connection it cannot well unite with matter, and thus, for the greater part, remains unconnected with it; to this part matter is given that actually always comes from time to time from man's previous incarnation, and there is but a loose connection between this finely woven soul-spiritual element and what belongs to the body, what has actually been held together out of the foregoing incarnation. Your physiognomy, in its arrangement and characteristics, you carry over, my dear friends, from your previous incarnation. And those who are thoroughly able to explain man actually look through the physiognomy of the head; not through what has its origin in the luciferic within men, but more through the manner in which he adapts himself to the universe. The physiognomy must be looked upon as though it were stamped into man, not to the extent of being the product of this stamping, but rather one has to see in it the negative of the soul; it is this that is seen in the negative of the face. If you were to make an impression of any face you would actually see there the physiognomy that relentlessly betrays what has been made of the last incarnation. On the other hand, all that I have sketched down there as being only connected with the surging sea of the world of soul and spirit, all that is to be understood as corresponding to man's subconscious or unconscious, is closely related to the bodily nature; it permeates the bodily nature. The bodily nature is united with the spiritual in such a way that the spiritual is wholly incapable of appearing as such. For this reason were we to look down we should see this seething and merging of the spiritual and the bodily behind the threshold of memory. It is this that pares the head of the next incarnation and seeks to transform what will take definite material form only in the future and will not become head until the next incarnation. For man's head is something that outstrips his stage of development. The head in its development therefore—as you may remember from lectures previously held here—has actually come to an end by man's twenty-seventh, twenty-eighth year. (See NSL 122-123 Historical Necessity and Free Will and R-LII Ancient Myths and Their Meaning). In the form of the head there is already our development of man. But, strange as it may seem, the rest of man is also a head only it is not so far advanced as the other head. If you picture to yourself a decapitated man, what remains is another head but at a more primitive stage. When further developed it become head, whereas what you have as the human head is the rest of the organism of a previous incarnation. If you picture what in your present organism is discarnated, free of the body, if you think away the head of your present organism, the organism that will become head in the next incarnation (and this organism is but an image, everything physical being an image of something spiritual), if you imagine the spiritual element of what in its external form has not yet appeared in man, then you see this in the Group in our luciferic figure—there you have it! Now imagine compressed into the human head all the soul-spiritual that is merged into man, and held back in you from the head, all that forms a barrier, that is to say, which man cannot penetrate (see right in diagram 2); then man will not have the old dignified head that he ordinarily has; he will have a bony head, and will be altogether bony, like the figure of Ahriman in our Group. (see Der Baugedanke des Goetheanum.) What I have here been explaining to you has not only great significance for understanding man, but also great significance for understanding what is going on spiritually in mankind's evolution. If we have not a fundamental comprehension of these things we shall never understand how Christianity and the Christ-impulse have entered human evolution. Neither shall we understand what part is played by the Catholic Church, what part is played by the Jesuits and similar currents, what functions belong to the East, what to the West, if all this cannot be considered in connection with these things. I shall take upon myself to tell you something of these currents tomorrow, currents such as those of East and West, Jesuitism, and the tendency to put everything into terms of mathematics, which really can only be rightly understood if we take into consideration what lies at the basis of soul-spiritual man.
|
| 183. Occult Psychology: Lecture III
19 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 183. Occult Psychology: Lecture III
19 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Yesterday I was at pains to give you a picture of man as a being of soul. Vast in connection with this picture of man as soul we want particularly to deal with today is to be the two boundary zones we learned about yesterday. The one boundary zone is seen in how man is obliged to come to a halt when he tries to look through the external world as it appears to him perceptibly. Scientists, philosophers, then speak of boundaries to knowledge. We know that these boundaries to knowledge do not in truth exist, but that in actual fact they are present for man's physical sense-perception. The other boundary is the result of everything found in our consciousness, or entering into consciousness, being mirrored back, reflected back, on to an inner zone and, by this reflection, being enabled to become memory. What we have in consciousness does not go right into the depths of the region that lies in man's subconsciousness. We will draw these two boundaries the boundary of memory (left) and what we might at once refer to as the boundary of the capacity for love (right) which is at the same time the of our knowledge of nature. We have indicated this in the lemniscates we drew which are open to the outside (see diagram 8) and we had here to draw lemniscates with the loop turned crack towards the inside. This is the external region therefore into which man can no longer look with his ordinary powers of sense-perception—this, it is imperceptible. And there underneath is the inwardly directed boundary of conscious life, into which man cannot descend with his consciousness. He remains with his consciousness above this limit. Should he dive down with his conscious conceptions he would have no memory. 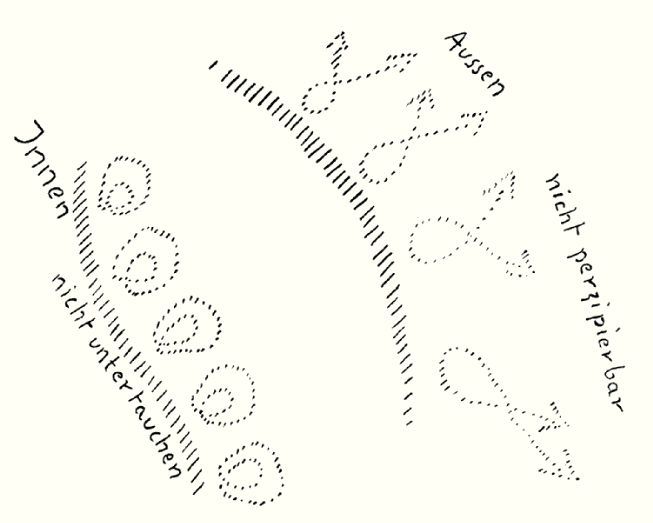 Now in connection with these two boundaries there is something quite definite to be said about this very life of the man of soul. If we go back in human evolution, go back perhaps farther than the eighth pre-Christian century (you remember that the year 747 begins the fourth post-Atlantean epoch), if we go back beyond this point of time into the earlier post-Atlantean epochs, then whet lies beyond this boundary was to a certain degree accessible to the human consciousness into which it worked. The atavistic clairvoyance still existing at that time rested indeed upon this. Certain impulses from the cosmos came through in those days and made themselves felt as atavistic powers of vision. We could therefore say that what is here outside us first became increasingly impenetrable—I mean intellectually impenetrable—after the eighth century before Christ. We are living now in the fifth post-Atlantean epoch, and it is still impenetrable. And people are knocking at the boundary today, quite extraordinarily while continuing to maintain that no one is able to penetrate to the thing—call it how you will—lying beyond this boundary. It may be said on the other hand that another tendency makes itself increasingly felt, and will make itself still more felt as the sixth post-Atlantean epoch approaches—the zone here(left) will become penetrable. The time will come when out of the depths of human nature whet I described to you yesterday as something seething, into which man should not look (above all should not look in the sense of what the imaginative, the fantastic, mystic wants), out of this sphere from the sixth post-Atlantean epoch onwards all manner of things will seep through. This time indeed will begin before the end of the fifth post-Atlantean epoch—our epoch; all kinds of things will want to leak through. This will show itself above all in far more people than we think today understanding from purely inner experience that there are repeated lives on earth, and things of that kind. One may say that already today these things are breaking through, though not very often. I have frequently mentioned the name here of a remarkable man of the present day—Otto Weininger (Das Rätsel des Mensch {The Riddle of Man} - Lecture 1, not translated)—who is particularly well known by reason of his book Geschlecht und Charakter [Race and Character]. But still more interesting is his book published after his death by his friend Rappaport, in which all kinds of most interesting things appear. These are mostly aphorisms, and the whole bears the title Über die letzten Dinge (About ultimate questions), the greater part of it being aphorisms. One of these aphorisms is approximately to this effect—Weininger maintains that the human soul during life before birth might have developed a certain dread of itself and because of this have longed to forget this life and bury itself in oblivion—which means incarnating. Thus Weininger expressly talks of pre-earthly life and of incarnating, only he speaks in a gloomy, pessimistic way of how the soul seeks to bemuse itself about its life before birth, and seeks this oblivion through incarnation in a physical human body. Many such direct impressions are received by present-day can concerning the path of the soul and they will become ever more numerous. One can already see in such a man as Weininger how today the ego is lying hold of man inwardly in what I may call a more solid and compact way; one can already see very clearly in Weininger's case how this boundary is becoming as it were penetrable, and all manner of things are pressing through. What he has written down about his death, for instance, is interesting. In his early years, when only twenty-three, he committed suicide. He made a whole series of notes which are extraordinarily interesting because they exactly represent Imaginations seen in the astral. All this is in accordance with a certain trend of character that led him to take Beethoven's room in Vienna one day and then the next day to kill himself—at the age of twenty-three. And it was all noted now he would be driven to suicide because otherwise he might become haunted by the fear of a vague impulse urging him on to murder and he would have to kill someone else. It can be seen how most terrible things are here making their presence felt in the soul of an extraordinarily gifted man who cannot act in accordance with the dictates of his consciousness because so much rises up from his subconscious. You will understand that one is in certain way justified in showing how the ordinary cleverness that man is now able to develop does not extend to knowledge of what arises from the unexplored depths. For it should not arise: it should remain, nevertheless it will arise. Just as, up to the year 747, something came in from outside, henceforward something will rise up from within. What man attains through his ordinary normal cleverness will not be able—will in fact be far from able—to overcome this. For what is here is the understanding of the wor1d acquired through Spiritual Science. It is possible for harmony, inner firmness and inner dignity, to permeate man's life of soul only when there is the desire to order and harmonise this life of soul through what can be acquired by working for knowledge of the spirit. In his development man is striving towards a condition where more will spring up out of his innermost depths than is the normal case today. The things of which I am speaking now were actually quite well known in the various centres of Initiation. The whole of eastern spiritual life, the whole life of the spirit in Asia, is still redolent of that ancient knowledge which was accessible to man up to the eighth century before Christ. Indeed it is not only the spiritual life in Asia that tells of it. Fundamentally it is Asiatic culture as a whole. This it is that makes it so difficult for a European to understand what is said by an oriental about the civilisation of the East. If we would understand these people it is necessary indeed for us to have different conceptions and to form our thoughts differently. For example, it must be very interesting for many people today to consider anything so characteristic as the address about the spirit of Japan given by the Indian, Rabindranath Tagore. (Tagore as you know is the Indian author who has been awarded the Nobel prize for literature). He gave a lecture about the spirit of Japan. What he said about the spirit of Japan is of less moment than the spirit out of which he spoke, the spirit of the oriental today, which can be understood only when we know how in the oriental something still remains of that rising-up and that coming-in—no longer perceptible to the external world. When speaking to most Europeans in the spirit of the spirit of their civilisation men of the East are really almost unintelligible. Usually there is no understanding whatever for what they are saying. And we also have this other phenomenon—that what actually should only arise in the future can be experienced in a way in advance. I might compare this with children who as children have the characteristics of old age; they assume these characteristics when quite young. Irregularity enters evolution when something is thrust into it that should only come later. Whereas in oriental thinking, in oriental conceptions, even in the most outstanding spirits there rules, as I have shown, what is left over from a previous age, there is dominant in the spirits who think in accordance especially with what is American, something that is to enter later, something is introduced which belongs to a later time. If one can go deeply into such matters it is clearly distinguishable that the most outstanding minds receive a great deal that seeps through here (left). You get an idea of what thus seeps through if you read, for example, the address given by Woodrow Wilson concerning the evolution of the American people, in particular the North American people. One cannot imagine anything more to the point nor more apt than this lecture of Woodrow Wilson's about the evolution of the American people! Every word of it gives the feeling that the whole matter is characterised and dealt with in the most shrewd manner. And this is particularly surprising since in this case, Wilson emphasises how a great number even of Americans hold the view that is justified only if one considers the American people as still being a dependency of the English—which is certainly not Wilson's opinion. Woodrow Wilson is most definitely in opposition to those who look upon the Americans as originating in—being a branch of—the English in Europe, and consider that they do not at all understand the actual evolution of the American people during the nineteenth century. And Wilson speaks right out of the spirit of America, most pregnantly and to the point, when he says that Americans first begin to oe Americans at the moment when they sever the links binding their souls to what proceeds from England, and start blazing their trail from East to West, from the eastern coast of America to its western coast. In this trekking through the primeval forest, in the work with pickaxe and spade, in the labour with horse and plough, in overcoming all obstacles on the road from east to west, there developed what he calls the western man. And in a way that is direct and convincing Wilson sees in this manner of conquering the ground, the actual nerve of American evolution. In all this one has the definite feeling—the "how" must be understood here, not merely the "what"—the feeling that in all this something greater is speaking than Wilson. For when Wilson himself speaks—well, what is said is not very clever; it sounds much more as though the man were speaking out of whet lived within him as a kind of possession; demonic natures speak, giving out indeed grandiose secrets of the future, secrets that would have to be penetrated by man for himto understand evolution. Today a real distinction has to be made between the understanding of the world that is scientific and in accordance with time—an understanding that is easy and universally popular—and the true understanding of the world. This true understanding of the world must be able to recognise such contrasting things as I have here been discussing, namely, the entering in of something from the peoples of the east that lies there outside (see right of diagram 8) and the arising of something from the American people that lies here (left). And what arises here is not necessarily something to be looked down upon, in a certain sense it can be a majestic ahrimanic, manifestation. For it is essentially an ahrimanic manifestation which is given in this excellent utterance of Woodrow Wilson's upon the evolution of the American people. The initiates of the East and the initiates of the American people know what it is necessary to make of these things. There is the will absolutely to guide the evolution of mankind from both directions into a certain course. The eastern peoples, that is to say their initiates, have quite definite views for the future evolution of mankind. These people see what is right for evolution and, as far as it lies in man's power, seek to influence this right evolution. They try to give it a definite direction, a definite impulse. And the impulse that the initiates of the East wish to give to evolution rests essentially upon man no longer reclining on human generation after the first half of the sixth post-Atlantean epoch. After this time it will be sought to renounce the earthly human race. The desire will be to bring human evolution to the point when man no longer returns to a physical body, when souls are so spiritualised that they do not descend to earth any more in bodily form. From the middle of the sixth post-Atlantean epoch man will already be seeking to found for himself the Kingdom of the spirit. This would be possible only were certain ingredients of culture rejected. It is not only the initiates of the East who feel a decided aversion to certain European characteristics but every cultured oriental instinctively feels it also—he feels an aversion for just those characteristics on which the European particularly prides himself. For example, he has no use for the purely technical, material culture which has arisen both in Europe and in its off-shoot America. Those who study man's evolution, particularly in the nineteenth century and on into the twentieth, find they have to admit that technics has carried things very far, that technics has deprived man of his power for work. When it is said today that the earth has so and so many hundred millions of inhabitants, this is not, actually entirely correct, for it can also be reckoned how many inhabitants the earth has according to how much work is done. Now we are perfectly justified in saying that since the last third of the eighteenth century man's power of labour has been fixed by the machines that have been increasingly produced. It can be reckoned, and reckoned pretty exactly, how many millions more men would have to be apportioned to the earth if all the work produced by machines were to be produced by men. The earth would have to have 500,000,000 more men. It can indeed be said that the earth today has not so many men if they are to be counted according to their two legs and their head, but according to labour power the earth has 500,000,000 more men; machines do duty as labour-power. But, my dear friends, there is nothing material that has not behind it what is spiritual. These 500,000,000 human forces are the opportunity for the same number of ahrimanic demons to take up their abode in human culture! These ahrimanic demons are certainly there. And the man of the East instinctively turns right away from these ahrimanic demons, and will have nothing to do with them. You see this in every manifestation of a highly culture oriental; he turns from this ahrimanic demonology. For this ahrimanic demonology weighs men down, weighs them down and deprives them of the possibility to bring about the aim of oriental initiation, namely, the end of the human race on earth from the middle of the sixth post-Atlantean epoch. This will be held back by what is developed in this demoniacal ahrimanic way. American initiates are striving towards another goal; they strive towards the opposite goal. They endeavour to form a more inner bond than is normal in the course of man's evolution between the human soul and that bodily nature that is to be found upon earth, the dense, coarse corporeality which from the sixth post-Atlantean epoch on, will be found on earth. The culture of the soul will be deepened, what is of a bodily nature will coarsen. A more inward connection with this bodily nature then is normal is, however, striven for in the least, in America, a more intensive descent into the body. Man will go towards what seeps through, will approach it by an intensive penetration into what is of the body. Whereas the Orientals wish to found a culture that takes no account of the human body, in the future earthly evolution, in the American culture of the West there will be an endeavor to chain the soul to the future evolution of the earth. There is a desire so to form the body that when souls have passed through the gate of death, they will be able to return as quickly as possible into a body and spend as short a time as possible from sojourning in the spiritual world and there will be the desire to return to earth as soon as possible, to be as closely united as possible with earthly life. These are tendencies that must be recognised, my dear friends. Strange as it may seem to man today when one speaks of such tendencies, it will all the same be harmful to him should they happen. For it is necessary for man to take his stand consciously where he himself is concerned, in what is sought after, and in connection with which he is, unfortunately, often placed in a position to justify the remark that he lets just anything happen to him. This western ideal, however, to give man over to demonology, will be possible only should the American tendency, this soul and spirit tendency in America, receive the support of another stream of world-outlook far more closely connected with that of America then is recognised. The most striking feature of the American tendency, as you have seen, is essentially its leaning towards an ahrimanic culture. But this American characteristic would be increased were it supported by another world conception, and the relation between the two is closer than is supposed. I refer to Jesuitism. The outlook of the Jesuits and that of the Americans are very closely related. For at the beginning of the fifth post-Atlantic epoch it was a question of an impulse having been found in which man was placed in a position to be lead as far as possible from the understanding of Christ. And the endeavor in cultural development that took on the task of obliterating the understanding of Christ, of completely eradicating all understanding of Christ, this is Jesuitism. Jesuitism strives gradually to root out every possibility of understanding the Christ. For what lies at the bottom of this is indeed closely connected with a deep mystery. Now, with man's ability always to receive within him what came from without, was connected as I have told you, his old atavistic clairvoyance, possessed by him before the seventh, eighth century of the Christian era; moreover with this atavistic clairvoyance men perceived Christ in the cosmos. The Christ was something that could be seen with ancient clairvoyance. I have often pointed this out. I have pointed it out in Occult Science, and the whole meaning of my book Christianity as Mystical Fact ultimately centres in this. Christ was seen in the cosmos; Christ was seen in the universe. But think now from the seventh, eighth pre-Christian century we men have been losing the possibility of seeing into the universe. What then would men have lost had nothing else arrived but this possibility of knowing anything about a Christ spirit at all had not the Christ come to them through the Mystery of Golgotha, had not Christ descended to earth. In the historic moment of time when man was no longer able to see Christ in the cosmos, Christ came down to earth and united Himself with Jesus. From then it has been man's task to apprehend the Christ within man. We have to save the possibility of recognising the Christ by what seeps through here (see right of diagram 8). For Christ descended to mankind; Jesus is a man in whom lived the Christ. Real knowledge of the human self must bear the seed of Jesus—through which man will be able to move on into the future. There is deep meaning when we speak of a Christ-Jesus. For the Christ corresponds with what is cosmic; but what is thus cosmic has come down to earth and has dwelt in the Jesus. And Jesus corresponds with what is of the earth, with the whole of the future of the earth. (see From Jesus to Christ) If there is a desire for man to be cut off from the spiritual he will also be severed from the Christ. And then the possibility arises to make use of the Jesus in such a way that the earthly aspect of the earth alone remains. You will therefore find in the Christology of the Jesuits a continual fight, a strong emphasis on there being a host, an army to fight for Jesus. Yes, indeed it is natural that Spiritual Science should be the means for making these things known, and for removing the scales from men's eyes! For this reason some who wish to remain unknown become increasingly angry about the aims of Spiritual Science; one sees this growing anger—the July number of the Jesuits publication Voices of the Times contains not only one article against me but two at the same time. And those who can put this in connection with what is now developing elsewhere among the Jesuits will be able to see something deeper in all this. Today, however, one speaks of these things unfortunately to men who are asleep. Where the most important things are concerned men like to sleep through them and to close their ears to what is now actually determining the future. As I said the day before yesterday, everything will come upon men as a surprise. They will have it thus. When at the earliest possible moment one speaks of the things lying in the womb of time, men look upon it as something upsetting. For they are worthy members of the bourgeoisie who would like, as long as they can, to sit comfortably in their easy chairs, even if they have responsibilities as leaders of their fellow men. Those, however, who are interested in Spiritual Science should have it engraved on their souls that everything will be done to make Spiritual Science ineffective. Above all, it is not good when we within our circle are too fast asleep where what is going on in the world is concerned. Sometimes it is hard to see all that is particularly important and essential at the present time, namely, watching the way in which the great affairs of mankind are gradually developing. You see, my dear friends, what starts great impulses of will really comes from various sources which are to be taken seriously. Such an impulse as the one I have referred to, for example, is indeed to be taken in a certain more serious sense. We must be able to give it its right value. Naturally in this connection we need not take those nice little attacks seriously that are constantly rising up from what is sub-earthly in our Society, attacks that look rather bad simply because there is so frequently a noticeable tendency for people to sympathise greatly with those who seek maliciously to slander what is striven for earnestly in our midst. When the harm is actually done gradually people decide to open their eyes; up to now several people have been made much of who afterwards caused harm. I am not saying this because I think this or that ought to be different, but because I really feel it my duty to draw attention, my dear friends, to the necessity for men to wake up, and above all of the necessity for joining those who are striving for the truth. In certain spheres today we can do everything within out power. But what I refer to as man's sleep which can be overcome only by his penetrating into the spiritual world, this sleep of man is extraordinarily difficult to surmount. And in connection with spreading the knowledge of Spiritual Science this sleep can be as great an obstacle as an opponent. I will not dwell on any particular instance of this, but in all our culture at present there is something of a sleepy nature about the very impulses everywhere sprouting above men's heads. Two things are necessary, my dear friends, two things that like golden rules must be engraved upon our souls. Never was there more necessity than in our fifth post-Atlantean epoch for men to exert themselves more and more to attain what is of particular value, namely, the understanding of what is known as Spiritual Science. For there is no doubt that there are men able to do this. It is certainly a necessity for the knowledge of Spiritual Science to be sought by seeing into the spiritual world clairvoyantly. It goes without saying that there must be clairvoyants to penetrate into the spiritual world, that there must be those who strive after supersensible knowledge. This is, first, something obvious and, secondly, something that is not so important as for people to find the intellectual power to understand the matter, where the knowledge of Spiritual Science, is concerned. Today it is particularly necessary to have a reasoning, intellectual grasp of Spiritual Science, for it is this by which the opposing cultural powers can be overcome. Man's intellect today is so great that if the desire is only there the whole of Spiritual Science can be understood. And to strive for just this understanding is not an egoistic cultural interest but one that is universal and human. For this understanding can be our goal when those intellectual forces applied today in scientific spheres on all kinds of pedantry, when those intellectual forces applied so fruitlessly in the modern economic sphere and, finally, those forces used in soul-destroying technics—when all these forces will be suitably applied and men are no longer misguided from their earliest childhood. Then will be seen how easily spiritual gifts of the spirit can be brought to the understanding of the human being! This is one side. The other golden rule is this—that we men today need some tiling more in our culture for the gifts of the spirit to become fruitful. The first is something that must be wrested from Ahriman. Men today are very clever, Ahriman sees to it that men should be clever—oh, men are clever! But they apply their cleverness only to what is of material interest. Men are not merely clever, they are more than clever. We shall speak more of this in our next lectures for you to recognise what an enormous influence this ahrimanic element has at the present time upon human super-cleverness, but there is something else necessary. There is much still to be wrested from another spirit. We do not need only cleverness with which to permeate our gifts of the spirit, but above all we need most urgently—how shall I express it?—we need in the human soul receiving these gifts of the spirit, feeling, enthusiasm, fire, warmth. We have need of men who approach what they receive from the spirit with their whole undivided soul. In the spiritual sphere this is just what must be wrested from the luciferic forces which are so active in the world in other ways! There is a lovely vista, my dear friends, it is a picture of someone who quietly, clearly accepting knowledge of the spirit can produce within himself, because it is a necessity for him, a glow of inner fire and enthusiasm. There is another picture—this is one of seeking to receive spiritual knowledge as if it were a lullaby to make us dreamy, to let warmth pour into us, to enable us to go out into universal forces and unite ourselves with the divine all. These are contrasting pictures which present-day man may do well to contemplate, which it is necessary for him to contemplate. For it will not be easy for us to incorporate into human culture what we receive from the spirit. And it must be incorporated, for man has need of it. Man will not only have to learn to think very differently, he will also have to learn to feel and experience in quite another way! I might, it is true, add a great deal more to what I have just been saying, but perhaps it will better to stop now, to give you the chance for reflection. There is much that can be reflected upon in what has been suggested by certain malicious incidents I have intentionally introduced into the truths that have just been spoken. |
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture I
24 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture I
24 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Should anyone wish to understand the age in which he is actually living, he must do so out of wider cosmic connections. The pettiness of this age lies in man refusing, out of these wider connections, to enlighten himself about the impulses, the forces, working into the present time. And to understand what is working anywhere nowadays it will become increasingly necessary to hark back to the conditions through which mankind's development passed at the time of the Mystery of Golgotha—this Mystery of Golgotha—we have presented it from the most various points of view, and have seen how deeply and with what significance it has taken hold of the whole course of evolution, the whole evolution of man. We know how differently men perceived and experienced before and after the Mystery of Golgotha. Naturally one condition did not pass over immediately into the other. But when we make a retrospective survey, we discover what has been stated from so many points of view. Today, so that a certain basis may be made for our further studies, there is one thing to which I should particularly like to point. If we consider the mood, the condition of man's soul, before the Mystery of Golgotha, we can say in general that in the culture of mankind, the mankind from whom the present cultural life has arisen, a certain capacity existed in the soul to look into the secrets of the cosmic, spiritual world. Before the Mystery of Golgotha it went without saying that men did not look up to the starry heavens in the way they do today. We know how men now look at the stars and say: other planets are connected with our earth and with it revolve around the sun, and there are innumerable other fixed stars also having their planets. And if men notice what kind of thoughts they are harboring in these reflections they have to own that they are thinking of a great world machinery. Present day man has very little idea that anything beyond the forces of this great world machinery is ruling and working; but for man before the Mystery of Golgotha this was more or less self-evident. It was particularly natural for him to regard the Sun, for example, quite differently from the way in which the modern physicist regards it—roughly speaking, simply as a kind of glowing ball in universal space. Before the Mystery of Golgotha men knew that the Sun thus spoken of in physics is only one element of the whole Sun, at the basis of which lies what is of the soul and what is of the spirit. And the Spiritual lying at the Sun's basis the wise men of Greece called the universal good of the world, the goodness of the world, the unity, the good seething through the universe. That was to him the spirit of the Sun. To this Greek sage it would have seemed crass superstition to think as the modern physicist thinks—that there outside in universal space a mere glowing ball is floating. To him this glowing, floating ball was the manifestation of unified goodness, the active centre of the world. With this central good that is of a spiritual nature there was united what was of a soul nature called by the Greeks Helios. Then, third, there came the physical expression of the Good and of Helios, the physical Sun. Thus, where the Sun is, the man of that day saw what was threefold. And with this three foldness then seen in the Sun, the men who were thinking at the time of the Mystery of Golgotha, prepared as the were by their knowledge of this Mystery of Golgotha, and also of the ancient mysteries—united the threefold Sun-mystery of the sages with the Christ Mystery, with the Mystery of Golgotha itself. For those who knew, veneration of the Sun was one with veneration of the Christ; for them the Sun-wisdom was united with the Christ-wisdom. To feel all this in accordance with nature, to experience it as a matter of course, it was necessary to have the constitution of soul existing at that time. But this constitution of soul vanished. It was already vanishing by the eight pre-Christian century, beginning in the year 747 before the Mystery of Golgotha—747 the actual date of the Foundation of Rome. At the time of the Foundation of Rome the old possibility was vanishing of seeing the spiritual outside in the Cosmos, and as Rome enters history, what we may call the ‘prosaic element' comes into human evolution. The Greeks, for instance, preserved in the whole of their world-conception the power of seeing the other two Suns behind the Sun—the soul and the spirit of the Sun—and only because the Mystery of Golgotha did not descend purely into the wisdom and perception of Greece, but into the wisdom and perception of Rome, has it happened that knowledge of the connection of Christ with the spiritual Sun has been cut off. Thus the Christian gathers and Teachers of the Church have had particularly to concern themselves with shrouding the Mystery of the Sun, making mankind forget this mystery, not allowing it to become known. Throughout the further course of the development of Christianity (as it is called) a veil was destined to be spread over the deep, the significant and all-embracing wisdom of Christ's connection with Sun-Mystery.1 Should we wish to define the task of the Church, the Church that owed its origin to Christianity having come down into all that was Roman, we should have to say that this Christian Church, colored as it was by Rome, had the particular task of shrouding as far as possible the Christ-Mystery, as far as possible keeping people in ignorance of it. The organisation the Church experienced through Romanism was especially suited to keep men as far as possible from knowledge of the Christ-Mystery. By this, the Church has become an institution for holding back the mystery of Christ, an institution for admitting the world as little as it could to the Christ-Mystery. This is something that today must become ever clearer to mankind, for the age must begin that is in the position to work with other concepts than those of Rome. Roman concepts are precisely those that have the hard outlines, the hard form of the corpse. The concepts that are developed to grasp, for example, the truth about man, as I drew him on the blackboard for you a week ago, in what I might call his normal aura, the concepts necessary for man's true reality to be grasped again and through that the reality of the world, these concepts must be flexible, they should not have sharp outlines. For reality is not rigid, it is something that is becoming. And should we want to understand reality with our concepts and ideas, we have with these to pursue the flow, the becoming of reality. When this fluidity of the concept is ignored there arises what to the undoing of mankind can be observed today in countless places. Take a phenomenon that forces itself on the attention of any observer of the world who is wide awake and in earnest. It is as follows: you will allow it to be true that we have among us in the world men of learning in the most various spheres. These learned ones are the champions, the keepers of knowledge. Although modern man is not a believer in authority, in spite of having rid the world of such superstition, he takes on trust everything upheld in the various spheres by the learned. And these among themselves, always believe their brethren concerning a matter outside their own sphere. Men today do not willingly see into these connections for should they do so they would be shocked at the disconnected and chaotic nature of our culture. We have, however, experienced the following, for example. Let us suppose some learned man—and we can always pick one out of the various spheres has for his particular sphere, let us say, Egyptology—I will take something exotic, so let it be Egyptology. So, we will agree that his profession is to instruct other men, unable to avail themselves of the sources of such knowledge, concerning the particular qualities of the Egyptian people. He gives these men instruction also concerning the relations of the Egyptians to other peoples of antiquity. It is the part of these men to take all this on trust for the instructor is an authority on Egyptology. Now something most unfortunate is a feature of our age—a great number of these learned men who represent such special subjects have not remained silent. It would have been better had they kept silence but this they have not done; for instance, they have today applied their way of thinking, their thought structure, under the impression of these events to their own people and its relation to other peoples. Here we have a good opportunity of seeing what nonsense is talked. Now from this we have to draw our conclusions, and conclusions founded on reality in thought. We may say that quite a number who are authorities in the domain of Egyptology, and are thought to hold incontestable concepts in regard to the particular qualities of the Egyptian people and their relations to other peoples, now, suddenly at the present time, are talking utter nonsense about their own people and the relation of these to other folk: Do you really believe that they are talking, have talked, more intelligently about the Egyptians and their relations to other peoples? When Balfour speaks today about the relation of his people to the rest of the world, or when Houston Stewart Chamberlain is continually uttering rubbish about the connections between men, one can gather without much reflection that they are simply talking nonsense—pure nonsense: And now Chamberlain has written The Foundation of Culture in the Nineteenth Century, and a number of other books for which there has not been the opportunity to verify the history. In these he will naturally have talked exactly the same nonsense. Already now the time of testing has come, the time of trial, when we have at last to see that it is not a matter simply of delivering judgment that only has limited value by being right in a certain sphere—that is true of almost every judgment, the most false is right in some particular—but what matters is to seek for that flexible, fluid judgment that presses on to the reality, and only through spiritual science can that be found. How remarkable it is what conflict today comes to the surface between sound thinking and the thinking of the times. Recently we have heard of a religious discussion that has taken place in what was St. Petersburg. A religious discussion right in the midst of Bolshevism: About a religion and its development there spoke Socialists, Priests of the Greek Church, and it goes without saying, all kinds of bourgeois folk who naturally were not the most intelligent of the speakers. And from the discussion that was carried on there—which was of course tinged with modern colour, but throughout had recourse to the most rigid and ancient concepts—from this discussion, as it appears, it was possible to learn much. For instance, one Priest brought forward something of the greatest interest. He felt himself obliged, it seems, to speak as he was accustomed to address his flock. Now formerly he had naturally told his flock that everything in the world—including Czarism, of course and indeed everything—was from God. And what can this good Priest do now? Naturally he still has somehow to follow the same theme that he used in speaking to his flock—no longer now his flock—for he has no wish to take on new concepts. So he says: The world is from God, all comes from God. As we now have Soviet rule that is from God too. Bolshevism is certainly sent man by God. Since everything is from God, Bolshevism as well must come from Him.—What else was he to say? I am quite sure that the deduction could be pressed further; why should it not be made beautifully plausible that the devil is from God? Naturally the devil is appointed by God—according to the same deduction. This is how things are—by getting deeper light on what is necessity, it is natural that one should meet on all sides with the strongest opposition. But no one can go to sleep who has undertaken to play a part in the remodeling of man's powers of conception. Now concepts worked out by materialism—concepts that pass current as being incontestable belong to all that must be most thoroughly overcome. Nothing meets us with more persistence from the so-called authority of science than what is known as the law of the conservation of energy and of matter, of force and of substance. That has grown very near to man's heart. It is true, is it not, that the world conception that has become entirely mechanistic and physical, wants to be deaf in face of the actual presence of the spirit. As it refuses to recognise the spirit it cannot ascribe to it either duration or eternity so it ascribes eternity to its little idol, the atom, or anyhow to some matter or force. But the truth is, my dear friends, that of all that is extended around you as what you can look upon with your senses, what surrounds you in the world as matter and forces—of all this in accordance with normal laws there will be nothing left by the time of the Venus age. We know that after the Earth evolution there follows that of Jupiter, after the Jupiter evolution that of Venus, and then that of Vulcan. As man finds himself again in different incarnations, so the earth finds itself as Jupiter, from the Jupiter evolution as Venus and then again as Vulcan. What today from any experiment in physics is found as matter and the structure of matter, will not be there after the Venus existence. There is no conservation of matter and force, the matter and force of which physicists speak, beyond the existence of Venus. The whole law of the conservation of matter and of force is pure superstition, and is something by which all concepts in physics are governed. Something is concealed, however, when the world is spoken of as consisting of indestructible matter that is continuously being submitted to different grouping, different arrangement. And what is thus concealed is the answer to the question: what then remains of all that is so widely spread out before our senses when this is no longer there—when the Venus age has come or when it is already half way through its term? What then remains? Where is there anything? What is still there? Now, my dear friends, direct your gaze outside into the vast circumference that you can see. Look at everything, look at the whole of the kingdoms of mineral, plant, animal and man; look at all you can see in the way of stars, light-phenomena; see what happens in air and water; look wherever you like, include everything that can possibly be included in your external sense perceptions—then ask yourselves: Where is anything in which there will remain a vestige of our present existence? And the answer is: In no animal, in no plant, in no mineral, not in any air, or any water—nowhere but in man: Of what you see today man himself alone contains anything that in accordance with law continues beyond the Venus existence—Nowhere else can you seek anything permanent, anything that can be referred to by the concept of eternity—nowhere save in man. That is to say, if we are looking for the seeds of the real future of the world where have we to seek? We must seek them in man. We cannot look for them in any other creation or any other kingdom. But before the Mystery of Golgotha, men of old naturally in spirit—saw through the kingdoms the cosmic All. If we take the representative, the Sun, they saw a glowing ball, but through the glowing ball they saw Helios and the Good. Nevertheless this glowing sphere of the Sun will not exist beyond the Venus age; it will then disappear. And everything through which man, in ancient times, saw in a veiled way, the constituents of some spiritual existence will also disappear. And of all that is here now there will remain for the future only what is planted seedwise into man. What then has actually happened? Before the Mystery of Golgotha men used to look out into the wide Cosmos; they saw stars upon stars, they saw Sun and Moon, air and water, the various kingdoms. But they did not see them in the same way as modern man, for they saw them all with the divine spiritual being behind. And behind all that, they saw the Christ who had not then descended to earth. In those olden times Christ was seen to be united with the cosmos; he was seen outside the earth. There is nothing in which Christ was thus seen that will last beyond the Venus age. Everything through which the spiritual and also Christ in the cosmos were revealed to man before the Mystery of Golgotha will last only to the Venus existence. Before the Mystery of Golgotha men lived with the heavens, but these heavens are so physical that they too will vanish with the Venus existence. What will last longer than that has its seed in man alone. The Christ had to come to man out of the cosmos if He wished to tread with man the path to eternity. Because all that I have described to you is so, Christ descended from the cosmos in order henceforth to be with what as seed in man, will last on into eternity. That is the great cosmic event that must be understood. Before the Mystery of Golgotha men could worship the God, the Christ, in the cosmos. Since the Mystery of Golgotha the time has come when the seed for the eternal future of the world is increasingly only in man; and the men who were to come after had to have a Christ who is not outside in the cosmos which will disintegrate, but be united with man, united with the human organisation, with the human kingdom. It is literally true that what are there for the senses in the whole wide circumference as stars, as heavenly bodies, will pass away.2 But the word will remain, the Logos, who has appeared in the Christ and is united with the eternal essential being of man. And this is literally true, as things in the real occult, religious primal record are literal truth. That is also the reason why a double name has to be given—I have already given indications of this—the double name Christ-Jesus. It must not be forgotten that on the one hand we must recognise the Christ who belongs to the cosmos beyond the earth, the spiritual being who before the mystery of Golgotha was not bound up with man on earth. Then He descended and united Himself with human nature—with the Jesus. In the twofold name Christ-Jesus there lies what it is necessary to understand. In the Christ we have to see the cosmic, the spiritual; in Jesus we must see that through which this cosmic, spiritual being entered historic evolution, binding Himself to mankind in such a way that He can now live on with the seed of man into eternity. And as the centuries flowed on it was the task of the Church to conceal, to misrepresent, this mystery of Christ which was connected with the ancient mysteries. Just try really to study what during all those early centuries was passed through by man, try to see clearly how it was with the individual man who really wanted to seek Christ-Jesus, who really wanted to find the path to Him—it was a long path of martyrdom. Christ-Jesus had always to be sought in defiance of convention—as even today he must be sought against the stream of those conventions that still persist. One cannot, however, come near the Christ-Mystery if one does not connect it with the mystery of nature. For you see what we have placed before our souls, namely, the necessity for the descent of Christ from cosmic heights to the seed in man, the mystery of Christ becoming Jesus, can be understood only when the study of nature, the study of the world, cosmology, the knowledge of man's becoming, and of the divine in man—when all these form a unity. In a certain sphere it is sought to prevent natural science becoming at the same time spiritual science, or spiritual science becoming natural science. That is what most theologians try to do, and, in another domain, what most modern physicists try to do—to erect a barrier between physical science, on the one side, spiritual science on the other. On no account must anything be said about Christ-Jesus that is connected at the same time with the evolution of the earth; nor anything be said about earth-evolution, that is, about its details, that is connected with the great spiritual mystery. Touching on these things, one actually touches on what is of most importance, of supreme importance in the life of modern man. For confused chatter about all kinds of spiritual things, that has indeed been brought to one's attention by our friends, brought to one's attention ad nauseam—this sort of confused chatter profits no one. I am referring to how constantly people come to one saying: Just listen: So and so has been speaking quite theosophically—or anthroposophically he has said such and such a thing: This facile looking around for support in the present confusion is not what we are meant to be striving for: we should stand on the firm ground that spiritual science will surely give us. The time is too grave for further compromise, particularly in this sphere. For to build the bridge between the knowledge of nature, that is, the knowledge of anything perceived, and the knowledge to which belong sin and redemption, in short, the religious truths—to set up a bridge between these two domains can be done only when man finds the courage really to penetrate to the spiritual. And what is more, should he not have this same courage he will never be able to discover reason where the truths of life are concerned. For penetrating spiritual reality we need above all the possibility of being able to in some measure look back to the threefold Sun-Mystery of olden days, to look back, however, in the new way suitable for present-day mankind. Precisely in the same way as the sun is a trinity so also is man. But it is important that we should really study this threefold man, and this study is of the utmost importance at the present time. Today I should like to give you diagrammatically something of a preparatory nature that can guide you to the path that must really be sought for the understanding of threefold man. Tomorrow and the day after we shall bring this important subject to a close. Just imagine the following. What I am now sketching is only meant as a diagram. (see diagram 1). Imagine you had a figure that was merely a picture, an image, having no meaning in itself, in fact an image. I shall draw it like this—in a simple circle (see blue in diagram 1) a circular surface, that is, a form that is the image of something else, but through being an image has entirely consumed that something, of which it is the image. It sounds strange when I say the following but just consider it. In our cupola, in the small cupola, four ladies are working. Let us suppose these four ladies—two on either side—paint their own portraits, and that this has a particular sequel. Imagine these four ladies painting their own pictures in the small cupola, portraying themselves there, imagine that this self-portraiture has a quite definite sequel—the ladies disappear, pass over into their image and cease to exist. Having completed their work they no longer are there. Through the coming into existence of their images they are no longer there. Behind what I have here sketched, picture to yourselves a figure like that, a figure that has originated through being made by something of which it is the image but this something being absorbed, sucked up by the existence of the image. Now what is thus absorbed is not alone in the world. Picture to yourselves that we have not finished with these four ladies. Very good; these four ladies have disappeared—they have painted their own portraits and disappeared but the pictures are still there. And they are not alone there in the cosmos, the cosmos is still there with its forces besides. The ladies have vanished and have been as it were sucked up by the pictures; but by the pictures being there substance is assembled again out of the cosmos and the ladies are built up anew, as children new, it is true, but new; they gradually grow up again, grow up near by. And so, by the side of this figure, its original image blossoms anew (see yellow in diagram). I must make a little addition to the drawing, put it by the side—this is the archetypal image. It is the archetype, the prototype, but there is a very loose connection between the image and its prototype, a very loose connection indeed. The one has almost nothing to do with the other. The image has definitely hardened and has almost lost all connection with its prototype. And now imagine a second figure. I will sketch the second figure so that I make it also as an image (see violet in centre diagram), only the first is inside the second. Thus I boldly draw the second over the first. This is again an image of the same kind. Again an image resembling another that I will draw here also (see red in diagram); but these have now to be more closely connected. Therefore, as the matter stands, I cannot use the same comparison as I did earlier with the four ladies, but now when I want to make a comparison with regard to this picture and its image I must say: The four ladies are there: they are painting in the small cupola, and as they paint something actually—goes out from them, is sucked out. They are, however, only half sucked out, and finally they are—no I will say something else that will not call up an inartistic comparison—from one the left half of the body is sucked up while the right projects out of the picture; from the other the right side is sucked out, the left still projecting. Thus they are partly sucked out and partly still jut out. That is the second.  Now picture a third that again embraces the first and also the second (see green in diagram.) This, however, is to a great extent connected with its image, not yet separated from it. So that if I want to keep strictly to the comparison I have to say: The ladies are painting, but they are still there as ladies, and everything I have before me as a whole is the ladies and their images—that is there (see orange in diagram) and the greatest part is also present in the prototype. So you have here drawn diagrammatically, first above, an image grown hard, crystallized, that has as little as possible to do with its prototype; the latter being by the side of it, newly arising. That is indeed your head, the most material and the hardest part of human nature. Its prototype has just nothing to do with it, arises afresh. And when you reach twenty-eight years of age, your head becomes so that out of itself nothing is forthcoming, nothing is to be developed. In the constitution of man the greatest materialist is the head. A second figure is breast and breathing and everything belonging to these. I could almost use the second as a model. That is rather more connected, spirit and matter depending more upon each other; here it is more permeated with spirit. All that is lung and breathing process is for the earth already more spiritual. And what remains, the limb system in connection with all that has to do with sex, there spiritual and physical are one, there they are still together. This belongs to the third diagram. And you have threefold man. Today I have been able to draw this only diagrammatically on the board. This majestic and profound mystery, at the same time wonderful and fearful, is connected with the Mystery of the threefold Sun. This again is connected with all the truths that we need, as we need the bread of life, for everything that must be put in place of what is chaos, what has reached a blind alley, and has led to the present human catastrophe. We shall speak of this further tomorrow.
|
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture II
25 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture II
25 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Yesterday I showed you threefold man diagrammatically. It is indeed true that in our present life of spirit very little feeling exists for the understanding of man's being as it must be grasped from the standpoint of spiritual science. Nevertheless, we must bestir ourselves to get a clearer understanding of man's being. For it is out of the understanding bound up with threefold man that we are able to master also the most significant conceptions that must be gained concerning the whole of human life, including man's development between death and a new birth. Today let me just consider in detail this threefold man. Yesterday indeed we saw how first of all we have to point to man's head. In a certain sense this human head is really a kind of independent form of being. You can picture to yourselves the human skeleton and how easily the head can be detached; it can be lifted off like a ball. It is true that in reality the separation between the three members of man's nature is not so simple that we can describe what can thus easily be lifted off like a ball as the head part. Things are not so definitely separated. We have gradually to work ourselves away from the purely diagrammatic away too, from what nature herself suggests, to a living feeling, a living experience And, as you saw, I had yesterday to draw not indeed three circles lying next each other, but one circle for the head, a second circle that overlapped the head, and a third circle that overlapped both the others. So that if we would draw threefold man diagrammatically in accordance with his physical nature, we should have to show him thus: Head part (see circle A in diagram 1; body (oval); and the limb-system; really three balls even if these balls have to be drawn out longwise. With the head part, with what is here shown as the red circle A, is connected the spiritual which is, as you saw yesterday, a young formation (see small yellow circle) This spiritual part of the head is a young spiritual formation whereas the head itself is an old physical formation, a physical form-being. For the head, what is applied to man in general is pre-eminently right; it is not right when applied thus in general but for the head it is right. What with regard to the head, I have shown here as white, spiritual, is outside the head when you are asleep. When you are awake it is united with the head and then for the most part inside the physical head. It is therefore separated most easily from the physical head, going out and coming back inside again.  That is certainly not so as soon as we come to the middle man, the breast man, shall we call him? What is enclosed by the thorax, by the breast cavity, enclosed by the ribs and the backbone, is bound up with the spiritual, and when you sleep the spiritual is not so pronouncedly outside; for this breast man during sleep it remains in close connection with the physical. And for the third man of the limb-system, to which sex man belongs, there is practically no real separation between the sleeping and waking conditions. One definitely cannot say that the soul-spiritual actually disconnects itself in sleep; it remains more or less united. So that one can well draw this other diagram of waking man saying: when physical man is awake (see a in diagram 1) then the spiritual man would be thus (yellow with circle a) And this would be sleeping man (see b diagram 1); the spiritual remains you see more or less connected with the body, and only this goes outside. From a certain standpoint this would be the actual drawing for the contrast between waking and sleeping man. Now if you are to understand the important things now to be described, you will only do so by crossing this membering of threefold man with another membering of man that is linked with what I was describing here recently. And if once more we go over head, breast man, man of the limb system, we can say that in the truest sense man is only breast-man. He it is into whom the Elohim breathed the breath of life. He is the breathing man. The division here is not so simple as in the skeleton; the breathing process through nose and mouth belongs to the breast man. Thus the partition in reality is not so easy, to show diagrammatically as one would wish. However these are the difficulties to be expected in understanding a matter of this kind. Thus the actual man, man on earth, is in a sense breast-man. And head-man, as physical form, is something that is not man through and through. It cannot be said that it is man all through. It even has in it much that is ahrimanic. In effect, it is organized as it is because certain formative principles are particularly present in it that have remained there since the old Sun—the second stage of earth-evolution. Our head, in all its complicated formation, would not be as it is had it not received its first form in those primeval days of the old Sun-evolution. Thus they are actually old, primeval formative principles today projected into the earth-sphere, and for this reason we must call them ahrimanic. Survivals of old principles are always to be looked upon according to the point of view as either ahrimanic or luciferic. The middle-man, the breast-man is what makes man of the earth, and where the principles of becoming earthly are mainly in play. Neither is the man of the limb-system wholly man, but is permeated by the luciferic; its formative principles are not yet complete in their development, and will not be so until the earth has reached its Venus stage, or till the Jupiter age is passing over into the Venus age. By the time the Venus age has come these formative principles will be working at their full intensity, in their correct form. (He might say that today they are still developing mere shadows of the real being of this third part of man's nature, the extremities-man.) Thus we presuppose what will only be in existence at the time of Venus, and make an incomplete picture of it in seed form, not letting it go beyond the seed form. This is how the matter stands when considered cosmically. To look cosmically at our formation, in our heats-forces we are repeating the old Sun-period, in our breast we carry the earth evolution, and in so far as we are extremity man we bear in us the seed of the Venus evolution. This is regarded from the cosmic point of view. Considered humanly—it is rather different. There we must look upon the human individuality as it progresses from incarnation to incarnation. Then we have to say: what in this incarnation we carry as our head, shows itself to be connected with our previous incarnation; what we now bear in us as breast-man is really only related to our present incarnation; what we have in us as as extremity man will become head in our next incarnation, is already related to our next incarnation. I have said previously: there is something revealing in the head especially in its negative. If you were to take an impression of the physiognomy of your head and consider it, you would recognise in this negative much of what had its origin in your previous incarnation.1 It is just the other way round with the extremities man. You cannot here take an impression but must proceed differently. Think away in man the head and the breast-system. But imagine all that your hands and legs do now—make a picture of what they do. Here you have to make a kind of map. You see, every time you do anything with your hands this is done at another place. They go around outside, they come into relation with other beings. If you would paint all that your hands and legs do, if you would draw a picture of what your hands and feet, arms and legs do in the course of your life—and this would be a very animated picture!—in this drawing you would discover a complicated map, where you would find revealed what is stored up in you karmically for your next incarnation. In this map you would be able to read a great deal of the karma of your next incarnation. This is of profound significance. As the negative impression of the physiognomy when at rest, reveals in the firm outlines of the drawing, what in the previous incarnation has already happened, so what one can jot down of the movements of arms, hands, legs and feet are extraordinarily instructive about what the man will do in his next incarnation. This is particularly instructive about what he will carry out, where he will go, where his legs will take him. If you simply follow in his track to all the places where his legs will carry him, you could make a map of it. You would get remarkable patterns on which men's secret inclinations are not without their influence. Much of man's secret inclinations are not without their influence. Much of man's secret inclination is expressed in these patterns. These traces that are there are most revealing for what his next incarnation will bring to a man. Now we have been considering this from the human point of view, whereas the other was a cosmic view. This membering of man that has the present in view signifies, however, a connection with the secrets of the old Mysteries, in which the matter was recognized in a more atavistic way, but where the secrets I have just been disclosing to you were already known. There is a beautiful saga concerning King Solomon about the certainty with which man sets his foot on the place where he is destined to meet his death. The meaning of the saga is that a definite place exists on earth where man will die, and thither man directs his footsteps.2 This is connected with the old Mystery-Knowledge. Now when man is living his ordinary life he has actually only his ordinary consciousness; but as we have seen this man is a highly complicated being. When he is awake, when he has his head, his most recent spiritual member, in his physical head, he knows nothing of this head. You will be right in saying: Thank God we do not know anything of our head for knowing of our head means to have a headache. Men only know about their head when it aches; then they are conscious of having a head, otherwise they are unconscious of it—unconscious to a most remarkable degree, far more so than in the case of any other member of the human physical body. Man may count himself lucky when in normal consciousness he knows nothing of his head. But beneath this consciousness of the head that ordinarily takes notice only of the outer world, that only gets as far as knowing what is around it—beneath this consciousness lies another, a kind of dream consciousness, dream-knowing. Your head, my dear friends, is always dreaming. And while you are conscious of the outer world in the way familiar to you, under the threshold of consciousness, in the subconscious, you are actually perpetually dreaming. And what you are dreaming, if you were able to bring this head dreaming into your consciousness and fully grasp it, would give you a picture, a correct comprehensive picture, of your previous incarnation. For in your head unconsciously, you are dreaming of your former incarnation. That is indeed so. There is always a slight consciousness of your previous incarnation going on, a dreaming consciousness, only it is overpowered by the strong light of of ordinary consciousness. By the year 747 before the Mystery of Golgotha, the external consciousness had become so strong that gradually this subconsciousness of the previous incarnation was completely extinguished. Before that year, however, man knew a great deal about this dream consciousness of the head. For this reason you find everywhere at the basis of the ancient cultures repeated lives on earth treated as a fact. This is due simply to the sub-consciousness of the head not then having receded so completely into the background as it did in the course of the fourth, but principally the fifth post-Atlantean age. Even in ordinary consciousness very little is known of what is connected in a soul-spiritual way with the thorax and the middleman. It is in itself of a dream nature. This middle, thorax consciousness sometimes pushes up into man's dream consciousness, but only very chaotically and irregularly. If a man is able to breathe regularly, when his heart beat even is when in fact all the functions of man's thorax, his middle part, are in order, the consciousness of this part is not so clear as that of the head; it too in ordinary life runs its course dream fashion. We dream in our feeling, as I have stated here during past years, in feeling we dream of this middle man. But when we bring to light through consciousness, that becomes more clairvoyant, what lies in the feeling, what man experiences only in his feeling, or to put it differently, when man learns to look at what is going on in his thorax, as otherwise he can only look at what is in his head consciousness, then the consciousness of the thorax, the middle-body splits definitely into two parts. One part dreams itself back into the whole time between the previous death and the most recent birth or conception. Therefore while in your head consciousness in a dream way, in deep dreaming, you have unconsciously what was in your previous incarnation, in the dreams of your thorax you have what has meantime been passing since that incarnation up to your present birth. And in the dreams that belong more to the lower part of the thorax you have a definite consciousness of what there will be between your coming death and next earth life. Thus the consciousness concentrated in the breast, which, however, for modern man remains more or less subconscious, is in reality a dream consciousness of both the time before this birth and the time after the next death. For this subconsciousness in the middle man the riddle is solved of what lies between our last earthly death and the following earthly conception, with the exception of or even including what we are now experiencing between birth and death. Out of the third man, out of the subconsciousness of the extremities man, the tableau of the next incarnation on earth can be developed in what during the whole of life remains strictly subconscious. This can only be brought to the surface when a man is able to draw it up through ceaseless activity in the study and exercises of spiritual science, so that certain moments of sleep-life that otherwise would pass in unconscious sleep, are lifted to the surface and the man then becomes conscious during sleep. What today man has as waking consciousness is really a kind of collateral impulse of his which rays into the head from outside. Behind this consciousness, however, lies another that stretches itself over the former incarnation, over the life of that incarnation to this one, over the life of this incarnation to the next, and then over the next again. But man sleeps away this consciousness. In the head it is the consciousness of the previous incarnation. In all the organs that principally serve the out-breathing there works a strong consciousness of the life between the previous incarnation and this one. In all the principle functions that serve the in-breathing works a consciousness of the present incarnation up to the next incarnation on earth. And in the limb-system, in all its most secret processes, works a consciousness of the next human incarnation, which remains pre-eminently subconscious. These states of consciousness have become more less veiled since the beginning of the fourth post-Atlantean period, 747 years before the Mystery of Golgotha. And the cry of our age is for the definite consciousness of the concrete events of cosmic and human evolution to be brought back out of the general chaos of human consciousness. We must meet all that I have just been developing with another aspect of what is part of the being of man. You see it is really necessary that we should enter into these difficult details, otherwise we cannot arrive at an exact understanding. I should very much welcome it if such knotty points were met not only by a certain passive acceptance, but—and this is so necessary for present day man—that even for these difficult matters a little enthusiasm were aroused, a little keen participation, which is exactly what is so hard in any society today.  Now, you turn your senses outward. There by means of your senses you find the external world spread out as something perceptible. I will draw diagrammatically what lies around us outside as something spread out for the senses. Allow this (see blue in diagram 2) to be what is lying outside. When you direct your eyes, your ears, your sense of smell, or whichever sense you like, to the external world, the inner side of this outside turns towards you, turns towards your senses Thus this is the inner side of the outside (see left of diagram). Suppose you turn your senses here to what I have drawn (see arrows). These are the senses directed towards the outer world and you see what here inside inclines within. Now follows the difficult conception to which, however, I have to come. Everything you look at there presents itself to you from inside. Imagine it must also have an outside. So I will call it up diagrammatically before your souls saying: When you look out thus you see the permanent as the limit of your vision; that is approximately so, only I have drawn it small. But now imagine you could quickly fly out there, fly beyond there and take a peep through from the other side and from the other side see your sense impressions. You could look out thus (see upper arrows in diagram). No, naturally you do not see this but, could you thus look at it, it would be the other aspect. You would have to go outside yourself, you would have to look from the other side at your whole perceptible world. You would see the reverse side of what meets you as color, what meets you as sound, and so on. You would see the reverse of what comes to you as smell, you would receive the smell in your nose from behind. Thus, imagine your view of the world from the other side; imagine the perceptible things spread out like a carpet, and now the carpet viewed from the other side. You see only a little bit of this reverse side, a very little bit indeed. I can only represent this little bit by doing it like this. Imagine now that I am drawing in red what you would see from the other side, so that I can say, one sees the perceptible diagrammatically thus. To one's ordinary view it appears blue; seen from the other side it appears red (but naturally one does not see it.) In what you would see red, is hidden first that is experienced between death and a new birth; secondly, everything described in Occult Science as the evolutions of Saturn, Sun, Moon, Earth and so forth. Everything hidden from sense perception lies there stored up. There it is, on the other side of the sphere, but you see only a little bit. I can indicate this best by saying: take this small bit of red; this goes over (see below in diagram) and crosses the blue, so that the blue instead of being, as now, in front, is behind. (were I to draw in accordance with reality, I should have to do so in four dimensions, so I can only keep to what is quite diagrammatic.) Thus the senses here are now turned to the blue (left); there they do not turn to the blue but to the red which moreover you do not see. Behind the red, however, there crosses what otherwise would be seen and that is now underneath. And this little bit that crosses the other there, you see continually with your ordinary consciousness. It is indeed your stored up memories. What arises as memory does not arise in accordance with the laws of the outer world of the senses but according to laws suitable to this world that is behind. What is within as your memories is what is suited to the other side (right). As you look within on all your memories you are actually looking at a bit of the world on the other side; the other projects inwards a little and then you see the world from the other side. And if now you could slip through your memories thus received (I spoke of this a week ago,)3 if you could get underneath and see below your memories, look at them from the other aide from down there (see right in diagram), you would see them as your aura, There you would see man as a being with a soul-spiritual aura just as ordinarily you look at the external world of sense perceptions. But as I showed you a week ago this would be hardly pleasant because man on this other side is not yet beautiful. Thus these are the interesting features of what must work across the other knowledge we have of threefold man. This crossing takes place here in the middle man, the breast-man. You remember the drawing I made a week ago where I had the lemniscates with one loop reversed, turned inside out; I must draw those here I must draw here the breast man with the leminscates described. (see below on left of diagram.) That would coincide with the sphere of memory. So that in his middle part the threefold man has this turnabout where the inner becomes outer and the outer inner. Here you now have in your own small microcosmic memory a tableau, what otherwise you would see as the cosmic tableau—as the great cosmic memory. In your ordinary consciousness you see what you have been collecting since about your third year until now; this is an inner record, a little bit of what is of the same kind as the other record for the whole world-evolution and lies on the other side.  It was not without reason that I once told you that man actually has twelve senses. Most of you know this quite well and I have mentioned it also in the notes at the end of my last book Riddles of the Soul. We must think of the senses in this way: that a number of them are turned towards what is sense-perceptible, whereas others are directed backwards. Below they are directed towards what is turned back. Those directed towards what is perceptible to the senses are: the ego sense, and the senses of thinking, speech, hearing, seeing, taste and smell; they go towards what is sense perceptible. The other senses do not come into man's consciousness because they are first of all directed toward what is within him and then to what in the world is reversed. These are the senses of warmth, life, balance, movement and touch. We can therefore say that for the ordinary consciousness seven senses lie in the light (above in diagram 3) and five in the dark (below). And the five senses lying in the dark are turned to the other side of the cosmos, turned also to the reverse side in man (see diagram 2). You therefore have a complete parallel between the senses and something else of which we are going to speak. (see diagram 3) Let us suppose we have to note down as senses: hearing, speaking, thinking, the ego-sense, and the senses of warmth, balance, movement, touch, smell, taste, sight; then you will have essentially all of them from ego-sense to sense of smell lying in the light, in what is accessible to the ordinary consciousness (see shading in diagram 3). And all that is turned away from ordinary consciousness, as night turns away from day, belongs to the other senses. Naturally the boundary is also diagrammatic, there is an overlapping—reality is not always accommodating. But this membering of man according to his senses is so that, even in the diagram, you only need draw in place of the senses the signs of the Zodiac, and you have Ram, Bull, Twins, Cancer, Lion, Virgin, Scales, seven signs for the light side and five for the dark: Scorpion, Archer, Goat, Waterman, Fishes; day, night: night,day, Here you have a perfect parallel between microcosmic man—what is turned towards his senses and what is turned away but really turned towards the senses—and what in the cosmos signifies the change from day to night. In a way the same thing happens to man, as in the cosmic edifice. In the cosmic edifice there is an interchange between day and night, in man there is also the interchange of day and night in his waking and sleeping, even though both may have emancipated themselves from each other for the present cycle of man's consciousness. During the day man is turned towards his day-senses, or we might say to Ram, Bull, Twins, Cancer, Lion, Virgin, Scales, as we might say ego-sense, sense of thinking, speech and so on. Every ego can see that of another man, you can understand the thoughts of another man, you can hear, see, taste, smell—those are day-senses. In the night it is the same with man as when the earth is turned towards the other side; man is turned in the night to his other senses, only these are not yet fully developed. Not until the Venus age will they be so fully developed that they can perceive what is on the other side. They are not yet sufficiently developed to perceive what is towards the other side. This is shrouded by night just as the earth is shrouded when passing by night through the other heavenly bodies, the other pictures of the zodiac. The passage of man through his senses is a perfect parallel with the course—whether you say the course of the sun round the earth or the earth round the sun is immaterial for our purpose; but those things are connected. And with these connections, the wise men of the Old Mysteries were very well acquainted. In the fourth post-Atlantean period this gradually vanished from consciousness but it must be brought back in spite of the resistance put up against this; it must be reinstated in the cultural life of mankind. For in these concepts that man makes his own there lies what lets us see quite clearly all that is happening now in the social, historical life. So long as you separate the life of nature from that of the spirit, as modern man loves to do, you do not arrive at concepts that can play a part in historical evolution; you are overpowered by the concepts that are working in historical life. Overpowered: There are indeed many instances of this. Now you will agree that men believe that, shall we say, for two hundred years they have been thinking a tremendous deal. We can gather up what they have been thinking for two hundred years, what they have developed as ideals, what they have talked of still talk of, as great ideals. We can do this from the time of the ideals of the age of enlightenment to that of the great would-be Caesar, Woodrow Wilson. All that is talked of about the various ideals, men have been thinking during these centuries, these last two centuries; this has formed men's thoughts. World history, however, is very little affected by these thoughts, world history has been affected by something quite different, by the thoughts that have been working and weaving in things. And in reality never were the thoughts filling men's heads farther removed from the great cosmic thoughts living in things than at the present time. What for the last hundred and fifty years, shall we say, has prompted man to work for a definite fashioning of the world is not thoughts of freedom, equality, brotherhood, justice, and so on and so forth, it is the thoughts interwoven with the coming of the machine loom. That the machine loom arose in modern development in the second half of the eighteenth century; that this significant invention took the place in mankind's evolution of the old hand-weaving; that from the machine loom came the whole machine civilisation of modern times; in all this there weave the objective thoughts the real thoughts, that have given the world its present form, out of which has arisen the present chaotic catastrophe. Should we wish to write a history of this catastrophe, we have not to turn to the thoughts teeming in human consciousness; we must turn to the objective thoughts of the founding, the invention, of the machine loom up to the development of big industry with its shadow, socialism. for even if these two things, big industry and socialism, appear as opposites they are polaric opposites belonging to one another, and as such inseparable. We must put our questions to these objective thoughts and observe history in its becoming. Then we find that during the eighteenth century, all through the nineteenth, and especially so far as we have gone in this our twentieth century, men have given themselves up to many illusions. They are given over to illusion in their thoughts; but the objective, historic-cosmic thoughts have completely overwhelmed them. These are weaving in things. And an interest—though terribly one-sided—for these objectively weaving thoughts has really been gradually developed only by those who have built up socialism as a world-conception. That is something tremendously characteristic. If you follow the course of the nineteenth century you will see that the bourgeoisie increasingly loses interest in the great questions of world outlook. These great questions are indeed becoming most distasteful to the bourgeoisie; where possible they relegate them to aesthetics. A perfectly average bourgeois will listen in the theatre to all kinds of discussions about whether there are spiritual beings or not, when there is no need to believe in them, and when it is not a question of the truth of anything. Then the most varied matters can be put forward by Björnsen and people of that ilk. And what concerns the conception of the world is today for the bourgeoisie transferred into the realm of aesthetics, into all manner of dabbling with so-called art. In recent years people have been breaking each others heads over questions concerning conceptions of the world in the sphere of socialism. (I don't look on this as an ideal in a physical sense but in a spiritual sense in a certain way it is so. You know how I have hinted emphatically that I like a little warmth even in the treatment of anthroposophical truths.) The other people have not troubled themselves about this head-breaking but have left those alone who have looked at the world from what is really a very narrow point of view, those who have only seen the world from the aspect of the factory, from the inside of factories, from the inside of printing works, and so on. And it is extremely interesting what kind of world outlook has been produced out of the point of view of the factory—for that is socialism, my dear friends. It is the factory aspect, the aspect of men who know nothing beyond the inside of their factories. And in all that has developed in this sphere, little interest has been really shown by the bourgeoisie with their abstract ideas; the bourgeoisie who even concern themselves with aesthetics in an abstract way to avoid the breaking of heads. Thus in a curious way the bourgeoisie have found themselves between the old completely moribund world-conception bereft of the spiritual that would prefer to relegate all great questions to the realm of aesthetics, and what has newly arisen as socialism. This socialism has so far no concepts at all; it is a system founded entirely on words. This is because as yet it has no view of the world whatever and can only see the factory, and even so only the most external part of the mechanism. Just imagine what it really means when a man has no inner knowledge of the kingdoms of the minerals, the plants, the animals, and only knows of the way in which a certain cock is moved mechanically up or down in a machine, this or that filed or planed, and things of that kind: Socialism is a world-outlook founded on the perception of a purely mechanical world. It is the bit of the world cut out by the socialist—the bit that is mechanical, and on this he builds his concepts. This has been allowed to arise through men adopting the principle of only troubling themselves about things aesthetically. When the Theosophical Society was first formed it had as its basis principle the mutual love of all mankind. How this was breached: But I have said enough on that point; its easiness equals its fruitlessness. But this also arises from the desire whenever possible to push what has actual content into the realm of what has none. So there could be no genuine interest in the real course of things. Individual people however have found pleasure in the peculiar—we should say conventional—way of considering history. Now let us take an example of this; let me take whatever example you like from the time of the Caesars; try to learn about this time from the text books, or any books written by the great historical authorities. I fancy you will gain very little knowledge in this way about a certain personality who in the reign of Nero played an important political part (so even under Nero you could have political aspirations!) This personality aroused quite special notice and gained considerable influence on Roman politics under Vespasian and Titus, so much so that it may be said that he was the soul of the Government under these two emperors. Then this personality went over to the other side in the reign of Domitian considering him as a disaster for the Roman Empire. He turned to the other side and a lawsuit was brought against him, a lawsuit that made a great deal of stir in Rome and was of much interest. During this case Domitian changed suddenly from the tyrant into one who did not know how to proceed in the lawsuit and was therefore unable to pass sentence on the man. Then again, as Nero succeeded Domitian, we see this personality actively connected with the Emperor, the Caesar. We watch him creating out of the whole world-conception of that day what was great in politics, and at the same time see how he once more sought to implant for the last time during the Roman Empire into the political events really vast concepts brought down from the cosmos. Strangely enough in no current history book do you find any accurate account of this personality, not even in Seutonius or Tacitus, only in Philostratus. And Philostratus describes him in such a way that one does not know whether he is giving a picture of any Roman or of a real man—he paints the life of Apollonius of Tyana. For it is Apollonius of Tyana of whom I have been speaking as having had so great an influence on politics from the time of Nero to that of Nerva, and especially under Vespasian and Titus; and Philostratus describes him. Bauer the theologian and historian of Tübingen was absolutely astounded that one should thus find nothing about such a personality as Apollonius who played a part of the utmost importance in what is historically represented. Naturally Bauer did not see into the real reason for this; for it is a question of our having in Apollonius a historical personality wielding indeed this great influence but drawing down his principles straight from the cosmos above. That was in the highest degree fatal for the Christianity then arising in Rome. And now I shall ask you to take notice that everything in history is there by grace of the Church. There is nothing in history except what the Church has allowed man to have. Not without justification has an old and by no means foolish man maintained that there was never a Plato nor a Sophocles, but that monks in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries wrote their plays—for there is no proof, no strict proof of their existence. Even though the assertion is untenable, is indeed nonsense, nevertheless, as we have often emphasised, all that is conventional history is most uncertain. And we should be quite clear about it. We must indeed bring the present into connection with the past, for we are now coming to a great and pregnant question. We have once more this time from the modern point of view, referred to threefold man, his connection with cosmic truths and the necessity for all this again to be disclosed. Now, my dear friends, in what has consisted the main activity of the Church, especially since the eighth Ecumenical Council in Constantinople in 869? What has been its chief activity? Its chief activity has been to wipe out, to blot out from man's consciousness, what in those ancient times even Christianity still understood as the connection of man with the cosmos, with the great spiritual world. Everything betraying this connection has been suppressed in real alarm. And only because not everything can be suppressed, because Karma is working against this suppression, have such works remained as those of Philostratus. Therefore you can understand when now you bring the present into connection with the past that certain churchman are made terribly uneasy by the growing tendency to foster the connection between what makes roan a cosmic being, this man himself, and his task. It is important that we do not merely pursue half-asleep what should be the will of the Anthroposophical Movement. We must pursue it as indeed is necessary with our consciousness full of life and force. With this I have indicated what is to be continued and enlarged upon tomorrow.
|
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture III
26 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture III
26 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Certain questions will increasingly obtrude themselves upon those who really think, even though in these times of overwhelming materialism these thinkers would prefer to keep them more or leas at a distance. There are many such questions, and today I should like, out of all of them, to pick a few that arise from man, in spite of resisting it, becoming aware of the spiritual world. To such questions belong those, for instance, raised in the course of everyday life; certain men die young, others in old age, others again in middle life. Concerning the fact that on the one hand young children die and on the other hand people grow to old age and then die—concerning this fact questions arise in man to which by the means today called scientific the answer can never be found. Everyone has to own this after inner reflection. Yet in human life these are burning questions; and surely anyone can feel that infinitely much in life must receive enlightenment when we can really get down to these questions: why do some human beings die early, some as children, some as adolescents, some in the middle of the normal period of life? Why do other die old? What significance has this in the whole cosmos? Men still had ideas, concepts, with which to answer these questions up to that point of time described in these lectures, the time at the beginning of the fourth post-Atlantean period, that is, up to approximately the middle of the eighth pre-Christian century. Men had concepts that came down out of ancient wisdom. In those olden times before the eighth pre-Christian century, ideas were in fact circulating everywhere in the cultural life of the earth giving men, in conformity with the mind of those times, the solution to such questions as are here mentioned. What today we call science cannot connect the right meaning with these questions and has no idea that there is something in them for which men should be seeking a possible answer. All this arises because since the point of time indicated, all conceptions related to spiritual and therefore to immortal man have actually been lost. Only these conceptions remain that are connected with man's transitory nature, man between his birth and his death. I have drawn attention to how in all the old world-conceptions they spoke of the Sun as being threefold; the same sun that is perceived out there by the physical senses as a shining sphere in cosmic space. But behind this sun the wise men of old saw the soul-sun, according to the Greeks Helios, and behind this soul-Sun again, the spiritual-Sun, still identified by Plato, for example, with the Good. Modern men do not see any real sense in speaking of Helios, the soul-Sun, or for that matter of the spiritual-Sun, the Good. But as the physical sun shines upon us here between birth and death, there shines into our ego, if I may say so, during the time we pass between death and a new birth, the spiritual sun identified by Plato with the Good. And during this time between death and a new birth, to speak of a shining sphere in the way it is spoken of in our modern materialistic world-conception has no meaning. Between death and a new birth there is only meaning when we speak of the spiritual-Sun Plato still referred to as the Good. A concept of this kind is just what should show us something. It should lead us to reflect how the matter really stands with regard to the physical representation we form of the world. It is not taken seriously in its full sense, at any rate not so seriously that our outlook on life is actually permeated by it, that in all our physical representations of the world, in what is spread out perceptibly before us, we have to see a kind of illusion, Maya. It is indeed fundamentally this kind of representation of the Sun that anyone accepts when taking as his authority modern physics, astrophysics, whatever you like to call it. If he were able to travel to the place where the physicist places the sun, on approaching it he would—now let us turn from the conditions of human life and assume that absolute conditions of life could prevail—he would become aware of overpowering heat, this is how he would picture it. And when he had arrived inside the space that the physicist considers to be filled by the sun, he would find in this space red hot gas or something of the kind. This is what the physicist considers to be filled by the sun, he would find in this space red hot gas or something of the kind. This is what the physicist actually pictures—a ball of glowing gas or something like it. But it is not so, my dear friends, that is definitely maya, complete illusion. This representation cannot hold water in face of true physical perception that is possible, let alone what can actually be perceived spiritually. Were it possible to get near the sun, to reach where the sun is, we should find yes, indeed, an getting near, we should find something that would have the same effect as going through floods of light. But when we came right inside, where the physicist supposes the sun to be, we should find first what we could only call empty space. Where the physical sun is supposed to be there is nothing at all, absolutely nothing. I will draw it diagrammatically (blue centre in yellow circle, diagram not available) but in reality nothing is there; there is nothing, there is empty space. But it is a strange kind of empty space: When I say there is nothing there I am not speaking quite accurately—there is less than nothing there. It is not only empty space for there is less than nothing there. And that is something that is an extraordinarily difficult idea for the modern western man to picture. Even today men of the east take this as a matter of course; for them there is absolutely nothing strange or difficult to understand when they are told that less than nothing is there. The man of the west thinks to himself—especially when he is a hard and fast follower of Kant, and there are far more followers of Kant today than those who are consciously so—he thinks to himself that if there is nothing in space then it is just empty space! However this is not the case, there can also be exhausted space. And if indeed you were to look right through this corona of the sun, you would feel the empty space into which you would then enter most uncomfortable—that is to say it would tear you asunder. By that it would show its nature, that it is more—or it is less, however we can best express it, than empty space. You need only seek the help of the simplest mathematical concept and when I say empty space is less than just emptiness you will no longer find my meaning so puzzling. Now let us assume you possess some kind of property. It can also happen that you have given away what you possess and have nothing. But we can have less than nothing, we can have debts. Then we do actually have less than nothing. If we pass from fullness of space to its ever diminishing fullness, we can come to empty space; and we can still go an beyond mere emptiness just as we can go beyond having nothing to having debts. It is a great weakness of the modern world outlook that it does not know this particular kind of—if I may so express it—negative materiality, that it only knows emptiness or fullness and not what is less than emptiness. For because knowledge today, the world outlook today is ignorant of what is less than emptiness, this world outlook is more or less held in the bonds of materialism, strictly confined by materialism—I should like to say, under the ban of materialism. For in man also there is a place that is emptier than empty, not in the whole of him but where there are layers of what is emptier than empty. As a whole, man, physical man, is a being who materially fills a certain space; but there is a certain member of man's nature, of the three I have referred to, that actually has something in it like the sun, emptier than empty. That is—yet, my dear friends, you'll have to put up with it—it is the head. And it is just because man is so organised that his head can become empty and in certain parts more than empty, that this head has the power to make room for the spiritual. Now just picture the matter as it actually is. Naturally we have to picture things diagrammatically, but use your imagination and picture that everything materially filling your head I am going to draw in the following way. This is the diagram of your head (see red in diagram 5). but now, if I want to draw it properly, I shall have to leave empty places in this head, these naturally are not very big; but there inside are empty places. And into these empty places can enter what I have recently been calling the young spirit. In these spaces the young spirit with its rays, as it were, is drawn (see yellow in diagram 5).  Now, my dear friends, the materialists say that the brain is the instrument of the soul-life, of the thinking. The reverse is the truth. The holes in the brain, what indeed is more than holes, or one could just say as well less than holes, what therefore is emptier than empty, that is the instrument of the soul-life. And here where the soul-life is not, into which the soul-life is continually pushing, where the space in our skull is filled with brain substance here nothing is thought, here is no soul-experience. We do not need our physical brain for our life of soul; we need it only to lay hold of our soul-life, physically to lay hold of it. And if the soul-life were not actually alive in the holes of the brain, pushing up everywhere, it would vanish, it would never reach our consciousness. But it lives in the holes of our brain that are emptier than empty. Thus we have gradually to correct our concepts. When we stand in front of a mirror we do not perceive ourselves but only our reflected image. We could forget ourselves ... We see ourselves in the mirror. In the same way man does not experience himself by putting together with his brain what is lying in the holes in that brain. He experiences the way in which his soul-life is everywhere reflected by pushing up against the brain substance. It is reflected everywhere, and man experiences it; what he experiences is actually its reflected image. All that has slipped into the holes, however, because it is then permeated by consciousness in the contrary sense is what makes man conscious when without the resistance of the brain he goes through the gate of death. Now I should like to draw another diagram. Take the following: forgive me if I am rather drastic in portraying the brain and how the holes are left (blue in diagram 6). Here is the brain substance and here the brain leaves its holes and into these holes goes the life of the soul. (yellow)  This soul-life, however, continues, just outside the holes. There come to what naturally is only seen near man but projects indefinitely—man's aura. Now let us think away the brain and imagine we are looking at the soul-life of an ordinary man between birth and death. We should then have to say that seen in this way the condition of the real man between birth and death is such that actually his face is turned to his body thus (see lilac). It is true I shall have to draw this diagram differently. He turns his soul-life to the corporeal. And when we look at the brain the soul-life stretches out like a feeler that creeps into the holes of the brain. What there I made yellow here I make lilac, because that is more appropriate for the view into the living man. Thus, that would be what runs into the brain of the living man. If after this I want to draw, let us say, physical man, I could best indicate that by perhaps here drawing in for you the boundary set to the faculty of memory. You would go outside there and there you would have the outer boundary, the boundary of cognition, of which I have also spoken to you. For that you will just have to remember diagram 5 and diagram 3 drawn yesterday). But now this is the reality—when man is looked at spiritually from without, his soul-life stretches into him thus... so I will draw the single elongation only where the brain is concerned (diagram 7). But this soul-life in itself is also differentiated. So to follow up this soul-life further I should have to draw... another region here (red under the lilac), here another region blue); thus all this would belong to what constitutes man's aura. Then another region (green). You see how this part I am now drawing lies beyond the boundary of man's cognition. Then the region (yellow)—in reality all this belongs to man—and this region (orange.)  When man is asleep this moves more or less out of the body, as it was drawn yesterday (diagram 2), but when man is awake it is more or lass within the body. So that actually, perceived with the soul, the aura is in the immediate vicinity of the body. And if the physical man is described this is done by saying that this physical man consists of lungs, heart, liver, gall and so on; This is done in physical anatomy, this is done in physiology. But you can do the same when describing the man of soul and spirit who in this way actually stretches out into the holes in man, in what is more than empty in man. You can describe this in the same way—only then you must mention of what this soul-and spirit man consists. just as in physical man the organs are differentiated, here the different currents must be separated. It can be said: in here where it is red, physical man would stand thus in profile, the face turned in this direction, for example, the eyes here (diagram 7), and here would be the region of burning desire (red). That would be part of the man of soul-and-spirit who has taken his substance from the region known in my book Theosophy as the region of burning desire. Thus something taken from burning desire and introduced into man gives this part of him. If I am describing this in detail what I have here colored lilac I should have to call soul-life. As you know, a certain part of the soul-sphere, of the soul-land, has been given the name soul-life. This substance of it would have this violet color,this lilac, and forms in man a part of his soul-spiritual being. And if we continue in this way the orange here would have to be called active soul-force. So that you have to remember that your soul-life is what during your life between birth and death enters you with most intensity by way of your senses. And behind, checking itself, not so well able to enter, held up by the soul-life, there is the active soul-force. Still further behind there is what is called soul-light (yellow in diagram 8). To a certain extent attached to this soul-light, pressing itself through, there would be what is taken from the region of liking and disliking which I should have to give to the green area. Wishes, we should ascribe to the sphere of what is approximately blue. And now pushing up here, the real blue, that is approaching blue red, this would be the region of mobile susceptibility. These are auric currents that I here call burning desire, mobile susceptibility, and wishes. As you know, these auric currents, these auric streams, constitute the world of soul, they also constitute the man of soul and spirit who may be said to be built out Then when death comes the physical body falls away, and man withdraws what has projected into the holes in the body. He takes it away and by so doing (we can now think away physical man) he comes into a certain relation with the soul-world and then with the spirit-land as you will find it described in Theosophy. He has this relationship by having in him its ingredients, but during physical life these are bound up with the physical body and then they become free. Becoming free, however, as a whole it is gradually changed. During physical life—if I leave out the differentiations and draw the soul-life thus—the feelers (lilac in diagram 8) reach out into our holes; after death these feelers are drawn back. By their being drawn back, however, the soul-life itself becomes hollowed out and the life of the spirit coming from the other side rises into the life of soul (yellow).  In the same degree as man ceases to dive into the physical, the soul-spiritual lights up and, from the other side, penetrates his aura with light. And just as man is able to acquires a consciousness through the reflection caused by the continual pushing of the soul-spiritual against the physical body, he now acquires a consciousness by drawing himself back against the light. This light is that of the Sun, the original light that is the Good. Thus, whereas during his physical life as man of soul and spirit he pushes against what is related to the Sun, namely, against the more than empty holes in the brain, after death when he withdraws himself he pushes against the other Sun, the Good-Sun, the original sun. You see, my dear friends, how the possibility of receiving concepts of life between death and a new birth is bound up with the basic ideas of primeval mysteries. For we are placed into this whole cosmic life in true way I have been picturing during these last few days. It is true, however, that we have to go more deeply into the framework of actual human evolution throughout earthly time to come to correct concepts of these matters. I think you will agree it might be possible that someone through a special stroke of luck—if one might so call it—were able to see clairvoyantly, the whole of what I have been describing. This stroke of luck, however, could only bring him to the point of seeing ever changing images. It is something like this—a man through some kind of miracle—but nowadays it would not happen through a miracle—or let us say through clairvoyant vision, super-sensible vision, a man might see something of the nature of what I have been trying to picture, namely man's life of soul and spirit. You will find it obvious that this should look rather different from what a short time ago I was describing as the normal aura, if you understand what I was describing only a few days ago as the aura revealed when the whole man is seen, that is, physical man with his encircling aura. But now I have taken out the man of soul und spirit, so that this man of soul and spirit has been abstracted from the physical man. From this you recognise that in one case the colors have to be arranged in one way, in another case in another way; you recognise also that for super-sensible consciousness things look very different. Try simply to see man's aura—as it is while man is in the physical body—then look at this aura. Turn your attention that is, from the man of soul and spirit, and try to see the man why stretches out his organs into physical man. But when you see the man during the time between death and a new birth, then you also see how the whole changes. Above all, the region that is red here (Diagram 7) goes away, goes here, and the yellow goes below, the whole gradually gets into disorder. These things can be perceived but the percept has something confusing about it. Therefore it will not be easily possible for modern man to bring meaning and significance into this confusion if he does not turn to other expedients. Now we have shown that man's head points to the past whereas the extremities man points to the future. This is entirely a polaric contrast, both the head and the extremities of man (remember what was said yesterday) are actually one and the same, only the head is a very old formation, it is overformed. That is why it has the holes; so far the extremities man has not these holes; on the surface he is still full of matter. To have these holes is a sign of over development. Development in a backward sense can be seen in the head and much hangs on that. Much depends too on man being able to understand that extremities man is a recent metamorphosis—the head an old metamorphosis. And because extremities man is a recent metamorphosis he has not so far developed the capacity to think in physical life but his consciousness remains unconscious; he does not open up to the man of soul and spirit such holes as are in the brain. You see it is infinitely important for spiritual culture, and will in future become more and more so, for us to perceive that these two things that outwardly, physically, are as totally different from one another as the head man and extremities man, are according to soul and spirit, one and the same, and only differ because they are at different stages of development in time. Many mysteries lie in this particular fact that two equal physical things at different stages of their development in time, can be really one and the same that, though outwardly physically different, this is only due to the conditions of their change, of their metamorphosis. Goethe with his theory of metamorphosis began in an elementary way to form concepts by which all this can be understood. Whereas otherwise since ancient times there has been a deadlock in the formation of concepts, with Goethe the faculty of forming concepts once more arose. And these concepts are those of living metamorphoses. Goethe, it is true, always began with the most simple. He said: when we look at a plant we have its green leaf; but the green leaf changes into the flower petal, into the colorsome petal of the flower. Both are the same, only one is the metamorphosis of the other. And as the green leaf of the plant and the red petal of the rose are different metamorphoses, the same thing at a different stage, man's head and his extremities organism too are simply metamorphoses of one another. When we take Goethe's thought on the metamorphosis of the plant we have something primitive, simple; but this thought can blossom into something of the greatest and can serve to describe man's passing from one incarnation to the next. We see the plant with its green leaf and its blossom, and say: this blossom, this red blossom of the rose is the metamorphosis of the green leaf of the plant. We see a man standing before us and say: that head you are carrying is the metamorphosis of arms, hands, legs, feet of your previous incarnation, and what you now have as arms, hands, legs and feet will be changed into your head of the next incarnation. Now, however, will come an objection that evidently sits heavily on your souls. You will say: good gracious but I leave my legs and feet behind, my arms and hands too; I do not take them into my next incarnation ... how then should my head be made out of them? It is true, this objection can be made. But once again you are coming here up against Maya. It is not true that you actually leave behind your legs, feet, hands, arms. It is indeed untrue. You say that because you still cling to Maya, the great illusion. What indeed with the ordinary consciousness you refer to as your arms, hands, legs and feet, are not your arms, hands, legs and feet at all, but what as blood and other juices fills out the real arms, hands, feet and legs. This again is a difficult idea but it is true. Suppose that here you have arms, hands, feet and legs, but that what is here is spiritual, spiritual forces. Now please to think that your arms, hands, legs and feet are forces—super-sensible forces. Had you these alone you would not see them with your eyes; they are filled out, these forces, with juices, with the blood, and you see what as mineral substance, fluid or partly solid—the smallest part solid—fills out what is invisible (hatching in diagram 9). What you leave in the grave or what is burnt is only what might be called the mineral enclosure. Your arms and hands, legs and feet are not visible, they are forces and you take them with you, you take the forms with you. You say: I have hands and feet. Anyone who sees into the spiritual world does not say: I have hands and feet, he says; there are spirits of form, Elohim, they think cosmic thoughts, and their thoughts are my arms and hands, my legs and feet; and their thoughts are filled out with blood and other fluids. But neither are blood and the other fluids what they appear physically; these again are the ideas of spirits of wisdom, and what the physicist calls matter is only outer semblance. The physicist ought to say when he comes to matter: here I come to the thoughts of the spirits of wisdom, the Kyriotetes. And where you see arms, hands, feet, legs, you cannot touch them but should say: here the spirits of form are building into these shapes their cosmic thoughts.  In short, my dear friends, strange as it sounds, there are no such things as your bodies, but where your body is in space there intermingled with one another live the cosmic thoughts of the higher hierarchies. And were you able to see correctly and not in accordance with Maya, you would say: into here there project the cosmic thoughts of the Exusiai, the spirits of form, the Elohim. These cosmic thoughts make themselves visible to me by being filled out with the cosmic thoughts of the spirits of wisdom. That gives us arms and hands, legs and feet. Nothing, absolutely nothing, as it appears in Maya is there before the spiritual vision, out there stand the cosmic thoughts. And these cosmic thoughts crowd together, are condensed, pushed into one another; for this reason they appear to us as these shadow figures of ours that go around, which we believe to have reality. Thus, as far as the physical man is concerned, he does not exist at all. With certain justification we can say that in the hour of death the spirits of form separate their cosmic thoughts from those of the spirits of wisdom. The spirits of form take their thoughts up into the air, the spirits of wisdom sink their material thoughts into the earth. This brings it about that in the corpse an aftershadow of the thoughts of the spirits of wisdom still exists when the spirits of form have taken back their thoughts into the air. That is physical death—that is its reality. In short, when we begin to think about the reality we come to the dissolution of what is commonly called the physical world. For this physical world derives its existence from the spirits of the higher hierarchies pushing in their intermingled thoughts, and I beg you to imagine that finely distributed quantities of water are introduced in some way which form a thick mist. That is why your body appears as a kind of shadow-form, because the thoughts of the spirits of form penetrate those of the spirits of wisdom, the formative thoughts enter the thoughts of substance. In face of this conception the whole world dissolve into the spiritual. We must, however, have the possibility of imagining the world to be really spiritual, of knowing that it is only apparent that my arms and hands, my feet and legs are given over to the earth. That is what it seems; in reality the metamorphosis of my arms and legs, hands and feet begins there and comes to completion in the life between death and a new birth, when my arms and legs, hands and feet become the head of my next incarnation. I have been here telling you many things that perhaps at least in their form may have struck you as something strange. But what is all this ultimately of which we have been speaking but an ascending from man as he appears, to man as he really is, ascending from what lives externally in Maya to the successive ranks of the hierarchies. It is only when we do this, my dear friends, that we are able to speak in a form that is ripe today of how man is permitted to know a so-called higher self. When we simply rant about a higher self, when we simply say: I feel a higher self within me . . . then this higher self is a mere empty abstraction with no content; for the ordinary self is in the hands of Maya, is itself Maya. The higher self has only one meaning when we speak of it in connection with the world of the higher hierarchies. To talk of the higher self without paying heed to the world that consists of the spirits of form and the angels, archangels and so on, to speak of the higher self without reference to this world, means that we are speaking of empty abstractions, and at the same time signifies that we are not talking of what lives in man between death and a new birth. For as here we live with animals, plants and minerals, between death and a new birth we live with the kingdoms of the higher hierarchies of whom we have so often spoken. Only when we gradually come nearer to these ideas and concepts (in a week, perhaps, we shall be speaking of them) shall we approach what can answer the question: why do many human beings die as mere children, many in old age, others in middle age? Now, my dear friends, what I have just given you in outline are concrete concepts of what is real in the world. Truly they are not abstract concepts I have been describing, they are concrete concepts of world reality. These concrete concepts were given, for a more atavistic perception, it is true, in the ancient mysteries. Since the eighth pre-Christian century they have been lost to human perception, but through a deepening of our comprehension of the Christ-Being they must be found again. And this can only be realised on the path of spiritual science. Let us make ourselves from a certain point of view another kind of picture of human evolution. We will here keep before us exceedingly important concepts. Now it can be said that when we go back in the evolution of man we discover—and I have often described this—that in ancient days men had more of the group-soul, and that the individual souls were membered into what was group-soul. You can read about this in various cycles:1 we can then diagrammatically represent human evolution and say: in olden days there were group-souls and each of these split up (it would appear thus to soul perception but different for the perception of the spirit). But each of these souls clothed itself with a body that here in this figure I indicate with red strokes. (Diagram 10). Up to the time of the Pythagorean school this drawing, or something like it, was always made and it was said: look at your body, so far as that is concerned men are separated, each having his own body (that is why the red strokes are isolated). Where the souls are concerned however, mankind is a unity, since we go back—it is true a long way back—to the group-soul. There we have a unity. If you think away the red, the while will form a unified figure (see diagram.)  There is sense in speaking of this figure only if we have first spoken of the spiritual as has been done here today; for then we know everything that is working together in these souls, how the higher hierarchies are working together on these souls. There is no sense in speaking of this figure if our gaze is not fixed on the hierarchies. It was thus that they spoke up to the time of the Pythagorean School; and it was from the Pythagorean School that Apollonius learned what I spoke about yesterday and about which I shall be talking further in these next weeks. But then after the eighth pre-Christian century, when the Pythagorean Schools were in their decadence, the possibility of thus speaking was lost. And gradually the concepts that are concrete, that have reality by being related to the higher hierarchies—these concepts have become confused and hazy to people. Thus there has come to them in the place of Angels, Archangels, Archai, Spirits of Form, Spirits of Movement, Spirits of Wisdom, Thrones, instead of all this concrete weaving of the spirit, they arrived at a concept that now played a certain part in the perception of the Greeks—the concept of the pneuma. Everything became hazily confused: Pneuma, universal spirit, this indistinct concept still so loved today by the Pantheists ... spirit, spirit, spirit ... I have often spoken of how the Pantheists place spirit everywhere; that goes back to Greek life. Again this figure is portrayed ... but you can now see how what was once concrete, the fullness of the Godhead, now became an abstract concept—Pneuma. The white is Pneuma, the red physical matter (see diagram 10) if we are considering the evolution of man. The Greeks, however, at least still preserved some perception of this Pneuma, for they always saw something of the aura. Thus, for them, what you can picture in these white branches was always of an auric nature, something really perceptible. There is the great significance of the transition from that constituted Greece to all that was Roman—that the Greeks still in their perception experienced Pneuma as something actual and spiritual, but that the Romans did so no longer. Everything now becomes quite abstract with the Romans, completely abstract; concepts and nothing more. The Romans are the people of abstract concepts. My dear friends, in our days you find in science the same diagram! You can come upon it today in materialistic books on science. You will find the same diagram, exactly the same, as you would have found in the old Mysteries, in the Pythagorean Schools, where everything was still related to the hierarchies. You have it with the Greeks where everything is related to the Pneuma; again today you find it drawn, and we shall see what it has now become. Today the scientist says as he makes this same drawing on the blackboard for his students: in the propagation of the human race the substance of the parents' germ cells passes over to the children; but part of this substance remains so that it can again pass over to the children and and again there remains some of this to pass over anew to the children. And another part of the germ cell substance develops so that it can form the cells of the physical body. You have exactly the same diagram, only the modern scientist sees in the white (see diagram) the continuity of the substance of the germ cell. He says; if we go back to our old human ancestors and take this germ cell substance of both male and female, and then go to present day man and take his, it is still the same stream, the substance is continuous. There always remains in this germ substance something eternal—so the scientist imagines—and only half of the germ plasma goes over into the new body. The scientist has still the same figure but no longer has the pneuma; the white is now for him the material germ substance—nothing is left of soul and spirit, it is just material substance. You can read this today in scientific books, and it is taken as a great and significant discovery. That is the materialising of a higher spiritual perception that has passed through the process of abstraction; in the midst stands the abstract concept. And it is really amusing that a modern scientist has written a book (for those whose thinking is sound, it is amusing) in which he says right out: what the Greeks still represented as Pneuma is today the continuity of the germ substance. Yes, it is foolish, but today it counts for great wisdom. From this you can, however, see one thing, it is not the drawing that does it! And you will therefore understand why to a certain extent I have always been against drawing diagrams so long as we were still trying to run our Anthroposophy within the Theosophical Society. One had only to enter any theosophical branch and the walls as a rule would be plastered with all manner of diagrams; there were drawings of every possible thing with words attached; there ware whole genealogical trees and every possible kind of sketch. However, my dear friends, these drawings are not important. What matters is that we should really be able to have living conceptions; for the same drawing can represent the soul-spiritual in the flowing of hierarchies, the purely material in the continuous germ-plasm. These things are seen very hazily by modern man. Therefore it is so important to be clear that the Greeks still knew something of the real self in man, of the real spiritual and that it was the Romans who made the transition to the abstract concept. You can see all this in what is external. When the Greek talked about his Gods, he did so in a way that made it quite evident that he was still picturing concrete figures behind these Gods. For the Romans the Gods, in reality, ware only names, only expressions, abstractions and they became abstractions more and more. For Greek a certain idea was ever present that in the man before him the hierarchies were living, that in each man the hierarchies were living a different life. Thus the hierarchies were living differently in every man. The Greek knew the reality of man, and when he said, that is Alcibiades, that is Socrates, or that is Plato, he still had the concept that there in Alcibiades, Socrates or Plato ware rising up, within each in a different way, the cosmic thoughts of the hierarchies. And because the cosmic thoughts arose differently these figures appeared different. All this was entirely lacking in the Roman. For this reason he formed for himself a system of concepts that reached its climax when from the time of Augustus on and actually from an earlier date, the Roman Caesar was held to be God. The Godhead gradually became an abstraction and the Roman Caesar was himself a God because the concept of God had become completely abstract. This applies to the rest of their concepts; and it was particularly the case with the concepts that lived deeply in the Roman nature as concepts of rights, moral concepts. Thus, in place of all that in olden days was a living reality, there arose a number of abstractions. And all these abstractions lasted on as a heritage throughout the middle ages and descended to modern times, remaining as heritage down to the nineteenth century—abstract concepts carried into every sphere. In the nineteenth century there came something startling. Man himself was entirely lost sight of among all these abstract concepts! The Greeks still had a presentiment of the real man who descends here after being formed and fashioned out of the cosmos; in the time of the Roman empire all knowledge of him was lost. The nineteenth century was needed to rediscover him through all the connections I have been showing you and will go on showing you even more exactly. The discovery of man took place now from the opposite pole. Greece wanted to see man as descending from the hierarchies, divine man; in place of this the Romans set up a series of abstract concepts; the nineteenth century—the eighteenth century too but particularly the nineteenth—was needed to rediscover man from the other side, from his animal side. And he could not be grasped with abstract concepts; this was the great shock. This was the great shock and the deep cleft that arose; what is this actually that stands there on two legs and fidgets with its hands, and eats and drinks all manner of things; what is it? The Greeks still knew, then a change took place when concepts became abstract. Now it comes as something startling to men of the nineteenth century; it stands there and there are no concepts with which to grasp it. It is taken for simply a higher form of animal. On the one hand, in science it produces Darwinism, on the other hand, in the spiritual it brings about socialism which would place man into society as a mere animal. Here is man standing transfixed before himself—what is this thing? And he is powerless to answer the question. That is the situation today; that is the situation that will produce not only concepts that are right or wrong according as men will them, but is called upon to create facts either catastrophic or beneficial. And the situation is—the shock men have when seeing themselves. We must find the elements once more for te understanding of spiritual man. These elements will not be found unless we turn to the theory of metamorphosis. There lies the essential point. Goethe's concepts of metamorphosis are alone able to grasp the ever changing phenomena which offer themselves to the perception of the reality. Now one might say that spiritual evolution has always moved in this direction. Even at the time when the Chemical Wedding of Christian Rosenkreutz in the seventeenth century was being published in so wonderful a way—other writings too—the endeavour was already there to provide for the arising of a social structure for man compatible with his true nature. (In Das Reich I have referred to this in a series of articles concerning The Chemical Wedding). In this way the Chemical Wedding of Christian Rosenkreutz by the so-called Valentin Andreae arose. On the other hand, however, there also arose the book he called Reformation des Ganzer Menschengeschlectes (Reformation of the whole Human Race), where he gives a great political survey of how social conditions ought to be. Then, it was the thirty years war that swept the thing away! Today, there is the possibility that the ordering of the world either sweep things away once more ... or carry them right into human evolution. With this we are touching an the great fundamental questions of the day, with which men should be occupying themselves instead of with all the secondary matters that engross them. If only men concerned themselves about basic questions they would find means and ways of bringing fruitful concepts into modern reality—then we could get away from abstract concepts. It is not very easy to distinguish reality from illusion. For that, we must have the will to go right into life with all seriousness and all good will, and not be bound down by programmes and prejudices. I could tell many tales about this but now I will refer to one fact only. In the beginning of the nineties of the last century a number of people foregathered in various towns of Europe and brought about something of an American nature, namely, the Movement for Ethical Culture. At that time it was the intellectuals who were connected with founding these societies for Ethical Culture. These people produced very beautiful things, and if today you read the articles written at that time by the promoters of Societies for Ethical Culture ... if you have a taste for butter, you will probably even today be enchanted by all the beautiful, wonderfully beautiful ideals, in which these people indulged. And indeed it was no pleasant task to go against this reveling in butter: However, I wrote an article at the time in one of the first numbers of Die Zunkunft (The Future), against all this oiliness in “ethical culture,” and denounced it in awful words. Naturally it was a shameful deed—how should it not have been when these people had set out to make the whole world ethical, moral—how should it not have been disgraceful to turn upon anything so good: At that time I was living in Weimar but on paying a visit to Berlin I had a conversation with Herman Grimm who said: “What is the matter with ‘ethical culture'? Go and see the people themselves. You will find that here in Berlin those who hold meetings about ethics are really thoroughly nice kind people—one could not have any objection to them. They can even be congenial and very pleasant.” This was not to be denied and at the moment Herman Grimm had just as much right on his side as I had. Outwardly and momentarily, one of us was as right as the other, one could be proved right just as well as the other. And I am not for maintaining that from the point of view of pure logic my grounds for opposing these ethical philosophers were any more sound than those brought forward by them—I wouldn't be sure. But, my dear friends, from all this highfalutin idealism the present catastrophe has arisen! And only those people were right, and have been justified by events, who said at the time; with all your talking and luxuriating in buttery ideals, by means of which you would bring universal peace and universal morals to man, you have produced nothing but what I then called social carcinoma that had to end in this catastrophic present. Time has shown who was working with concrete concepts, who with merely those that are abstract. When they are simply abstract in character, there is no distinguishing who is right and who is wrong. The only thing that decides is whether a concept finds its right setting in the course of actual events. A professor teaching science in a university can naturally prove everything he says to be right in a most beautiful and logical way. And all this goes into the holes in the head (and this today I naturally may be allowed to say with the very best intention). But you see it is not a question of bringing forward apparently good logical grounds; for when these thoughts sink into a head such as Lenin's they become Bolshevism. What matters is what a thought is in reality, not what can be thought about it or felt about it in an abstract way, but what force goes to the forming of it in its reality. And if we test the world-conception that is chiefly talked of today—for the others, specified yesterday, were more in picture form—when one brings socialism to the test, it is not a question today of sitting oneself down to cram (as we say for ‘study') Karl Marx, or Lassalle, or Bernstein, to study their books, to study these authors. No! It is a question of having a feeling, a living experience for what will become of human progress if a number of men—the sort of men who stand at a machine—have these thoughts. That is what matters, and not to have thoughts about the social structure in the near future that are learnt in the customary course of modern diplomatic schooling, Now is the time when it is important to weigh thoughts so as to be able to answer the question: what are the times wanting for the coming decades? Today the time has already come when it is not allowed to sit in comfort in the various magisterial seats and to go on cherishing what is old. The time has come when men must bear the shock of seeing themselves, and when the thought must rise up in those responsible anywhere for anything: How is this question to be solved out of the spiritual life?
|

